Abstract
EuCr2Al20, cubic,
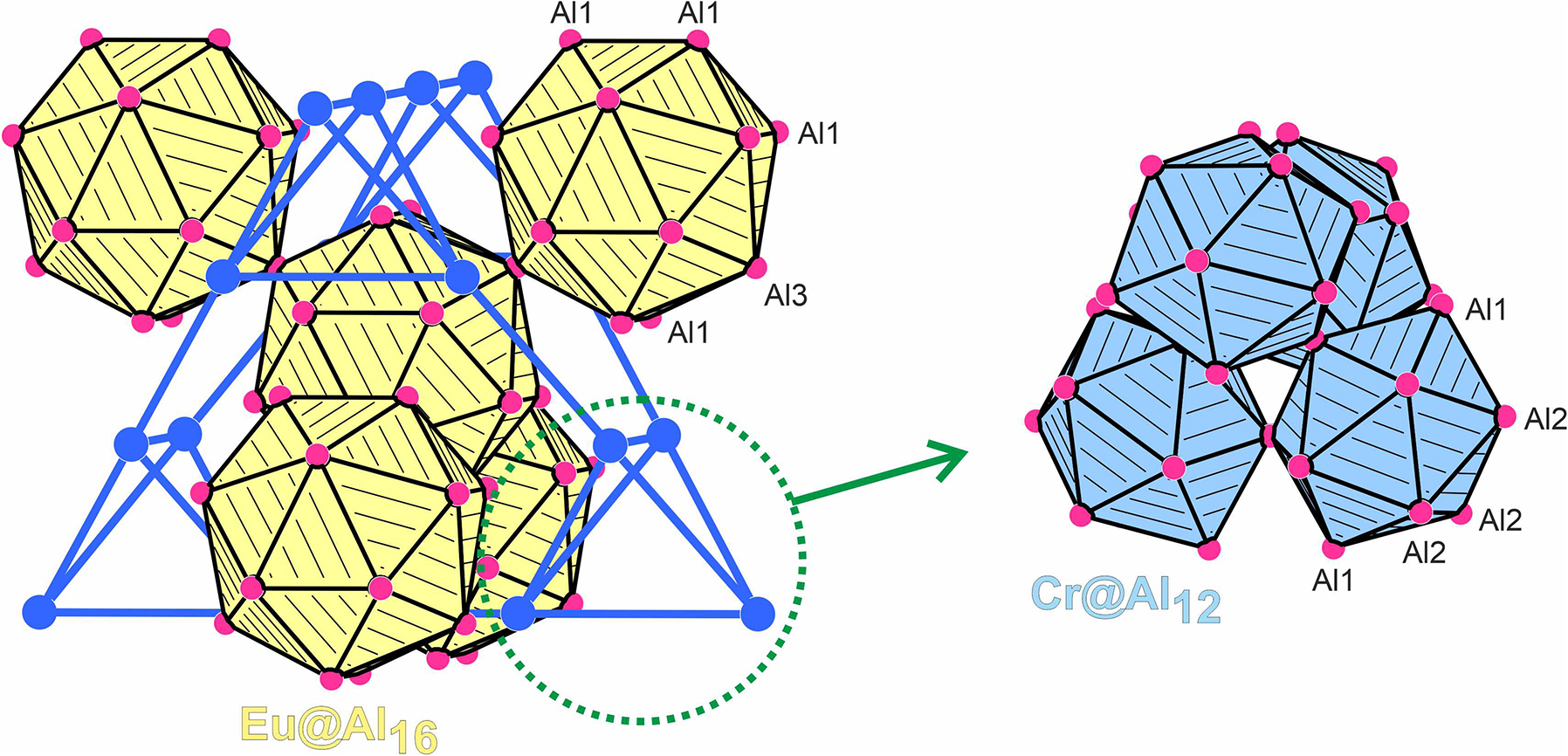
The structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Silvery irregular shape |
| Size: | 0.04 × 0.06 × 0.08 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 6.31 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | IPDS Stoe |
| θ max, completeness: | 33.4°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 16,086, 325, 0.119 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 267 |
| N(param)refined: | 18 |
| Programs: | X-Area [1], JANA2006 [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu1a | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.00870 (8) |
| Cr1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.00697 (12) |
| Al1 | 0.05861 (4) | 0.05861 (4) | 0.32600 (5) | 0.01114 (17) |
| Al2 | 0.48756 (7) | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.0088 (2) |
| Al3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0225 (3) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.938 (5).
Cutout of the EuCr2Al20 structure. Chromium and aluminum atoms are drawn as blue and magenta circles, respectively. The condensation pattern of the Eu@Al16 and Cr@Al12 polyhedra is emphasized. The left-hand drawing shows the chromium substructure.
1 Source of material
The aluminum-rich phases EuT 2Al20 (T = Ti, V, Cr, Nb, Mo, Ta, W) were obtained by reaction of the elements using the aluminum self-flux technique [3]. Starting materials were europium ingots (American Elements, 99.99%), titanium (Strem Chemicals, 99.7%), chromium (Alfa Aesar, 99.95%), niobium (Alfa Aesar, 99.6%), molybdenum (Ventron, 99.9%), tantalum (Strem Chemicals, 99.98%) and tungsten (Strem Chemicals, 99.95%) powder, vanadium sheet (Alfa Aesar, 99.7%) and aluminum turnings (Koch Chemicals, 99.9%). The elements were mixed in the atomic ratios Eu:T:Al = 1:2:40, placed in alumina crucibles and sealed in evacuated silica ampoules. The mixtures were heated to 1120 K at a rate of 50 K/h, kept for 300 h and finally cooled to room temperature at a rate of 6 K/h. The excess aluminum was dissolved in diluted hydrochloric acid.
2 Experimental details
The phase purity of the polycrystalline products was investigated by means of powder X-ray diffraction (Enraf-Nonius FR552 Guinier camera, imaging plate detector, Fujifilm BAS-1800 read-out system, Cu-K
α1 radiation and α-quartz (a = 491.30 and c = 540.46 pm) as an internal standard. The refined lattice parameter (1448.77(5) pm) agrees with the earlier study (1479.7(2) pm) [4]. EuCr2Al20 crystals were selected from the mechanically fragmented sample extracted from the aluminum flux. The crystal quality was tested through Laue photographs (Buerger camera, image plate detection system). Single crystal X-ray diffraction was performed at room temperature on a Stoe IPDS-II diffractometer (graphite monochromatized Mo-
3 Comment
EuCr2Al20 crystallizes with the CeCr2Al20 type structure [7], space group
Interatomic distances (/pm) in the first coordination spheres of europium and chromium.
| Eu: | 4 | Al3 | 314.5 (1) | Cr: | 6 | Al2 | 257.4 (1) |
| 12 | Al1 | 322.2 (1) | 6 | Al1 | 279.9 (1) |
EuCr2Al20 and the isotypic aluminides EuT 2Al20 with T = Ti, V, Nb, Ta, Mo and W were studied by 151Eu Mössbauer spectroscopy at room temperature. The isomer shifts (Table 4) show a narrow range from −8.34(1) mm s−1 (EuCr2Al20) to −8.97(2) mm s−1 (EuW2Al20). The spectra gave no hint for any Eu(III) contribution. The isomer shift values are in the usual range observed for divalent europium intermetallics with pronounced covalent bonding. This is in close agreement with the magnetic behavior of these europium intermetallics [8, 14, 15]. The course of the isomer shifts shows no simple correlation with the valence electron count and the lattice parameter.
Fitting parameters for 151Eu Mössbauer spectra of aluminides EuT 2Al20. The measurements were carried out in transmission geometry with a 151Sm:EuF3 source at room temperature. δ = isomer shift, Γ = experimental line width. Due to the cubic site symmetry of europium, no quadrupole splitting occurs. The lattice parameters and the valence electron count are listed for comparison.
| Compound | δ/mm s−1 | Γ/mm s−1 | a/pm | VEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EuTi2Al20 | −8.77 (1) | 2.49 (3) | 1472.26 (5) | 70 |
| EuV2Al20 | −8.58 (1) | 2.43 (3) | 1454.92 (7) | 72 |
| EuNb2Al20 | −8.94 (1) | 2.55 (4) | 1478.3 (2) | 72 |
| EuTa2Al20 | −8.94 (2) | 2.50 (6) | 1477.27 (9) | 72 |
| EuCr2Al20 | −8.34 (1) | 2.53 (2) | 1448.77 (5) | 74 |
| EuMo2Al20 | −8.54 (1) | 2.50 (3) | 1460.56 (6) | 74 |
| EuW2Al20 | −8.97 (2) | 2.51 (6) | 1459.81 (4) | 74 |
Acknowledgements
We thank Dipl.–Ing. J. Kösters for the intensity data collection.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. X-Area. The Stoe Single Crystal Diffraction Software Package; STOE & Cie GmbH: Darmstadt, Germany.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Petříček, V., Dušek, M., Palatinus, L. Crystallographic computing system JANA2006: general features. Z. Kristallogr. 2014, 229, 345–352; https://doi.org/10.1515/zkri-2014-1737.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Kanatzidis, M. G., Pöttgen, R., Jeitschko, W. The metal flux – a preparative tool for intermetallic compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6996–7023; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200462170.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Manyako, M. B., Yahson, T. L., Zarechnyuk, O. S. Phase transformations in the Ca–V(Cr)–Al systems at 770 K. Russ. Metall. 1990, 2, 199–201.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Palatinus, L. The charge-flipping algorithm in crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2013, B69, 1–16; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768112051361.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Palatinus, L., Chapuis, G. SUPERFLIP – a computer program for the solution of crystal structures by charge flipping in arbitrary dimensions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 786–790; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807029238.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Krypyakevych, P. I., Zarechnyuk, O. S. The RCr2Al20 compounds in the systems of the rare earth metals and calcium and their crystal structures. Dopov. Akad. Nauk Ukr. RSR Ser. A 1968, 364–367.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Thiede, V. M. T., Jeitschko, W., Niemann, S., Ebel, T. EuTa2Al20, Ca6W4Al43 and other compounds with CeCr2Al20 and Ho6Mo4Al43 type structures and some magnetic properties of these compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 267, 23–31; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-8388(97)00532-x.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Frank, F. C., Kasper, J. S. Complex alloy structures regarded as sphere packings. I. Definitions and basic principles. Acta Crystallogr. 1958, 11, 184–190; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0365110x58000487.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Frank, F. C., Kasper, J. S. Complex alloy structures regarded as sphere packings. II. Analysis and classification of representative structures. Acta Crystallogr. 1959, 12, 483–499; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0365110x59001499.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Emsley, J. The Elements; Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1999.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Donohue, J. The Structures of the Elements; Wiley: New York, 1974.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Okuyama, D., Tsujimoto, M., Sagayama, H., Shimura, Y., Sakai, A., Magata, A., Nakatsuji, S., Sato, T. J. Crystal structure in quadrupolar Kondo candidate PrTr2Al20 (Tr = Ti and V). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 88, 015001; https://doi.org/10.7566/jpsj.88.015001.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Swatek, P., Kaczorowski, D. Magnetic properties of EuCr2Al20. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 348–352; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.04.086.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Ramesh Kumar, K., Nair, H. S., Bhattacharyya, A., Thamizhavel, A., Strydom, A. M. Metamagnetism, sign reversal and low temperature magnetocaloric effect in single-crystalline EuV2Al20. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 452, 205–209; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.12.066.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

