Abstract
C26H14Br2F4I2N4, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 8.7472(4) Å, b = 8.7822(4) Å, c = 9.4065(4) Å, α = 102.745(4)°, β = 105.489(4)°, γ = 91.949(4)°, V = 675.88(5) Å3, Z = 1, Rgt(F) = 0.0336, wRref(F2) = 0.0813, T = 290 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.27 × 0.26 × 0.21 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 5.33 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 29.4°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 10224, 3228, 0.033 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2689 |
| N(param)refined: | 172 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 0.87034(3) | 0.59413(3) | 0.32720(2) | 0.04508(11) |
| F1 | 0.8726(3) | 0.2679(2) | 0.0926(2) | 0.0528(5) |
| F2 | 0.9632(3) | 0.1984(2) | −0.1590(3) | 0.0557(6) |
| C1 | 0.9489(4) | 0.5374(4) | 0.1323(4) | 0.0369(8) |
| C2 | 0.9342(4) | 0.3849(4) | 0.0469(4) | 0.0387(8) |
| C3 | 0.9830(4) | 0.3487(4) | −0.0811(4) | 0.0386(8) |
| Br1 | 0.75346(8) | 1.12978(6) | 1.40853(6) | 0.0885(2) |
| N1 | 0.7613(4) | 0.6775(5) | 0.5885(4) | 0.0601(9) |
| N2 | 0.4511(4) | 0.7471(4) | 1.1471(4) | 0.0598(9) |
| C4 | 0.6924(5) | 0.5728(6) | 0.6395(5) | 0.0609(11) |
| H4 | 0.6755 | 0.4691 | 0.5838 | 0.073* |
| C5 | 0.6444(5) | 0.6076(5) | 0.7697(4) | 0.0508(10) |
| H5 | 0.5943 | 0.5293 | 0.7986 | 0.061* |
| C6 | 0.6709(4) | 0.7595(4) | 0.8573(4) | 0.0408(8) |
| C7 | 0.7470(5) | 0.8685(4) | 0.8069(4) | 0.0511(9) |
| H7 | 0.7688 | 0.9724 | 0.8622 | 0.061* |
| C8 | 0.7903(5) | 0.8227(5) | 0.6747(5) | 0.0608(11) |
| H8 | 0.8429 | 0.8978 | 0.6440 | 0.073* |
| C9 | 0.4979(4) | 0.7165(5) | 1.0205(5) | 0.0538(10) |
| H9 | 0.4443 | 0.6319 | 0.9421 | 0.065* |
| C10 | 0.6227(4) | 0.8041(4) | 0.9991(4) | 0.0400(8) |
| C11 | 0.6976(4) | 0.9304(4) | 1.1162(4) | 0.0443(9) |
| H11 | 0.7805 | 0.9936 | 1.1074 | 0.053* |
| C12 | 0.6492(5) | 0.9619(4) | 1.2451(4) | 0.0461(9) |
| C13 | 0.5277(5) | 0.8663(5) | 1.2573(5) | 0.0565(11) |
| H13 | 0.4987 | 0.8871 | 1.3474 | 0.068* |
Source of material
The 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine was purchased from Jinan Heng Hua Technology Co. Ltd. (Shandong, China), and 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene was purchased from J&K Scientific Ltd. (Beijing, China). Both were used without further purification. The 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine (2.35 mg, 0.01 mmol) and 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (4.02 mg, 0.01 mmol) were dissolved in approximately 10 mL of trichloromethane with gentle stirring at room temperature. The undissolved materials were removed by filtration. The filtrate was set aside for crystallization by slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature. After about two days, clear light colourless crystals of title compound were obtained.
Experimental details
Carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Comment
In recent years, both the experimental and theoretical studies of the halogen bond are very hot in the field of noncovalent bonds [5], [6], [7], [8], [9]. The molecule 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine has two electron-rich nitrogen atoms. Theoretically, it can form two halogen bonds with two different 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene molecules upon cocrystal formation. However, the introduction of the electron-withdrawing bromine atom in one pyridine ring maybe make the case a little bit more complex. Therefore, this work can contribute to the question how many halogen bonds one 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine molecule can form.
All bond lengths and angles in the title crystal structure are in the normal ranges [10]. The 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine molecules and 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene molecules are linked by the halogen bonds with d(I1⋯N1) = 2.827 Å and ∠(C1—I1⋯N1) = 178.59° (see the Figure 1). The N2 atom does not form the halogen bond with other iodine atoms. This is understandable because the electron-withdrawing bromine leads to the decrease of the electron density at N2. Besides the C1—I1⋯N1 halogen bonds, there are other noncovalent interactions such as the π⋯π stacking interactions, C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds which may contribute to the formation of the 3D structure. According to our quantum chemical calculations at the ωB97X-D/def2-TZVPP level of theory [11], the binding energy of the C1—I1⋯N1 halogen bond is 6.57 kcal/mol; the binding energy of the π⋯π stacking interaction between 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine and 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene is 9.07 kcal/mol; the binding energy of the C—H⋯F hydrogen bond is 1.46 kcal/mol; the binding energy of the C—H⋯N hydrogen bond is 2.55 kcal/mol. It must be pointed out that our previous study has shown that the ωB97X-D/def2-TZVPP calculations are reliable for the study of the molecular interactions considered in this study [12]. This study clearly shows that one 5-bromo-3,4-bipyridine molecule forms only one halogen bond with 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene in the crystal structure.
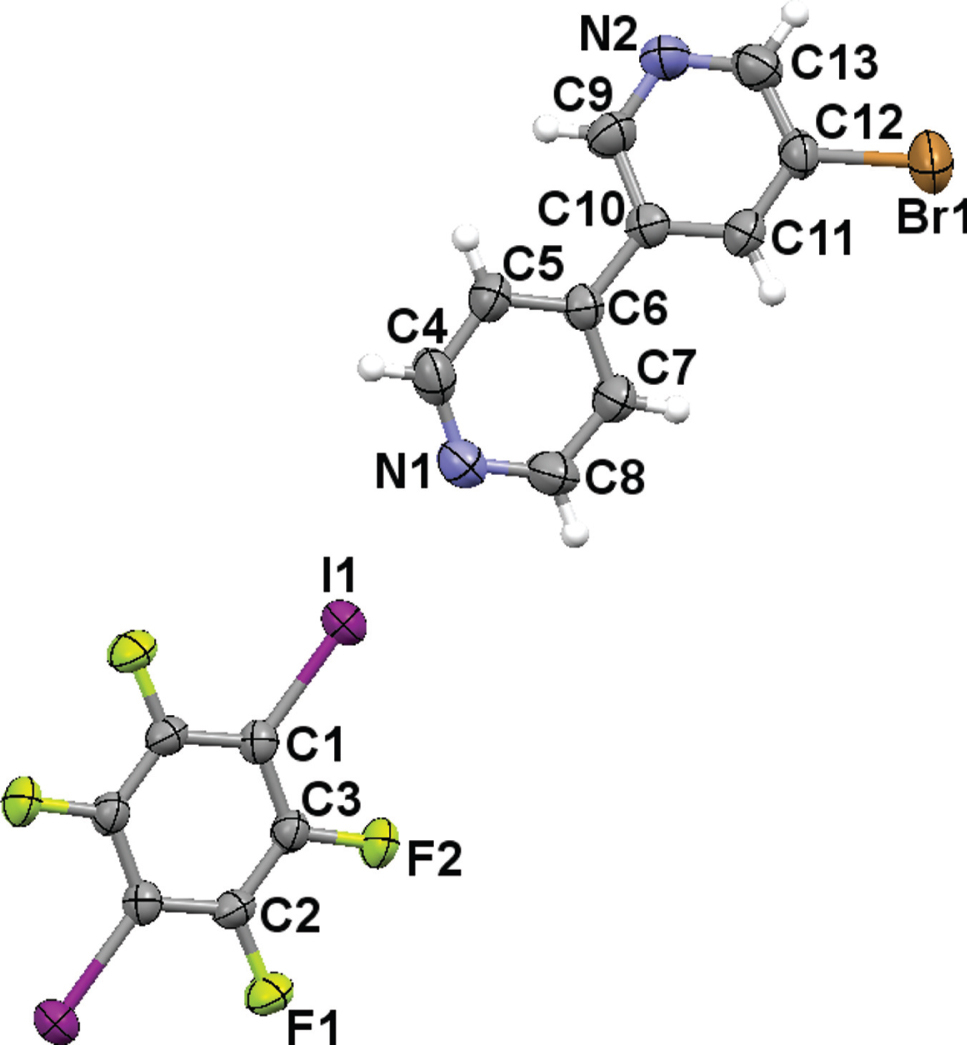
Molecular structure of the title complex with dispalcement ellipsoids draw at the 50% proability level.
Funding source: National Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21773104
Funding source: Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 13HASTIT015
Funding statement: This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21773104) and the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. 13HASTIT015). Computer time was provided by the National Supercomputing Center in Shenzhen.
References
1. Agilent Technologies: CrysAlisPRO Software system, version 1.171.38.41r. Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Oxford, UK (2015).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Search in Google Scholar
5. Gilday, L. C.; Robinson, S. W.; Barendt, T. A.; Langton, M. J.; Mullaney, B. R.; Beer, P. D.: Halogen bonding in supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Rev. 115 (2015) 7118–7195.10.1021/cr500674cSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Jin, W. J.: σ-Hole bond vs π-hole bond: a comparison based on halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 116 (2016) 5072–5104.10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00527Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G.: The halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 116 (2016) 2478–2601.10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00484Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Wang, W.; Wong, N.-B.; Zheng, W.; Tian, A.: Theoretical study on the blueshifting halogen bond. J. Phys. Chem. A 108 (2004) 1799–1805.10.1021/jp036769qSearch in Google Scholar
9. Wang, W.; Hobza, P.: Origin of the X-Hal (Hal = Cl, Br) bond-length change in the halogen-bonded complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 112 (2008) 4114–4119.10.1021/jp710992hSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Wang, J.-G.; Wang, W.: Crystal structure of halogen-bonded 2-chloro-1,10-phenanthroline — 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C30H14Cl2F4I2N4. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 232 (2017) 323–324.10.1515/ncrs-2016-0263Search in Google Scholar
11. Chai, J.-D.; Head-Gordon, M.: Long-range corrected hybrid density functionals with damped atom–atom dispersion corrections. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10 (2008) 6615–6620.10.1039/b810189bSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-B.: Unexpected strong stacking interactions between the homogeneous dimers of C6FxI(6-x) (x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5). Comput. Theor. Chem. 1023 (2013) 88–94.10.1016/j.comptc.2013.09.014Search in Google Scholar
©2019 Weizhou Wang, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3


