Abstract
C22H32N2O6S3, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 6.1543(1) Å, b = 14.4991(2) Å, c = 15.3859(3) Å, α = 64.545(2)°, β = 81.828(1)°, γ = 89.505(1)°, V = 1224.93(4) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0290, wRref(F2) = 0.0787, T = 100 K.
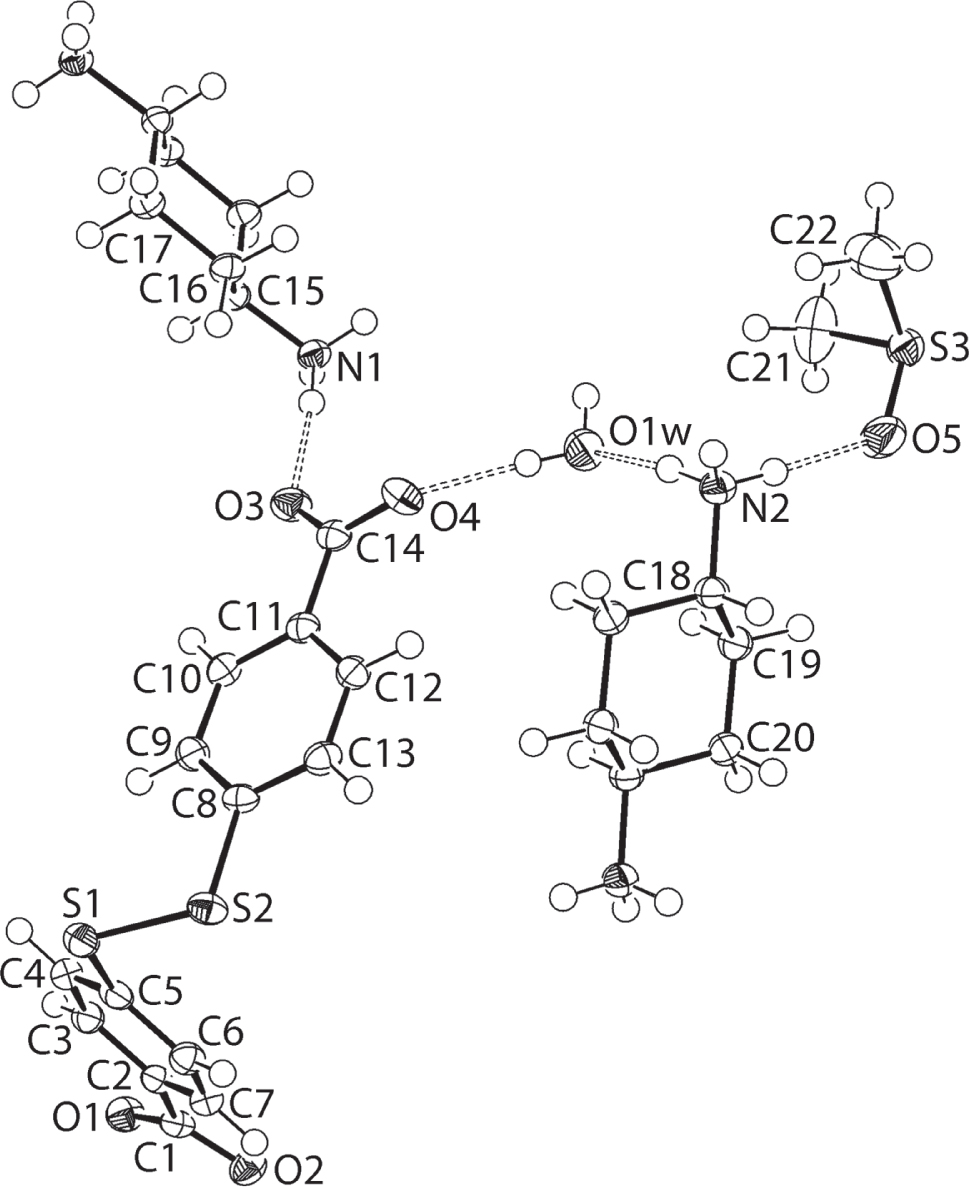
The molecular structures comprising the asymmetric unit are shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.09 × 0.07 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 3.12 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 76.4°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 30970, 5103, 0.037 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4683 |
| N(param)refined: | 324 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.90210(5) | 1.15089(2) | 0.04074(2) | 0.01692(9) |
| S2 | 1.03810(5) | 1.02360(2) | 0.13167(2) | 0.01706(9) |
| S3 | 0.63431(6) | 0.05256(3) | 0.66794(3) | 0.02236(9) |
| O1 | 0.07177(16) | 1.31298(8) | 0.26879(8) | 0.0207(2) |
| O2 | 0.27333(16) | 1.24570(8) | 0.38903(7) | 0.0199(2) |
| O3 | 0.30020(16) | 0.65920(8) | 0.16828(8) | 0.0205(2) |
| O4 | 0.56915(16) | 0.56263(7) | 0.23725(8) | 0.0202(2) |
| O5 | 0.7754(2) | 0.14306(10) | 0.65425(9) | 0.0382(3) |
| O1W | 0.55760(18) | 0.38313(9) | 0.40157(8) | 0.0250(2) |
| H1W | 0.557(4) | 0.4379(11) | 0.3506(11) | 0.037* |
| H2W | 0.480(3) | 0.3392(13) | 0.3952(16) | 0.037* |
| N1 | −0.00784(19) | 0.52137(9) | 0.17650(8) | 0.0154(2) |
| H1N | 0.013(3) | 0.4539(8) | 0.2122(11) | 0.018* |
| H2N | 0.103(2) | 0.5621(12) | 0.1772(12) | 0.018* |
| H3N | −0.1389(19) | 0.5387(13) | 0.1995(12) | 0.018* |
| N2 | 0.9334(2) | 0.31328(9) | 0.48360(9) | 0.0172(2) |
| H4N | 0.817(2) | 0.3347(13) | 0.4496(12) | 0.021* |
| H5N | 1.039(2) | 0.2941(13) | 0.4476(12) | 0.021* |
| H6N | 0.886(3) | 0.2574(10) | 0.5407(9) | 0.021* |
| C1 | 0.2349(2) | 1.26793(10) | 0.30319(10) | 0.0163(3) |
| C2 | 0.3999(2) | 1.23624(10) | 0.23985(10) | 0.0151(3) |
| C3 | 0.3533(2) | 1.24200(10) | 0.15154(10) | 0.0165(3) |
| H3 | 0.2165 | 1.2659 | 0.1313 | 0.020* |
| C4 | 0.5045(2) | 1.21327(10) | 0.09278(10) | 0.0168(3) |
| H4 | 0.4706 | 1.2167 | 0.0332 | 0.020* |
| C5 | 0.7062(2) | 1.17940(10) | 0.12212(10) | 0.0155(3) |
| C6 | 0.7552(2) | 1.17368(10) | 0.20995(10) | 0.0165(3) |
| H6 | 0.8928 | 1.1507 | 0.2298 | 0.020* |
| C7 | 0.6021(2) | 1.20170(10) | 0.26833(10) | 0.0164(3) |
| H7 | 0.6354 | 1.1973 | 0.3284 | 0.020* |
| C8 | 0.8590(2) | 0.91885(10) | 0.14953(10) | 0.0145(3) |
| C9 | 0.6600(2) | 0.92785(10) | 0.11397(10) | 0.0161(3) |
| H9 | 0.6080 | 0.9935 | 0.0787 | 0.019* |
| C10 | 0.5383(2) | 0.83991(10) | 0.13053(10) | 0.0155(3) |
| H10 | 0.4029 | 0.8460 | 0.1061 | 0.019* |
| C11 | 0.6120(2) | 0.74294(10) | 0.18245(9) | 0.0142(3) |
| C12 | 0.8092(2) | 0.73554(10) | 0.21943(10) | 0.0163(3) |
| H12 | 0.8594 | 0.6699 | 0.2562 | 0.020* |
| C13 | 0.9330(2) | 0.82253(11) | 0.20328(10) | 0.0168(3) |
| H13 | 1.0671 | 0.8165 | 0.2287 | 0.020* |
| C14 | 0.4829(2) | 0.64774(10) | 0.19709(9) | 0.0149(3) |
| C15 | −0.0182(2) | 0.53829(10) | 0.07443(9) | 0.0141(3) |
| H15 | −0.0573 | 0.6103 | 0.0364 | 0.017* |
| C16 | 0.2064(2) | 0.52265(10) | 0.02785(10) | 0.0152(3) |
| H16A | 0.2525 | 0.4534 | 0.0679 | 0.018* |
| H16B | 0.3167 | 0.5734 | 0.0253 | 0.018* |
| C17 | 0.1967(2) | 0.53471(10) | −0.07528(10) | 0.0156(3) |
| H17A | 0.1657 | 0.6061 | −0.1170 | 0.019* |
| H17B | 0.3409 | 0.5203 | −0.1031 | 0.019* |
| C18 | 1.0182(2) | 0.39790(10) | 0.50289(10) | 0.0150(3) |
| H18 | 1.1581 | 0.3780 | 0.5306 | 0.018* |
| C19 | 0.8508(2) | 0.41634(10) | 0.57622(10) | 0.0161(3) |
| H19A | 0.8265 | 0.3538 | 0.6386 | 0.019* |
| H19B | 0.7087 | 0.4321 | 0.5513 | 0.019* |
| C20 | 0.9343(2) | 0.50546(10) | 0.59297(10) | 0.0158(3) |
| H20A | 0.8224 | 0.5186 | 0.6387 | 0.019* |
| H20B | 1.0701 | 0.4873 | 0.6227 | 0.019* |
| C21 | 0.3953(3) | 0.10143(16) | 0.61431(14) | 0.0408(4) |
| H21A | 0.3139 | 0.1372 | 0.6489 | 0.061* |
| H21B | 0.3016 | 0.0448 | 0.6188 | 0.061* |
| H21C | 0.4390 | 0.1492 | 0.5457 | 0.061* |
| C22 | 0.7633(3) | 0.01471(15) | 0.57737(14) | 0.0395(4) |
| H22A | 0.7847 | 0.0741 | 0.5136 | 0.059* |
| H22B | 0.6695 | −0.0384 | 0.5753 | 0.059* |
| H22C | 0.9061 | −0.0122 | 0.5936 | 0.059* |
Source of material
The title salt mixed solvate was prepared through solvent drop grinding of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (Acros, Geel, Antwerp, Belgium) (0.154 g, 1 mmol) and N,N′-bis((pyridine-2-yl)methylene)-cyclohexane-1,4-diamine [5] (0.292 g, 1 mmol) in a 1:1 molar ratio. The mixture was ground for 15 min in the presence of a few drops of methanol which lead to a beige slurry. The slurry was taken up in dimethylsulphoxide (2 mL) and carefully layered with benzene (2 mL). Colourless crystals formed after a week. M.pt: 410.8–412.1 K. IR (Bruker Vertex 70v, cm−1): 3065–2854(w) ν(C—H), 1675(m) ν(C=O), 1589(s)–1432(s) ν(C=C), 1376(s) ν(C—N), 755(s) δ(C=C).
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). The O- and N-bound H atoms were located in difference Fourier maps but were refined with distance restraints of O—H = 0.84 ± 0.01 Å and N—H = 0.91 ± 0.01 Å, respectively, and with Uiso(H) set to 1.5Ueq(O) and 1.2Ueq(N), respectively.
Comment
The isolation and crystallographic characterization of the title salt mixed solvate came about during recent co-crystallization studies of isomeric n-mercaptobenzoic acid co-formers [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], for n = 2, 3 and 4, as well as of isomeric Schiff bases appended with pyridyl donors, i.e. N,N′-bis((pyridine-n-yl)methylene)cyclohexane-1,4-diamines [5], again for n = 2, 3 and 4 [8], [9], [10], [11]. When these co-formers are combined in co-crystallization trials, each undergoes chemical reaction. For example, 2-mercaptobenzoic acid undergoes oxidation to form the disulfide 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid (2,2′-dithiodibenzoic acid; 2-DTBA) or salts thereof [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]; the instability of this co-former is well documented [7], [12], [13]. Thus far, in the case when n = 4, the Schiff base has been observed to decompose/react when co-crystallized with 2-mercaptobenzoic acid, leading to a cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium di-cation [9], [11]. A more spectacular outcome was noted when the Schiff base with n = 2 was co-crystallized with 2-mercaptobenzoic acid whereby the original Schiff based was converted to a 2-(4-ammoniocyclohexyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)imidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-ylium di-cation [8]. In on-going investigations in this area, herein the title salt mixed solvate is described whereby the original 4-mercaptobenzoic acid is present as the di-anion of 4-DTBA, and the original Schiff base with n = 4 is present as a cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium di-cation. The salt co-crystallized as a hydrate, dimethylsulphoxide mixed solvate.
The molecular structures of the five-component crystal are shown in the figure (70% probability displacement ellipsoids with unlabelled atoms for the N1- and N2-di-cations being −x, 1 − y, −z and 2 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z, respectively). The product comprises two independent cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium di-cations, each located about a centre of inversion, a 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate di-anion, and a molecule each of dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO) and water. The di-cation/di-anion assignments are confirmed based on the pattern of hydrogen bonding in the crystal, as discussed in detail below, and in the closeness of the C1—O1, O2 [1.2478(17), 1.2750(17) Å] and C14—O3, O4 [1.2505(17), 1.2699(17) Å] bond lengths. Each of the centrosymmetric di-cations adopts a chair conformation so that the 1,4-ammonium groups have an anti-disposition. The di-anion is twisted as seen in the C5—S1—S2—C8 torsion angle of 85.47(7)°, and in the dihedral angle between the two phenyl rings of 78.39(7)°. To a first approximation, the carboxylate groups are co-planar with the phenyl rings which they are attached with the O1-carboxylate group exhibiting a greater twist out of the plane. This is quantified in the values of the O1—C1—C2—C7 [169.05(12)°] and O4—C14—C11—C10 [173.76(12)°] torsion angles.
Significant hydrogen bonding interactions contribute to the cohesion of the molecular packing. Each of the six ammonium and two water hydrogen atoms forms donor interactions to an oxygen acceptor (carboxylate-O, water-O and DMSO-O). The N1-ammonium cation forms charge-assisted hydrogen bonds to carboxylate-O atoms exclusively, forming a single link to three different carboxylate residues [N1—H1n⋯O1i: H1n⋯O1i = 1.900(14) Å, N1⋯O1i = 2.8053(18) Å with angle at H1n = 171.6(14)°; N1—H2n⋯O3: H2n⋯O3 = 1.814(17) Å, N1⋯O3 = 2.7173(17) Å with angle at H2n = 171.4(16)° and N1—H3n⋯O4ii: H3n⋯O4ii = 1.885(13) Å, N1⋯O4ii = 2.7876(16) Å with angle at H3n = 170.5(17)° for symmetry operations (i) x, −1 + y, z and (ii) −1 + x, y, z]. By contrast, the N2-ammonium cation forms charge-assisted hydrogen bonds to disparate oxygen atoms, namely water-O, carboxylate-O and DMSO-O atoms [N2—H4n⋯O1w: H4n⋯O1w = 1.860(14) Å, N2⋯O1w = 2.7673(17) Å with angle at H4n = 168.6(15)°; N2—H5n⋯O2iii: H5n⋯O2iii = 1.882(16) Å, N2⋯O2iii 2.7890(17) Å with angle at H5n = 172.2(15)° and N2—H6n⋯O5: H6n⋯O5 = 1.859(14) Å, N2⋯O5 = 2.7705(18) Å with angle at H6n = 176.8(18)° for (iii) 1 + x, −1 + y, z]. Finally, the water-O—H forms donor interactions to carboxylate-O atoms [O1w—H1w⋯O4: H1w⋯O4 = 1.890(16) Å, O1w⋯O4 = 2.7325(16) Å with angle at H1w = 177.2(18)° and O1w—H2w⋯O2i: H2w⋯O2i = 1.91(2) Å, O1w⋯O2i = 2.7487(17) Å with angle at H2w = 172.5(19)°]. Globally, the di-anions and water molecules establish a three-dimensional framework with the DMSO molecules lying in channels parallel to the a axis direction.
The Hirshfeld surfaces, as well as the two-dimensional fingerprint plot (full and delineated), were also calculated using literature procedures [14] and Crystal Explorer 17 [15]. Such an analysis has proved useful in distinguishing multiple molecules in a crystallographic asymmetric unit [16]. Overall, for the asymmetric unit illustrated in the figure, there are five types of contacts making a significant contribution (>1%) to the Hirshfeld surface: H⋯H [45.8%], O⋯H/H⋯O [27.4%], C⋯H/H⋯C [14.3%], S⋯H/H⋯S [6.0%] and S⋯C/C⋯S [4.4%]. To a first approximation, these values mirror those in the analogous 2-DTBA structure with DMF [9] rather than DMSO, i.e. H⋯H [45.7%], O⋯H/H⋯O [30.1%], C⋯H/H⋯C [16.0%], S⋯H/H⋯S [5.8%] and S⋯C/C⋯S [0.5%]. The only differences are seen in the O⋯H/H⋯O, C⋯H/H⋯C and S⋯C/C⋯S contacts, i.e. variations of up to a few percent. The analysis of the contacts formed by the two independent di-cations in the title salt prove instructive. For the N1-di-cation, four different types of contacts are evident, namely H⋯H [51.8%], O⋯H/H⋯O [30.9%], C⋯H/H⋯C [14.3%] and S⋯H/H⋯S [2.9%]. Quite different percentage contributions are seen for the N2-di-cation: H⋯H [59.3%], O⋯H/H⋯O [36.4%] and C⋯H/H⋯C [4.2%], i.e. with significant increases in the H⋯H and O⋯H/H⋯O contacts at the expense of the C⋯H/H⋯C and S⋯H/H⋯S contacts. It is argued that these differences are systematic and correlate with the nature of the N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding patterns. Thus, a tighter network of hydrogen bonds are apparent for the N1-di-cation which forms three charge-assisted ammonium-N—H⋯O(carboxylate) interactions. By contrast, the N2-dication forms charge-assisted hydrogen bonds to disparate oxygen atoms, namely to carboxylate-O, water-O and DMSO-O acceptors. With a less-tight, more diffuse, hydrogen bonding arrangement, the percentage of O⋯H/H⋯O surface contacts increases at the expenses of weaker interactions. A similar analysis of the individual di-cations in the DMF analogue [9] was also conducted. Here, for the N1-di-cation which forms two charge-assisted ammonium-N—H⋯O(carboxylate) interactions as well as a charge-assisted hydrogen bond to the O(DMF), the percentage contributions compute to H⋯H [56.5%], O⋯H/H⋯O [33.2%], C⋯H/H⋯C [9.6%] and S⋯H/H⋯S [0.8%]. For the N2-di-cation, systematic variations are again apparent with the percentage contributions being H⋯H [52.3%], O⋯H/H⋯O [43.4%], C⋯H/H⋯C [2.4%] and S⋯H/H⋯S [1.6%]. As well as forming two charge-assisted ammonium-N—H⋯O(carboxylate) interactions, this cation forms a charge-assisted hydrogen bond to a water molecule, which also forms donor interactions to carboxylate-O and DMF-O atoms, leading to a more open arrangement and hence, greater percentage contribution by O⋯H/H⋯O surface contacts. Finally, it is noteworthy that there is a systematic variation in the percentage contributions afforded by the H⋯H and O⋯H/H⋯O surface contacts in that values in the DMF-containing structure, lie between the extremes of the DMSO-containing structure.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant No. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001–2019.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, UK (2018).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Lai, C. S.; Mohr, F.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: The importance of C—H⋯N, C—H⋯π and π⋯π interactions in the crystal packing of the isomeric N1,N4-bis((pyridine-n-yl)methylene)cyclohexane-1,4-diamines, n = 2, 3 and 4. CrystEngComm 8 (2006) 909–915.10.1039/B613603FSearch in Google Scholar
6. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: A 1:1:1 co-crystal solvate comprising 2,2′-dithiodibenzoic acid, 2-chlorobenzoic acid and N,N-dimethylformamide: crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and computational study. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 475–481.10.1107/S205698901900375XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: A 1:2 co-crystal of 2,2′-thiodibenzoic acid and triphenylphosphane oxide: crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and computational study. Acta Crystallogr. E74 (2018) 1764–1771.10.1107/S205698901801544XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of 2-(4-ammoniocyclohexyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)imidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-ium 2-[(2-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dihydrate, [C18H22N4][C14H8O4S2]⋅2H2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 797–799.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0120Search in Google Scholar
9. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium 2-[(2-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate — dimethylformamide — monohydrate (1/1/1), [C6H16N2][C14H8O4S2]⋅C3H7NO⋅H2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 903–905.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0131Search in Google Scholar
10. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of the co-crystal 4-[(4-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid –(1E,4E)-1-N,4-N-bis(pyridin-4-ylmethylidene) cyclohexane-1,4-diamine (1/1), C14H10O4S2⋅C18H20N4 Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 1121–1123.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0488Search in Google Scholar
11. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of hemikis(cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) (pyridine-2-carboxylate), [C6H16N2]0.5[C6H4NO2]. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 749–751.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0091Search in Google Scholar
12. Broker, G. A.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Co-crystal formation between 2,2′-dithiodibenzoic acid and each of 4,4′-bipyridine, trans-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene and 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane. CrystEngComm 9 (2007) 1096–1109.10.1039/b707690hSearch in Google Scholar
13. Rowland, C. E.; Cantos, P. M.; Toby, B. H.; Frisch, M.; Deschamps, J. R.; Cahill, C. L.: Controlling disulfide bond formation and crystal growth from 2-mercaptobenzoic acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 11 (2011) 1370–1374.10.1021/cg101619ySearch in Google Scholar
14. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Turner, M. J.; Mckinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Search in Google Scholar
16. Jotani, M. M.; Wardell, J. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Supramolecular association in the triclinic (Z′ = 1) and monoclinic (Z′ = 4) polymorphs of 4-(4-acetylphenyl)piperazin-1-ium 2-amino-4-nitrobenzoate. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 234 (2019) 43–57.10.1515/zkri-2018-2101Search in Google Scholar
©2019 Sang Loon Tan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of [aqua[2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-5-carboxy)-κ4N3,N3′,O4,O4′] zinc(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N4O9Zn⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-methylcarbamoyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C15H17N3O4
- 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-phenyl-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbothioamide–dimethylformamide (2/1), C27H23F2N3S, 0.5(C3H7NO)
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(hydrazonomethylene)diphenol dihydrate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxyphenyl-3-phenylpropiolate, C16H12O3
- Crystal Structure of tris(tetrakis{1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN}copper(II)) bis[tri-μ2-bromido-tetrabromido-bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazole-κN)tetracopper(I)], C80H96N32Cu11Br14
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(diethylamino)-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazide, C37H36N6O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-3-methyl-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,5-diphenylpiperidine, C24H23FN2O4S
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,12-dibenzyl-6,10-diphenyl-3,12-diazapentacyclo [6.3.1.02.7.04.11.05.9]-dodecane-7,11-dicarboxylate — acetone (2/1), C40H38N2O2 ⋅ 0.5C3H6O
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ4O:O′:N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C9H8AgO3N3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylate-κ4O1,O2:O3,O4)(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C27H23N3O5Cd
- The synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-methylbenzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-(N,N′-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)iridium(III), C33H30N3S4Ir
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide, C12H6N4Cl2F6O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ4O,O′:O′,O′′)-nitrato-κO-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)glycinate, C14H17NO3
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 5-bromo-3,4′-bipyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C26H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tetrakis(μ2-3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(3-(phenylsulfonamido)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C84H84Gd2N12O24S6
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ2O:O′)bis(μ2-pyrazin-κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C14H16Ag2N5O8S2
- The crystal structure of 1,6-di-tert-butyl-1,1,3,3,4,4,6,6-octamethyl-2,2,5,5-tetrakis (trimethylsilyl)hexasilane, C28H78Si10
- Crystal structure of discandium triruthenium tetrasilicide, Sc2Ru3Si4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-4-amino-1,5-naphthalenedisulfonato-κ4O,N:O′, N′)bis(μ2-hexamethylenetetramino-κ2N;N′)silver(I)], {C22H30Ag2N9O6S2}n
- Crystal structure of diaqua[5,5′-dicarboxy-2,2′-(propane-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)]zinc(II) dihydrate, C13H18N4O12Zn
- The crystal structure of poly [(μ3-N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide-κ3-O:N:N′)-(p-toluenesulfonato-κ2O,O′)silver(I)], C25H27Ag1N4O5S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(3-bromophenoxy) ethane, C14H12Br2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-3-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ1O) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Cl2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of 1,5-dinitro-2,3,4-trichlorobenzene, C6H1Cl3N2O4
- The crystal structure of the solid solution of 3,5-dinitropyrazole and 4-chlorine-3,5-dinitropyrazole, C3H1.24Cl0.76N4O4
- The cocrystal structure of 4-nitropyrazole — acetic acid (1/1), C5H7N3O4
- The crystal structure of propan-2-one O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) oxime, C9H8N4O7
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)benzo[d] thiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)acetate, C15H17NO4S
- Crystal structure of (acetic acid-κ1O)-bis(μ2-2-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(2-chlorobenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-hydroxy-κ2O:O)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dimanganese(II) — methanol (1/1), C48H37Cl3Mn2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C15H12N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-acetyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)benzen-1-ido-κ2C,N)-pyridine-κN-palladium(II), C19H17ClN2OPd
- Crystal structure of (4-methyl-benzoato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C24H45ClN4NiO7
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl(potassium, rubidium) — ammonia (1/2), [K0.3Rb0.7(18-crown-6)]Cp*⋅2 NH3, C22H45K0.3N2O6Rb0.7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C51H38Cl2F2N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,6-dihydropyren-1-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide — methanol (1/1), C24H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonato-κ3N,O:O′)-(μ4-hexamethylenetetramino-κ4N:N′:N′′:N′′′)disilver(I)] monohydrate, C12H21Ag2N5O8S2
- Crystal structure of bis(acridin-10-ium) 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate — 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (1/1), C21H15NO6
- The crystal structure of 1,12-diazaperylene, C18H10N2
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C17H14N2OFCl
- Crystal structure of (4aR,6aR,6bR,10S,12aR)-10-acetoxy-1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a, 12b,13,14b-icosahydro-2,2,4a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethylpicene-6a-carboxylic acid, C32H50O4
- The crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis{1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl}-(μ2-pyrimidine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(IV) — dichloromethane (1/2), C60H80Cl8N6Pd2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-yl 4-nitrobenzoate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-N-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)pyridin-2-amine, C11H12N4
- The crystal structure of 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid dihydrate, C8H8Cl2O6
- The crystal structure of 2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine — dimethylformamide (1/1), C33H28N10O
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonamide, C22H28N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-4-(3,5-dicarboxy-κ1O-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C16H12CdO11
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzoato-κ2N:O)manganese(II)], C22H22MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of 9-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione, C25H23NO3
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2,4,6-tris[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1,3,5-triazine-k3N:N′:N′′)-(nitrato-k2O,O)-(nitrato-k1O)zinc(II)] - N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/2), C38H39N13O8Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ7-4-(3,5-dicarboxylatophenoxy)phthalato)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dizinc(II)], C28H14N2O9Zn2
- The crystal structure of methyl 2-(benzylamino)-5-(benzyloxy)benzoate, C22H21NO3
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)palladium(II) tetracyanoplatinate(II), C14H24N8PdPt
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]palladium(II), C17H12N2O2Pd
- Crystal structure of (cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) 4-[(4-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dimethylsulphoxide hydrate (1/1/1/1), [C6H16N2]2+[C14H8O4S2]2−⋅C2H6OS⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of the 2:1 co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2(C14H10O4S2)⋅C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-dimethyl-(phenylpiperazine-1-carbodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C13H19ClN2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of (N-n-butyl, N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2 S,S′)-chlorido-dimethyl-tin(IV), C8H18ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-bromobenzyl)dibromidotin(IV), C24H20Br4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridyl)bis(4-chlorobenzyl)dichloridotin(IV), C24H20Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of N-methyl-N-phenyl(methylsulfanyl)carbothioamide, C9H11NS2
- Crystal structure of 4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium (4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)carbothioylsulfanide, [C10H15N2][C11H13N2S2]
- Crystal structure of catena-{di-aqua-sodium [n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanide}n, [C6H16NNaO2S2]n
- Crystal structure of (2-([1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxyethyl]iminomethyl)-5-(n-decyl)phenolato)-dimethyl-tin(IV), C23H39NO5Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide – a Z′ = 3 structure, C16H15ClN2O3

