Abstract
C22H28N2O2S, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 9.2516(7) Å, b = 10.5122(8) Å, c = 19.7782(15) Å, β = 98.9530(10)°, V = 1900.1(2) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0356, wRref(F2) = 0.1004, T = 100(2) K.
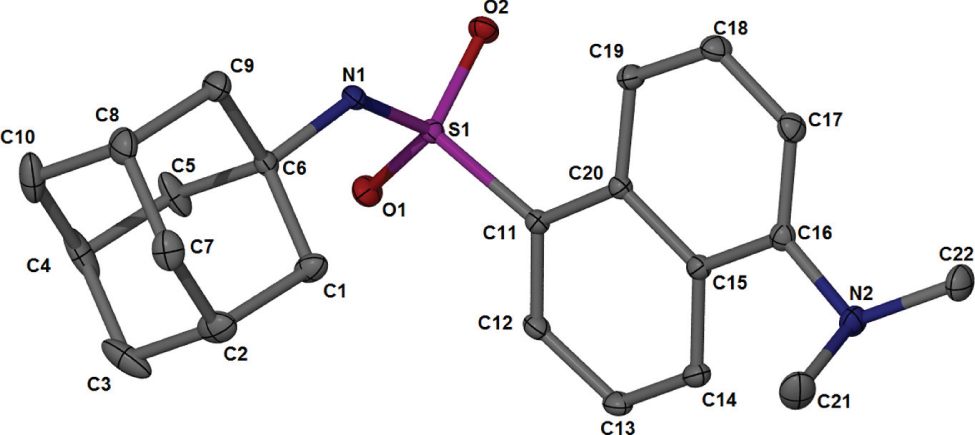
The molecular structure is shown in the figure (H atoms are omitted for clarity). Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Source of materials
A solution of dansyl chloride (systematic name: 5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride) (1.0 eq.) and amantadine (systematic name: 1-aminoadamantane; 1.0 eq.) in dichloromethane (DCM) (10 mL) was stirred in a sealed tube under microwave irradiation conditions (150 W, 373 K, 150 psi) for 10 min. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified via repeated crystallization from ethanol at room temperature to afford the product. Yield 95%; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ/ppm = 8.53–8.51 (dd, J = 6.3, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 8.32–8.29 (dd, J = 6.3, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.25–8.23 (dd, J = 6.3, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.58–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.19–7.17 (dd, J = 6.4, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 2.90 (s, 6H), 1.95 (s, 3H), 1.74 (s, 6H), 1.59–1.48 (m, 6H); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ/ppm = 151.6, 138.7, 130.0, 129.9, 129.6, 129.0, 128.0, 123.4, 119.2, 115.0, 55.5, 45.5, 43.0, 35.8, 29.5. The title compound (10.0 mg) was dissolved in ethanol, and the solvent was evaporated slowly at ambient conditions. Crystals formed over a period of 3 days.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless shard |
| Size: | 0.40 × 0.20 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.19 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II DUO, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 30.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 60522, 5782, 0.039 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5118 |
| N(param)refined: | 250 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], X-Seed [3], [4], WinGX/ORTEP [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.14508(12) | 0.61431(11) | 0.60688(6) | 0.0162(2) |
| H1A | 0.111191 | 0.632305 | 0.557847 | 0.019* |
| H1B | 0.189105 | 0.692946 | 0.628658 | 0.019* |
| C2 | 0.01439(13) | 0.57337(12) | 0.64151(7) | 0.0205(2) |
| H2 | −0.060563 | 0.642667 | 0.636652 | 0.025* |
| C3 | 0.06800(14) | 0.54803(15) | 0.71770(7) | 0.0286(3) |
| H3A | 0.112141 | 0.626258 | 0.739896 | 0.034* |
| H3B | −0.015560 | 0.523213 | 0.740613 | 0.034* |
| C4 | 0.18177(14) | 0.44104(16) | 0.72476(6) | 0.0274(3) |
| H4 | 0.216718 | 0.424695 | 0.774418 | 0.033* |
| C5 | 0.31256(13) | 0.48128(14) | 0.69008(6) | 0.0212(2) |
| H5A | 0.358414 | 0.558699 | 0.712484 | 0.025* |
| H5B | 0.386789 | 0.412701 | 0.694924 | 0.025* |
| C6 | 0.25962(11) | 0.50790(10) | 0.61396(5) | 0.01121(18) |
| C7 | −0.05386(13) | 0.45170(12) | 0.60823(6) | 0.0189(2) |
| H7A | −0.138054 | 0.426079 | 0.630508 | 0.023* |
| H7B | −0.090066 | 0.467374 | 0.559163 | 0.023* |
| C8 | 0.05972(13) | 0.34525(11) | 0.61546(6) | 0.0188(2) |
| H8 | 0.014643 | 0.266312 | 0.593145 | 0.023* |
| C9 | 0.19056(13) | 0.38521(11) | 0.58088(6) | 0.0167(2) |
| H9A | 0.157359 | 0.399610 | 0.531432 | 0.020* |
| H9B | 0.264473 | 0.316370 | 0.585765 | 0.020* |
| C10 | 0.11244(14) | 0.31939(14) | 0.69147(7) | 0.0266(3) |
| H10A | 0.185234 | 0.249644 | 0.696665 | 0.032* |
| H10B | 0.028897 | 0.293318 | 0.714087 | 0.032* |
| C11 | 0.42199(11) | 0.79573(10) | 0.55727(5) | 0.01079(18) |
| C12 | 0.40813(12) | 0.89081(10) | 0.60349(5) | 0.01268(19) |
| H12 | 0.441036 | 0.877155 | 0.650868 | 0.015* |
| C13 | 0.34528(12) | 1.00857(10) | 0.58094(6) | 0.0145(2) |
| H13 | 0.338342 | 1.074640 | 0.613051 | 0.017* |
| C14 | 0.29411(12) | 1.02813(10) | 0.51283(6) | 0.0138(2) |
| H14 | 0.250869 | 1.107455 | 0.498261 | 0.017* |
| C15 | 0.30502(11) | 0.93113(10) | 0.46381(5) | 0.01112(18) |
| C16 | 0.25293(11) | 0.95183(10) | 0.39230(5) | 0.01220(19) |
| C17 | 0.28194(12) | 0.86282(11) | 0.34488(5) | 0.0138(2) |
| H17 | 0.252056 | 0.878057 | 0.297414 | 0.017* |
| C18 | 0.35586(12) | 0.74932(11) | 0.36682(6) | 0.0143(2) |
| H18 | 0.377207 | 0.689726 | 0.333641 | 0.017* |
| C19 | 0.39766(12) | 0.72296(10) | 0.43492(5) | 0.01245(19) |
| H19 | 0.442377 | 0.643691 | 0.448414 | 0.015* |
| C20 | 0.37448(11) | 0.81346(10) | 0.48535(5) | 0.01025(18) |
| C21 | 0.02252(14) | 1.05688(13) | 0.38842(7) | 0.0240(3) |
| H21A | −0.032854 | 0.995380 | 0.357334 | 0.036* |
| H21B | −0.024275 | 1.140561 | 0.381979 | 0.036* |
| H21C | 0.024324 | 1.029099 | 0.435846 | 0.036* |
| C22 | 0.17367(14) | 1.10701(12) | 0.30315(6) | 0.0187(2) |
| H22A | 0.274874 | 1.113415 | 0.294488 | 0.028* |
| H22B | 0.126240 | 1.190364 | 0.296221 | 0.028* |
| H22C | 0.120377 | 1.045240 | 0.271502 | 0.028* |
| N1 | 0.38407(10) | 0.53698(9) | 0.57701(5) | 0.01117(16) |
| H1 | 0.3742(18) | 0.5081(17) | 0.5354(9) | 0.024(4)* |
| N2 | 0.17296(10) | 1.06525(9) | 0.37360(5) | 0.01513(18) |
| O1 | 0.54260(9) | 0.66769(8) | 0.66343(4) | 0.01504(16) |
| O2 | 0.61620(8) | 0.61719(8) | 0.55114(4) | 0.01376(15) |
| S1 | 0.50335(3) | 0.65063(2) | 0.59084(2) | 0.01044(7) |
Experimental details
Single-crystal X-ray intensity data were collected on a Bruker 3-circle Apex II DUO X-ray diffractometer equipped with an INCOATEC IμS HB microsource. Data collection and reduction were carried out using the Bruker software package APEX3 [1] using standard procedures. The structure was solved and refined using SHELX-2016 [2] employed within the X-Seed [3], [4] environment. Hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions using riding models. ORTEP-3 [5] was used to generate the publication material.
Comment
The title compound was investigated as part of an ongoing study into the development of adamantane conjugated fluorophores that could be used as potential neurobiological fluorescent ligands [6], [7]. The 5-dimethylamino-naphtalene sulfonyl (dansyl) moeity acts as the fluorophore [7], [8]. Continued development of fluorescent adamantane molecules is motivated by their good biological activity, e.g. as nitric oxide synthase inhibitors [6], [9], anti-oxidants [9], N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists and voltage-gated calcium channel blockers [7], [9], [10].
The bond lengths, angles and torsion angles of the adamantane ring system and the conjugated 5-dimethylamino-naphtalene sulfonyl moiety are consistent with previously published structures [11], [12], [13], [14]. The conformation of the investigated molecule is dependant on the sulfonylamide link, connecting the naphtalene ring and adamantane fragment. Two important torsion angles t1 [C6—N1—S1—C11, −77.19(10)°] and t2 [C12—C11—S1—N1, 115.88(9)°] describe the conformation of the molecule. Crystal packing analysis reveals that the molecules associate into cyclic dimers. These dimers are connected via a classical intermolecular hydrogen bond, N1—H1⋯O2i with an H⋯A distance of 2.38 Å, and an angle of 119.8°. Symmetry code: (i) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1. The dimers are uniformly packed in the (ac) plane and create alternate stacking in the proximity of the (ac) plane.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2018).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
3. Barbour, L. J.: X-Seed – a softwaretool for supramolecular crystallography. J. Supramol. Chem. 1 (2001) 189–191.10.1016/S1472-7862(02)00030-8Search in Google Scholar
4. Atwood, J. L.; Barbour, L. J.: Molecular Graphics: From science to art. Cryst. Growth Des. 3 (2003) 3–8.10.1021/cg020063oSearch in Google Scholar
5. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
6. Joubert, J.; van Dyk, S.; Malan, S. F.: Fluorescent polycyclic ligands for nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 (2008) 8952–8958.10.1016/j.bmc.2008.08.049Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Joubert, J.; van Dyk, S. V.; Green, I. R.; Malan, S. F.: Synthesis, evaluation and application of polycyclic fluorescent analogues as N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor and voltage gated calcium channel ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 (2011) 5010–5020.10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.08.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Joubert, J.; van Dyk, S. V.; Malan, S. F.: Small molecule fluorescent ligands as central nervous system imaging probes. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 13 (2013) 682–696.10.2174/1389557511313050005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Joubert, J.; van Dyk, S. V.; Green, I. R.; Malan, S. F.: Synthesis and evaluation of fluorescent heterocyclic aminoadamantanes as multifunctional neuroprotective agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 (2011) 3935–3944.10.1016/j.bmc.2011.05.034Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Kadernani, Y. E.; Zindo, F. T.; Kapp, E.; Malan, S. F.; Joubert, J.: Adamantane amine derivatives as dual acting NMDA receptor and voltage-gated calcium channel inhibitors for neuroprotection. Med. Chem. Commun. 5 (2014) 1678–1684.10.1039/C4MD00244JSearch in Google Scholar
11. Joubert, J.; Samsodien, H.; Baber, Q. R.; Cruickshank, D. L.; Caira, M. R.; Malan, S. F.: Synthesis and structural analysis of novel neuroprotective pentacyclo[5.4.1.02,6.03,10.05,9]undecane- and adamantane-derived propargylamines. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 44 (2014) 194–204.10.1007/s10870-014-0501-ySearch in Google Scholar
12. Voronin, A. P.; Volkova, T. V.; Ilyukhin, A. B.; Trofimova, T. P.; Perlovich, G. L.: Structural and energetic aspects of adamantane and memantine derivatives of sulfonamide molecular crystals: experimental and theoretical characterisation. CrystEngComm 20 (2018) 3476–3489.10.1039/C8CE00426ASearch in Google Scholar
13. Bhatt, P.; Govender, T.; Kruger, H. G.; Maguire, G. E. M.: N-Benzyl-5-(dimethylamino)-naphthalene-1-sulfonamide. Acta Crystallogr. E67 (2011) o2458–o2459.10.1107/S1600536811033083Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Su, Z.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Y.: N-(2-Aminoethyl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide. Acta Crystallogr. E65 (2009) o1452.10.1107/S160053680901962XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2019 Jacques Joubert, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3

