Abstract
C14H19ClN2O, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 8.9579(3) Å, b = 12.2172(4) Å, c = 12.5669(5) Å, V = 1375.33(8) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0541, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1449, T = 193 K.
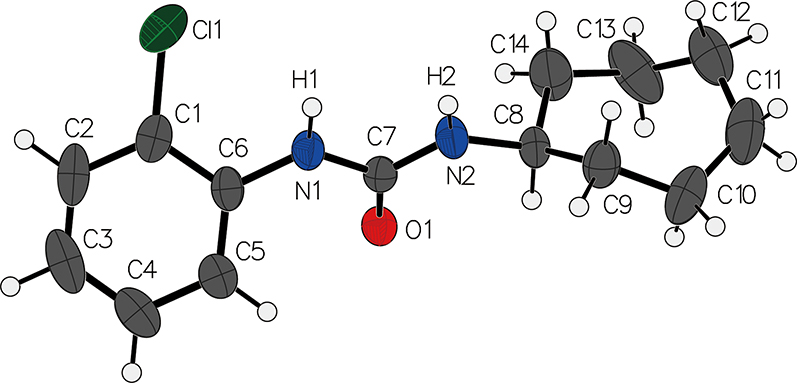
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size | 0.57 × 0.48 × 0.41 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.27 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Discover, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 29.3°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 14,926, 3749, 0.054 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3022 |
| N(param)refined: | 163 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.6087 (4) | 0.0331 (3) | 0.3092 (3) | 0.0417 (8) |
| C2 | 0.6462 (4) | −0.0709 (3) | 0.2741 (4) | 0.0542 (10) |
| H2A | 0.627276 | −0.091697 | 0.202505 | 0.065* |
| C3 | 0.7108 (5) | −0.1435 (3) | 0.3431 (4) | 0.0663 (13) |
| H3 | 0.736201 | −0.214952 | 0.319557 | 0.080* |
| C4 | 0.7390 (5) | −0.1129 (3) | 0.4474 (4) | 0.0579 (10) |
| H4 | 0.786016 | −0.162825 | 0.494690 | 0.069* |
| C5 | 0.6988 (4) | −0.0094 (3) | 0.4828 (3) | 0.0448 (8) |
| H5 | 0.717223 | 0.010683 | 0.554672 | 0.054* |
| C6 | 0.6324 (3) | 0.0647 (3) | 0.4146 (3) | 0.0350 (7) |
| C7 | 0.6605 (3) | 0.2344 (2) | 0.5182 (2) | 0.0302 (6) |
| C8 | 0.6455 (4) | 0.4074 (2) | 0.6182 (3) | 0.0341 (6) |
| H8 | 0.737524 | 0.376941 | 0.652107 | 0.041* |
| C9 | 0.5373 (4) | 0.4343 (3) | 0.7075 (3) | 0.0459 (8) |
| H9A | 0.450436 | 0.473370 | 0.676989 | 0.055* |
| H9B | 0.500233 | 0.364915 | 0.738511 | 0.055* |
| C10 | 0.6026 (6) | 0.5032 (4) | 0.7954 (3) | 0.0681 (13) |
| H10A | 0.542887 | 0.490450 | 0.860527 | 0.082* |
| H10B | 0.704873 | 0.476323 | 0.809831 | 0.082* |
| C11 | 0.6107 (9) | 0.6213 (4) | 0.7775 (5) | 0.099 (2) |
| H11A | 0.685074 | 0.651143 | 0.827981 | 0.119* |
| H11B | 0.512727 | 0.652617 | 0.797490 | 0.119* |
| C12 | 0.6497 (6) | 0.6651 (3) | 0.6674 (4) | 0.0704 (13) |
| H12A | 0.556303 | 0.670449 | 0.625637 | 0.084* |
| H12B | 0.689225 | 0.740258 | 0.675842 | 0.084* |
| C13 | 0.7598 (5) | 0.6006 (3) | 0.6041 (5) | 0.0757 (16) |
| H13A | 0.841249 | 0.576414 | 0.651921 | 0.091* |
| H13B | 0.804188 | 0.648841 | 0.549364 | 0.091* |
| C14 | 0.6937 (6) | 0.5005 (3) | 0.5495 (4) | 0.0642 (12) |
| H14A | 0.606149 | 0.524849 | 0.507632 | 0.077* |
| H14B | 0.768557 | 0.472473 | 0.498405 | 0.077* |
| Cl1 | 0.52770 (12) | 0.12470 (9) | 0.22082 (7) | 0.0576 (3) |
| N1 | 0.5842 (3) | 0.1682 (2) | 0.4493 (2) | 0.0371 (6) |
| H1 | 0.498270 | 0.192273 | 0.424702 | 0.045* |
| N2 | 0.5828 (3) | 0.3211 (2) | 0.5522 (2) | 0.0394 (6) |
| H2 | 0.488357 | 0.326145 | 0.533656 | 0.047* |
| O1 | 0.7912 (2) | 0.21490 (17) | 0.54628 (17) | 0.0347 (5) |
1 Source of materials
In a 3-neck round bottom flask, 1-chloro-2-isocyanatobenzene (0.15 g 1 mmol), cycloheptanamine (0.11 g 1 mmol), and dichloromethane (15 mL) were added and stirred under reflux for 5 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and then concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation technique. A solution of the pure compound in ethanol was prepared by slowly adding the crude product (50 mg) to a mixture of ethanol and dichloromethane (10 mL, 1:1 v/v) at room temperature and stirring overnight. The crystal of the title compound was obtained after three days with solution evaporation in the capless bottle.
2 Experimental details
The crystal structure was refined using the SHELXT package [3] in OLEX2 software [4].
3 Comment
Phenylurea herbicides are widely utilized in agriculture for the control of broadleaf weeds in cereal crops [5]. The molecular structure and intermolecular interaction, especially the hydrogen bonds, were the important factors affecting the properties of phenylurea herbicides. This highlights the need for further research on these herbicides. Many phenylurea derivative structures [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14] and synthetic methods [15], [16], [17], [18] were reported. In this paper, we show a phenylurea crystal structure named 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea.
It’s also worth mentioning that crystal structures of other urea derivatives such as 1-[3-(hydroxymethyl) phenyl]-3-phenylurea [15], 1,1′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(3-phenylurea) [16], and N, N′–diphenylureas [9] have been reported. The molecular structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea consists of a cycloheptylurea moiety and a 2-chloroaniline moiety linked through a C–N single bond. The cycloheptyl ring adopts a chair conformation. The 2-chloroaniline moiety is planar, and the N–H bond is involved in hydrogen bonding interactions in the crystal.
The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea is made up of a three-dimensional network of hydrogen bonds involving the carbonyl oxygen and the amide nitrogen atoms. The crystal structure can be described as layers of molecules stacked along the a-axis, with the layers held together by N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds (N2–H2⋯O1 and N1–H1⋯O1). The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea is similar to other crystal structures of cycloheptylurea derivatives, where the same type of hydrogen bonding interactions is observed [19]. These comparisons can provide insight into the structural features that are important for the formation and stability of the crystal structure [20].
Funding source: Natural Science Foundation of Shannxi Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019JQ-924
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021JQ-883
Funding source: Collaborative Innovation Center of Green Manufacturing Technology
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019XT-1–03
Funding source: Shaanxi University Association for Science and Technology Young Talent Support Program Project
Award Identifier / Grant number: 20210313
Funding source: Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Drug Synthesis of Xianyang City
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021QXNL-PT-0008
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Natural Science Foundation of Shannxi Province (2019JQ-924, 2021JQ-883), Key breeding program by Collaborative Innovation Center of Green Manufacturing Technology for Traditional Chinese Medicine in Shaanxi Province (2019XT-1–03), Shaanxi University Association for Science and Technology Young Talent Support Program Project (20210313) and Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Drug Synthesis of Xianyang City (2021QXNL-PT-0008).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Hussain, S., Arshad, M., Springael, D., SøRensen, S. R., Bending, G. D., Devers-Lamrani, M., Maqbool, Z., Martin-Laurent, F. Abiotic and biotic processes governing the fate of phenylurea herbicides in soils: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1947–1998; https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.1001141.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Lefranc, J., Tetlow, D. J., Donnard, M., Minassi, A., Gálvez, E., Clayden, J. Geometry-selective synthesis of E or Z N-vinyl ureas (N-carbamoyl enamines). Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 296–299; https://doi.org/10.1021/ol1027442.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Koshti, V. S., Thorat, S. H., Gote, R. P., Chikkali, S. H., Gonnade, R. G. The impact of modular substitution on crystal packing: the tale of two ureas. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 7078–7094; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ce01324d.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Wróbel, T. M., Kiełbus, M., Kaczor, A. A., Kryštof, V., Karczmarzyk, Z., Wysocki, W., Fruziński, A., Król, S. K., Grabarska, A., Stepulak, A., Matosiuk, D. Discovery of nitroaryl urea derivatives with antiproliferative properties. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 608–618; https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2015.1057716.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Yamasaki, R., Iida, M., Ito, A., Fukuda, K., Tanatani, A., Kagechika, H., Masu, H., Okamoto, I. Crystal engineering of N, N′-diphenylurea compounds featuring phenyl-perfluorophenyl interaction. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5858–5866; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.7b00951.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Legrand, Y.-M., Michau, M., van der Lee, A., Barboiu, M. Homomeric and heteromeric self-assembly of hybrid ureido-imidazole compounds. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 490–492; https://doi.org/10.1039/b717015g.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Kasatkina, S. O., Geyl, K. K., Baykov, S. V., Novikov, M. S., Boyarskiy, V. P. “Urea to urea” approach: access to unsymmetrical ureas bearing pyridyl substituents. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 1295–1304; https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.202101490.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Regueiro-Figueroa, M., Djanashvili, K., Esteban–Gómez, D., de Blas, A., Platas-Iglesias, C., Rodríguez-Blas, T. Towards selective recognition of sialic acid through simultaneous binding to its cis-diol and carboxylate functions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 3237–3248; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201000186.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Kang, G., Kim, J., Kwon, E., Kim, T. H. Crystal structure of pencycuron. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, E71, o532; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989015012414.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Guo, W., Gónzalez-Fabra, J., Bandeira, N. A. G., Bo, C., Kleij, A. W. A metal-free synthesis of N-aryl carbamates under ambient conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11686–11690; https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201504956.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Choi, H., Shim, Y. S., Han, B. H., Kang, S. K., Sung, C. K. 1-[3-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-3-phenylurea. Acta Crystallogr. 2011, E67, o2094; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536811028315.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
16. Pansuriya, P., Naidu, H., Friedrich, H. B., Maguire, G. E. M. 1,1′-(Propane-1,3-diyl)bis(3-phenylurea). Acta Crystallogr. 2011, E67, o2552; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536811035343.Suche in Google Scholar
17. Gooch, A., McGhee, A. M., Renton, L. C., Plante, J. P., Lindsay, C. I., Wilson, A. J. Design, synthesis and binding properties of conformer-independent linear ADA hydrogen-bonding arrays. Supramol. Chem. 2009, 21, 12–17; https://doi.org/10.1080/10610270802468397.Suche in Google Scholar
18. Rajnikant, Dinesh, Deshmukh, M. B., Kamni. Synthesis, x-ray structure and N–H, O interactions in 1,3-d iphenyl-urea. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2006, 29, 239–242; https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02706491.Suche in Google Scholar
19. Gao, K., Zha, S.-E., Liu, C.-Y., Wang, Q.-J., Wang, E.-Q. The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 117–118; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0486.Suche in Google Scholar
20. Zhu, J.-L., Liu, X.-H. The crystal structure of 2-chloro-N-((2-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl)nicotinamide, C13H9Cl2N3O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 787–788; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0255.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

