Abstract
C12H18N2O4, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 7.1591(14) Å, b = 10.236(2) Å, c = 16.713(3) Å, V = 1224.7(4) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0333, wRref(F2) = 0.0810, T = 293(2) K.
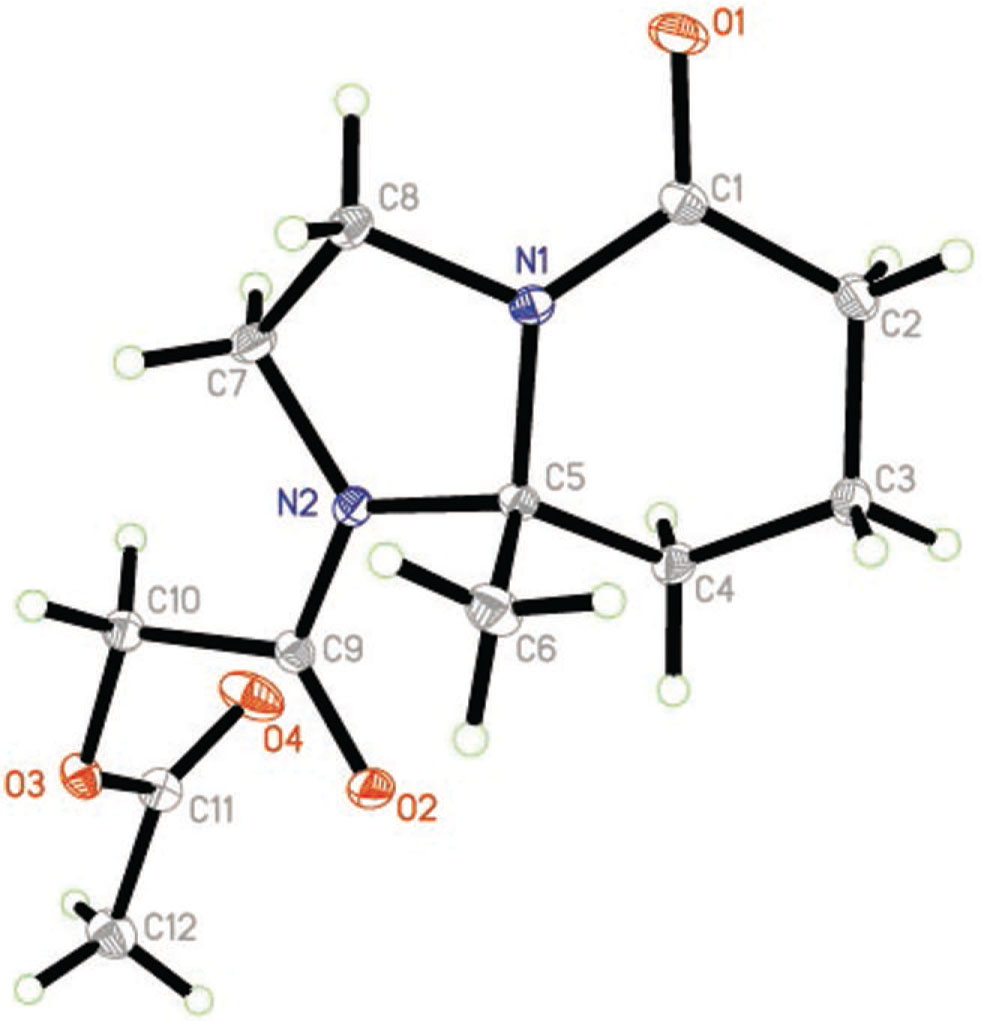
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains details on crystal structure and measurement conditions. Table 2 lists the atoms with their coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.5 × 0.37 × 0.29 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.0 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur Eos, ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 55.2°, >98% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11509, 2762, 0.030 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2578 |
| N(param)refined: | 165 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], DIAMOND [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.53972(19) | 0.27779(13) | 0.13868(8) | 0.0186(3) |
| C2 | 0.70264(19) | 0.22773(14) | 0.09026(9) | 0.0213(3) |
| H2A | 0.6698 | 0.2328 | 0.0340 | 0.026* |
| H2B | 0.7209 | 0.1362 | 0.1031 | 0.026* |
| C3 | 0.8867(2) | 0.29834(15) | 0.10231(8) | 0.0212(3) |
| H3A | 0.8880 | 0.3777 | 0.0706 | 0.025* |
| H3B | 0.9886 | 0.2432 | 0.0843 | 0.025* |
| C4 | 0.91409(18) | 0.33215(14) | 0.19019(8) | 0.0198(3) |
| H4A | 0.9142 | 0.2527 | 0.2219 | 0.024* |
| H4B | 1.0337 | 0.3751 | 0.1974 | 0.024* |
| C5 | 0.75837(19) | 0.42157(13) | 0.21847(7) | 0.0163(3) |
| C6 | 0.7778(2) | 0.56147(14) | 0.18699(9) | 0.0253(3) |
| H6A | 0.7804 | 0.5603 | 0.1296 | 0.038* |
| H6B | 0.8915 | 0.5991 | 0.2068 | 0.038* |
| H6C | 0.6735 | 0.6127 | 0.2049 | 0.038* |
| C7 | 0.54488(19) | 0.40630(14) | 0.33291(8) | 0.0210(3) |
| H7A | 0.5057 | 0.4770 | 0.3677 | 0.025* |
| H7B | 0.5293 | 0.3240 | 0.3609 | 0.025* |
| C8 | 0.43522(19) | 0.40735(15) | 0.25495(8) | 0.0216(3) |
| H8A | 0.3320 | 0.3460 | 0.2567 | 0.026* |
| H8B | 0.3873 | 0.4939 | 0.2432 | 0.026* |
| C9 | 0.88080(19) | 0.46000(13) | 0.35571(8) | 0.0179(3) |
| C10 | 0.8241(2) | 0.47257(14) | 0.44338(8) | 0.0192(3) |
| H10A | 0.7320 | 0.5414 | 0.4489 | 0.023* |
| H10B | 0.7678 | 0.3915 | 0.4612 | 0.023* |
| C11 | 1.0940(2) | 0.39984(14) | 0.50945(8) | 0.0219(3) |
| C12 | 1.2563(2) | 0.44058(16) | 0.56010(10) | 0.0302(3) |
| H12A | 1.2579 | 0.3897 | 0.6083 | 0.045* |
| H12B | 1.2447 | 0.5315 | 0.5733 | 0.045* |
| H12C | 1.3703 | 0.4267 | 0.5311 | 0.045* |
| N1 | 0.57506(15) | 0.36746(11) | 0.19624(7) | 0.0183(2) |
| N2 | 0.73955(16) | 0.42411(11) | 0.30687(7) | 0.0180(2) |
| O1 | 0.38063(15) | 0.23619(11) | 0.12753(7) | 0.0279(3) |
| O2 | 1.03976(14) | 0.48316(11) | 0.33279(6) | 0.0245(2) |
| O3 | 0.98281(13) | 0.50183(9) | 0.49238(6) | 0.0201(2) |
| O4 | 1.06353(17) | 0.29059(11) | 0.48714(8) | 0.0377(3) |
Source of materials
Ethyl 4-acetylbutyrate (0.05 mol) and ethylenediamine (0.14 mol) were mixed with 25 mL EtOH, refluxed for 8 h, and then the solvent was removed via vacuum distillation. The intermediate 5-methyl-9-oxa-1,4-diazabicyclo[3.4.0]nonane was purified by column chromatography on silica gel eluting with CH2Cl2 and EtOH (6:1). (Et)3N (1.72 g, 0.017 mol) was added to the intermediate (0.007 mol) in THF (30 mL) at 0–5°C. Acetoxyacetyl chloride (0.01 mol) was added dropwise to the mixture. The reaction was quenched with water. The solution was washed with sat. NH4Cl (aq), sat. Na2CO3 (aq), and water. The organic phase was dried over anhydrous MgSO4. After removal of the solvent, the products were crystallized from EtOH and light petroleum as a white solid with 52.1% yield.
Experimental details
The C—H atoms were constrained to an ideal geometry, with C—H distances of 0.96–0.97 Å. The Uiso values of the hydrogen atoms of methyl groups were set to 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl) and the Uiso values of all other hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Discussion
Diazabicyclo derivatives are widely used as biological active materials. They were also used as anticancer agents, antibiotics, antibacterial agents, and so on [4], [5], [6], [7]. Moreover, they also acted as a useful intermediate in the synthesis of compounds with special properties [8, 9] . Dichloroacetyl diazabicyclo derivatives were reported as novel herbicide safener protecting crops from injury by chlorine acetamide herbicides, sulfonylurea herbicides, and imidazolinone herbicides since BASF employed 5-dichloroacetyl-3,3,6-trimethyl-9-oxo-1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0] nonane as safeners which increased the toleration of crops to acetanilides herbicides [10], [11], [12].
The title compound is a bicyclic molecule with N1 and C5 as the bridge carbon atoms. The dihedral angle between the plane I (C1/C2/C3/C4/C5/N1) and the plane II (N1/C5/N2/C7/C8) is 29.5°. Plane I adapted half-chair conformation. Plane II is in an envelope conformation with C5 forming the flap. The bond distances of C1—N1 and C9—N2 [1.3535(18) Å and 1.3505(17) Å, respectively] are shorter than the normal C—N distance, which indicates the existence of a p-π conjunction effect. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked by intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces.
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge support by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (31572042) and the Research Science Foundation in Technology Innovation of Harbin (2015RAYXJ010).
References
Oxford Diffraction Ltd, CrysAlisPRO, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar
Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 3.2i. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
Villa, S.; Barlocco, D.; Cignarella, G.; Papp, G. J.; Balati, B.; Takacs, J.; Varro, A.; Borosy, A.; Keseru, K.; Matyus, M.: 3,8-Diazabicyclo-[3.2.1]-octane derivatives as analogues of ambasilide, a class III antiarrhythmic agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 36 (2001) 495–506.10.1016/S0223-5234(01)01246-6Search in Google Scholar
Taylor, R. R. R.; Twin, H. C.; Wen, W. W.; Mallot, R. J.; Lough, A. J.; Gray-Owen, S. D.; Batey, R. A.: Substituted 2,5-diazabicyclo[4.1.0]heptanes and their application as general piperazine surrogates: synthesis and biological activity of a Ciprofloxacin analogue. Tetrahedron 66 (2010) 3370–3377.10.1016/j.tet.2010.02.046Search in Google Scholar
Holl, R.; Schepmann, D.; Bednarski, P. J.; Grunert, R.; Wunsch, B.: Relationships between the structure of 6-substituted 6,8-diazabicyclo [3.2.2]nonan-2-ones and their sigma receptor affinity and cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 (2009) 1445–1455.10.1016/j.bmc.2009.01.012Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Loriga, G.; Ruiu, S.; Manca, I.; Murineddu, G.; Dessi, C.; Pani, L.; Pinna, G. A.: 3-{2-[Bis-(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl}-6-substituted-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]heptanes as novel potent dopamine uptake inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 (2007) 3748–3755.10.1016/j.bmc.2007.03.035Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Gentry, P. R.; Kokubo, M.; Bridges, T. M.; Kett, N. R.; Harp, J. M.; Cho, H. P.; Smith, E.; Chase, P.; Hodder, P. S.; Niswender, C. M.; Daniels, J. S.; Conn, P. J.; Wood, M. R.; Lindsley, C. W.: Discovery of the first M-5-selective and CNS penetrant negative allosteric modulator (NAM) of a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: (S)-9b-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3,4-difluorobenzoyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo [2,1-a]isoindol-5(9bH)-one (ML375). J. Med. Chem. 56 (2013) 9351–9355.10.1021/jm4013246Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Bond, S.; Draffan, A. G.; Fenner, J. E.; Lambert, J.; Lim, C. Y.; Lin, B.; Luttick, A.; Mitchell, J. P.; Morton, C. J.; Nearn, R. H.; Sanford, V.; Stanislawski, P. C.; Tucker, S. P.: The discovery of 1,2,3,9b-tetrahydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-5-ones as a new class of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) fusion inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25 (2015) 969–975.10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.11.018Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Ye, F.; Li, G. Y.; Ding, L.; Fu, Y.; Xing, Z. Y.: Synthesis, crystal structure, and bioactivity of N-dichloroacetyl diazabicyclo compounds. Heterocycl. Commun. 19 (2013) 75–78.10.1515/hc-2012-0174Search in Google Scholar
Fu, Y.; Xu, Z. Z.; Ye, F.: Synthesis, characterization and crystal structure of 4-dichloroacetyl-2,5-dimethyl-8-oxo-1,4-diazabicyclo [3.3.0]octane. Asian J. Chem. 26 (2014) 2896–2898.10.14233/ajchem.2014.15959Search in Google Scholar
Milhomme, H.; Bastide, J.: Uptake and phytotoxicity of the herbicide metsulfuron methyl in corn root tissue in the presence of the safener 1,8-naphthalic anhydride. Plant Physiol. 93 (1990) 730–738.10.1104/pp.93.2.730Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2017 Fei Ye et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10

