Abstract
C24H60AgClN12O6P4, tetragonal, P42/nmc (no. 137), a = 14.1874(3) Å, c = 9.8721(3) Å, V = 1987.08(1) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0148, wRref(F2) = 0.0417, T = 100 K.
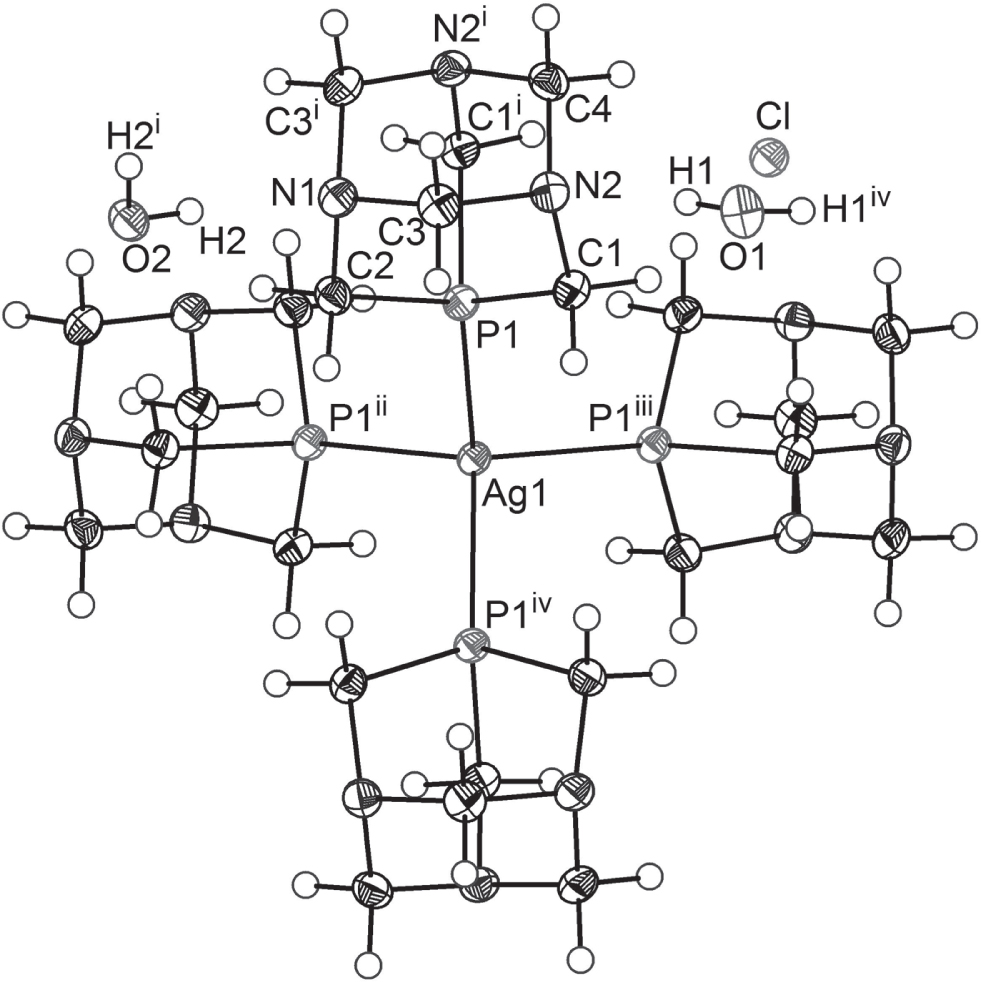
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless cuboid |
| Size: | 0.52 × 0.36 × 0.26 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 7.9 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 56°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 55782, 1291, 0.024 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1214 |
| N(param)refined: | 72 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SIR2014 [2], DIAMOND [3], ORTEP [4], SHELX [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.65153(8) | 0.41564(7) | 0.50996(11) | 0.0189(2) |
| H1A | 0.5917 | 0.4176 | 0.4584 | 0.023* |
| H1B | 0.6475 | 0.3629 | 0.5753 | 0.023* |
| C2 | 0.75 | 0.50994(10) | 0.30730(16) | 0.0196(3) |
| H2Aa | 0.8064 | 0.515 | 0.2487 | 0.023* |
| H2Ba | 0.6936 | 0.515 | 0.2487 | 0.023* |
| C3 | 0.66570(8) | 0.58639(7) | 0.49257(11) | 0.0220(2) |
| H3A | 0.6634 | 0.6451 | 0.5466 | 0.026* |
| H3B | 0.6089 | 0.585 | 0.4344 | 0.026* |
| C4 | 0.75 | 0.50462(11) | 0.66677(16) | 0.0213(3) |
| H4A | 0.75 | 0.4479 | 0.7251 | 0.026* |
| H4B | 0.75 | 0.5605 | 0.7268 | 0.026* |
| N1 | 0.75 | 0.58877(9) | 0.40522(13) | 0.0201(3) |
| N2 | 0.66285(7) | 0.50518(6) | 0.58538(9) | 0.01967(19) |
| P1 | 0.75 | 0.39341(3) | 0.39143(4) | 0.01630(9) |
| Cl | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.01964(15) |
| Ag1 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.01466(7) |
| O1 | 0.49539(6) | 0.50461(6) | 0.75 | 0.0269(3) |
| H1 | 0.5449(13) | 0.5058(12) | 0.7069(18) | 0.049(5)* |
| O2 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.23494(17) | 0.0230(3) |
| H2 | 0.75 | 0.7045(17) | 0.287(2) | 0.045(7)* |
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Source of materials
1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA) (0.1023 g, 0.6510 mmol) and silver chloride (0.0235 g, 0.1642 mmol) were dissolved in acetonitrile (10 cm3) and heated under reflux overnight. The mixture was filtered and the filtrate was left to crystallize. Colourless crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained in 85.2% yield (0.488 g).
Experimental details
The aliphatic H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.99 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C). H atoms at the water molecules were refined isotropically.
Comment
The complex obtained is a water soluble four-coordinate silver complex with chloride counterions. The known cytotoxicity and cell malignity of silver and silver nanoparticles suggests that this compound may be a candidate for anticancer development [6]. Many variants of silver complexes have been developed and proved to demonstrate excellent antibacterial and antifungal properties [7], [8], [9], [10]. 1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA) was selected as the ligand for this complex due to its ability to solubilize transition metal complexes [11], allowing for the introduction into the blood circulatory system as aqueous solubility is a key parameter to help determine rate and extent of drug absorption [12]. Adamantane complexes have also seen considerable success in aqueous phase and biphasic homogenous catalysis; 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane complexes of rhodium and ruthenium has been found to be catalytically active for the conversion of aldehydes to alcohols [13, 14] .
In the title compound the Ag atom is in a four-coordinate environment and adopts a distorted tetrahedral geometry, with the Ag and Cl atoms on special positions. As the complex crystallizes with high symmetry the Ag—P bond lengths are identical: 2.4676(4) Å. The P—Ag—P angles of the title compound are either 108.67(1)° or 111.08(1)° and the effective cone angle [15] is 108.53(1)°. The crystal structure is stabilized by an array of weak C—H⋅⋅⋅Cl and strong O—H⋅⋅⋅N hydrogen bonds. The title structure is structurally closely related to a Au(I) complex [16].
Acknowledgement
Financial assistance from the University of the Free State is gratefully acknowledged. This work is based on the research supported in part by the National Research Foundation of South Africa, Unique Grants No. 93957 and 99139.
References
Bruker: APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA (2012).Search in Google Scholar
Burla, M. C.; Caliandro, R.; Carrozzini, B.; Cascarano, G. L.; Cuocci, C.; Giacovazzo, C.; Mallamo, M.; Mazzone, A.; Polidori, G.: Crystal structure determination and refinement via SIR2014. J. Appl. Cryst. 48 (2015) 306–309.10.1107/S1600576715001132Search in Google Scholar
Brandenburg, K.; Putz, H.: DIAMOND. Visual crystal structure information system. Release 4.1.3. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany (2014).Search in Google Scholar
Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for windows: An update. J. Appl. Cryst. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
Foldbjerg, R.; Dang, D. A.; Autrup, H.: Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in the human lung cancer cell line, A549. Arch.Toxicol. 85 (2011) 743–750.10.1007/s00204-010-0545-5Search in Google Scholar
Panáčeka, A.; Kolářb, M.; Večeřováb, R.; Pruceka, R.; Soukupováa, J.; Kryštofc, V.; Hamalb, P.; Zbořila, R.; Kvítek, L.: Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomaterials. 30 (2009) 6333–6340.10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.065Search in Google Scholar
Nomiya, K.; Takahashi, S.; Noguchi, R.; Nemoto, S.; Takayama, T.; Oda, M.: Synthesis and characterization of water-soluble silver(I) complexes with l-Histidine (H2his) and (S)-(-)-2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid (H2pyrrld) showing a wide spectrum of effective antibacterial and antifungal activities. crystal structures of chiral helical polymers [Ag(Hhis)]n and [Ag(Hpyrrld)]2n in the solid state. Inorg. Chem. 39 (2000) 3301–3311.10.1021/ic990526oSearch in Google Scholar
Tsyba, I.; Mui, B. B.; Bau, R.; Noguchi, R.; Nomiya, K.: Synthesis and structure of a water-soluble hexanuclear silver(I) nicotinate cluster comprised of a cyclohexane-chair-type of framework, showing effective antibacterial and antifungal activities: Use of sparse matrix techniques for growing crystals of water-soluble inorganic complexes. Inorg. Chem. 42 (2003) 8028–8032.10.1021/ic030149mSearch in Google Scholar
Mastrolorenzo, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C. T.: Antifungal activity of silver and zinc complexes of sulfadrug derivatives incorporating arylsulfonylureido moieties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 11 (2000) 99–107.10.1016/S0928-0987(00)00093-2Search in Google Scholar
Phillips, A. D.; Gonsalvi, L.; Romerosa, A.; Vizza, F.; Peruzzini, M.: Coordination chemistry of 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA): Transition metal complexes and related catalytic, medicinal and photoluminescent applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 248 (2004) 955–993.10.1016/j.ccr.2004.03.010Search in Google Scholar
Jimenez, J.; Chakraborty, I.; Rojas-Andrade, M.; Mascharak, P. K.: Silver complexes of ligands derived from adamantylamines: Water-soluble silver-donating compounds with antibacterial properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 168 (2017) 13–17.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.12.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Darensbourg, D. J.; Joo, F.; Kannisto, M.; Katho, A.; Reibenspies, J. H.: Water-soluble organometallic compounds. 2. Catalytic hydrogenation of aldehydes and olefins by new water-soluble 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane complexes of ruthenium and rhodium. Organometallics. 11 (1992) 1990–1993.10.1021/om00042a006Search in Google Scholar
Darensbourg, D. J.; Joo, F.; Kannisto, M.; Katho, A.; Reibenspies, J. H.; Daigle, D. J.: Water-soluble organometallic compounds. 4. Catalytic hydrogenation of aldehydes in an aqueous two-phase solvent system using a 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane complex of ruthenium. Inorg. Chem. 33 (1994) 200–208.10.1021/ic00080a006Search in Google Scholar
Tolman, C. A.: Steric effects of phosphorus ligands in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 77 (1977) 313–348.10.1021/cr60307a002Search in Google Scholar
Forward, J. M.; Bohmann, D.; Fackler, J. P.: Crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane)gold(I) chloride dihydrate. Z. Kristallogr. 211 (1996) 485–486.10.1524/zkri.1996.211.7.485Search in Google Scholar
©2017 Runé Oosthuizen et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10

