Abstract
C18H12F4O, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 7.9400(8) Å, b = 8.1071(9) Å, c = 13.3238(15) Å, α =
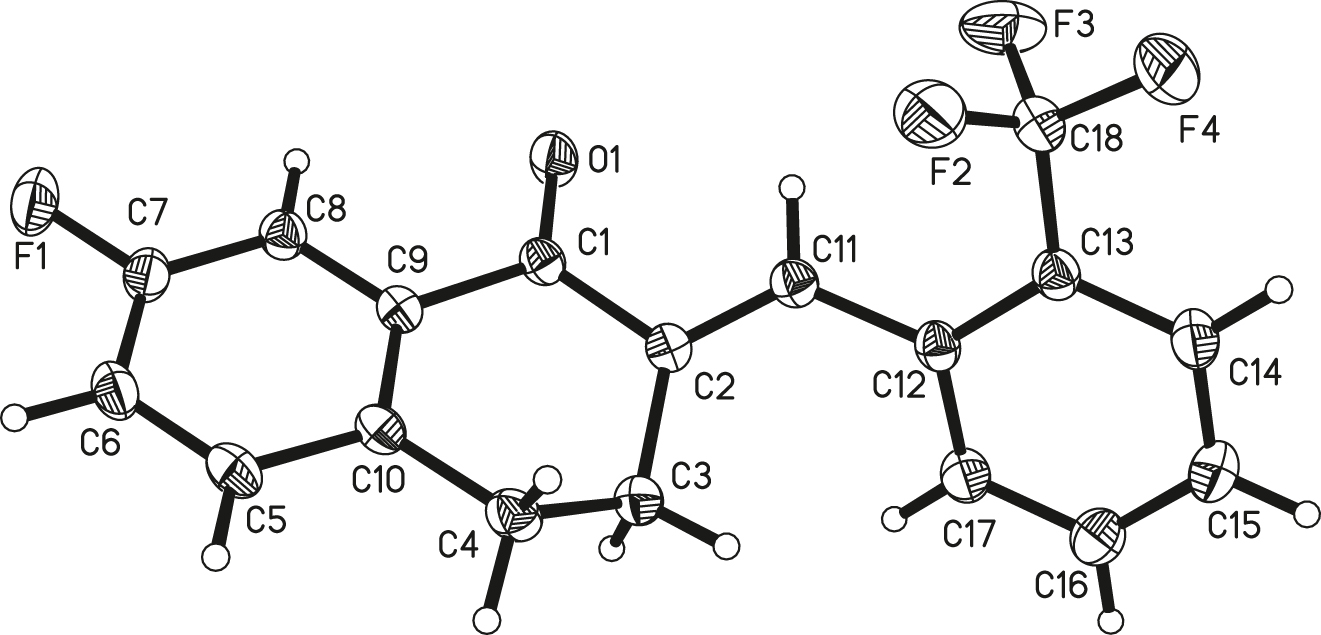
The crystal structure is shown in figure. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 20% probability level.
Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.13 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.12 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl) measured , N(hkl) unique, R int: | 5090, 2757, 0.018 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl) gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 1886 |
| N(param)refined: | 208 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2,3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.3021 (3) | 0.1159 (3) | 0.44630 (15) | 0.0467 (5) |
| C2 | 0.4080 (3) | 0.0627 (3) | 0.33376 (14) | 0.0454 (5) |
| C3 | 0.5253 (3) | 0.1620 (3) | 0.29075 (16) | 0.0566 (6) |
| H3A | 0.567905 | 0.136452 | 0.215629 | 0.068* |
| H3B | 0.640379 | 0.116239 | 0.317107 | 0.068* |
| C4 | 0.4058 (4) | 0.3704 (3) | 0.32088 (16) | 0.0599 (6) |
| H4A | 0.489801 | 0.428872 | 0.299560 | 0.072* |
| H4B | 0.304894 | 0.418905 | 0.283863 | 0.072* |
| C5 | 0.2672 (3) | 0.5915 (3) | 0.48469 (18) | 0.0593 (6) |
| H5 | 0.297861 | 0.675030 | 0.446001 | 0.071* |
| C6 | 0.1780 (3) | 0.6394 (3) | 0.58907 (19) | 0.0614 (6) |
| H6 | 0.146742 | 0.754411 | 0.621083 | 0.074* |
| C7 | 0.1361 (3) | 0.5131 (3) | 0.64492 (17) | 0.0587 (6) |
| C8 | 0.1763 (3) | 0.3443 (3) | 0.60074 (16) | 0.0527 (5) |
| H8 | 0.144977 | 0.262291 | 0.640638 | 0.063* |
| C9 | 0.2651 (3) | 0.2971 (3) | 0.49480 (15) | 0.0439 (5) |
| C10 | 0.3127 (3) | 0.4202 (3) | 0.43546 (15) | 0.0482 (5) |
| C11 | 0.3828 (3) | −0.0611 (3) | 0.28211 (15) | 0.0503 (5) |
| H11 | 0.294817 | −0.100206 | 0.319308 | 0.060* |
| C12 | 0.4775 (3) | −0.1433 (3) | 0.17318 (15) | 0.0488 (5) |
| C13 | 0.3769 (3) | −0.1758 (3) | 0.10799 (16) | 0.0513 (5) |
| C14 | 0.4727 (4) | −0.2554 (3) | 0.00690 (18) | 0.0677 (7) |
| H14 | 0.404360 | −0.275303 | −0.035509 | 0.081* |
| C15 | 0.6667 (4) | −0.3055 (4) | −0.03190 (19) | 0.0770 (7) |
| H15 | 0.729358 | −0.358716 | −0.100242 | 0.092* |
| C16 | 0.7680 (4) | −0.2771 (4) | 0.0303 (2) | 0.0738 (7) |
| H16 | 0.899727 | −0.310549 | 0.004040 | 0.089* |
| C17 | 0.6757 (3) | −0.1991 (3) | 0.13151 (18) | 0.0617 (6) |
| H17 | 0.747248 | −0.183081 | 0.173210 | 0.074* |
| C18 | 0.1659 (4) | −0.1226 (4) | 0.14540 (18) | 0.0653 (6) |
| F1 | 0.0486 (2) | 0.5596 (2) | 0.74883 (11) | 0.0901 (5) |
| F2 | 0.0566 (2) | 0.0534 (2) | 0.18312 (14) | 0.1006 (6) |
| F3 | 0.1271 (3) | −0.2185 (3) | 0.22106 (14) | 0.1131 (7) |
| F4 | 0.0901 (2) | −0.1483 (3) | 0.07227 (13) | 0.1153 (7) |
| O1 | 0.2475 (3) | 0.0147 (2) | 0.49754 (11) | 0.0672 (5) |
1 Source of material
7-Methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one (0.70 g, 4.26 mmol) and 2-(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde (0.74 g, 4.26 mmol) were dissolved in 10 mL acetic acid. Then dry hydrogen chloride gas was flowed continuously into the solution lasting 45 min. After gas insertion, the reaction system was stirred at room temperature for 5 days. The response endpoint was detected by thin layer chromatography (TLC). When the reaction was stopped, the precipitate was filtered from the reaction system, then it was dissolved in distilled water and regulated to a neutral pH with saturated aqueous Na2 CO3 solution. The precipitate was filtered and dissolved with dichloromethane. The organic phase was washed successively with deionized water and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and condensed under vacuum. The crude product was purified by silica-gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 8:1, v:v). Crystals were obtained under ambient conditions via solvent evaporation in the mixed solvents of dichloromethane and methanol (2:1, v:v) and drying under vacuo at 333 K for 3 h.
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d (C–H) = 0.97 Å (methylene), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq (C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq (C).
3 Comment
3,4–Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one (DHN) is a ketone derivative that is often used as an intermediate in molecular synthesis blocks. Many compounds contain this structure [4], [5], [6]. In this work, we have synthesized novel DHN derivative E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, using the Claisen-schmidt condensation reaction and report their single crystal structures. This provides an important basis for the study of DHNs derivatives.
The ORTEP diagram is presented in the Figure. The title compound contains one drug molecule in the asymmetric unit (cf. the figure). The 7 position of the aromatic ring in the parent nucleus of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one is fluorinated [7,8]. The trifluoromethyl group replaces the hydrogen in the benzene ring at position 13. And the carbons at positions 3 and 4 are saturated carbons containing two hydrogens. The carbonyl group at position 11 is an alpha and beta unsaturated ketone formed by the Claisen-schmidt condensation of the parent nucleus of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one with 4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde. In terms of the C(12)=C(11) olefin bond, the E stereochemical structure is formed [9]. Due to the distortion of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, the 7-methoxy and 2-(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde groups are not coplanar with each other and their dihedral angle is about 69.5°. Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. The title molecular has an approximately linear structure [10,11].
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Science and Technology Innovation Development Plan of Yantai (No.2020XDRH105) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81473104).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Zhang, X. F., Luan, M. Z., Yan, W. B., Zhao, F. L., Hou, Y., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of novel 5,6-dihydrobenzo [h]quinazolin-2-amine derivatives in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114322.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Sun, Y., Zhou, Y. Q., Liu, Y. K., Zhang, H. Q., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G., Hou, Y. Potential anti-neuroinflammatory NF-κB inhibitors based on 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1631–1640. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1804899.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Luan, M. Z., Zhang, X. F., Yang, Y., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G. Anti-inflammatory activity of fluorine-substituted benzo [h]quinazoline-2-amine derivatives as NF-κB inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, published online ahead of print, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106360.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Zhang, X. F., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 507–509. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0603.Search in Google Scholar
8. Sun, J. J., Zhang, X. F., Meng, Q. G., Li, H. J., Wang, C. H. Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl) methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 1097–1099. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0234.Search in Google Scholar
9. Zhang, S. N., Zhao, F. L., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 1–3; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0382.Search in Google Scholar
10. Zhang, X. F., Wang, H. Y., Song, J., Liang, L. H., Xu, Y. R., Zhao, F. L., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluo romethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0492.Search in Google Scholar
11. Ma, G. Q., Zhao, F. L., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0378.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

