Abstract
C15H17N3O2S, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 9.0650(15) Å, b = 16.342(3) Å, c = 10.1187(17) Å, β = 91.061(5) Å. V = 1498.7(4) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0645, wRref(F2) = 0.1323, T = 308 K.
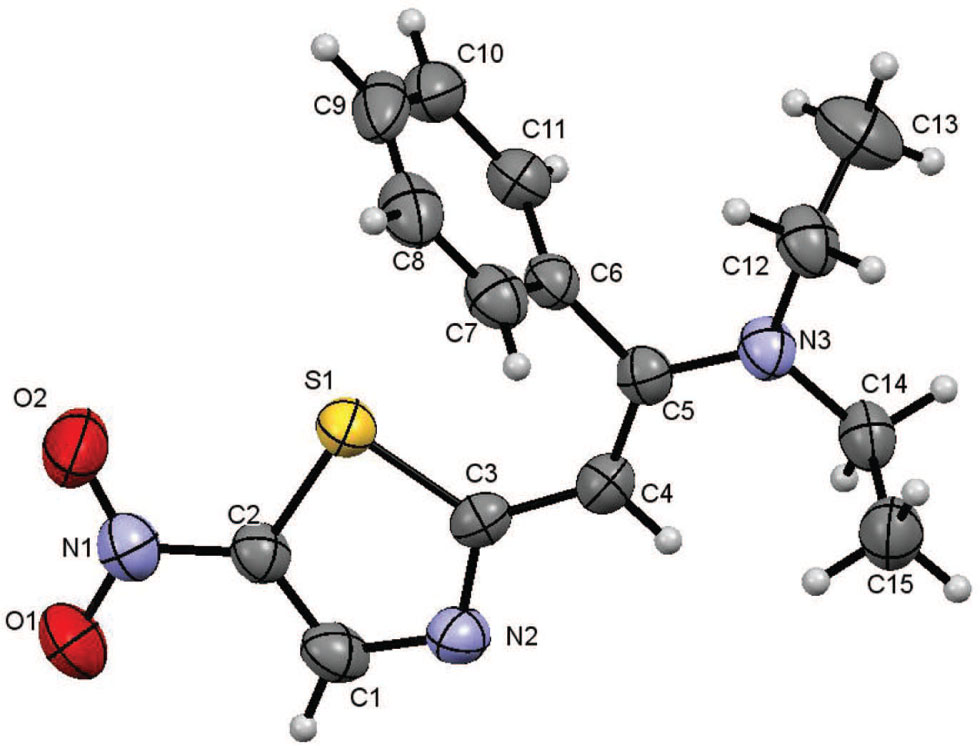
The title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains details on crystal structure and measurement conditions. Table 2 lists the atoms with their coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.46 × 0.35 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.2 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART APEX, ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 56.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 38065, 3694, 0.171 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1880 |
| N(param)refined: | 191 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], PLATON [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.26201(8) | 0.10068(4) | 0.47756(7) | 0.0470(2) |
| O1 | 0.4724(2) | 0.07587(15) | 0.1519(2) | 0.0784(7) |
| O2 | 0.5499(2) | 0.08282(16) | 0.3544(2) | 0.0826(8) |
| N1 | 0.4499(3) | 0.08231(15) | 0.2708(3) | 0.0557(7) |
| N2 | 0.0524(2) | 0.09474(14) | 0.3003(2) | 0.0481(6) |
| N3 | −0.1649(2) | 0.13767(13) | 0.7209(2) | 0.0449(6) |
| C1 | 0.1802(3) | 0.08721(16) | 0.2366(3) | 0.0501(7) |
| H1A | 0.1837 | 0.0811 | 0.1453 | 0.060* |
| C2 | 0.3035(3) | 0.08905(16) | 0.3135(3) | 0.0425(7) |
| C3 | 0.0761(3) | 0.10336(14) | 0.4305(2) | 0.0374(6) |
| C4 | −0.0452(3) | 0.11319(15) | 0.5152(3) | 0.0417(6) |
| H4A | −0.1383 | 0.1069 | 0.4762 | 0.050* |
| C5 | −0.0423(3) | 0.13083(15) | 0.6478(3) | 0.0388(6) |
| C6 | 0.1002(3) | 0.14565(16) | 0.7180(2) | 0.0393(6) |
| C7 | 0.1627(3) | 0.22314(17) | 0.7157(3) | 0.0482(7) |
| H7A | 0.1157 | 0.2650 | 0.6691 | 0.058* |
| C8 | 0.2938(3) | 0.2384(2) | 0.7817(3) | 0.0588(9) |
| H8A | 0.3357 | 0.2903 | 0.7795 | 0.071* |
| C9 | 0.3625(3) | 0.1766(3) | 0.8507(3) | 0.0641(10) |
| H9A | 0.4499 | 0.1872 | 0.8971 | 0.077* |
| C10 | 0.3039(3) | 0.0993(2) | 0.8522(3) | 0.0596(8) |
| H10A | 0.3525 | 0.0576 | 0.8980 | 0.072* |
| C11 | 0.1722(3) | 0.08324(18) | 0.7855(3) | 0.0481(7) |
| H11A | 0.1323 | 0.0308 | 0.7861 | 0.058* |
| C12 | −0.1625(3) | 0.16785(18) | 0.8579(3) | 0.0545(8) |
| H12A | −0.2408 | 0.2077 | 0.8679 | 0.065* |
| H12B | −0.0694 | 0.1954 | 0.8754 | 0.065* |
| C13 | −0.1815(4) | 0.1006(2) | 0.9588(3) | 0.0812(11) |
| H13A | −0.1791 | 0.1237 | 1.0460 | 0.122* |
| H13B | −0.1031 | 0.0615 | 0.9509 | 0.122* |
| H13C | −0.2746 | 0.0738 | 0.9435 | 0.122* |
| C14 | −0.3122(3) | 0.12774(17) | 0.6616(3) | 0.0475(7) |
| H14A | −0.3792 | 0.1086 | 0.7286 | 0.057* |
| H14B | −0.3086 | 0.0865 | 0.5929 | 0.057* |
| C15 | −0.3710(3) | 0.20648(18) | 0.6031(3) | 0.0585(8) |
| H15A | −0.4676 | 0.1972 | 0.5654 | 0.088* |
| H15B | −0.3061 | 0.2251 | 0.5354 | 0.088* |
| H15C | −0.3767 | 0.2472 | 0.6711 | 0.088* |
Source of materials
The title compound was synthesized from the Sonogashira Coupling-Aminovinylation Sequence reaction [4]. In a nitrogen atmosphere, a THF solution of phenylacetylene (1.1 mmol in 5 mL THF) was added dropwisely into a stirred mixture of 2-bromo-5-nitrothiazole (1 mmol), Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 (14 mg, 0.02 mmol), CuI (7 mg, 0.04 mmol), and 11 mL of THF/NEt3 (10:1). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight until conversion was complete (monitored by TLC). Then, a solution of diethylamine (2 mmol) in 5 mL of methanol was added, and the mixture was heated to reflux for ca. 9 hour until complete conversion (monitored by TLC). The solvents were evaporated in vacuo, and the residue was purified by chromatography over a short pad of aluminum oxide eluting with dichloromethane followed by acetone to yield 60% of the entitled compound. The residue was then recrystallized in dichloromethane by evaporation in vacuo, which yielded dark red crystals. After several attempts a suitable crystal for single X-ray diffraction study was obtained.
Experimental details
H atoms were fixed geometrically at ideal positions and allowed to ride on the parent atoms with C–H = 0.93–0.97 Å, with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) (for CH3)and 1.2 Ueq(C) (for CH2 and CH).
Comment
Thiazole derivatives are important heterocyclic compounds for biological and pharmaceutical activities. The role of the thiazole is already exhibited by most epotilones used against multi-drug resistant tumor [5] and treatment of type 2 diabetes [6]. Organic non-linear optics (NLO) materials formed by a donor-acceptor pair in their molecular system exhibit noteworthy NLO characteristics [7]. Thiazoles with a push-pull system containing electron-withdrawing and electron donating groups have been studied in the past years in order to develop derivatives to be used as NLO materials [7, 8] . On the other hand, it is well known as an excellent ligand [9, 10] .
The title compound consists of a nitrothiazole and a benzyldiethylamine group connected by the C4–C5 double bond. It adopts the E configuration. The whole molecule is not planar. However, the nitrothiazole S1/O1/O2/N1/N2/(C1–C4) fragment is almost planar with maximum deviation of 0.029(2) Å for O1 from the least-squares plane. This plane and the plane of the phenyl moiety enclose an angle of 82.57(10)°. The double bond C4—C5 has a length of 1.372(3) Å. Distances C2—S1 and C3—S1 are 1.719(3) Å and 1.743(3) Å respectively, showing a partial double bond character for the bonds compared to 1.714(2) and 1.713(2) Å in 2-bromo-4-phenyl-1,3-thiozole [11]. The N2—C3 bond distance of 1.338(3)° is longer than that of the analoguous one (1.295(2) Å) indicating a degree of delocalisation due to the conjugation effect. Other bond lengths and angles are in normal ranges.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education (MoHE) of Malaysia for Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2015/ST05/UPNM/03/1). Research facilities provided by the Centre of Research and Instrumentation (CRIM) is very much appreciated.
References
Bruker AXS Inc., SMART, SAINT and SADABS, Madison, Wisconsin, USA (2000).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar
Spek, A. L.: Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. D65 (2009) 148–155.10.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar
Karpov, A. S.; Rominger, F.; Müller, T. J. J.: Facile one-pot coupling-aminovinylation approach to push-pull chromophores: alkyne activation by sonogashira coupling. J. Org. Chem. 68 (2002) 1503–1511.10.1021/jo026470oSearch in Google Scholar
Nicolaou, K. C.; King, N. P.; Finlay, M. R. V.; He, Y.; Roshangar, F.; Vourloumis, D.; Vallberg, H.; Sarabia, F.; Ninkovic, S.; Hepworth, D.: Total synthesis of Epothilone E and related side-chain modified analogues via a stille coupling based strategy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 7 (1999) 665–697.10.1016/S0968-0896(98)00153-9Search in Google Scholar
Li, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Jiao, L.; Su, X.; Pan, M.; Huang, W.; Qian, H.: Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of new thiazole-based free fatty acid receptor 1 agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 113 (2016) 246–257.10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.02.040Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Machado, A. E. H.; Neto, M. B. N.; Ueno, L. T. P.; Paula, L. F. D.; Araujo, D. M. S.; Oliveira, G. S.; Gomes, W. R.; Paula, R. D.; Franzen, P. L.; Zilio, S. C.; Oliveira-campos, A. M. F.; Fonseca, A. M.; Rodrigues, L. M.; Nkeonye, P. O.; Hrdina, R.: Study of the spectroscopic properties and first hyperpolarizabilities of disperse azo dyes derived from 2-amino-5-nitrothiazole. J. Photochem. Photobio. A: Chem. 199 (2008) 23–33.10.1016/j.jphotochem.2008.04.012Search in Google Scholar
Wang, Y.-K.; Shu, C.-F.; Breitung, E. M.; McMahon, R. J.: Synthesis and characterization of thiazole-containing chromophores for second-order nonlinear optics. J. Mater. Chem. 9 (1999) 1449–1452.10.1039/a900820iSearch in Google Scholar
Suh, S. W.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, I.-H.: Bis(2-amino-1,3-thiazole)κN3 diazido zinc(II). Acta Crystallogr. E67 (2011) m135–m136.10.1107/S1600536810053766Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Du, M.; Wang, Y.-L.; Liu, B.-X.; Xu, D.-J.: [(E)-But-2-enoato-[κ]O]chlorido(2,2′-diamino-4,4′-bi-1,3-thiazole-[κ]2N3,N3′)zinc(II) monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. E66 (2010) m466.10.1107/S160053681001113XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Bunev, A. S.; Rudakova, Y. I.; Statsyuk, V. E.; Ostapenko, G. I.; Krushtalev, V. N.: 2-Bromo-4-phenyl-1,3-thiazole. Acta Crystallogr. E70 (2014) o139.10.1107/S160053681400066XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2017 Nur Farahin Pairan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10

