Abstract
C27H44N4O7S, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 10.216(3) Å, b = 18.133(5) Å, c = 17.036(5) Å, β = 98.371(3)°, V = 3122.2(16) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0435, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1333, T = 296(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.15 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 20,315, 5496, 0.025 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 4660 |
| N(param)refined: | 352 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Shelx [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.29582 (16) | 0.12453 (9) | 0.95133 (11) | 0.0394 (4) |
| N1 | −0.35892 (16) | 0.09333 (10) | 0.49290 (10) | 0.0594 (5) |
| H1A | −0.4300 | 0.1191 | 0.4911 | 0.071* |
| H1B | −0.3545 | 0.0586 | 0.4590 | 0.071* |
| O1 | 0.41940 (13) | 0.04032 (7) | 1.06220 (8) | 0.0544 (4) |
| S1 | 0.38869 (4) | 0.11686 (2) | 1.04727 (3) | 0.04099 (15) |
| C2 | 0.18696 (18) | 0.17094 (11) | 0.94029 (12) | 0.0498 (5) |
| H2A | 0.1657 | 0.1997 | 0.9818 | 0.060* |
| N2 | −0.14583 (16) | 0.06837 (10) | 0.54895 (11) | 0.0606 (5) |
| H2B | −0.0781 | 0.0780 | 0.5837 | 0.073* |
| H2C | −0.1419 | 0.0337 | 0.5149 | 0.073* |
| O2 | 0.31935 (13) | 0.15680 (8) | 1.10117 (8) | 0.0543 (4) |
| C3 | 0.11055 (19) | 0.17365 (11) | 0.86634 (12) | 0.0520 (5) |
| H3A | 0.0374 | 0.2047 | 0.8583 | 0.062* |
| N3 | −0.26318 (16) | 0.16009 (9) | 0.59952 (10) | 0.0529 (4) |
| H3B | −0.3343 | 0.1858 | 0.5977 | 0.063* |
| H3C | −0.1965 | 0.1691 | 0.6352 | 0.063* |
| O3 | −0.04629 (15) | 0.17454 (10) | 0.71916 (9) | 0.0734 (5) |
| C4 | 0.14098 (17) | 0.13096 (10) | 0.80408 (11) | 0.0444 (4) |
| N4 | 0.08536 (18) | 0.15126 (10) | 0.27330 (9) | 0.0553 (4) |
| O4 | 0.07160 (14) | 0.08491 (9) | 0.67381 (8) | 0.0615 (4) |
| C5 | 0.25260 (17) | 0.08600 (11) | 0.81627 (11) | 0.0464 (4) |
| H5A | 0.2753 | 0.0581 | 0.7745 | 0.056* |
| O5 | 0.88805 (13) | 0.35269 (8) | 1.02285 (11) | 0.0665 (4) |
| C6 | 0.33000 (17) | 0.08245 (10) | 0.88976 (11) | 0.0457 (4) |
| H6A | 0.4042 | 0.0521 | 0.8977 | 0.055* |
| O6 | 1.00180 (12) | 0.25136 (8) | 1.06179 (9) | 0.0600 (4) |
| C7 | 0.04827 (19) | 0.13080 (12) | 0.72564 (12) | 0.0519 (5) |
| O1W | 0.25168 (18) | 0.03266 (9) | 0.58227 (12) | 0.0818 (5) |
| H1WA | 0.2052 | 0.0470 | 0.6166 | 0.123* |
| H1WB | 0.2946 | 0.0723 | 0.5642 | 0.123* |
| C8 | 0.53784 (16) | 0.16473 (9) | 1.04204 (10) | 0.0378 (4) |
| C9 | 0.65150 (17) | 0.12744 (10) | 1.03027 (11) | 0.0427 (4) |
| H9A | 0.6501 | 0.0767 | 1.0224 | 0.051* |
| C10 | 0.76715 (16) | 0.16707 (10) | 1.03040 (11) | 0.0436 (4) |
| H10A | 0.8447 | 0.1424 | 1.0240 | 0.052* |
| C11 | 0.76919 (16) | 0.24311 (10) | 1.04004 (10) | 0.0383 (4) |
| C12 | 0.65278 (18) | 0.27931 (11) | 1.04854 (13) | 0.0510 (5) |
| H12A | 0.6524 | 0.3304 | 1.0528 | 0.061* |
| C13 | 0.53724 (18) | 0.24042 (11) | 1.05075 (13) | 0.0510 (5) |
| H13A | 0.4599 | 0.2649 | 1.0580 | 0.061* |
| C14 | 0.89718 (17) | 0.28569 (10) | 1.04169 (11) | 0.0429 (4) |
| C15 | −0.25641 (17) | 0.10712 (10) | 0.54782 (11) | 0.0444 (4) |
| C16 | 0.1906 (3) | 0.11511 (15) | 0.33308 (14) | 0.0744 (7) |
| H16A | 0.1640 | 0.0646 | 0.3406 | 0.089* |
| H16B | 0.1926 | 0.1403 | 0.3835 | 0.089* |
| C17 | 0.3304 (3) | 0.1143 (2) | 0.31212 (19) | 0.0955 (10) |
| H17A | 0.3267 | 0.1234 | 0.2557 | 0.115* |
| H17B | 0.3811 | 0.1538 | 0.3404 | 0.115* |
| C18 | 0.3975 (4) | 0.0446 (2) | 0.3320 (4) | 0.1507 (19) |
| H18A | 0.4850 | 0.0466 | 0.3178 | 0.226* |
| H18B | 0.4031 | 0.0358 | 0.3880 | 0.226* |
| H18C | 0.3488 | 0.0053 | 0.3034 | 0.226* |
| C19 | 0.0783 (2) | 0.11491 (11) | 0.19247 (12) | 0.0570 (5) |
| H19A | 0.0099 | 0.1396 | 0.1564 | 0.068* |
| H19B | 0.1617 | 0.1235 | 0.1731 | 0.068* |
| C20 | 0.0507 (3) | 0.03360 (14) | 0.18826 (16) | 0.0810 (8) |
| H20A | −0.0353 | 0.0239 | 0.2038 | 0.097* |
| H20B | 0.1168 | 0.0077 | 0.2247 | 0.097* |
| C21 | 0.0530 (3) | 0.00610 (15) | 0.10529 (19) | 0.0919 (9) |
| H21A | 0.0353 | −0.0459 | 0.1031 | 0.138* |
| H21B | −0.0132 | 0.0314 | 0.0694 | 0.138* |
| H21C | 0.1386 | 0.0152 | 0.0903 | 0.138* |
| C22 | −0.0447 (2) | 0.14257 (14) | 0.30508 (14) | 0.0674 (6) |
| H22A | −0.0344 | 0.1628 | 0.3584 | 0.081* |
| H22B | −0.0630 | 0.0903 | 0.3090 | 0.081* |
| C23 | −0.1638 (3) | 0.17903 (19) | 0.25638 (18) | 0.0880 (8) |
| H23A | −0.1564 | 0.2322 | 0.2620 | 0.106* |
| H23B | −0.1654 | 0.1670 | 0.2008 | 0.106* |
| C24 | −0.2910 (3) | 0.1534 (2) | 0.2833 (3) | 0.1161 (12) |
| H24A | −0.3648 | 0.1771 | 0.2518 | 0.174* |
| H24B | −0.2990 | 0.1010 | 0.2770 | 0.174* |
| H24C | −0.2900 | 0.1661 | 0.3381 | 0.174* |
| C25 | 0.1177 (2) | 0.23175 (12) | 0.26025 (12) | 0.0615 (6) |
| H25A | 0.2025 | 0.2339 | 0.2411 | 0.074* |
| H25B | 0.0519 | 0.2511 | 0.2186 | 0.074* |
| C26 | 0.1238 (4) | 0.28223 (15) | 0.33148 (15) | 0.0921 (9) |
| H26A | 0.0409 | 0.2798 | 0.3528 | 0.111* |
| H26B | 0.1941 | 0.2663 | 0.3725 | 0.111* |
| C27 | 0.1491 (4) | 0.36003 (16) | 0.30769 (18) | 0.0967 (10) |
| H27A | 0.1528 | 0.3917 | 0.3531 | 0.145* |
| H27B | 0.2317 | 0.3623 | 0.2872 | 0.145* |
| H27C | 0.0789 | 0.3758 | 0.2675 | 0.145* |
Source of materials
4,4′-Sulfonyldibenzoic acid (A. R.), guanidine hydrochloride (A. R.) and tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (25% aqueous solution) were mixed in a molar ratio of 10:10:1. The mixture was dissolved in a minimum amount of ethanol and water to form the clean solution, then the solution was stirred for about 0.5 h. Subsequently the clean solution was set aside to allow it slow evaporation at room temperature. Colorless block crystals were obtained about seven days later.
Comment
4,4′-Sulfonyldibenzoic acid, as a V-shape molecule with flexible benzene rings, can take part in the formation of various hydrogen bonds after the deprotonation of the terminal carboxyl groups. Searching in the CSD database [4], there exist hundreds of MOFs constructed with 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoic acid. It can be concluded that this compound can display varied spatial configurations and has strong abilities to form hydrogen bonds. However, the pure organic crystal structures of 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoic acid are seldom reported compared with the related MOFs [5, 6]. Thus, the crystal structure of the title compound will enrich the corresponding organic crystal structures.
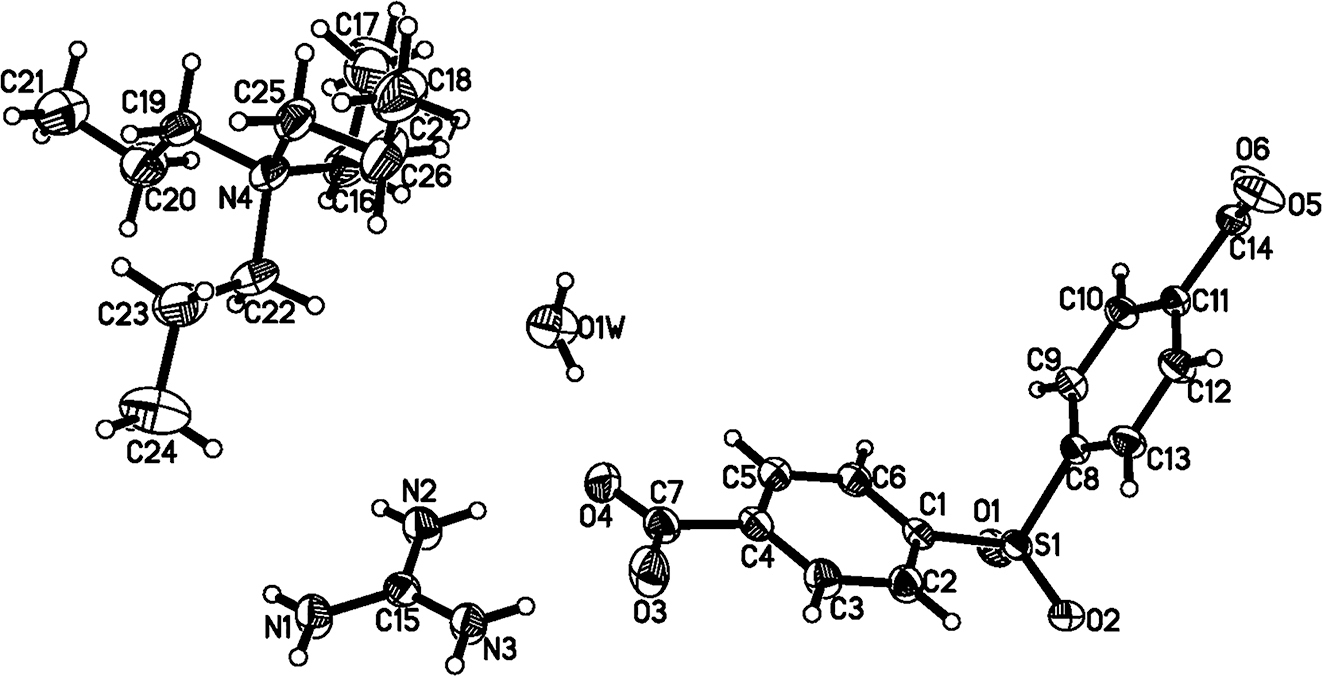
In the asymmetric unit of the title compound, the contents are one 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate, one guanidinium cation, one tetrapropylammonium cation and one water molecule. In the anion, the dihedral angle between two benzene rings is 107.1°, and two terminal carboxyl groups are distorted 4.5° and 24.5° from their related benzene rings. Obviously, the anion displays the V-shape skeleton and two terminal carboxyl groups are not coplanar with their mother rings [7]. From the crystal packing model, it can be seen that 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate can link with guanidine cation by N–H⋯O contacts, and the linkage motif can be further connected with the water molecules by N–H⋯O and O–H⋯O hydrogen bonds to generate a three-dimensional host lattice with regular channels. It is noticeable that the weak hydrogen bonds of C–H⋯S and C–H⋯O are also present to further consolidate the crystal.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support by Henan University of Chinese Medicine.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Henan University of Chinese Medicine.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker . Saint, Apex2 and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Allen, F. H., Taylor, R. Research applications of the Cambridge structural database (CSD). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 463–475; https://doi.org/10.1039/b309040j.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Yang, Y. X., Zhang, H. X., Xia, S. Y., Li, H. Y. Similar hydrogen-bonded ribbons in three 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoic anion/boric acid and tetrabutylammonium inclusion compounds. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 702, 64–75; https://doi.org/10.1080/15421406.2020.1727104.Search in Google Scholar
6. Wu, X., Zeng, H., Yang, Y. Composite host lattices of 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate water/boric acid in two tetrapropylammonium inclusion compounds. Acta Crystallogr. 2018, C74, 1026–1031; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229618011580.Search in Google Scholar
7. Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. Ethane-1,2-diaminium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate. Acta Crystallogr. 2011, E67, o2966; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536811041274.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

