Abstract
C21H45N9O3S2, orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 9.5299(6) Å, b = 16.5181(9) Å, c = 36.886(2) Å, β = 90°, V = 5806.4(6) Å3, Z = 8, R gt(F) = 0.0568, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1420, T = 296(2) K.
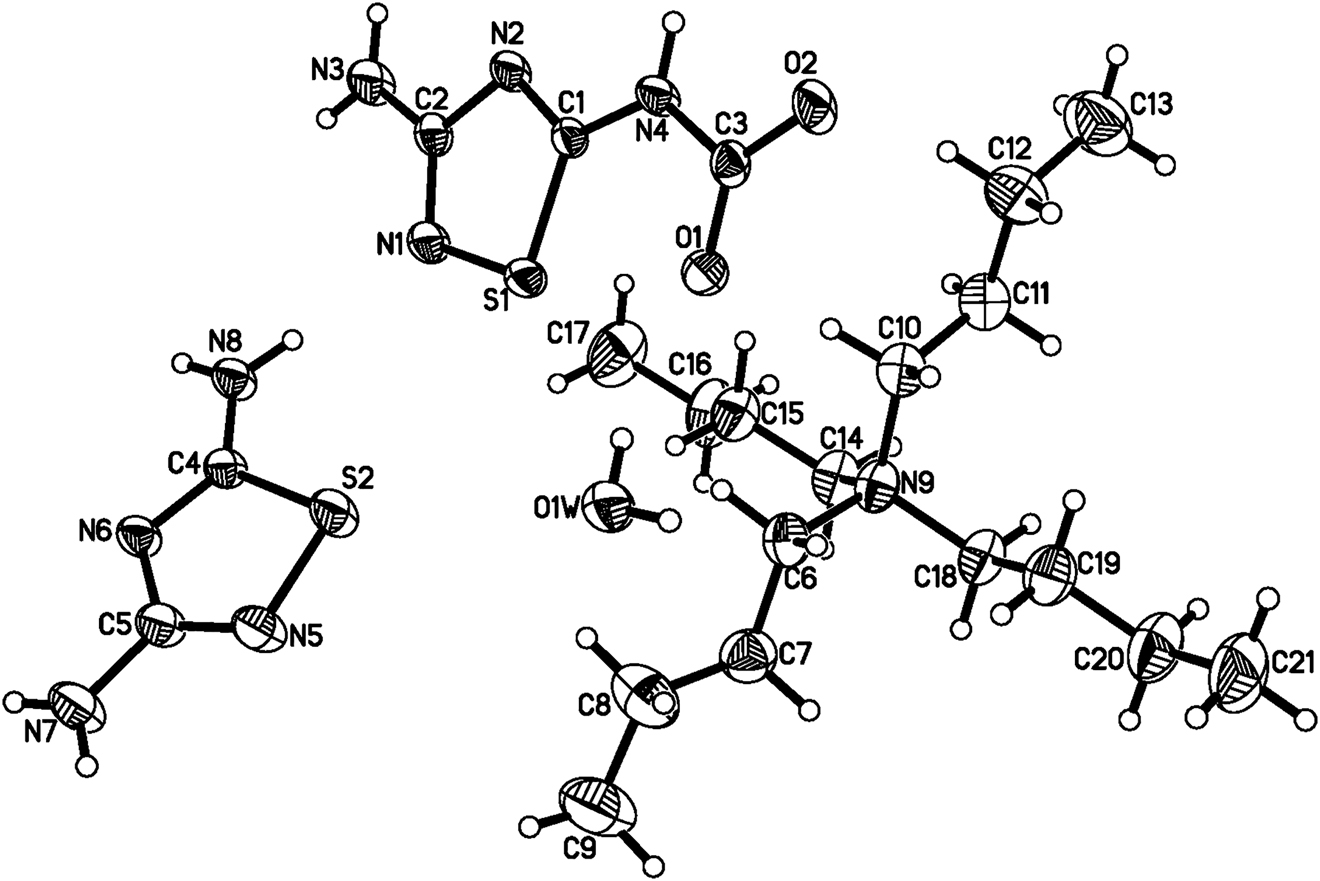
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.30 × 0.28 × 0.28 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.22 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 27,778, 5110, 0.032 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 4338 |
| N(param)refined: | 322 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | X | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.5290 (2) | 0.04175 (15) | 0.05309 (6) | 0.0378 (5) |
| N1 | 0.7546 (2) | 0.07756 (15) | 0.08019 (6) | 0.0521 (6) |
| O1 | 0.30458 (18) | 0.05046 (12) | 0.09974 (5) | 0.0519 (5) |
| S1 | 0.58747 (7) | 0.07287 (5) | 0.09501 (2) | 0.0488 (2) |
| O1W | 0.3454 (2) | 0.03028 (18) | 0.17907 (6) | 0.0728 (7) |
| H1WA | 0.356 (4) | 0.038 (3) | 0.1562 (4) | 0.109* |
| H1WB | 0.2571 (14) | 0.029 (3) | 0.1837 (9) | 0.109* |
| C2 | 0.7558 (3) | 0.05466 (16) | 0.04604 (7) | 0.0446 (6) |
| N2 | 0.6314 (2) | 0.03440 (14) | 0.02957 (5) | 0.0438 (5) |
| O2 | 0.16293 (17) | 0.01508 (13) | 0.05376 (5) | 0.0552 (5) |
| S2 | 0.79275 (7) | 0.07199 (6) | 0.17583 (2) | 0.0622 (2) |
| C3 | 0.2784 (2) | 0.03095 (16) | 0.06774 (7) | 0.0411 (6) |
| N3 | 0.8734 (2) | 0.05215 (16) | 0.02551 (7) | 0.0608 (7) |
| H3A | 0.9528 | 0.0660 | 0.0347 | 0.073* |
| H3B | 0.8687 | 0.0367 | 0.0033 | 0.073* |
| C4 | 0.9662 (2) | 0.06170 (16) | 0.16266 (7) | 0.0418 (6) |
| N4 | 0.39442 (19) | 0.02597 (14) | 0.04410 (5) | 0.0453 (5) |
| H4A | 0.3780 | 0.0117 | 0.0221 | 0.054* |
| C5 | 0.9645 (3) | 0.0350 (2) | 0.22064 (7) | 0.0546 (7) |
| N5 | 0.8299 (2) | 0.04829 (18) | 0.21880 (6) | 0.0645 (7) |
| C6 | 0.3189 (3) | 0.23839 (18) | 0.15525 (8) | 0.0600 (8) |
| H6A | 0.2415 | 0.2036 | 0.1623 | 0.072* |
| H6B | 0.3898 | 0.2042 | 0.1442 | 0.072* |
| N6 | 1.0471 (2) | 0.04201 (15) | 0.19002 (6) | 0.0489 (5) |
| C7 | 0.3806 (4) | 0.2754 (2) | 0.18931 (10) | 0.0749 (9) |
| H7A | 0.4498 | 0.3158 | 0.1827 | 0.090* |
| H7B | 0.3069 | 0.3022 | 0.2029 | 0.090* |
| N7 | 1.0269 (3) | 0.0121 (2) | 0.25208 (7) | 0.0784 (9) |
| H7C | 0.9774 | 0.0060 | 0.2714 | 0.094* |
| H7D | 1.1159 | 0.0036 | 0.2527 | 0.094* |
| C8 | 0.4480 (5) | 0.2126 (3) | 0.21264 (11) | 0.1010 (14) |
| H8A | 0.3769 | 0.1736 | 0.2197 | 0.121* |
| H8B | 0.5173 | 0.1841 | 0.1982 | 0.121* |
| N8 | 1.0093 (2) | 0.07486 (14) | 0.12864 (6) | 0.0506 (6) |
| H8C | 1.0968 | 0.0706 | 0.1233 | 0.061* |
| H8D | 0.9495 | 0.0876 | 0.1121 | 0.061* |
| C9 | 0.5176 (5) | 0.2432 (4) | 0.24612 (12) | 0.1217 (17) |
| H9A | 0.5575 | 0.1986 | 0.2592 | 0.183* |
| H9B | 0.5905 | 0.2806 | 0.2396 | 0.183* |
| H9C | 0.4497 | 0.2701 | 0.2611 | 0.183* |
| N9 | 0.2659 (2) | 0.29728 (13) | 0.12659 (7) | 0.0537 (6) |
| C10 | 0.2126 (3) | 0.24676 (17) | 0.09520 (8) | 0.0575 (7) |
| H10A | 0.2886 | 0.2121 | 0.0871 | 0.069* |
| H10B | 0.1386 | 0.2118 | 0.1042 | 0.069* |
| C11 | 0.1567 (4) | 0.2923 (2) | 0.06262 (9) | 0.0664 (8) |
| H11A | 0.0902 | 0.3331 | 0.0705 | 0.080* |
| H11B | 0.2332 | 0.3193 | 0.0502 | 0.080* |
| C12 | 0.0856 (4) | 0.2340 (2) | 0.03709 (10) | 0.0854 (11) |
| H12A | 0.0106 | 0.2067 | 0.0500 | 0.102* |
| H12B | 0.1530 | 0.1932 | 0.0297 | 0.102* |
| C13 | 0.0256 (5) | 0.2737 (3) | 0.00366 (11) | 0.1118 (16) |
| H13A | −0.0179 | 0.2334 | −0.0113 | 0.168* |
| H13B | −0.0430 | 0.3132 | 0.0107 | 0.168* |
| H13C | 0.0995 | 0.2998 | −0.0096 | 0.168* |
| C14 | 0.3833 (3) | 0.35338 (17) | 0.11423 (9) | 0.0604 (8) |
| H14A | 0.3455 | 0.3903 | 0.0963 | 0.072* |
| H14B | 0.4130 | 0.3856 | 0.1348 | 0.072* |
| C15 | 0.5110 (3) | 0.31264 (19) | 0.09831 (10) | 0.0681 (9) |
| H15A | 0.5528 | 0.2771 | 0.1162 | 0.082* |
| H15B | 0.4835 | 0.2800 | 0.0776 | 0.082* |
| C16 | 0.6166 (4) | 0.3748 (2) | 0.08664 (13) | 0.0893 (12) |
| H16A | 0.6427 | 0.4073 | 0.1075 | 0.107* |
| H16B | 0.5734 | 0.4104 | 0.0690 | 0.107* |
| C17 | 0.7477 (4) | 0.3384 (3) | 0.07029 (14) | 0.1085 (15) |
| H17A | 0.8109 | 0.3809 | 0.0634 | 0.163* |
| H17B | 0.7924 | 0.3040 | 0.0878 | 0.163* |
| H17C | 0.7230 | 0.3071 | 0.0493 | 0.163* |
| C18 | 0.1509 (3) | 0.35124 (18) | 0.14186 (9) | 0.0630 (8) |
| H18A | 0.1889 | 0.3806 | 0.1624 | 0.076* |
| H18B | 0.1260 | 0.3908 | 0.1235 | 0.076* |
| C19 | 0.0182 (3) | 0.3087 (2) | 0.15396 (10) | 0.0725 (9) |
| H19A | −0.0219 | 0.2791 | 0.1338 | 0.087* |
| H19B | 0.0401 | 0.2704 | 0.1730 | 0.087* |
| C20 | −0.0861 (4) | 0.3700 (3) | 0.16769 (13) | 0.0932 (12) |
| H20A | −0.0446 | 0.3991 | 0.1878 | 0.112* |
| H20B | −0.1049 | 0.4089 | 0.1486 | 0.112* |
| C21 | −0.2231 (4) | 0.3337 (3) | 0.17992 (14) | 0.1152 (16) |
| H21A | −0.2843 | 0.3759 | 0.1883 | 0.173* |
| H21B | −0.2664 | 0.3059 | 0.1600 | 0.173* |
| H21C | −0.2060 | 0.2961 | 0.1993 | 0.173* |
Source of materials
Amidinothiourea and tetrabutylammonium hydroxide (10% aqueous solution) were mixed in a molar ratio of 1:2. The mixture was dissolved in a minimum amount of ethanol/water, then the mixture was vigorously stirred for about 1.5 h. Subsequently the clean solution was set aside to allow it slow evaporation at room temperature. Colorless block crystals were obtained about 15 days later. It can be concluded that one part of amidinothiourea molecules form 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine molecules under basic conditions, and another part of amidinothiourea molecules should absorb CO2 of the atmosphere to convert to the corresponding 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate anions under basic conditions.
Comment
Amidinothiourea, which is a derivative of thiourea, is a key pharmaceutical intermediate of famotidine [4]. Observing the structure of amidinothiourea, it can be regarded as a plane molecule composed of two triangular parts, which can generate more than nine hydrogen bonds. As the related literatures [5], [6], [7] indicated, amidinothiourea is unstable and it can form heterocycle under specific conditions, such as 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate or 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine. In 2012, two compounds of 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate were reported with the existence of tetrapropylammonium and tetrabutylammonium [5]. In 2022, one dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate was reported [6]. As to 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine, it can be concluded that it is also a derivative of amidinothiourea under basic conditions, just like 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate. Compared with 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine doesn’t absorb extra CO2 to further yield the additional carboxyl group to link with the heterocycle derived from amidinothiourea during the actual experimental process. It is noticeable that 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine is normally synthesized by amidinothiourea with the existence of H2O2 [7]. But in this manuscript, with the absence of H2O2, 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine can also be obtained under basic conditions.
In the asymmetric unit of the crystal structure, there exist one tetrabutylammonium, one 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine and one water molecule. As the calculation implies, the carbamate anion and neutral diamine have qualified planarity with the mean deviation values from the least-square planes of 0.0050 Å and 0.0027 Å. In the carbamate, the bond lengths of the deprotonated carboxyl group tend to be average with the values of 1.249(3) Å and 1.244(3) Å. Analyzing the hydrogen bonds, it can be seen that one pair of 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate firstly connect with each other to form a hydrogen-bonded dimer by two N–H⋯N hydrogen bonds and two N–H⋯O hydrogen bond, then the adjacent dimers are further linked with N–H⋯O contacts to generate the extended ribbons along the a axis. Additionally, two neighboring 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine molecules are connected with N–H⋯N hydrogen bonding to yield a ziazag hydrogen-bonded chain along the a axis. Consecutively, the hydrogen-bonded chains interact with the anionic hydrogen-bonded ribbons mentioned above by the water molecules to finally construct the 2-dimensional layer. As to tetrabutylammonium cations, they are regularly contained between the layers to form the ultimate sandwich-like crystal structure. From this, it can be seen that 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate and 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine, as two derivatives of amidinothiourea, both display excellent abilities of forming hydrogen bonds, which can be further explored in the related crystal structures.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Henan University of Chinese Medicine.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXTL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Adane, L., Bhagat, S., Arfeen, M., Bhatia, S., Sirawaraporn, R., Sirawaraporn, W., Chakraborti, A. K., Bharatam, P. V. Design and synthesis of guanylthiourea derivatives as potential inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase enzyme. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, A24, 613–617; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.12.009.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Zhang, W. H., Li, K., Li, Q., Mak, T. C. W. Two inclusion compounds of guanylthiourea and 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate. J. Inclus. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 74, 353–359; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-012-0122-z.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Tan, X. K., Zhu, X. Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 525–526; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0128.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Melenchuk, T. V., Danilova, E. A., Stryapan, M. G., Islyaikin, M. K. Synthesis and properties of diaminothiadiazoles. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2008, 78, 480–484; https://doi.org/10.1134/s1070363208030237.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

