Abstract
C34H24Cu2F8N4O8, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a =13.074(3) Å, b = 20.229(4) Å, c = 14.419(3) Å, β = 108.889(2)°, V = 3608.2(12) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0512, wRref(F2) = 0.1465, T = 296(2) K.
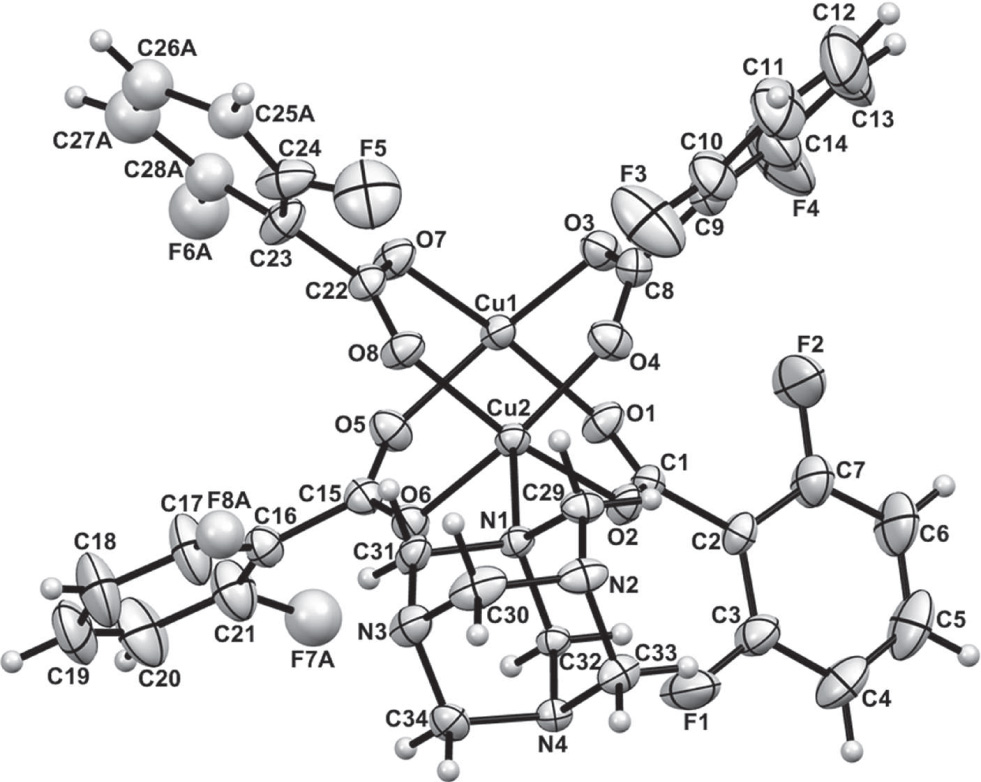
A part of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Green needle |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 12.8 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker CCD, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 56.8°, 98.7% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 33606, 8923, 0.050 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5323 |
| N(param)refined: | 498 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.81154(4) | 0.28704(2) | 0.16716(3) | 0.03845(13) |
| Cu2 | 0.69321(4) | 0.20461(2) | 0.03194(3) | 0.03659(13) |
| O1 | 0.7756(2) | 0.35179(12) | 0.06081(19) | 0.0505(7) |
| C1 | 0.7297(3) | 0.33562(18) | −0.0262(3) | 0.0407(8) |
| O2 | 0.6882(2) | 0.28056(12) | −0.05585(18) | 0.0474(6) |
| C2 | 0.7254(3) | 0.38642(18) | −0.1026(3) | 0.0474(9) |
| C3 | 0.6329(4) | 0.3987(2) | −0.1803(3) | 0.0642(12) |
| F1 | 0.5449(2) | 0.36447(17) | −0.1859(2) | 0.1021(11) |
| C4 | 0.6287(6) | 0.4457(3) | −0.2517(4) | 0.0920(18) |
| H1 | 0.5649 | 0.4535 | −0.3026 | 0.110* |
| C5 | 0.7202(7) | 0.4799(3) | −0.2451(5) | 0.107(2) |
| H2 | 0.7189 | 0.5109 | −0.2931 | 0.128* |
| C6 | 0.8137(6) | 0.4698(3) | −0.1698(5) | 0.101(2) |
| H3 | 0.8758 | 0.4935 | −0.1662 | 0.121* |
| C7 | 0.8144(5) | 0.4249(3) | −0.1008(4) | 0.0750(14) |
| F2 | 0.9072(3) | 0.4140(2) | −0.0273(3) | 0.1231(14) |
| O3 | 0.9271(2) | 0.24890(14) | 0.1207(2) | 0.0538(7) |
| C8 | 0.9145(3) | 0.2049(2) | 0.0571(3) | 0.0495(10) |
| O4 | 0.8266(2) | 0.17840(14) | 0.0092(2) | 0.0558(7) |
| C9 | 1.0117(4) | 0.1800(3) | 0.0346(3) | 0.0601(12) |
| C10 | 1.0200(5) | 0.1152(3) | 0.0054(4) | 0.0797(15) |
| F3 | 0.9405(3) | 0.07354(18) | −0.0003(4) | 0.1351(16) |
| C11 | 1.1086(6) | 0.0909(4) | −0.0136(5) | 0.109(2) |
| H4 | 1.1111 | 0.0468 | −0.0311 | 0.131* |
| C12 | 1.1924(7) | 0.1317(5) | −0.0068(6) | 0.135(3) |
| H5 | 1.2532 | 0.1152 | −0.0191 | 0.162* |
| C13 | 1.1896(6) | 0.1960(5) | 0.0177(7) | 0.131(3) |
| H6 | 1.2463 | 0.2244 | 0.0197 | 0.157* |
| C14 | 1.0989(5) | 0.2188(3) | 0.0401(6) | 0.100(2) |
| F4 | 1.0965(3) | 0.2831(2) | 0.0639(4) | 0.1477(19) |
| O5 | 0.6739(2) | 0.30572(14) | 0.1941(2) | 0.0536(7) |
| C15 | 0.5907(3) | 0.27400(18) | 0.1509(3) | 0.0436(9) |
| O6 | 0.5755(2) | 0.23955(13) | 0.07484(18) | 0.0469(6) |
| C16 | 0.5007(3) | 0.2741(2) | 0.1938(3) | 0.0504(10) |
| C17 | 0.4573(5) | 0.2165(3) | 0.2149(5) | 0.097(2) |
| C18 | 0.3792(6) | 0.2139(3) | 0.2576(6) | 0.116(3) |
| H7 | 0.3540 | 0.1732 | 0.2713 | 0.139* |
| C19 | 0.3383(5) | 0.2700(4) | 0.2801(5) | 0.103(2) |
| H8 | 0.2836 | 0.2686 | 0.3082 | 0.124* |
| C20 | 0.3765(6) | 0.3277(4) | 0.2621(5) | 0.110(2) |
| H9 | 0.3493 | 0.3669 | 0.2784 | 0.132* |
| C21 | 0.4554(5) | 0.3292(3) | 0.2198(5) | 0.0838(16) |
| O7 | 0.8285(2) | 0.21164(12) | 0.2549(2) | 0.0529(7) |
| C22 | 0.7839(3) | 0.15707(18) | 0.2271(3) | 0.0447(9) |
| O8 | 0.7267(2) | 0.14165(13) | 0.14296(19) | 0.0513(7) |
| C23 | 0.8007(4) | 0.1055(2) | 0.3051(3) | 0.0611(12) |
| C24 | 0.8319(4) | 0.0419(2) | 0.2940(4) | 0.0741(15) |
| F5 | 0.8464(3) | 0.02582(16) | 0.2104(3) | 0.1195(13) |
| C25Aa | 0.8639(9) | −0.0091(5) | 0.3512(8) | 0.065(3)* |
| H11a | 0.8827 | −0.0500 | 0.3322 | 0.078* |
| C25Ba | 0.8407(9) | −0.0018(6) | 0.3825(9) | 0.067(3)* |
| H12a | 0.8713 | −0.0436 | 0.3863 | 0.080* |
| C26Aa | 0.8654(11) | 0.0081(6) | 0.4482(10) | 0.083(3)* |
| H13a | 0.8845 | −0.0246 | 0.4960 | 0.100* |
| C26Ba | 0.8069(12) | 0.0181(7) | 0.4515(10) | 0.097(4)* |
| H14a | 0.8135 | −0.0120 | 0.5019 | 0.116* |
| C27Aa | 0.8407(12) | 0.0695(7) | 0.4753(10) | 0.097(4)* |
| H15a | 0.8384 | 0.0785 | 0.5379 | 0.116* |
| C27Ba | 0.7629(13) | 0.0770(7) | 0.4610(11) | 0.111(4)* |
| H16a | 0.7397 | 0.0871 | 0.5139 | 0.134* |
| C28Aa | 0.8189(10) | 0.1179(6) | 0.4009(8) | 0.074(3)* |
| C28Ba | 0.7551(10) | 0.1213(6) | 0.3851(8) | 0.076(3)* |
| F6Aa | 0.7947(7) | 0.1803(4) | 0.4238(6) | 0.114(2)* |
| F6Ba | 0.7119(7) | 0.1802(4) | 0.3880(6) | 0.106(2)* |
| N1 | 0.5802(2) | 0.14315(13) | −0.07898(19) | 0.0342(6) |
| C29 | 0.6332(3) | 0.09934(18) | −0.1318(3) | 0.0456(9) |
| H17 | 0.6732 | 0.1261 | −0.1641 | 0.055* |
| H18 | 0.6844 | 0.0710 | −0.0849 | 0.055* |
| N2 | 0.5554(3) | 0.05837(15) | −0.2046(2) | 0.0520(9) |
| C30 | 0.4938(4) | 0.01888(19) | −0.1549(3) | 0.0654(13) |
| H19 | 0.4415 | −0.0082 | −0.2029 | 0.079* |
| H20 | 0.5430 | −0.0105 | −0.1080 | 0.079* |
| N3 | 0.4376(3) | 0.06010(16) | −0.1040(2) | 0.0540(9) |
| C31 | 0.5179(3) | 0.10028(19) | −0.0323(3) | 0.0463(9) |
| H21 | 0.5675 | 0.0715 | 0.0151 | 0.056* |
| H22 | 0.4818 | 0.1279 | 0.0026 | 0.056* |
| C32 | 0.5036(3) | 0.18553(16) | −0.1516(2) | 0.0329(7) |
| H23 | 0.5430 | 0.2131 | −0.1834 | 0.039* |
| H24 | 0.4673 | 0.2143 | −0.1185 | 0.039* |
| N4 | 0.4219(2) | 0.14643(13) | −0.22678(19) | 0.0344(6) |
| C33 | 0.4799(3) | 0.10225(18) | −0.2754(3) | 0.0472(9) |
| H25 | 0.4278 | 0.0758 | −0.3246 | 0.057* |
| H26 | 0.5195 | 0.1289 | −0.3082 | 0.057* |
| C34 | 0.3644(3) | 0.10398(19) | −0.1754(3) | 0.0494(10) |
| H27 | 0.3268 | 0.1319 | −0.1422 | 0.059* |
| H28 | 0.3106 | 0.0777 | −0.2234 | 0.059* |
| F7Aa | 0.4713(7) | 0.3874(4) | 0.1734(6) | 0.103(2)* |
| F7Ba | 0.5128(5) | 0.3870(3) | 0.2247(5) | 0.0749(16)* |
| F8Aa | 0.4726(5) | 0.1590(3) | 0.1682(5) | 0.0746(16)* |
| F8Ba | 0.5227(6) | 0.1598(3) | 0.2194(5) | 0.0883(19)* |
aOccupancy: 0.50.
Source of materials
An aqueous solution (10 mL) of 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid (dfbaH) (315 mg, 2.0 mmol), NaHCO3 (160 mg, 2.0 mmol), and hexamethylenetetramine (70 mg, 0.5 mmol) was mixed with DMF/MeOH solution (10 mL) dissolving Cu(NO3)2⋅3H2O (300 mg, 2.2 mmol). The light blue solution was allowed to stand at room temperature to give green needle-like crystals within two weeks (yield 350 mg, 39% based on copper nitrate trihydrate).
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), C—H = 0.96 Å (methylene), and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Comment
Coordination polymers are of special interest because of their fascinating topological structures as well as their potential applications in many fields [3], [4], [5], [6], [7]. The self-assembly of organic molecules and metal ions construct a broad range of coordination polymers. The selection of organic ligands is a key point for rational design of targeted structures. A number of aromatic acids, especially aromatic multicarboxylates, have been used as bridging ligands. That is because the multicarboxylates not only have versatile coordination modes but also act as hydrogen bonding acceptors and donors [8]. Compared with the aromatic multicarboxylates, benzoic acid or its substituted derivatives possess a limited scope for the construction of coordination polymers [9]. However, polynuclear clusters with fascinating structures and properties which are constructed by benzoic acids have been reported [10, 11] . Meanwhile, the coordination polymers based on fluorine substituted organic molecules are found to be more stable to oxidation and show enhanced thermal stability [12].
On the other hand, the neutral N-containing heterocyclic molecules are ubquitously used as linker to construct coordination polymers. Lots of coordination polymers built from bipyridines and pyrazines are reported, while hexamethylenetetramine (hmt) was explored to a less extent [13]. However, hexamethylenetetramine has four coordinating N atoms which may link with different metal ions through various coordination modes that span from terminal monodentate to μ2-, μ3-, or μ4-bridging modes, which lead to one- (1D), two- (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) coordination polymers [14, 15] .
X-ray crystal structural analysis revealed that the asymmetric unit of the title complex is composed of two Cu2+ ions, four dfba− ligands and one hmt ligand. Each Cu2+ ion is coordinated in a square-pyramidal geometry with four oxygen atoms from four dfba− ligands and one nitrogen atom from a hmt ligand. The four oxygen atoms are located in the equatorial positions and the coordinated nitrogen atom is located at the axial position. The Cu2+ ions are deviated by 0.2179(14) Å for Cu1 and 0.2055(14) Å for Cu2 from the equatorial plane (defined by the four coordinated oxygen atoms) towards the axial N atoms, respectively. The four dfba− ligands using four carboxylate groups link two Cu2+ ions with distances of 2.6500(7) Å for Cu1⋯Cu2 to form the typical [Cu2(COO)4] paddlewheel building block. Hexamethylenetetramine ligands link the vertices of [Cu2(COO)4] paddlewheel units in a μ2-bridging mode. Therefore, a 1-D zigzag chain structure is formed in the structure of the title complex.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Nature Foundation of China [No. 21461011 and 31560712], the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province [No. 20112BBF60024, 20151BAB204014].
References
Bruker. SMART and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, (2012).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Qiu, S.; Zhu, G.: Molecular engineering for synthesizing novel structures of metal–organic frameworks with multifunctional properties. Coord. Chem. Rev. 253 (2009) 2891–2911.10.1016/j.ccr.2009.07.020Search in Google Scholar
Kuppler, R. J.; Timmons, D. J.; Fang, Q.-R.; Li, J.-R.; Makal, T. A.; Young, M. D.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhuang, W.; Zhou, H.-C.: Potential applications of metal–organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 253 (2009) 3042–3066.10.1016/j.ccr.2009.05.019Search in Google Scholar
O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M.: Deconstructing the crystal structures of metal organic frameworks and related materials into their underlying nets. Chem. Rev. 112 (2012) 675–702.10.1021/cr200205jSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Zhang, W.; Xiong, R.-G.: Ferroelectric metal–organic framworks. Chem. Rev. 112 (2012) 1163–1195.10.1021/cr200174wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Cook, T. R.; Zheng, Y.-R.; Stang, P. J.: Metal–organic frameworks and self–assembled supramolecular coordination complexes: comparing and contrasting the design, synthesis, and functionality of metal–organic materials. Chem. Rev. 113 (2013) 734–777.10.1021/cr3002824Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Zhao, S.-Q.; Gu, J.-Z.: Syntheses, crystal structures and magnetic properties of Mn(II) and Ni(II) dinuclear coordination compounds constructed from biphenyl-2,4,4′-tricarboxylate and phenanthroline. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 32 (2016) 1611–1618.Search in Google Scholar
Majeed, Z.; Mondal, K. C.; Kostakis, G. E.; Lan, Y.; Anson, C. E.; Powell, A. K.: [LnNa(PhCO2)4] (Ln = Ho, Dy): the first examples of chiral srs 3D networks constructed using the monotopic benzoate ligand. Chem. Commun. 46 (2010) 2551–2553.10.1039/b923998gSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Leng, J.-D.; Liu, J.-L.; Tong, M.-L.: Unique nanoscale {CuII36LnIII24} (Ln = Dy and Gd) metallo-rings. Chem. Commun. 48 (2012) 5286–5288.10.1039/c2cc30521fSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Zeng, Y.-F.; Xu, G.-C.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Bu, X.-H.; Gao, S.; Sanudo, E. C.: Single–molecule–magnet behavior in a Fe12Sm4 cluster. Inorg. Chem. 49 (2010) 9734–9736.10.1021/ic1009708Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Peikert, K.; Hoffmann, F.; Froba, M.: Fluorine magic: one new organofluorine linker leads to three new metal–organic frameworks. CrystEngComm 17 (2015) 353–360.10.1039/C4CE00408FSearch in Google Scholar
Kirillov, A. M.: Hexamethylenetetramine: an old new building block for design of coordination polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 255 (2011) 1603–1622.10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.023Search in Google Scholar
Hazra, S.; Sarkar, B.; Naiya, S.; Drew, M. G. B.; Frontera, A.; Escudero, D.; Ghosh, A.: Self-assembled molecular complexes and coordination polymers of CdII, hexamine, and monocarboxylates: structural analysis and theoretical studies of supramolecular interactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 10 (2010) 1677–1687.10.1021/cg901245zSearch in Google Scholar
Fang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Xue, M.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y.; Qiu, S.; Xu, R.: A metal–organic framework with the zeolite MTN topology containing large cages of volume 2.5 nm3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44 (2005) 3845–3848.10.1002/anie.200462260Search in Google Scholar PubMed
©2017 Yuan Hou-Qun et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10

