Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
Abstract
C30H25N5O9Mn2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 15.5012(6) Å, b = 9.3423(3) Å, c = 19.7517(6) Å, β = 95.966(3)°, V = 2844.90(18) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0362, wRref(F2) = 0.0971, T = 293(2) K.
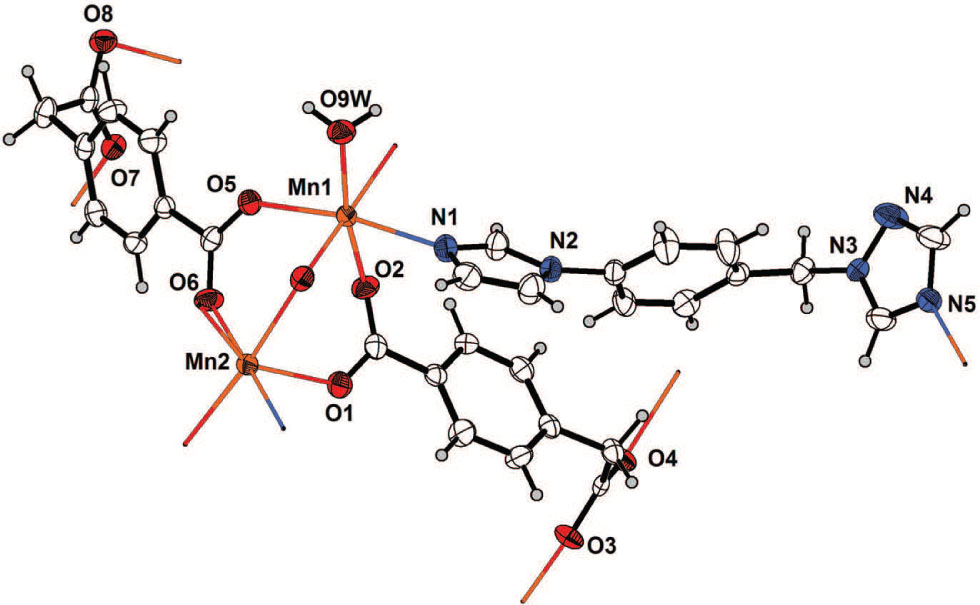
The asymmetric unit and additional atoms completing the coordination sphere of the manganese atoms is shown in the figure. Table 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions as well as a list of atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.33 × 0.26 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 9.6 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker CCD, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 56.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11611, 5284, 0.025 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4462 |
| N(param)refined: | 415 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn1 | 0.18825(2) | 0.43301(4) | 0.772156(19) | 0.02070(12) |
| Mn2 | 0.18330(3) | 0.04032(4) | 0.788712(19) | 0.02107(12) |
| N1 | 0.28336(16) | 0.5039(3) | 0.86187(12) | 0.0319(6) |
| N2 | 0.40409(15) | 0.5982(3) | 0.91189(11) | 0.0289(5) |
| N3 | 0.74980(14) | 0.9789(2) | 0.99272(11) | 0.0250(5) |
| N4 | 0.7368(2) | 1.1196(3) | 1.00114(13) | 0.0511(8) |
| N5 | 0.79267(16) | 1.0208(3) | 1.09943(11) | 0.0295(6) |
| O1 | 0.31300(12) | 0.1169(2) | 0.80289(10) | 0.0333(5) |
| O2 | 0.30030(12) | 0.3206(2) | 0.74380(10) | 0.0313(5) |
| O3 | 0.76940(13) | 0.1139(2) | 0.78621(9) | 0.0298(5) |
| O4 | 0.80634(12) | 0.3159(2) | 0.73664(9) | 0.0264(4) |
| O5 | 0.10780(13) | 0.3311(2) | 0.69144(9) | 0.0297(5) |
| O6 | 0.14822(13) | 0.1012(2) | 0.68653(9) | 0.0319(5) |
| O7 | 0.13766(12) | 0.2288(2) | 0.33976(9) | 0.0267(4) |
| O8 | 0.04882(12) | 0.4067(2) | 0.30999(10) | 0.0308(5) |
| O9W | 0.08538(13) | 0.5842(2) | 0.79658(10) | 0.0325(5) |
| H2W | 0.0429 | 0.5853 | 0.7657 | 0.049* |
| H1W | 0.1110 | 0.6647 | 0.7964 | 0.049* |
| C1 | 0.34375(18) | 0.2283(3) | 0.77824(14) | 0.0254(6) |
| C2 | 0.44020(18) | 0.2498(3) | 0.79057(13) | 0.0236(6) |
| C3 | 0.48222(18) | 0.3407(3) | 0.74929(14) | 0.0266(6) |
| H3 | 0.4503 | 0.3885 | 0.7137 | 0.032* |
| C4 | 0.57103(18) | 0.3615(3) | 0.76015(14) | 0.0273(6) |
| H4 | 0.5983 | 0.4190 | 0.7304 | 0.033* |
| C5 | 0.61996(17) | 0.2974(3) | 0.81501(13) | 0.0238(6) |
| C6 | 0.57768(19) | 0.2075(3) | 0.85668(14) | 0.0307(7) |
| H6 | 0.6092 | 0.1636 | 0.8936 | 0.037* |
| C7 | 0.48906(18) | 0.1817(3) | 0.84431(14) | 0.0320(7) |
| H7 | 0.4624 | 0.1188 | 0.8720 | 0.038* |
| C8 | 0.71597(17) | 0.3283(3) | 0.82925(14) | 0.0264(6) |
| H8A | 0.7356 | 0.3008 | 0.8756 | 0.032* |
| H8B | 0.7258 | 0.4303 | 0.8248 | 0.032* |
| C9 | 0.76825(17) | 0.2473(3) | 0.78033(13) | 0.0204(6) |
| C10 | 0.11354(17) | 0.2147(3) | 0.66125(13) | 0.0228(6) |
| C11 | 0.07718(17) | 0.2077(3) | 0.58712(12) | 0.0226(6) |
| C12 | 0.10314(18) | 0.1013(3) | 0.54466(13) | 0.0252(6) |
| H12 | 0.1402 | 0.0294 | 0.5626 | 0.030* |
| C13 | 0.07455(18) | 0.1010(3) | 0.47590(13) | 0.0267(6) |
| H13 | 0.0931 | 0.0294 | 0.4481 | 0.032* |
| C14 | 0.01843(18) | 0.2066(3) | 0.44796(13) | 0.0255(6) |
| C15 | −0.01006(19) | 0.3095(3) | 0.49120(14) | 0.0317(7) |
| H15 | −0.0497 | 0.3784 | 0.4738 | 0.038* |
| C16 | 0.01969(19) | 0.3112(3) | 0.56017(14) | 0.0302(7) |
| H16 | 0.0009 | 0.3822 | 0.5882 | 0.036* |
| C17 | −0.00769(19) | 0.2130(4) | 0.37170(13) | 0.0313(7) |
| H17A | −0.0615 | 0.2657 | 0.3626 | 0.038* |
| H17B | −0.0168 | 0.1168 | 0.3538 | 0.038* |
| C18 | 0.06330(17) | 0.2862(3) | 0.33733(12) | 0.0217(6) |
| C19 | 0.35541(19) | 0.5703(3) | 0.85222(15) | 0.0317(7) |
| H19 | 0.3713 | 0.5953 | 0.8097 | 0.038* |
| C20 | 0.2861(2) | 0.4865(3) | 0.93125(15) | 0.0367(7) |
| H20 | 0.2436 | 0.4409 | 0.9534 | 0.044* |
| C21 | 0.3591(2) | 0.5448(4) | 0.96250(15) | 0.0387(8) |
| H21 | 0.3756 | 0.5481 | 1.0091 | 0.046* |
| C22 | 0.48620(18) | 0.6711(3) | 0.91947(13) | 0.0273(6) |
| C23 | 0.4977(2) | 0.7878(4) | 0.96204(17) | 0.0427(8) |
| H23 | 0.4534 | 0.8177 | 0.9871 | 0.051* |
| C24 | 0.5763(2) | 0.8601(4) | 0.96711(17) | 0.0424(8) |
| H24 | 0.5847 | 0.9380 | 0.9964 | 0.051* |
| C25 | 0.64216(18) | 0.8185(3) | 0.92947(13) | 0.0257(6) |
| C26 | 0.63036(19) | 0.6972(3) | 0.88982(13) | 0.0303(7) |
| H26 | 0.6755 | 0.6643 | 0.8664 | 0.036* |
| C27 | 0.55228(19) | 0.6236(3) | 0.88430(14) | 0.0313(7) |
| H27 | 0.5448 | 0.5426 | 0.8569 | 0.038* |
| C28 | 0.72518(18) | 0.9037(3) | 0.92877(13) | 0.0291(6) |
| H28A | 0.7717 | 0.8394 | 0.9197 | 0.035* |
| H28B | 0.7180 | 0.9730 | 0.8920 | 0.035* |
| C29 | 0.7826(2) | 0.9230(3) | 1.05119(15) | 0.0395(8) |
| H29 | 0.7969 | 0.8269 | 1.0575 | 0.047* |
| C30 | 0.7641(2) | 1.1387(3) | 1.06597(15) | 0.0460(9) |
| H30 | 0.7634 | 1.2278 | 1.0869 | 0.055* |
| C13 | 0.5926(3) | −0.8622(3) | −0.5939(3) | 0.0207(7) |
| H13A | 0.6780 | −0.9025 | −0.5728 | 0.025* |
Source of material
A mixture of Mn(OAc)2 ⋅ 4H2O (24.5 mg, 0.1 mmol), homoterephthalic acid (H2htpa, 36.0 mg, 0.2 mmol), 1-(imidazolyl)-4-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene (itmb, 22.5 mg, 0.1 mmol) and H2O (7 mL) were placed in a 23 mL Teflon-lined autoclave at 393 K for 4 days, then cooled to room temperature. Colourless block crystals were obtained in ca. 86% yield. Elemental analysis calcd. (%) for C30H25N5O9Mn2: C, 50.74; H, 3.59; N, 9.88. Found: C, 50.79; H, 3.55; N, 9.87.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were modelled at their calculated positions and included in the refinement via the riding model. The Uiso of the H-atoms were constrained to 1.2 times Ueq of their bonding carbon atoms and 1.5 times Ueq for the hydrogen atoms at water.
Discussion
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are one of the most rapidly developing fields in chemical and material sciences and emerging as an important family of porous materials not only because of their fascinating structures, but also due to their excellent properties in the fields of luminescence, magnetism, gas adsorption and catalysis [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]. Although rapid progress in the construction of MOFs has been made, it is still a considerable challenge to control the final structures, because many factors, such as temperature [9, 10] , solvent [11, 12] , metal/ligand ratios [13], pH values [14, 15] , influence the formation of the final structure. O-donor organic ligands, rigid benzene multicarboxylate ligands have attracted considerable attention due to their various coordination modes (monodentate, bridging, chelating). In principle, the multicarboxylate ligands with the flexible functional groups may result in uncontrollable structures because of the rotation about the C—C bond and high sensitivity to reaction conditions [16].
The asymmetry unit of the title structure contains two Mn(II) atoms, two htpa dianions, one itmb molecule, and one coordinated water, as shown in the Figure. The central Mn1 is six-coordinated with distorted octahedral [MnNO5] geometry, and is coordinated by three O atoms from three symmetry-related htpa ligands and one coordinated water O atom (O9W) in the equatorial plane, one carboxylic O5 atom from one htpa dianion and one N1 atom from itmb coligand at the axial positions. The Mn2 ion is also six coordinated by five O atoms from three symmetry-related htpa ligands, and, one N atom from one itmb coligand (cf. the figure). Among them, the Mn—O bond lengths are in the range of 2.113(18) to 2.225(2) Å, and two Mn—N bond lengths are 2.282(2) Å and 2.275(2) Å, respectively. The adjacent Mn1 and Mn2 ions are connected by three carboxylato groups from three htpa ligands adopting triple-bridging coordination mode to form binuclear units [Mn2(COO)3N2O3] with the Mn1⋯Mn2 distance of 3.6847(5) Å. Adjacent binuclear units are extended by carboxylato ligands along b direction to expand into a metal-carboxylate chain with the Mn1⋯Mn2 distance = 5.6841(6) Å. The adjacent metal-carboxylate chains are further connected by htpa ligands adopting triple-bridging coordination mode with through-ligand Mn1⋯Mn2 separation of 9.5444(6) and 10.2142(6) Å to form infinite two-dimensional metal-carboxylate layers. Neighboring metal-carboxylate layers are linked together through htpa and itmb to produce a two-dimensional thick bilayer. The adjacent bilayers are stacked parallel along a direction by interlayer H-bond interactions between the coordinating water ligands and the carboxylate O atoms of htpa anions (O9W—H1W⋯O4: d = 2.857(3) Å; O9W—H2W⋯O8: d = 2.803(3) Å) to accomplish its entire three-dimensional supramolecular network. Stronger edge-to-face π-π interactions are observed between the benzene rings of htpa dianions and itmb coligands with the C—H⋯p distance of 2.7364(1) Å (the shortest C⋯C distance: 3.50 Å). It is obvious that the H-bonding bonds and π-π interactions among the coordination polymers play very important roles in the self-assembly and enhanced stability of the structure.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Foundation of Science and Technology of Henan Province (grant no. 162102210304).
References
Bruker AXS Inc., SMART, SAINT, SHELXTL, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, (2001).Suche in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
O’Keeffe, M.: Design of MOFs and intellectual content in reticular chemistry: a personal view. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38 (2009) 1215–1217.10.1039/b802802hSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Xuan, W. M.; Zhu, C. F.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.: Mesoporous metal-organic framework materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41 (2012) 1677–1695.10.1039/C1CS15196GSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Xie, S. L.; Wang, H. F.; Liu, Z. H.; Dai, R.; Huang, L. Z.: Fluorescent metal-organic framework based on pyrene chromophore for sensing of nitrobenzene. RSC Adv. 5 (2015) 7121–7124.10.1039/C4RA10835CSuche in Google Scholar
McGuirk, C. M.; Katz, M. J.; Stern, C. L.; Sarjeant, A. A.; Hupp, J. T.; Farha, O. K.; Mirkin, C. A.: Turning on Catalysis: Incorporation of a hydrogen-bond-donating squaramide moiety into a Zr metal-organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 (2015) 919–925.10.1021/ja511403tSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Lin, X. M.; Gao, G. M.; Zheng, L. Y.; Chi, Y. W.; Chen, G. N.: Encapsulation of strongly fluorescent carbon quantum dots in metal-organic frameworks for enhancing chemical sensing. Anal. Chem. 86 (2014) 1223–1228.10.1021/ac403536aSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Zhang, J. J.; Wojtas, L.; Larsen, R. W.; Eddaoudi, M.; Zaworotko, M. J.: Temperature and concentration control over interpenetration in a Metal-Organic Material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (2009) 17040–17041.10.1021/ja906911qSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Luo, F.; Luo, M. B.; Liu, Y. H.: Temperature-controlled structure diversity observed in the Zn(II)-oxalate-4,4′-bipyridine three-member system. CrystEngComm 12 (2010) 1750–1753.10.1039/b920320fSuche in Google Scholar
Qu, L. L.; Zhu, Y. L.; Li, Y. Z.; Du, H. B.; You, X. Z.: Solvent-induced synthesis of zinc(II) and manganese(II) coordination polymers with a semirigid tetracarboxylic acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 11 (2011) 2444–2452.10.1021/cg200229hSuche in Google Scholar
Fu, A. Y.; Jiang, Y. L.; Wang, Y. Y.; Gao, X. N.; Yang, G. P.; Hou, L.; Shi, Q. Z.: DMF/H2O Volume ratio controls the syntheses and transformations of a series of cobalt complexes constructed using a rigid angular multitopic ligand. Inorg. Chem. 49 (2010) 5495–5502.10.1021/ic902548fSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Hou, G. F.; Bi, L. H.; Li, B.; Wu, L. X.: Reaction controlled assemblies of polyoxotungstates(-molybdates) and coordination polymers. Inorg. Chem. 49 (2010) 6474–6483.10.1021/ic1001495Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
Liu, G. Z.; Wang, J. G.; Wang, L. Y.: Divalent metal coordination polymers assembled from dual linkers-semirigid carboxyphenylpropionate and dipyridyl type molecule. CrystEngComm 14 (2012) 951–960.10.1039/C1CE05760JSuche in Google Scholar
Ma, L. F.; Wang, L. Y.; Lu, D. H.; Batten, S. R.; Wang, J. G.: Structural variation from 1D to 3D: effects of temperature and pH value on the construction of Co(II)-H2tbip/bpp mixed ligands system. Cryst. Growth Des. 9 (2009) 1741–1749.10.1021/cg800732eSuche in Google Scholar
Liu, G. Z.; Li, S. H.; Wang, L. Y.: Five M(II) Coordination polymers assembled from various polynuclear units spaced by semirigid carboxyphenylpropionate and N-donor coligand. CrystEngComm 14 (2012) 880–889.10.1039/C1CE05926BSuche in Google Scholar
©2017 Yin Wei-Dong et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-7-propyl-5-methylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-one, C17H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ3-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-[μ3hydroxy-(1,3-di-(μ2-1,2,4-triazole-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C19H16Cu2N6O9
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-3,5-di(4H-1,2,4-triazolyl-4-κ3N,N′:N′′)benzenecarboxylato)silver(I)], C11H9AgN6O3
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium hydrogen carbonate, C13H29NO3
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)yttrium(III)] monohydrate, C20H24O17Y2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-κ2N,N′)]cadmium(II), C48H42Cd3Cl16N18
- Crystal structure of bis(tetraethylammonium) [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylate trihydrate, C30H54N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[(thiophene-3,4-dicarboxylato-κ1O)bis[1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I)] octahydrate, C30H42Ag2N4O12S
- The crystal structure of amine-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I) dihydrate, C9H13AgN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-cyanido-tris(pyridine)dicobalt(II/III)], C20H15Co2N8
- Crystal structure of bis(pyridine)-bis(2-formyl-4,6-dichlorophenolato)cobalt(II), C24H16Cl4CoN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ N:N′)-bis(benzoato-κO)zinc(II)], C24H18N6O4Zn
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a poly[aqua-(μ4-4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) dimanganese(II)], [Mn2(C9H6O4)2(C12H11N5)(H2O)]
- Crystal structure of diaqua-catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C20H24CoN14O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-2,2′-azanediylbis(ethan-1-olato)-κ5O:O,N,O′:O′)-tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-2-((2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)dicobalt(II)dicobalt(III), C16H38Cl4Co4N4O8
- Crystal structure of poly[μ4-(4-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN)manganese(II)] [Mn(C9H6O4)(C16H12N4)]
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-6-phenylpyrimidine, C10H7ClN2
- The crystal structure of [6-methoxy-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one]difluoroborane, C13H10BF5O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(1-phenylbut-1-en-1-olato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II), C24H26N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis((E)-N′-(2-bromobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κN)zinc(II) dinitrate, C26H28N8O12Br2Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13BrN2O2
- A single crystal study on tert-butyl-4-((4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yloxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate, C26H30BrFN4O4
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ3O,O′,N)zinc(II), C36H26N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5′-(pyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1H-[3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazol)]-2′-ide-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II) — bis(5-(pyridin-4-yl-κN)-1H,1′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole))octamolybdate – water (2/1/8), C27H33CoMo4N21O19
- Crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclohexylimino)-2,3-dihydro-6,8-diiodo-4H-1,3-benzoxazin-4-one, C20H24I2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-κO-bis(tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-(μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dimanganese(II) – methanol – water (1/6/2), C62H80Mn2N16O18
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxyethyl(phenyl)carbamodithioate)nickel(II), C18H20N2NiO2S4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methoxy-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylate, C14H16FNO4
- Crystal structure of di-μ-iodido-bis(6-(p-tolyl)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(I) — 2-(diphenylphosphoryl)benzoic acid (1/2), C36H29CuIN2O3P
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-bromo-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16BrFN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κO,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-dicadmium(II) monohydrate, C52H36Cd2Cl4N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(8a-methyl-5-oxo-hexahydroimidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-1(5H)-yl)-2-oxoethyl acetate, C12H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N,N-diethyl-2-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethen-1-amine, C15H17N3O2S
- Crystal structure of diazido-dimethanolato-bis(μ2-2-(((3-oxidopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,O′,N)dimanganese(III), C22H28Mn2N8O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C24H16CuF6O4
- Crystal structure of hexaaquanickel(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40N6NiO12S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C20H22CdF4N4O6
- Crystal structure of 3-benzyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C15H12N2OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-methanolato-κ2O,O)dicopper(II) tetrafluoroborate – acetonitrile (1/1), C49H40BCu2F4Fe2N5O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-κP)silver(I) chloride dihydrate, C24H60AgClN12O6P4
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C14H18O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-hexamethylenetetramine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II)], C34H24Cu2F8N4O8
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-(4-(m-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4- carboxylate, C25H24N3O3
- The crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)-(diphenylcyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H25NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of bis((pyrazin-2-ylmethyl)(pyrazine-2-carbonyl)amido-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II), C20H16CuN10O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-succinonitrile-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C4H12CoN4O10
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-bisisoquinoline, C18H12N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III) perchlorate dihydrate, C22H22ClCoN4O10

