Abstract
C16H12CdO11, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 14.6977(6) Å, b = 5.9706(2) Å, c = 20.7220(10) Å, β = 109.802(5)°, V = 1710.91(13) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0456, wRref(F2) = 0.1583, T = 296(2) K.
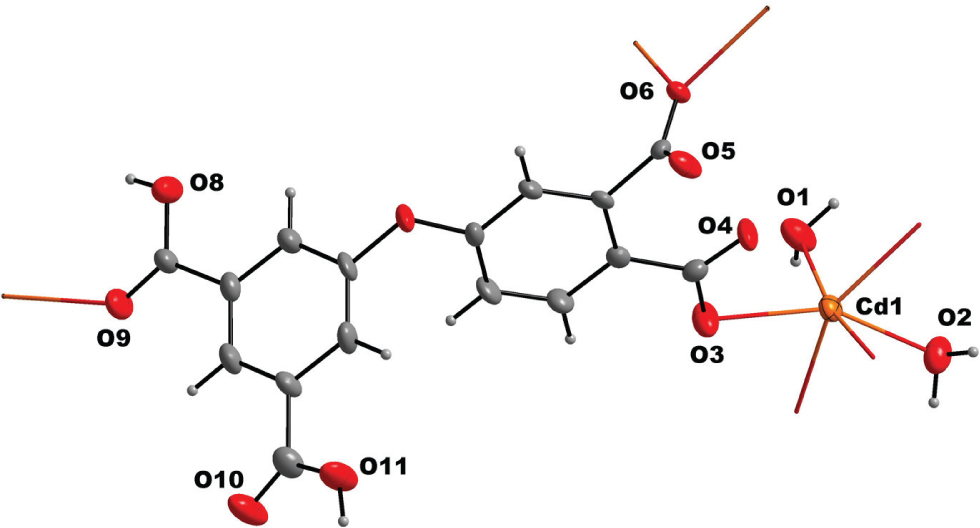
A part of the title structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.32 × 0.26 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.34 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 18198, 3178, 0.052 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2916 |
| N(param)refined: | 257 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd1 | 0.07442(3) | 0.05569(6) | 0.590967(19) | 0.0217(2) |
| O1 | 0.0404(3) | 0.2665(7) | 0.6729(2) | 0.0381(10) |
| H1A | 0.0594 | 0.1977 | 0.7125 | 0.057* |
| H1B | −0.0220 | 0.2779 | 0.6633 | 0.057* |
| O2 | −0.0064(3) | −0.2622(7) | 0.6020(2) | 0.0359(10) |
| H2A | 0.0338 | −0.3720 | 0.6178 | 0.054* |
| H2B | −0.0426 | −0.3094 | 0.5619 | 0.054* |
| O3 | 0.2155(3) | 0.2564(7) | 0.6226(2) | 0.0363(10) |
| O4 | 0.1131(3) | 0.4061(6) | 0.5318(2) | 0.0353(11) |
| O5 | 0.1391(3) | 0.7247(7) | 0.41855(19) | 0.0296(9) |
| O6 | 0.0794(2) | 0.8885(6) | 0.49060(19) | 0.0189(8) |
| O7 | 0.4668(3) | 1.0787(6) | 0.5822(2) | 0.0284(10) |
| O8 | 0.6795(3) | 1.5397(6) | 0.7724(3) | 0.0355(11) |
| H8 | 0.7067 | 1.6253 | 0.8040 | 0.053* |
| O9 | 0.8182(3) | 1.3466(7) | 0.8137(2) | 0.0336(10) |
| O10 | 0.8578(3) | 0.6499(9) | 0.6915(2) | 0.0460(12) |
| O11 | 0.7450(3) | 0.5875(8) | 0.5895(2) | 0.0415(12) |
| H11 | 0.7755 | 0.4710 | 0.5917 | 0.062* |
| C1 | 0.1933(4) | 0.4061(8) | 0.5768(3) | 0.0208(12) |
| C2 | 0.2660(4) | 0.5838(8) | 0.5789(3) | 0.0178(11) |
| C3 | 0.3582(4) | 0.5740(9) | 0.6273(3) | 0.0252(13) |
| H3 | 0.3738 | 0.4557 | 0.6583 | 0.030* |
| C4 | 0.4273(4) | 0.7333(9) | 0.6309(3) | 0.0272(12) |
| H4 | 0.4885 | 0.7242 | 0.6641 | 0.033* |
| C5 | 0.4039(4) | 0.9080(8) | 0.5841(3) | 0.0203(11) |
| C6 | 0.3126(4) | 0.9237(8) | 0.5359(3) | 0.0193(11) |
| H6 | 0.2975 | 1.0433 | 0.5053 | 0.023* |
| C7 | 0.2432(3) | 0.7636(8) | 0.5325(2) | 0.0160(10) |
| C8 | 0.1462(3) | 0.7896(8) | 0.4770(3) | 0.0169(10) |
| C9 | 0.5630(4) | 1.0607(8) | 0.6236(3) | 0.0256(13) |
| C10 | 0.6215(4) | 0.8939(10) | 0.6122(3) | 0.0273(13) |
| H10 | 0.5972 | 0.7921 | 0.5765 | 0.033* |
| C11 | 0.7174(4) | 0.8821(10) | 0.6553(3) | 0.0216(11) |
| C12 | 0.7536(4) | 1.0367(9) | 0.7082(3) | 0.0241(12) |
| H12 | 0.8170 | 1.0248 | 0.7382 | 0.029* |
| C13 | 0.6954(4) | 1.2063(9) | 0.7158(3) | 0.0239(12) |
| C14 | 0.5989(4) | 1.2160(9) | 0.6747(3) | 0.0250(12) |
| H14 | 0.5588 | 1.3269 | 0.6818 | 0.030* |
| C15 | 0.7375(4) | 1.3724(9) | 0.7725(3) | 0.0241(12) |
| C16 | 0.7815(4) | 0.6991(10) | 0.6472(3) | 0.0295(13) |
Source of material
A mixture of 5-(3′,4′-dicarboxylphenoxy)-isophthalic acid (35 mg, 0.1 mmol), and Cd(NO3)2⋅6H2O (29.1 mg, 0.1 mmol), were added to water (10 mL) in a 25 mL Teflon-lined autoclave. The mixture was heated at 423 K for 3 days and then slowly cooled down to room temperature. Red block crystals of the title compound were obtained.
Experimental details
The hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions riding on attached atoms with isotropic thermal parameters.
Comment
In recent years, research on coordination complexes has made considerable progress in the fields of supramolecular chemistry and crystal engineering, owing to their intriguing architectures and functional applications, such as catalysis, luminescence, gas storage, magnetism, molecular separation and sensors [4], [5], [6], [7]. It is well known that organic ligands play crucial roles in the design and construction of desirable frameworks [8], [9], [10]. And for this purpose, numerous multi-functional carboxylate ligands have been designed, synthesized and investigated deeply, owing to their inherent outstanding coordination capabilities and changeable coordination modes [11], [12]. The semi-rigid multicarboxylate ligand 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenoxy)phthalic acid has eight possible coordination sites which can supply varied patterns (monodentate, bridging, chelating) to construct coordination polymers. The asymmetric unit of the title structure contains Cd(II) ion and 5-(3′,4′-dicarboxylphenoxy)-isophthalate dianion as ligand to construct a new 2D coordination polymer. The cadmium atom Cd1 is six-coordinated by four oxygen atoms from 5-(3′,4′-dicarboxylphenoxy)-isophthalate ligands and two oxygen atoms from coordinated water molecules. The Cd—O bond lengths range from 2.290(4) to 2.416(4) Å and are in the expected ranges [13]. This compound exhibits a 3D structure through hydrogen bonds.
References
1. Bruker. APEX3, SAINT-Plus, XPREP. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2016).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.: Three Cd(II) complexes based on pyridine containing mercaptotriazole and aromatic multi-carboxylates: syntheses, structures and luminescent properties. J. Mol. Struct. 1173 (2018) 612–619.10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.07.025Search in Google Scholar
5. Ma, L. F.; Han, M. L.; Qin, J. H.; Wang, L. Y.; Du, M.: MnII coordination polymers based on bi-, tri-, and tetranuclear and polymeric chain building units: crystal structures and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 51 (2012) 9437–9442.10.1021/ic3012537Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Hogarth, G.: Metal-dithiocarbamate complexes: chemistry and biological activity. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 12 (2012) 1202–1215.10.2174/138955712802762095Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Wang, X. F.; Du, K. J.; Wang, H. Q.; Zhang, X. L.; Nie, C. M.: A novel asymmetric chair-like hydroxyl-bridged tetra-copper compound: synthesis, supramolecular structure and magnetic property. J. Mol. Struct. 1138 (2017) 155–160.10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.03.007Search in Google Scholar
8. Fu, H. R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, K. L.; Wang, H. F.; Han, M. L.: Construction of a pillared-layer framework based on charge balance: CO2 adsorption and luminescence. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 37 (2018) 461–466.Search in Google Scholar
9. Li, S. H.; Li, X. L.: A cadmium complex based on 5-methylisophthalic acid and 1,6-bis(imidazol-1-yl)hexane: synthesis, crystal structure, and photoluminescence properties. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem. 43 (2013) 710–713.10.1080/15533174.2012.753630Search in Google Scholar
10. Li, S. H.; Han, M. L.; Liu, G. Z.; Ma, L. F.; Wang, L. Y.: Guestinduced single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformations of a new 4-connected 3D cadmium(II) metal-organic framework. RSC Adv. 5 (2015) 17588–17591.10.1039/C5RA00621JSearch in Google Scholar
11. Zhao, Y.; Li, S. H.: Synthesis and crystal structure of a new three-dimensional complex constructed from thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylic acid. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem. 45 (2015) 921–925.10.1080/15533174.2013.843565Search in Google Scholar
12. Li, S. H.; Wu, H. X.; Chai, N.: A cobalt(II) complex based on 5-methoxyisophthalic acid and 1,6-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)hexane: synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Chem. 43 (2013) 1487–1491.10.1080/15533174.2012.757750Search in Google Scholar
13. Si, C.-D.; Hu, D.-C.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yao, X.-Q.; Yang, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-C.: Seven coordination polymers derived from semirigid tetracarboxylic acids and N-donor ligands: topological structures, unusual magnetic properties, and photoluminescences. Cryst. Growth Des. 15 (2015) 2419–2432.10.1021/acs.cgd.5b00205Search in Google Scholar
©2019 Tao Sun et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3

