Abstract
C16H15ClN2O3, orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 18.7178(2) Å, b = 15.2296(2) Å, c = 32.0558(3) Å, V = 9137.97(18) Å3, Z = 24, Rgt(F) = 0.0407, wRref(F2) = 0.1099, T = 100(2) K.
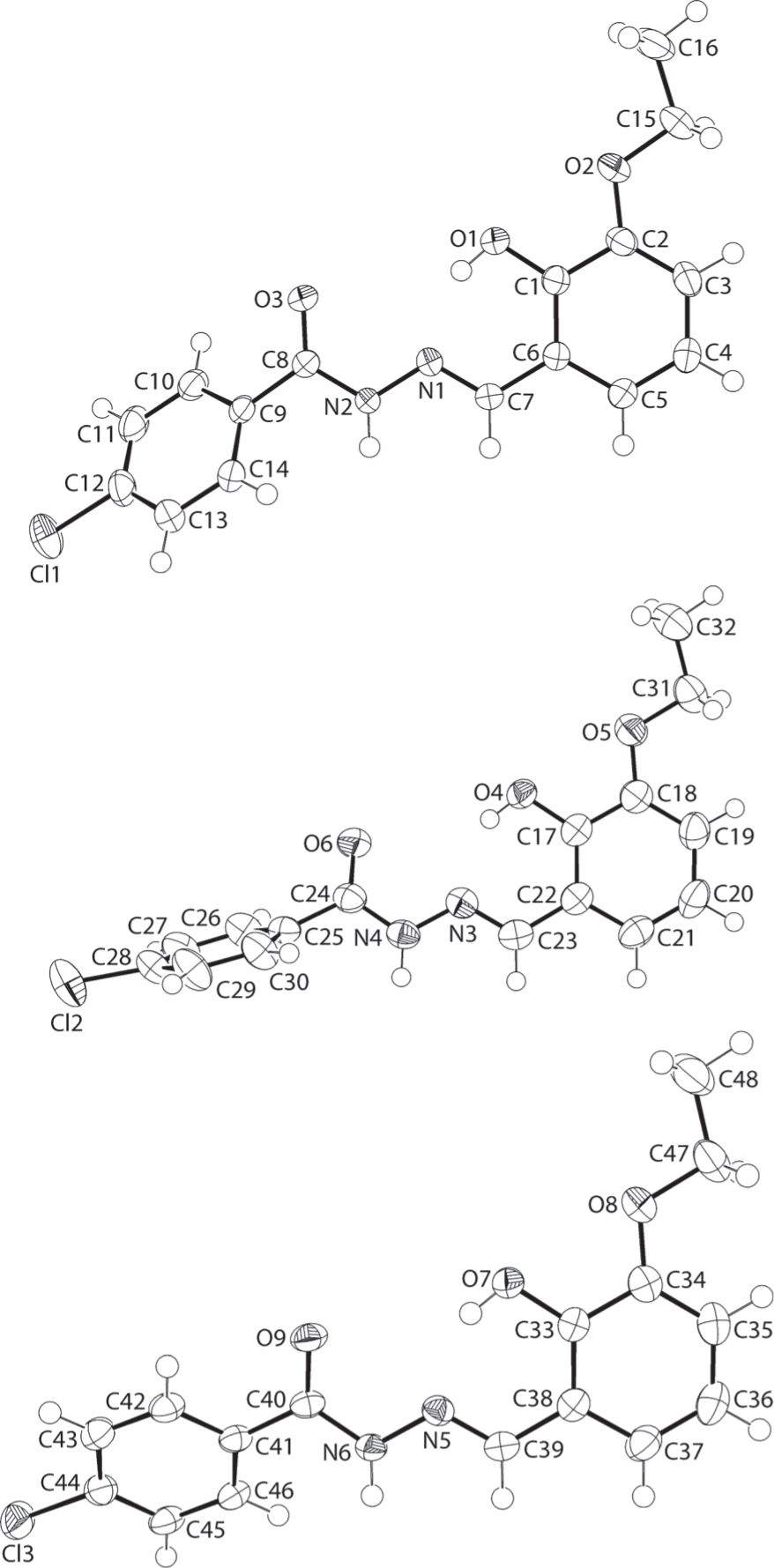
The three molecules comprising the asymmetric unit are shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.30 × 0.24 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 2.35 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 76.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 31906, 9519, 0.034 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 8480 |
| N(param)refined: | 616 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 | 0.70677(3) | 0.23421(4) | 0.08440(2) | 0.04725(13) |
| Cl2 | 1.02412(3) | 0.40652(4) | 0.45858(2) | 0.04883(14) |
| Cl3 | 0.70514(2) | 0.96072(3) | 0.10114(2) | 0.03421(11) |
| O1 | 0.51429(6) | 0.28828(8) | 0.38072(3) | 0.0256(2) |
| H1O | 0.5356(11) | 0.2820(15) | 0.3580(4) | 0.038* |
| O2 | 0.46888(6) | 0.29100(8) | 0.45669(3) | 0.0294(2) |
| O3 | 0.52798(6) | 0.26789(8) | 0.26463(3) | 0.0255(2) |
| O4 | 0.67005(6) | 0.56582(8) | 0.23750(3) | 0.0264(2) |
| H4O | 0.6892(12) | 0.5517(15) | 0.2602(4) | 0.040* |
| O5 | 0.59621(7) | 0.59094(8) | 0.16997(4) | 0.0328(3) |
| O6 | 0.80607(7) | 0.56269(10) | 0.31806(4) | 0.0396(3) |
| O7 | 0.67117(5) | 0.64894(7) | 0.37859(3) | 0.0218(2) |
| H7O | 0.6634(12) | 0.6760(13) | 0.3561(4) | 0.033* |
| O8 | 0.67684(6) | 0.54346(8) | 0.44266(3) | 0.0283(2) |
| O9 | 0.71534(5) | 0.78524(8) | 0.29089(3) | 0.0241(2) |
| N1 | 0.61641(6) | 0.26216(8) | 0.32920(4) | 0.0198(2) |
| H2N | 0.6870(5) | 0.2555(13) | 0.2839(6) | 0.024* |
| N2 | 0.64083(6) | 0.25484(9) | 0.28917(4) | 0.0206(2) |
| N3 | 0.67912(7) | 0.49141(9) | 0.30934(4) | 0.0255(3) |
| N4 | 0.72222(8) | 0.46748(9) | 0.34182(4) | 0.0262(3) |
| H4N | 0.7052(11) | 0.4381(13) | 0.3631(5) | 0.031* |
| N5 | 0.60035(7) | 0.70692(8) | 0.31556(4) | 0.0198(2) |
| N6 | 0.60059(6) | 0.75046(8) | 0.27797(4) | 0.0196(2) |
| H6N | 0.5608(7) | 0.7556(13) | 0.2637(5) | 0.023* |
| C1 | 0.56437(8) | 0.27817(10) | 0.41057(4) | 0.0199(3) |
| C2 | 0.54069(8) | 0.27973(10) | 0.45242(5) | 0.0218(3) |
| C3 | 0.58974(9) | 0.26936(10) | 0.48449(5) | 0.0246(3) |
| H3 | 0.5742 | 0.2717 | 0.5127 | 0.030* |
| C4 | 0.66195(9) | 0.25553(11) | 0.47545(5) | 0.0263(3) |
| H4 | 0.6950 | 0.2473 | 0.4976 | 0.032* |
| C5 | 0.68583(8) | 0.25371(10) | 0.43487(5) | 0.0232(3) |
| H5 | 0.7351 | 0.2448 | 0.4291 | 0.028* |
| C6 | 0.63712(8) | 0.26512(9) | 0.40187(4) | 0.0189(3) |
| C7 | 0.66222(7) | 0.25704(10) | 0.35905(4) | 0.0195(3) |
| H7 | 0.7115 | 0.2482 | 0.3533 | 0.023* |
| C8 | 0.59214(8) | 0.25925(10) | 0.25817(4) | 0.0196(3) |
| C9 | 0.62332(7) | 0.25333(10) | 0.21538(4) | 0.0203(3) |
| C10 | 0.59394(8) | 0.30620(11) | 0.18417(5) | 0.0252(3) |
| H10 | 0.5561 | 0.3456 | 0.1906 | 0.030* |
| C11 | 0.62024(9) | 0.30093(12) | 0.14376(5) | 0.0296(3) |
| H11 | 0.6009 | 0.3368 | 0.1223 | 0.036* |
| C12 | 0.67504(9) | 0.24271(12) | 0.13525(5) | 0.0296(3) |
| C13 | 0.70541(9) | 0.19004(12) | 0.16578(5) | 0.0274(3) |
| H13 | 0.7432 | 0.1508 | 0.1592 | 0.033* |
| C14 | 0.67928(8) | 0.19604(10) | 0.20624(4) | 0.0233(3) |
| H14 | 0.6996 | 0.1610 | 0.2277 | 0.028* |
| C15 | 0.43933(10) | 0.29242(15) | 0.49749(5) | 0.0374(4) |
| H15A | 0.4521 | 0.3479 | 0.5118 | 0.045* |
| H15B | 0.4583 | 0.2428 | 0.5141 | 0.045* |
| C16 | 0.35951(10) | 0.28498(14) | 0.49350(6) | 0.0378(4) |
| H16A | 0.3417 | 0.3317 | 0.4752 | 0.057* |
| H16B | 0.3375 | 0.2907 | 0.5211 | 0.057* |
| H16C | 0.3472 | 0.2277 | 0.4816 | 0.057* |
| C17 | 0.60095(9) | 0.53996(10) | 0.23869(5) | 0.0250(3) |
| C18 | 0.55938(9) | 0.55638(11) | 0.20300(5) | 0.0284(3) |
| C19 | 0.48673(10) | 0.53751(12) | 0.20322(6) | 0.0341(4) |
| H19 | 0.4583 | 0.5508 | 0.1795 | 0.041* |
| C20 | 0.45546(10) | 0.49912(13) | 0.23816(6) | 0.0375(4) |
| H20 | 0.4055 | 0.4879 | 0.2384 | 0.045* |
| C21 | 0.49641(10) | 0.47738(11) | 0.27228(6) | 0.0331(4) |
| H21 | 0.4750 | 0.4489 | 0.2955 | 0.040* |
| C22 | 0.56960(9) | 0.49704(10) | 0.27305(5) | 0.0265(3) |
| C23 | 0.61245(9) | 0.47228(10) | 0.30918(5) | 0.0267(3) |
| H23 | 0.5913 | 0.4426 | 0.3321 | 0.032* |
| C24 | 0.78782(9) | 0.50665(11) | 0.34305(5) | 0.0277(3) |
| C25 | 0.83791(9) | 0.47564(11) | 0.37638(5) | 0.0255(3) |
| C26 | 0.86842(11) | 0.53822(11) | 0.40257(5) | 0.0337(4) |
| H26 | 0.8513 | 0.5969 | 0.4020 | 0.040* |
| C27 | 0.92309(11) | 0.51612(12) | 0.42936(5) | 0.0346(4) |
| H27 | 0.9429 | 0.5585 | 0.4477 | 0.041* |
| C28 | 0.94831(10) | 0.43126(12) | 0.42892(5) | 0.0326(4) |
| C29 | 0.91801(12) | 0.36699(12) | 0.40424(6) | 0.0377(4) |
| H29 | 0.9354 | 0.3084 | 0.4051 | 0.045* |
| C30 | 0.86141(11) | 0.38974(11) | 0.37805(5) | 0.0332(4) |
| H30 | 0.8390 | 0.3461 | 0.3614 | 0.040* |
| C31 | 0.56162(11) | 0.58467(13) | 0.13011(6) | 0.0360(4) |
| H31A | 0.5196 | 0.6241 | 0.1292 | 0.043* |
| H31B | 0.5452 | 0.5238 | 0.1252 | 0.043* |
| C32 | 0.61505(12) | 0.61098(15) | 0.09745(6) | 0.0431(4) |
| H32A | 0.6308 | 0.6714 | 0.1026 | 0.065* |
| H32B | 0.5929 | 0.6074 | 0.0698 | 0.065* |
| H32C | 0.6563 | 0.5714 | 0.0986 | 0.065* |
| C33 | 0.60971(8) | 0.60769(10) | 0.38903(4) | 0.0204(3) |
| C34 | 0.61165(8) | 0.55055(10) | 0.42375(5) | 0.0237(3) |
| C35 | 0.55008(9) | 0.50664(11) | 0.43577(5) | 0.0294(3) |
| H35 | 0.5513 | 0.4686 | 0.4593 | 0.035* |
| C36 | 0.48643(9) | 0.51764(12) | 0.41383(6) | 0.0326(4) |
| H36 | 0.4446 | 0.4876 | 0.4226 | 0.039* |
| C37 | 0.48397(9) | 0.57194(11) | 0.37944(5) | 0.0283(3) |
| H37 | 0.4405 | 0.5790 | 0.3645 | 0.034* |
| C38 | 0.54564(8) | 0.61702(10) | 0.36634(5) | 0.0220(3) |
| C39 | 0.54352(8) | 0.66727(10) | 0.32763(5) | 0.0217(3) |
| H39 | 0.5009 | 0.6706 | 0.3117 | 0.026* |
| C40 | 0.66375(7) | 0.78660(9) | 0.26694(4) | 0.0194(3) |
| C41 | 0.66906(7) | 0.82919(10) | 0.22515(4) | 0.0197(3) |
| C42 | 0.72202(8) | 0.89326(10) | 0.22056(5) | 0.0230(3) |
| H42 | 0.7509 | 0.9087 | 0.2438 | 0.028* |
| C43 | 0.73302(8) | 0.93446(11) | 0.18268(5) | 0.0252(3) |
| H43 | 0.7686 | 0.9785 | 0.1797 | 0.030* |
| C44 | 0.69057(8) | 0.90969(11) | 0.14913(5) | 0.0241(3) |
| C45 | 0.63763(8) | 0.84671(11) | 0.15254(5) | 0.0237(3) |
| H45 | 0.6091 | 0.8315 | 0.1291 | 0.028* |
| C46 | 0.62692(7) | 0.80602(10) | 0.19093(4) | 0.0213(3) |
| H46 | 0.5909 | 0.7625 | 0.1938 | 0.026* |
| C47 | 0.68035(10) | 0.48873(12) | 0.47914(5) | 0.0333(4) |
| H47A | 0.6640 | 0.4286 | 0.4724 | 0.040* |
| H47B | 0.6492 | 0.5127 | 0.5013 | 0.040* |
| C48 | 0.75665(11) | 0.48689(15) | 0.49370(6) | 0.0435(5) |
| H48A | 0.7867 | 0.4607 | 0.4720 | 0.065* |
| H48B | 0.7601 | 0.4519 | 0.5193 | 0.065* |
| H48C | 0.7728 | 0.5469 | 0.4993 | 0.065* |
Source of material
General: The melting point of the compound was measured on a Electrothermal digital melting point apparatus and was uncorrected. The elemental analysis was performed on a Perkin-Elmer EA2400 CHN analyser. The IR spectrum was recorded using a Perkin-Elmer RX1 spectrophotometer equipped as a Nujol mull in between KBr cell from 4000 to 400 cm−1. The 1H and 13C{1H} NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3 solution on a Bruker AVN FT-NMR 400 MHz NMR spectrometer with chemical shifts relative to tetramethylsilane.
Synthesis: 4-Chlorobenzhydrazide (Fluka, 0.85 g, 5.0 mmol) and 3-ethoxysalicylaldehyde (Aldrich, 0.83 g, 5.0 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (50 mL) and refluxed for 3 h. The mixture was filtered and allowed to stand at room temperature for 2 days whereupon yellow crystals were formed. The crystals were filtered, washed with methanol and air-dried. Yield: 1.35 g (84.7%). M.pt: 433–434 K. Calcd for C16H15ClN2O3: C 60.29; H 4.74; N 8.79%. Found: C 60.24; H 4.34; N, 8.78%. IR (cm−1): 3448 (br) ν(O—H), 3217 (s) ν(N—H), 1655 (s) ν(C=O), 1610 (s) ν(C=N). 1H NMR (CDCl3, ppm): δ 1.39 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.98–4.08 (m, 2H, OCH2), 6.77–7.17 (m, 3H, Ar—H), 7.59–7.93 (m, 4H, Ph—H), 8.63 (s, 1H, HCN), 10.88 (s, 1H, N—H), 12.15 (s, 1H, O—H). 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3, ppm): δ 14.7 (CH3), 64.2 (CH2), 115.4, 118.9, 119.1, 121.0, 128.6, 129.5, 131.5, 136.8, 147.0, 147.5 (Ar—C).
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The O- and N-bound H-atoms were located in a difference Fourier map but were refined with distance restraints of O—H = 0.84±0.01 Å and N—H = 0.88±0.01 Å, respectively, and with Uiso(H) set to 1.5Ueq(O) and 1.2Ueq(N), respectively.
Comment
Crystal structure determinations of neutral benzyltin compounds containing Schiff base ligands related to the title hydrazone molecule, 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene] benzohydrazide, a potentially dianionic tridentate ligand, have sometimes revealed unexpected synthetic outcomes. Thus, while the anticipated (2-FC6H4CH2)2Sn(L1) product was obtained from the reaction of (2-FC6H4CH2)2SnCl2 and 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene] benzohydrazide (H2L1) [5], incompletely substituted species of composition (C6H5CH2)Sn(OHCH3)(L2)Cl [6] and (4-FC6H4CH2)Sn(OH2)(L3)Cl [7] were obtained when analogous reactions of the respective di-(substituted-benzyl)tin dichlorides with 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide (H2L2) and 1-hydroxy-N′-[(1E)-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl) methylidene]naphthalene-2-carbohydrazide (H2L3), respectively, were conducted. Studies in this area are largely motivated by the biological activity, especially in the context of the quest for new anti-cancer drugs, of organotin derivatives of these molecules [8], [9], [10]. Complementing the above, are structural studies of the Schiff bases themselves [11], [12] and it was in this context that the title compound was studied crystallographically.
The crystallographic asymmetric unit of the title structure comprises three independent molecules as shown in the figure (70% displacement ellipsoids). Each independent molecule, hereafter designated as the Cl1-, Cl2- and Cl3-molecules, comprises a central chromophore defined by the C(=O)N(H)N=C atoms which is planar with r.m.s. deviations of 0.0068 and 0.0171 Å for the Cl1 and Cl3 molecules, respectively. However, a difference in conformation for the Cl2-molecule is noted whereby a twist is evident as seen in the C23—N3—N4—C24 torsion angle of −166.67(14)°. The configuration about each of the imine-N1—C7 [1.2871(19) Å], N3—C23 [1.282(2) Å] and N5—C39 [1.283(2) Å] bonds is E. The dihedral angles between the central planes and appended hydroxy- and chloro-phenyl rings also reveal differences in conformation between the independent molecules, i.e. 4.49(3) & 38.97(7)°, 18.47(11) & 59.73(7)° and 9.83(10) and 25.05(7)°, for the Cl1–Cl3-molecules, respectively. The dihedral angles formed between the outer rings are 35.36(6), 77.69(6) and 31.3(7)°, respectively. Each molecule features an intramolecular hydroxy-O—H⋯N(imine) hydrogen bond [O1—H1o⋯N1: H1o⋯N1 = 1.798(19) Å, O1⋯N1 = 2.5572(16) Å with angle at H1o = 150.3(18) Å, O4—H4o⋯N3: H4o⋯N3 = 1.833(16) Å, O4⋯N3 = 2.5722(17) Å with angle at H4o = 146(2)° and O7—H7o⋯N5: H7o⋯N5 = 1.818(18) Å, O7⋯N5 = 2.5728(16) Å with angle at H7o = 148(2)°].
The crystal of the title compound features supramolecular, zig-zag chains along the a-axis direction sustained by amide-N—H⋯O(carbonyl) hydrogen bonds occurring between the Cl1- and Cl3-molecules [N2—H2n⋯O9i: H2n⋯O9i = 1.897(10) Å, N2⋯O9i = 2.7323(15) Å with angle at H2n = 157.8(18)° and N6—H6n⋯O3ii: H6n⋯O3ii = 1.903(14) Å, N6⋯O3ii = 2.7797(16) Å with angle at H6n = 177.1(15)° for symmetry operations (i) 3/2 − x, −1/2 + y, z and (ii) 1 − x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 − z]. Additional stability to the chains is afforded by π-stacking interactions between chlorophenyl rings [Cg(C9–C14)⋯Cg(C41–C46)i = 3.7110(9) Å with an angle of inclination = 2.52(8)°] The amide-N4H atom of the Cl2-molecule does not participate in a hydrogen bond. The chains are linked into supramolecular layers in the ab-plane via a combination of parallel carbonyl-O⋯π(hydroxyphenyl) [C8—O3⋯Cg(C17–C22)iii = 3.9502(14) Å with angle at O3 = 98.81(9)° for (iii) 1 − x, −1/2 + y, 1/2 − z] and C—H⋯O interactions with the closest of these being of the type methylene-C—H⋯O(hydroxy) [C31—H31a⋯O1ii: H31a⋯O1ii = 2.60 Å, C31⋯O1ii = 3.429(2) Å with angle at H31a = 141°]. The links between layers along the c-axis to consolidate the three-dimensional molecular packing are of the type hydroxyphenyl- and methylene-C—H⋯Cl [C4—H4⋯Cl1iv: H4⋯Cl1iv = 2.81 Å, C4⋯Cl1iv = 3.5952(17) Å with angle at H4 = 141° and C15—H15b⋯Cl2v: H15b⋯Cl2v = 2.73 Å, C15⋯Cl2v 3.699(2) Å with angle at H15b = 166° for (iv) x, 1/2 − y, 1/2 + z and (v) −1/2 + x, 1/2 − y, 1 − z].
Finally, an analysis of the calculated Hirshfeld surfaces was conducted. This was accomplished employing Crystal Explorer 17 [13] and literature procedures [14], including the calculation of the full and decomposed two-dimensional fingerprint plots. In particular, a recent study showed how such an analysis can be employed to differentiate between multiple molecules in the asymmetric unit [15]. The most prominent contacts on the Hirshfeld surface for each individual molecule are, not surprisingly, H⋯H contacts and the percentage contributions for the Cl1–Cl3-molecules, i.e. 38.5, 31.5 and 32.6%, differentiate between the Cl1-molecule on the one hand and the Cl2- and Cl3-molecules on the other. A similar differentiation is seen in the C⋯H/H⋯C contacts of 20.3, 26.7 and 25.6%, respectively. To a first approximation, the percentage contributions from the O⋯H/H⋯O [16.6, 17.0 and 17.5%] and Cl⋯H/H⋯Cl [15.6, 13.4 and 12.8%] contacts are about the same. The 3.6, 1.7 and 3.8% contributions from the C⋯C contacts and 1.1, 1.9 and 1.2% from the O⋯C/C⋯O contacts highlight small differences between the molecules.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant no. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Agilent Technologies: CrysAlisPRO. Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA (2010).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Suche in Google Scholar
5. Lee, S. M.; Lo, K. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of bis(2-fluorobenzyl) (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene]benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O´)bis(2-fluorobenzyl))tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0550.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0550Suche in Google Scholar
6. Lee, S. M.; Lo, K. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H19Cl2N2O3Sn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0530.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0530Suche in Google Scholar
7. Lo, K. M.; Lee, S. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)-tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0551.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0551Suche in Google Scholar
8. Lee, S. M.; Ali, H. M.; Sim, K. S.; Malek, S. N. A.; Nurestri, S.; Lo, K. M.: Synthesis, structural characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity of diorganotin complexes with Schiff base ligands derived from 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoylhydrazide. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 26 (2012) 310–319.10.1002/aoc.2862Suche in Google Scholar
9. Hong, M.; Geng, H.; Niu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Yin, H.: Organotin(IV) complexes derived from Schiff base N′-[(1E)-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methylidene]-pyridine-4-carbohydrazone: synthesis, in vitro cytotoxicities and DNA/BSA interaction. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 86 (2014) 550–561.10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.08.070Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Chow, K. M.; Lo, K. M.: Synthesis, spectral characterization and crystal structures of benzyltin complexes with (E)-4-chloro-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide. Polyhedron 81 (2014) 370–381.10.1016/j.poly.2014.06.043Suche in Google Scholar
11. Lee, S. M.; Halcovitch, N. R.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: N′-[1-(5-Bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]isonicotinohydrazide monohydrate: crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis. Acta Crystallogr. E73 (2017) 630–636.10.1107/S2056989017004790Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
12. Lo, K. M.; Lee, S. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0568.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0568Suche in Google Scholar
13. Turner, M. J.; McKinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Suche in Google Scholar
14. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Jotani, M. M.; Wardell, J. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Supramolecular association in the triclinic (Z′ = 1) and monoclinic (Z′ = 4) polymorphs of 4-(4-acetylphenyl)piperazin-1-ium 2-amino-4-nitrobenzoate. Z. Kristallogr. – Cryst. Mater. 234 (2019) 43–57.10.1515/zkri-2018-2101Suche in Google Scholar
©2019 See Mun Lee et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3


