Abstract
In the deep rock excavation process, the rock will produce deformation and damage under multiple dynamic disturbances, while there is also unrecoverable time-dependent deformation. In order to research this deformation characteristic, a sine wave disturbance triaxial loading test was carried out on red sandstone to simulate the failure process of deep underground rock mass under dynamic disturbance loads with low confining pressure. Based on the results that the deformation of the rock increases suddenly during dynamic disturbances and varies with the number of disturbances, a novel disturbance damage model relating the number of disturbances to the deformation of the disturbances is created to describe the deformation and damage accumulation of the rock under multiple disturbances and an operator is developed to ensure that the model works. In order to describe the time-dependent deformation of rocks, the elasticity model in the traditional Bingham model was improved to a nonlinear elasticity model that varies with time, and its viscous and plasticity models were retained. The time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model is obtained by combining the improved Bingham model with the disturbance damage model. The model parameters were identified according to the test data, and the finite-element calculation of the model was realized with the secondary development program. The results show the strain of rock increases suddenly under multiple disturbances, and the main reason for rock damage is the action of dynamic disturbances. The fitted curves and finite-element results are consistent with the experimental results. The time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model of rock not only reflects the decaying rheological and steady-state rheological properties of rock under static loading but describes the characteristics of strain surge and disturbance damage accumulation caused by dynamic disturbances. This article contributes to the characteristics of the deformation of deep rock mass.
1 Introduction
With the over-consumption of shallow resources of the earth, deep mining has gradually become normal. In deep underground engineering, the surrounding rock is subjected not only to high ground stress but also to dynamic disturbance loads, such as blasting vibration during excavation [1]. The essence of deep excavation is the process of unloading and the dynamic disturbance of rock mass in a high-stress state. The stability and failure of deep rock mass engineering present a typical deformation and damage problem that concerns the surrounding rock under dynamic and static combined loading.
Many researchers have carried out research into combined static and dynamic loading on rock samples. In terms of experimental research, Wang et al. [2] carried out a multi-cycle impact disturbance test and revealed the failure law of creep rock under impact disturbance from the perspective of energy. Liu et al. [3] conducted an impact compression test on sandstone using a split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) experimental device to study the influence of an axial static load on the dynamic characteristics of sandstone. Chen et al. [4] carried out a series of laboratory tests to study the fracture fractal characteristics and energy dissipation law of different dynamic disturbance–damaged rock masses using an SHPB system. Tang et al. [5] carried out a loading test of rock under the combined action of a one-dimensional static load and cyclic impact. The research showed that the pre-axial compression would affect the rock failure fragmentation and the probability of “rock burst” under dynamic disturbance. The aforementioned studies focused on the uniaxial disturbance impact test of rock, while the redistribution of in situ stress caused by excavation was not considered. When the deeply buried underground surrounding rock is damaged, it is in a low-confining pressure environment. Although triaxial disturbance loading tests on rocks have been conducted, such as those by Wang et al. [6,7], the confining pressure is determined on the condition that no damage occurs during static loading in these studies, so the confining pressure is generally set to be larger than normal. The disturbance load is usually applied in the form of a drop hammer impact, and the amplitude of the disturbance load is also large. This is different from the failure form of a deep rock mass caused by micro disturbances under low confining pressure.
In addition, the instability or failure of a project is controlled by the rheology of the material. One of the main subjects of rock rheological research is the establishment and application of rheological models. At present, research on the rheological constitutive model of rock under static load conditions is relatively mature [8–11]. The damage theory has been used to propose the rheological constitutive model to describe the rheology of rock [12–15]. At the same time, many nonlinear static constitutive models have been established to describe the deformation characteristics of rock [16–21]. However, the static constitutive model is not suitable for studying the dynamic characteristics of deep rock because of the high in situ stress and dynamic disturbance caused by blasting and excavation. At present, rock rheological models and rock dynamics are usually studied independently. There are few studies on the rock rheological constitutive model under dynamic disturbance [22,23,24]. Therefore, it is of great significance to establish a constitutive model that reflects the time-dependent deformation characteristics of deep rock mass under a disturbed load.
Based on this, the TFD-2000/D dynamic disturbance servo triaxial test system was used in the present study to apply an axial sine wave disturbance load to a rock sample under three-dimensional force to simulate the failure process of deep rock mass under the action of a disturbance load under low confining pressure after excavation. By analyzing the rheological properties of rock under dynamic disturbance, a damage constitutive model considering the time-dependent deformation characteristics of rock under dynamic disturbance was established, and the finite-element calculation of the model was realized. The research results provide a reference for revealing the deformation and failure of rock mass caused by dynamic disturbances resulting from deep engineering activities.
2 Rock disturbance loading test and analysis of results
2.1 Test equipment
The test equipment included the self-developed TFD-2000/D dynamic disturbance servo three-axis loading device. The test system is divided into four main parts: axial loading system, confining pressure loading system, disturbance application control system, and data acquisition control system. The axial loading system can apply a maximum test force of 2,000 kN, and the loading speed range is 0.01–20 kN/s to ensure the stable application of axial loading in the test. The confining pressure loading system can apply a maximum confining pressure of 100 MPa, and the loading speed is 0.001–1 MPa/s. The disturbance control system consists of a number of devices, including a disturbance cylinder, a displacement sensor, a disturbance rod, and more. The disturbance force applied to the sample in the test was achieved by the disturbance cylinder placed on the upper part of the three-axis testing machine. The maximum disturbance force that can be applied by the disturbance system is 300 kN, the highest disturbance frequency is 70 Hz, and the waveform types of the disturbance force include sine wave, triangle wave, and square wave.
2.2 Sample preparation and test scheme
The rock samples used in the experiment were taken from a block of red sandstone in a mine in Yunnan. It was processed by a rock coring machine for coring, cutting, and grinding processes to make a sample with a diameter of 50 mm and a height of 100 mm, as shown in Figure 1. A rock sample with a smooth surface and no cracks or missing corners was selected, and the size of the prepared sample was measured and weighed. The prepared samples were screened by acoustic detection to ensure that the wave velocities of all samples were close to each other.

Red sandstone specimen.
In the test, after the excavation and unloading of a high-stress roadway, the stress state of the rock changes from a triaxial state to a unilateral unloading state. To better simulate the process of rock failure caused by a disturbance near the tunnel wall, the value of the confining pressure in the test was set to three levels: 0, 5, and 10 MPa.
Because the mechanical characteristics of the rock change under different confining pressures, the applied axial pressure in the test was set to 85% of the peak compressive strength of the rock. Therefore, the basic mechanical parameters of red sandstone under different confining pressures had to be measured through basic tests before the test. The basic mechanical parameters and strength characteristics of red sandstone are shown in Tables 1 and 2. In the experiment, the waveform of the disturbance wave was set as a sine wave. Based on previous studies, the disturbance frequency range generated by underground excavation and vibration is 2–15 Hz [25,26], so the frequency of the dynamic disturbance sine wave group was set to 3 Hz [27]. The amplitude was set to 10 MPa [28], which is represented by “3 Hz, 10 MPa.”
Physical and mechanical parameters of red sandstone
| Initial elastic modulus (E 0) (GPa) | Poisson’ s ratio (μ) | Cohesion force (C) (MPa) | Internal friction angle (φ) (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.31 | 0.154 | 12.27 | 47 |
Strength characteristics of red sandstone under different confining pressures
| Confining pressure (MPa) | Peak compressive strength (MPa) | Yield strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 62.01 | 46.23 |
| 5 | 98.19 | 69.84 |
| 10 | 120.82 | 92.8 |
In the test, confining pressure and axial compression were first applied to the rock sample to the target stress level. When the deformation of the sample stabilized, the dynamic disturbance was applied. As the disturbance effect on the surrounding rock was continuous during the excavation process, it was necessary to apply the disturbance at multiple intervals. According to the loading results of the sample, the strain tended to be stable within 20 min after the start of static loading. Therefore, 20 min was selected as the time period for the disturbance loading test. After 20 min of static loading in each test, the disturbance load was applied to the sample, and the disturbance loading system was used to set the size, frequency, and waveform of the disturbance load. The disturbance loading time was set as 30 s. After the disturbance was applied, the static loading was repeated for 20 min, after which the next disturbance was applied. The above process was repeated until the rock sample failed. Figure 2 shows the loading mechanical model and loading path of the test.
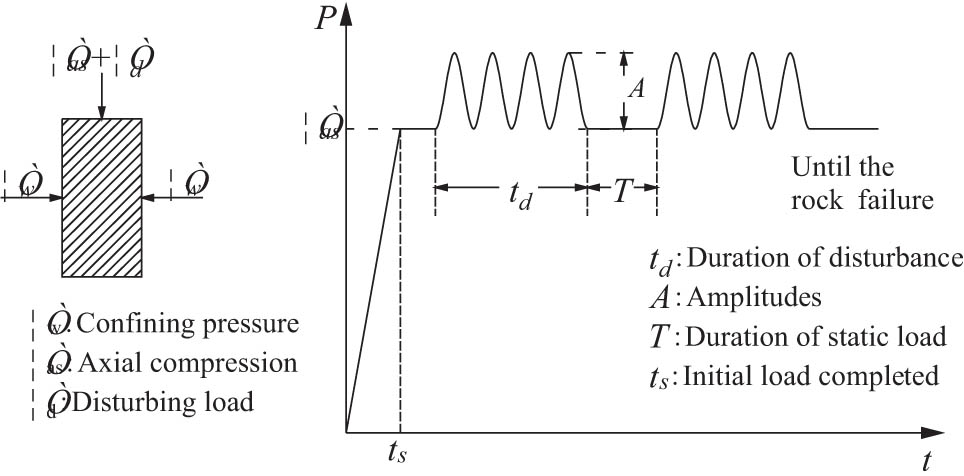
Schematic diagrams of test loading path and loading model.
2.3 Analysis of test results
The test results for axial strain under a disturbance load of “3 Hz, 10 MPa” and without disturbance are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen from Figure 3 that, under undisturbed action, the axial strain curve of the rock sample is basically parallel to the time axis shortly after loading, and the growth of axial strain slows down. However, under the action of disturbance, the strain of the sample undergoes a sudden change. With a continuous increase in the number of disturbances, the strain curve rises step by step, and the strain curve between two adjacent disturbances is similar to the strain curve under undisturbed action. Observing the dynamic disturbance action range (i.e., the local enlarged figure in Figure 3), it can be seen that a strain increment (Δε) will eventually form after the disturbance, and the axial strain of the sample will oscillate and rise with the disturbance load. As the amplitude of strain oscillation is obviously larger than that of the final strain increment, failure of the sample basically occurs in the loading process of dynamic disturbance. As shown in Figure 3, the sample is destroyed after eight disturbances, and the corresponding axial strain at failure is 14.66 × 10−3. The strain is composed mainly of two parts: creep caused by static load and strain increment caused by dynamic disturbance. From the beginning of the test to the first disturbance, the corresponding actual static load time was 0.55 h. The axial strain of rock rises rapidly from 0 to 11.20 × 10−3 under the action of confining pressure and axial pressure and enters the stable creep stage. The strain value reached 76.4% of the total axial strain. After the rock sample enters the stable creep stage, the deformation of the rock is caused mainly by the disturbance load. The strain increments caused by the eight disturbances are 1.26 × 10−3, 0.46 × 10−3, 0.40 × 10−3, 0.35 × 10−3, 0.38 × 10−3, 0.22 × 10−3, 0.18 × 10−3, and 0.11 × 10−3, respectively. The total strain increment caused by the disturbance is 3.36 × 10−3, which is 22.9% of the total axial strain. In addition, it can be seen that the static creep caused by confining pressure and axial pressure is only 0.1 × 10−3, accounting for 0.7% of the total axial strain from the first disturbance to rock failure. It can thus be concluded that the dynamic disturbance aggravates the damage of rock internal fiber particles and has a great impact on the rock failure characteristics.

Axial strain curve of rock with disturbance and without disturbance.
3 Time-dependent deformation and damage model considering disturbance effect
According to the above test results, the rock strain curve under dynamic disturbance rises step by step. To establish the time-dependent constitutive model under dynamic disturbance, the two methods should be combined: the constitutive equation describing the time-dependent characteristics of rock under a static load should be established, and the strain increment caused by disturbance should then be considered. The Bingham creep model can be used to describe the time-dependent characteristics of rock under static load, but the traditional Bingham model cannot describe the attenuation creep stage or the acceleration creep stage of rock, so it must be improved. The strain increment caused by dynamic disturbance can be described by establishing a damage component that considers disturbance. Finally, by combining the damage component with the improved Bingham model, a time-dependent deformation and damage model for disturbance can be obtained.
3.1 Improved Bingham viscoelastic plastic creep model
3.1.1 Improved one-dimensional Bingham viscoelastic plastic creep model
In the traditional one-dimensional Bingham model (Figure 4), a viscous component and a plastic component in parallel are connected in series with an elastic component. This model can describe the steady-state creep process of rock well, but it cannot describe the attenuation creep stage or the acceleration creep stage of rock. Considering that the material response is dominated by elasticity in the initial loading stage, it exhibits an accelerated creep phenomenon after loading is completed. Therefore, a nonlinear function is introduced to describe the decay creep stage after initial loading, which can be written as
where a denotes the coefficient and t s is the initial load completion time.
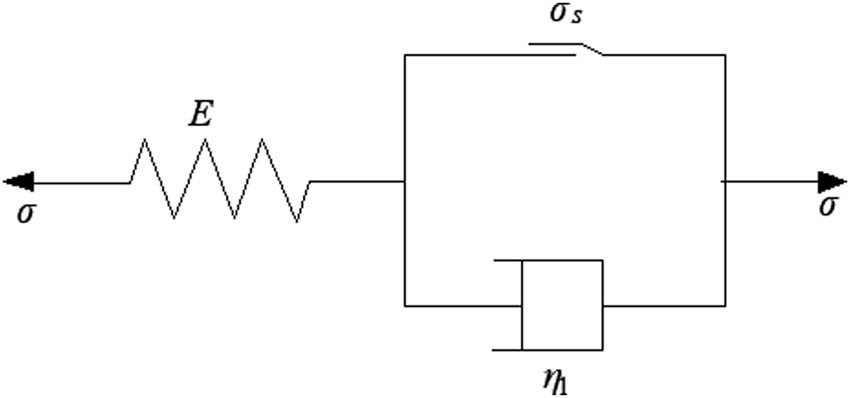
Bingham creep model.
It is assumed that the elastic coefficient attenuation law of the elastic component in the Bingham model satisfies
where E 0 denotes the initial elastic modulus of the nonlinear elastomer.
Therefore, the shear modulus and bulk modulus have the following relationship:
where G 0 denotes the initial shear modulus of the nonlinear elastomer and K 0 denotes the initial bulk modulus of the nonlinear elastomer.
By improving the elastic component of the Bingham model according to formula (2), an improved one-dimensional Bingham creep model was obtained. Based on component combination theory, there is
where η 1 denotes the viscosity coefficient.
The constitutive equation of the improved Bingham model under a three-dimensional stress state is
where K 0 and G 0 denote the bulk modulus and shear modulus of the elastic component, σ m δ ij denotes the spherical stress tensor, F denotes the yield function of rock, and F 0 denotes the initial value of the rock yield function.
The yield function adopts the Drucker–Prager plastic flow rule considering hydrostatic pressure:
where J 2 denotes the second invariant of the stress deviator, I 1 is the first invariant of the stress tensor, α and k are the material constants of the D–P plastic flow rule, and c and φ are the cohesion and internal friction angle, respectively.
3.2 Strain increment caused by the disturbance effect
Figure 5 shows the establishment of a disturbance damage component. The component works only in the disturbance action time, and its strain is the strain increment caused by disturbance.

Disturbance damage component.
Each time the dynamic disturbance acts, corresponding damage occurs inside the rock. The damage constitutive equation can be described as
where E 1 denotes the elastic modulus of the disturbed damage component.
As long as the strain caused by disturbance is determined, the variable for the law of damage evolution can be obtained according to the following expression:
where ε 0 is the axial strain at the beginning of the first disturbance loading at time D = 0. ε d is the axial strain after the last disturbance loading at time D = 1.
Because each disturbance causes a strain increment, Δε(k) is defined as the strain increment caused by the kth disturbance. From the experimental results, Δε(k) decays exponentially with an increase in the disturbance repetition numbers. Therefore, an attenuation function related to the number of disturbances is introduced as follows:
where k denotes the disturbance repetition numbers and b denotes the fitting coefficient.
Then,
The three-dimensional constitutive relationship is
where G 1 denotes the shear modulus of the disturbed damage component.
3.3 Construction of the time-dependent deformation and damage model considering disturbance effects
The time-dependent deformation and damage model under disturbance can be obtained by connecting the disturbed damage component in series with the improved Bingham creep model, as shown in Figure 6. According to the element combination theory, formulas (5) and (13) are combined, and an operator K(σ d) is introduced to ensure that the disturbance damage element works only during disturbance action, which satisfies the following formula:
where σ d denotes the disturbing load.

The time-dependent deformation and damage model considering disturbance.
Thus, the constitutive equation of the model under a three-dimensional stress state is obtained as follows:
According to the results of the triaxial compression test under the same confining pressure in the laboratory (σ 2 = σ 3), it can be concluded that
By substituting formula (16) into formula (15) and making the initial yield function F 0 = 1, the axial deformation equation of the time-dependent deformation and damage model considering the disturbance effect can be obtained as follows:
4 Parameter identification and application of the constitutive model
4.1 Parameter identification of model
Formula (17) has six undetermined parameters: the bulk modulus K 0, the shear modulus G 0, the viscosity coefficient η 1, the fitting coefficient a in F(t), the shear modulus G 1, and the fitting coefficient b in the disturbance damage component. In the test, the samples were composed of the same red sandstone, and its bulk modulus K 0 and shear modulus G 0 can be calculated based on the elastic modulus of the rock using the following formula:
Fitting coefficients a and b, viscosity coefficient η 1, and shear modulus G 1 were determined by mathematical optimization software 1stOpt through three sets of experimental data under different confining pressure conditions. Table 3 shows the specific parameters of the model, and Figure 7 shows the fitting results of the axial strain under three different confining pressure conditions.
Axial deformation parameters of the time-dependent deformation and damage model considering the disturbance effect
| Confining pressure (MPa) | Axial pressure (MPa) | Disturbance amplitude (MPa) | Disturbance frequency (Hz) | Improved Bingham model | Disturbance damage component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K 0 (GPa) | G 0 (GPa) | η 1 (GPa h) | a | G 1 (GPa) | b | ||||
| 0 | 52.71 | 10 | 3 | 4.00 | 3.60 | 150 | 35.77 | 10.8 | 1.1 |
| 5 | 83.6 | 10 | 3 | ||||||
| 10 | 102.70 | 10 | 3 | ||||||

Fitting curves and test curves under three confining pressures.
It can be seen from Figure 7 that the calculated strain increment caused by the first disturbance under zero confining pressure is slightly different from the test curve. The other fitting curves are in good agreement with the experimental results. Compared with the traditional Bingham model, the improved model better simulates the attenuation creep stage and the steady creep stage of the rock. When a disturbance load is applied, the disturbance damage component starts to work, causing a sudden increase in strain. The improved model can clearly describe the process by which the strain curve of rock rises in steps after being disturbed.
To further verify the applicability of the model and the parameters, the confining pressure was set to 5 MPa, and the axial pressure was set to 90% (88.37 MPa) of the peak compressive strength. The theoretical curve was calculated using formula (17) and the parameters in Table 3. The calculated theoretical curve and test curve are shown in Figure 8. It can be seen that the goodness of fit of the theoretical curve is good, which proves that the established time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model considering the disturbance effect can correctly describe the deformation characteristics of rock mass under dynamic disturbance.

Comparison of fitting curves and test curve.
4.2 Finite-element calculation of the constitutive model
In addition to fitting the test data, the ultimate goal of the constitutive model was to realize finite-element calculation. Using the secondary development function of the constitutive model provided by LS-DYNA software, the established damage constitutive model code was written and embedded in the LS-DYNA solver. The development and use of the constitutive model solver are shown in Figures 9 and 10.
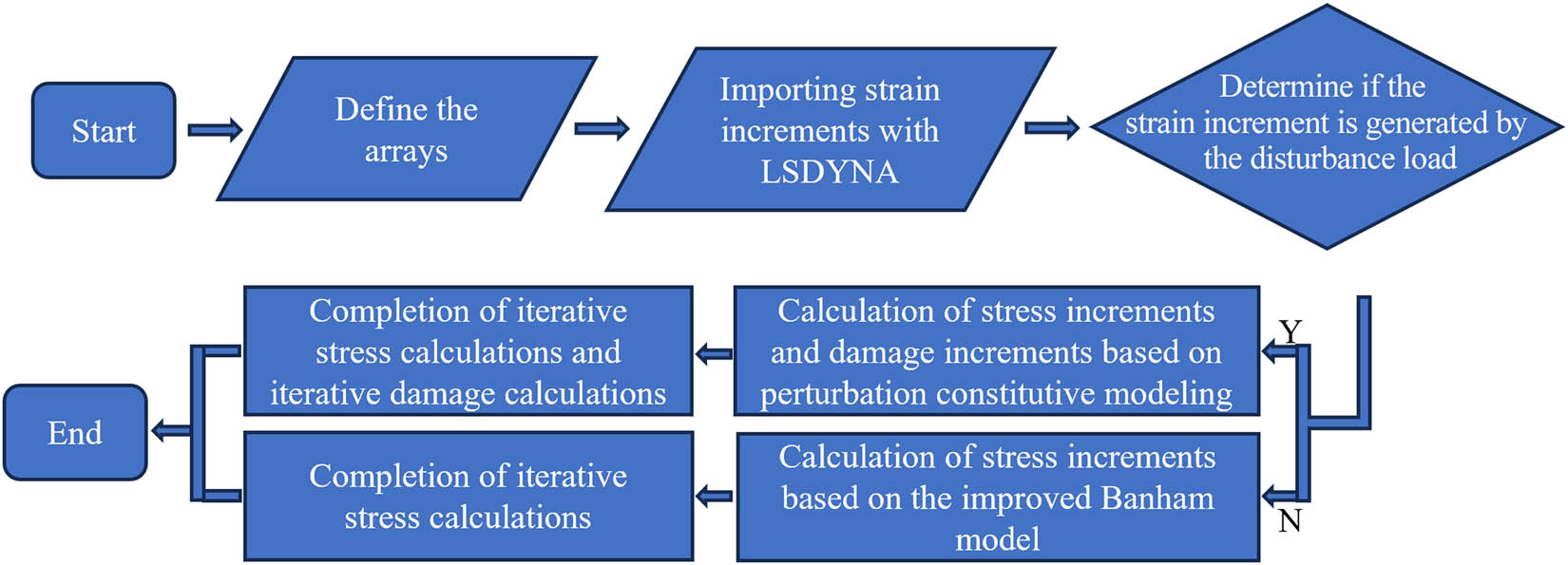
Secondary development process.

Solving process with solver.
Figure 11 shows the rock sample model established in the numerical simulation. The constraint in the Z direction was applied at the bottom of the finite-element model, and an axial uniformly distributed load of 43.41 MPa was applied at the top. As the sample deformation stabilized, a dynamic disturbance load was applied, with an amplitude of 10 MPa. The stress conditions were consistent with the test.

Numerical simulation model.
The deformation nephogram of the specimen under triaxial compression and dynamic disturbance was obtained by calculation. The axial strain was compared with the test curve, as shown in Figure 12. It can be seen from Figure 10 that the numerical simulation results are in good agreement with the curves of the triaxial compression dynamic disturbance test results, indicating that the damage model was successfully embedded in the LS-DYNA program.

Comparison of numerical simulation cloud diagram and strain results.
5 Conclusions
In this article, dynamic disturbance triaxial compression tests of rock are demonstrated, and the deformation characteristics of rock are analyzed in detail. Based on the deformation characteristics of the rock, a time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model is established, and it can describe the deformation characteristics of the rock under static loading and multiple dynamic disturbances.
In the dynamic disturbance loading test, the strain of the rock rises in the form of steps, and disturbance accelerates the failure of the rock. Every time a disturbance is loaded, the deformation of the rock suddenly increases, resulting in a corresponding increase in disturbance strain. The magnitude of the disturbance strain increment decreases with an increase in disturbing load repetition numbers.
The time-dependent deformation of the rock during the static loading stage is about 0.7% of the total axial strain, while the total strain increment of the rock produced by multiple dynamic disturbances is about 22.9% of the total axial strain, which is about 33 times of the time-dependent deformation, and much larger than the time-dependent deformation. Multiple dynamic disturbances are the main cause of rock damage.
The established disturbance damage model, combined with the introduced operator, accurately describes the phenomenon of sudden strain increase and the accumulation of disturbance damage in rock. The elastic component in the Bingham model is improved by introducing a nonlinear function, and it improves the shortcomings of the traditional Bingham model, which cannot describe the attenuation creep stage. The time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model, which combines the disturbance damage model and the improved Bingham model, not only accurately describes the strain sudden increase and the cumulative characteristics of disturbance damage under multiple dynamic disturbances, but also reflects the time-dependent deformation characteristics of rock under static loading.
The parameters of the constitutive model were identified by rock material characteristics and test data, and the secondary development program for this constitutive model was coded in LS-DYNA. According to the comparative analysis, the fitting curve and numerical simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results. It proves the applicability and correctness of the established time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model of rock and lays the foundation for the application of this constitutive model in numerical simulations.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51974136).
-
Funding information: This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51974136).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest or competing interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data, models, and code generated or used during the study are available on request from the authors.
References
[1] Xie HP. Research framework and anticipated results of deep rock mechanics and mining theory. Adv Eng Sci. 2017;49(02):1–16. 10.15961/j.jsuese.201700025.Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Wang QY, Liu J, Wang PT, Liu F. Experimental investigation of accelerated failure of creep rock induced by impact disturbance. Rock Soil Mech. 2020;41(03):781–8 + 798. 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.0592.Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Liu Y, Liu CW. Effect of axial static stress on mechanical properties of post-peak cracked sandstone under impact loading. J China Coal Soc. 2018;43(5):1281–8. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.0114.Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Chen X, Tang MG, Tang CA. Experimental study on the impact disturbance damage of weakly cemented rock based on fractal characteristics and energy dissipation regulation. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 2022;55:19–33. 10.1016/J.TAFMEC.2022.103665.Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Tang LZ, Wang C, Cheng LP, Gao LH. Experimental study of mechanical characteristics of skarn under one-dimensional coupled static and cyclic impact loads. J Cent South Univ (Sci Technol). 2015;46(10):3898–906. 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.10.045.Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Wang C, Tang LZ, Cheng LP, Chen Y, Liu T, Wei YH. Dynamic characteristics of skarn subjected to frequent dynamic disturbance under combined action of high axial compression and confining pressure. Rock Soil Mech. 2018;39(12):4537–46. 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.0635.Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Wang W, Liang XY, Zhang MT, Jia ZY, Zhang SY, Wang Q. Z.Experimental study on failure mechanism and crack density of sandstone under combined dynamic and static loading. Rock Soil Mech. 2021;42(10):2647–58. 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.0095.Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Cai T, Shi L, Jiang Y, Feng Z. A core damage constitutive model for the time-dependent creep and relaxation behavior of coal. Energies. 2022;15(11):1–16. 10.3390/en15114174.Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Ren X, Xin Y, Jia B, Gao K, Li X, Wang Y. Large stress-gradient creep tests and model establishment for red sandstone treated at high temperatures. Energies. 2022;15(20):1–16. 10.3390/en15207786.Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Lin H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Yong R, Fan X, Du S, et al. Improved nonlinear nishihara shear creep model with variable parameters for rock-like materials. Adv Civ Eng. 2020;15:1–15. 10.1155/2020/7302141.Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Zhao Y, Liu Q, Tang L, Xie S. The double Burgers model of fractured rock masses considering creep fracture damage. J Vibroengineering. 2019;21(4):974–87. 10.21595/jve.2019.20304.Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Wang W, Lv J, Wang HC. A creep-damage constitutive model for sandstone. Appl Mech Mater. 2012;170-173:289–94. 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.170-173.289.Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Wang RB, Xu WY, Wang W, Zhang JC. A nonlinear creep damage model for brittle rocks based on time-dependent damage. Eur J Environ Civ Eng. 2013;17(1):111–25. 10.1080/19648189.2013.834589.Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Liu HZ, Xie HQ, He JD, Xiao ML, Zhuo L. Nonlinear creep damage constitutive model for soft rocks. Mech Time-Dependent Mater. 2017;21:73–96. 10.1007/s11043-016-9319-7.Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Hou RB, Zhang K, Tao J, Xue XR, Chen YL. A nonlinear creep damage coupled model for rock considering the effect of initial damage. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 2019;52:1275–85. 10.1007/s00603-018-1626-7.Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Ping C, Wen YD, Wang YX, Yuan HP, Yuan BX. Study on nonlinear damage creep constitutive model for high-stress soft rock. Environ Earth Sci. 2016;75(10):1–8. 10.1007/s12665-016-5699-x.Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Wu F, L JF, Wang J. An improved Maxwell creep model for rock based on variable-order fractional derivatives. Environ Earth Sci. 2015;73:6965–71. 10.1007/s12665-015-4137-9.Suche in Google Scholar
[18] Zhao YL, Cao P, Wang WJ, Wan W, Liu YK. Viscoelasto-plastic rheological experiment under circular increment step load and unload and nonlinear creep model of soft rocks. J Cent South Univ Technol. 2009;16:488–94. 10.1007/s11771-009-0082-7.Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Yang WD, Zhang QY, Li SC, Wang SG. Time-dependent behavior of diabase and a nonlinear creep model. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 2014;47:1211–24. 10.1007/s00603-013-0478-4.Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Yu MY, Liu BG, Sun JL, Feng WL, Wang Q. Study on improved nonlinear viscoelastic-plastic creep model based on the Nishihara model. Geotechinal Geol Eng. 2020;38:3203–14. 10.1007/s10706-020-01217-5.Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Yang SQ, Xu P, Xu T. Nonlinear visco-elastic and accelerating creep model for coal under conventional triaxial compression. Geomech Geophysics Geo-Energy Geo-Resources. 2015;1:109–20. 10.1007/s40948-015-0014-y.Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Chen Y, Wu H, Pu H, Zhang K, Ju F, Wu Y, et al. Investigations of damage characteristics in rock material subjected to the joint effect of cyclic loading and impact. Energies. 2020;13(9):1–21. 10.3390/en13092154.Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Ou XF, Zhang XM, Zhang C, Feng H, Zhou XS, Zhao H. Study on bedding effect and damage constitutive model of slate under compressive dynamic loading. Chin J Rock Mech Eng. 2019;38(S2):3503–11. 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0391.Suche in Google Scholar
[24] Yu YJ, Liu F, Zhang W, Zhang GN. An experimental study on the rheological perturbation effect and a constitutive model of water-rich soft rock. J Vib Shock. 2019;38(12):199–205. 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.12.028.Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Dou LM, He J, Cao AY, Gong SY, Cai W. Rock burst prevention methods based on theory of dynamic and static combined load induced in coal mine. J China Coal Soc. 2015;40(7):1469–76. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.1815.Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Luo D, Su G, Zhang G. True-triaxial experimental study on mechanical behaviours and acoustic emission characteristics of dynamically induced rock failure. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 2019;53(3):1205–23. 10.1007/s00603-019-01970-x.Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Wang J, Sun Q, Liang B, Yang P, Yu Q. Mudstone creep experiment and nonlinear damage model study under cyclic disturbance load. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9305. 10.1038/s41598-020-66245-w.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Liu M, Chen S, Shi W, Cui G, Shen F, Li H. Time-dependent deformation characteristics of red sandstone under multiple dynamic disturbances. Chin J Geotech Eng. 2022;44(10):1917–24. 10.11779/CJGE202210018.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Diagenesis and evolution of deep tight reservoirs: A case study of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation (cg: 50.4-42 Ma) in Bozhong Sag
- Petrography and mineralogy of the Oligocene flysch in Ionian Zone, Albania: Implications for the evolution of sediment provenance and paleoenvironment
- Biostratigraphy of the Late Campanian–Maastrichtian of the Duwi Basin, Red Sea, Egypt
- Structural deformation and its implication for hydrocarbon accumulation in the Wuxia fault belt, northwestern Junggar basin, China
- Carbonate texture identification using multi-layer perceptron neural network
- Metallogenic model of the Hongqiling Cu–Ni sulfide intrusions, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insight from long-period magnetotellurics
- Assessments of recent Global Geopotential Models based on GPS/levelling and gravity data along coastal zones of Egypt
- Accuracy assessment and improvement of SRTM, ASTER, FABDEM, and MERIT DEMs by polynomial and optimization algorithm: A case study (Khuzestan Province, Iran)
- Uncertainty assessment of 3D geological models based on spatial diffusion and merging model
- Evaluation of dynamic behavior of varved clays from the Warsaw ice-dammed lake, Poland
- Impact of AMSU-A and MHS radiances assimilation on Typhoon Megi (2016) forecasting
- Contribution to the building of a weather information service for solar panel cleaning operations at Diass plant (Senegal, Western Sahel)
- Measuring spatiotemporal accessibility to healthcare with multimodal transport modes in the dynamic traffic environment
- Mathematical model for conversion of groundwater flow from confined to unconfined aquifers with power law processes
- NSP variation on SWAT with high-resolution data: A case study
- Reconstruction of paleoglacial equilibrium-line altitudes during the Last Glacial Maximum in the Diancang Massif, Northwest Yunnan Province, China
- A prediction model for Xiangyang Neolithic sites based on a random forest algorithm
- Determining the long-term impact area of coastal thermal discharge based on a harmonic model of sea surface temperature
- Origin of block accumulations based on the near-surface geophysics
- Investigating the limestone quarries as geoheritage sites: Case of Mardin ancient quarry
- Population genetics and pedigree geography of Trionychia japonica in the four mountains of Henan Province and the Taihang Mountains
- Performance audit evaluation of marine development projects based on SPA and BP neural network model
- Study on the Early Cretaceous fluvial-desert sedimentary paleogeography in the Northwest of Ordos Basin
- Detecting window line using an improved stacked hourglass network based on new real-world building façade dataset
- Automated identification and mapping of geological folds in cross sections
- Silicate and carbonate mixed shelf formation and its controlling factors, a case study from the Cambrian Canglangpu formation in Sichuan basin, China
- Ground penetrating radar and magnetic gradient distribution approach for subsurface investigation of solution pipes in post-glacial settings
- Research on pore structures of fine-grained carbonate reservoirs and their influence on waterflood development
- Risk assessment of rain-induced debris flow in the lower reaches of Yajiang River based on GIS and CF coupling models
- Multifractal analysis of temporal and spatial characteristics of earthquakes in Eurasian seismic belt
- Surface deformation and damage of 2022 (M 6.8) Luding earthquake in China and its tectonic implications
- Differential analysis of landscape patterns of land cover products in tropical marine climate zones – A case study in Malaysia
- DEM-based analysis of tectonic geomorphologic characteristics and tectonic activity intensity of the Dabanghe River Basin in South China Karst
- Distribution, pollution levels, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater in the main pepper production area of China
- Study on soil quality effect of reconstructing by Pisha sandstone and sand soil
- Understanding the characteristics of loess strata and quaternary climate changes in Luochuan, Shaanxi Province, China, through core analysis
- Dynamic variation of groundwater level and its influencing factors in typical oasis irrigated areas in Northwest China
- Creating digital maps for geotechnical characteristics of soil based on GIS technology and remote sensing
- Changes in the course of constant loading consolidation in soil with modeled granulometric composition contaminated with petroleum substances
- Correlation between the deformation of mineral crystal structures and fault activity: A case study of the Yingxiu-Beichuan fault and the Milin fault
- Cognitive characteristics of the Qiang religious culture and its influencing factors in Southwest China
- Spatiotemporal variation characteristics analysis of infrastructure iron stock in China based on nighttime light data
- Interpretation of aeromagnetic and remote sensing data of Auchi and Idah sheets of the Benin-arm Anambra basin: Implication of mineral resources
- Building element recognition with MTL-AINet considering view perspectives
- Characteristics of the present crustal deformation in the Tibetan Plateau and its relationship with strong earthquakes
- Influence of fractures in tight sandstone oil reservoir on hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of Yanchang Formation in southeastern Ordos Basin
- Nutrient assessment and land reclamation in the Loess hills and Gulch region in the context of gully control
- Handling imbalanced data in supervised machine learning for lithological mapping using remote sensing and airborne geophysical data
- Spatial variation of soil nutrients and evaluation of cultivated land quality based on field scale
- Lignin analysis of sediments from around 2,000 to 1,000 years ago (Jiulong River estuary, southeast China)
- Assessing OpenStreetMap roads fitness-for-use for disaster risk assessment in developing countries: The case of Burundi
- Transforming text into knowledge graph: Extracting and structuring information from spatial development plans
- A symmetrical exponential model of soil temperature in temperate steppe regions of China
- A landslide susceptibility assessment method based on auto-encoder improved deep belief network
- Numerical simulation analysis of ecological monitoring of small reservoir dam based on maximum entropy algorithm
- Morphometry of the cold-climate Bory Stobrawskie Dune Field (SW Poland): Evidence for multi-phase Lateglacial aeolian activity within the European Sand Belt
- Adopting a new approach for finding missing people using GIS techniques: A case study in Saudi Arabia’s desert area
- Geological earthquake simulations generated by kinematic heterogeneous energy-based method: Self-arrested ruptures and asperity criterion
- Semi-automated classification of layered rock slopes using digital elevation model and geological map
- Geochemical characteristics of arc fractionated I-type granitoids of eastern Tak Batholith, Thailand
- Lithology classification of igneous rocks using C-band and L-band dual-polarization SAR data
- Analysis of artificial intelligence approaches to predict the wall deflection induced by deep excavation
- Evaluation of the current in situ stress in the middle Permian Maokou Formation in the Longnüsi area of the central Sichuan Basin, China
- Utilizing microresistivity image logs to recognize conglomeratic channel architectural elements of Baikouquan Formation in slope of Mahu Sag
- Resistivity cutoff of low-resistivity and low-contrast pays in sandstone reservoirs from conventional well logs: A case of Paleogene Enping Formation in A-Oilfield, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea
- Examining the evacuation routes of the sister village program by using the ant colony optimization algorithm
- Spatial objects classification using machine learning and spatial walk algorithm
- Study on the stabilization mechanism of aeolian sandy soil formation by adding a natural soft rock
- Bump feature detection of the road surface based on the Bi-LSTM
- The origin and evolution of the ore-forming fluids at the Manondo-Choma gold prospect, Kirk range, southern Malawi
- A retrieval model of surface geochemistry composition based on remotely sensed data
- Exploring the spatial dynamics of cultural facilities based on multi-source data: A case study of Nanjing’s art institutions
- Study of pore-throat structure characteristics and fluid mobility of Chang 7 tight sandstone reservoir in Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin
- Study of fracturing fluid re-discharge based on percolation experiments and sampling tests – An example of Fuling shale gas Jiangdong block, China
- Impacts of marine cloud brightening scheme on climatic extremes in the Tibetan Plateau
- Ecological protection on the West Coast of Taiwan Strait under economic zone construction: A case study of land use in Yueqing
- The time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model of rock based on dynamic disturbance tests
- Evaluation of spatial form of rural ecological landscape and vulnerability of water ecological environment based on analytic hierarchy process
- Fingerprint of magma mixture in the leucogranites: Spectroscopic and petrochemical approach, Kalebalta-Central Anatolia, Türkiye
- Principles of self-calibration and visual effects for digital camera distortion
- UAV-based doline mapping in Brazilian karst: A cave heritage protection reconnaissance
- Evaluation and low carbon ecological urban–rural planning and construction based on energy planning mechanism
- Modified non-local means: A novel denoising approach to process gravity field data
- A novel travel route planning method based on an ant colony optimization algorithm
- Effect of time-variant NDVI on landside susceptibility: A case study in Quang Ngai province, Vietnam
- Regional tectonic uplift indicated by geomorphological parameters in the Bahe River Basin, central China
- Computer information technology-based green excavation of tunnels in complex strata and technical decision of deformation control
- Spatial evolution of coastal environmental enterprises: An exploration of driving factors in Jiangsu Province
- A comparative assessment and geospatial simulation of three hydrological models in urban basins
- Aquaculture industry under the blue transformation in Jiangsu, China: Structure evolution and spatial agglomeration
- Quantitative and qualitative interpretation of community partitions by map overlaying and calculating the distribution of related geographical features
- Numerical investigation of gravity-grouted soil-nail pullout capacity in sand
- Analysis of heavy pollution weather in Shenyang City and numerical simulation of main pollutants
- Road cut slope stability analysis for static and dynamic (pseudo-static analysis) loading conditions
- Forest biomass assessment combining field inventorying and remote sensing data
- Late Jurassic Haobugao granites from the southern Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Implications for postcollision extension of the Mongol–Okhotsk Ocean
- Petrogenesis of the Sukadana Basalt based on petrology and whole rock geochemistry, Lampung, Indonesia: Geodynamic significances
- Numerical study on the group wall effect of nodular diaphragm wall foundation in high-rise buildings
- Water resources utilization and tourism environment assessment based on water footprint
- Geochemical evaluation of the carbonaceous shale associated with the Permian Mikambeni Formation of the Tuli Basin for potential gas generation, South Africa
- Detection and characterization of lineaments using gravity data in the south-west Cameroon zone: Hydrogeological implications
- Study on spatial pattern of tourism landscape resources in county cities of Yangtze River Economic Belt
- The effect of weathering on drillability of dolomites
- Noise masking of near-surface scattering (heterogeneities) on subsurface seismic reflectivity
- Query optimization-oriented lateral expansion method of distributed geological borehole database
- Petrogenesis of the Morobe Granodiorite and their shoshonitic mafic microgranular enclaves in Maramuni arc, Papua New Guinea
- Environmental health risk assessment of urban water sources based on fuzzy set theory
- Spatial distribution of urban basic education resources in Shanghai: Accessibility and supply-demand matching evaluation
- Spatiotemporal changes in land use and residential satisfaction in the Huai River-Gaoyou Lake Rim area
- Walkaway vertical seismic profiling first-arrival traveltime tomography with velocity structure constraints
- Study on the evaluation system and risk factor traceability of receiving water body
- Predicting copper-polymetallic deposits in Kalatag using the weight of evidence model and novel data sources
- Temporal dynamics of green urban areas in Romania. A comparison between spatial and statistical data
- Passenger flow forecast of tourist attraction based on MACBL in LBS big data environment
- Varying particle size selectivity of soil erosion along a cultivated catena
- Relationship between annual soil erosion and surface runoff in Wadi Hanifa sub-basins
- Influence of nappe structure on the Carboniferous volcanic reservoir in the middle of the Hongche Fault Zone, Junggar Basin, China
- Dynamic analysis of MSE wall subjected to surface vibration loading
- Pre-collisional architecture of the European distal margin: Inferences from the high-pressure continental units of central Corsica (France)
- The interrelation of natural diversity with tourism in Kosovo
- Assessment of geosites as a basis for geotourism development: A case study of the Toplica District, Serbia
- IG-YOLOv5-based underwater biological recognition and detection for marine protection
- Monitoring drought dynamics using remote sensing-based combined drought index in Ergene Basin, Türkiye
- Review Articles
- The actual state of the geodetic and cartographic resources and legislation in Poland
- Evaluation studies of the new mining projects
- Comparison and significance of grain size parameters of the Menyuan loess calculated using different methods
- Scientometric analysis of flood forecasting for Asia region and discussion on machine learning methods
- Rainfall-induced transportation embankment failure: A review
- Rapid Communication
- Branch fault discovered in Tangshan fault zone on the Kaiping-Guye boundary, North China
- Technical Note
- Introducing an intelligent multi-level retrieval method for mineral resource potential evaluation result data
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Forest cover assessment using remote-sensing techniques in Crete Island, Greece”
- Addendum
- The relationship between heat flow and seismicity in global tectonically active zones
- Commentary
- Improved entropy weight methods and their comparisons in evaluating the high-quality development of Qinghai, China
- Special Issue: Geoethics 2022 - Part II
- Loess and geotourism potential of the Braničevo District (NE Serbia): From overexploitation to paleoclimate interpretation
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Diagenesis and evolution of deep tight reservoirs: A case study of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation (cg: 50.4-42 Ma) in Bozhong Sag
- Petrography and mineralogy of the Oligocene flysch in Ionian Zone, Albania: Implications for the evolution of sediment provenance and paleoenvironment
- Biostratigraphy of the Late Campanian–Maastrichtian of the Duwi Basin, Red Sea, Egypt
- Structural deformation and its implication for hydrocarbon accumulation in the Wuxia fault belt, northwestern Junggar basin, China
- Carbonate texture identification using multi-layer perceptron neural network
- Metallogenic model of the Hongqiling Cu–Ni sulfide intrusions, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insight from long-period magnetotellurics
- Assessments of recent Global Geopotential Models based on GPS/levelling and gravity data along coastal zones of Egypt
- Accuracy assessment and improvement of SRTM, ASTER, FABDEM, and MERIT DEMs by polynomial and optimization algorithm: A case study (Khuzestan Province, Iran)
- Uncertainty assessment of 3D geological models based on spatial diffusion and merging model
- Evaluation of dynamic behavior of varved clays from the Warsaw ice-dammed lake, Poland
- Impact of AMSU-A and MHS radiances assimilation on Typhoon Megi (2016) forecasting
- Contribution to the building of a weather information service for solar panel cleaning operations at Diass plant (Senegal, Western Sahel)
- Measuring spatiotemporal accessibility to healthcare with multimodal transport modes in the dynamic traffic environment
- Mathematical model for conversion of groundwater flow from confined to unconfined aquifers with power law processes
- NSP variation on SWAT with high-resolution data: A case study
- Reconstruction of paleoglacial equilibrium-line altitudes during the Last Glacial Maximum in the Diancang Massif, Northwest Yunnan Province, China
- A prediction model for Xiangyang Neolithic sites based on a random forest algorithm
- Determining the long-term impact area of coastal thermal discharge based on a harmonic model of sea surface temperature
- Origin of block accumulations based on the near-surface geophysics
- Investigating the limestone quarries as geoheritage sites: Case of Mardin ancient quarry
- Population genetics and pedigree geography of Trionychia japonica in the four mountains of Henan Province and the Taihang Mountains
- Performance audit evaluation of marine development projects based on SPA and BP neural network model
- Study on the Early Cretaceous fluvial-desert sedimentary paleogeography in the Northwest of Ordos Basin
- Detecting window line using an improved stacked hourglass network based on new real-world building façade dataset
- Automated identification and mapping of geological folds in cross sections
- Silicate and carbonate mixed shelf formation and its controlling factors, a case study from the Cambrian Canglangpu formation in Sichuan basin, China
- Ground penetrating radar and magnetic gradient distribution approach for subsurface investigation of solution pipes in post-glacial settings
- Research on pore structures of fine-grained carbonate reservoirs and their influence on waterflood development
- Risk assessment of rain-induced debris flow in the lower reaches of Yajiang River based on GIS and CF coupling models
- Multifractal analysis of temporal and spatial characteristics of earthquakes in Eurasian seismic belt
- Surface deformation and damage of 2022 (M 6.8) Luding earthquake in China and its tectonic implications
- Differential analysis of landscape patterns of land cover products in tropical marine climate zones – A case study in Malaysia
- DEM-based analysis of tectonic geomorphologic characteristics and tectonic activity intensity of the Dabanghe River Basin in South China Karst
- Distribution, pollution levels, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater in the main pepper production area of China
- Study on soil quality effect of reconstructing by Pisha sandstone and sand soil
- Understanding the characteristics of loess strata and quaternary climate changes in Luochuan, Shaanxi Province, China, through core analysis
- Dynamic variation of groundwater level and its influencing factors in typical oasis irrigated areas in Northwest China
- Creating digital maps for geotechnical characteristics of soil based on GIS technology and remote sensing
- Changes in the course of constant loading consolidation in soil with modeled granulometric composition contaminated with petroleum substances
- Correlation between the deformation of mineral crystal structures and fault activity: A case study of the Yingxiu-Beichuan fault and the Milin fault
- Cognitive characteristics of the Qiang religious culture and its influencing factors in Southwest China
- Spatiotemporal variation characteristics analysis of infrastructure iron stock in China based on nighttime light data
- Interpretation of aeromagnetic and remote sensing data of Auchi and Idah sheets of the Benin-arm Anambra basin: Implication of mineral resources
- Building element recognition with MTL-AINet considering view perspectives
- Characteristics of the present crustal deformation in the Tibetan Plateau and its relationship with strong earthquakes
- Influence of fractures in tight sandstone oil reservoir on hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of Yanchang Formation in southeastern Ordos Basin
- Nutrient assessment and land reclamation in the Loess hills and Gulch region in the context of gully control
- Handling imbalanced data in supervised machine learning for lithological mapping using remote sensing and airborne geophysical data
- Spatial variation of soil nutrients and evaluation of cultivated land quality based on field scale
- Lignin analysis of sediments from around 2,000 to 1,000 years ago (Jiulong River estuary, southeast China)
- Assessing OpenStreetMap roads fitness-for-use for disaster risk assessment in developing countries: The case of Burundi
- Transforming text into knowledge graph: Extracting and structuring information from spatial development plans
- A symmetrical exponential model of soil temperature in temperate steppe regions of China
- A landslide susceptibility assessment method based on auto-encoder improved deep belief network
- Numerical simulation analysis of ecological monitoring of small reservoir dam based on maximum entropy algorithm
- Morphometry of the cold-climate Bory Stobrawskie Dune Field (SW Poland): Evidence for multi-phase Lateglacial aeolian activity within the European Sand Belt
- Adopting a new approach for finding missing people using GIS techniques: A case study in Saudi Arabia’s desert area
- Geological earthquake simulations generated by kinematic heterogeneous energy-based method: Self-arrested ruptures and asperity criterion
- Semi-automated classification of layered rock slopes using digital elevation model and geological map
- Geochemical characteristics of arc fractionated I-type granitoids of eastern Tak Batholith, Thailand
- Lithology classification of igneous rocks using C-band and L-band dual-polarization SAR data
- Analysis of artificial intelligence approaches to predict the wall deflection induced by deep excavation
- Evaluation of the current in situ stress in the middle Permian Maokou Formation in the Longnüsi area of the central Sichuan Basin, China
- Utilizing microresistivity image logs to recognize conglomeratic channel architectural elements of Baikouquan Formation in slope of Mahu Sag
- Resistivity cutoff of low-resistivity and low-contrast pays in sandstone reservoirs from conventional well logs: A case of Paleogene Enping Formation in A-Oilfield, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea
- Examining the evacuation routes of the sister village program by using the ant colony optimization algorithm
- Spatial objects classification using machine learning and spatial walk algorithm
- Study on the stabilization mechanism of aeolian sandy soil formation by adding a natural soft rock
- Bump feature detection of the road surface based on the Bi-LSTM
- The origin and evolution of the ore-forming fluids at the Manondo-Choma gold prospect, Kirk range, southern Malawi
- A retrieval model of surface geochemistry composition based on remotely sensed data
- Exploring the spatial dynamics of cultural facilities based on multi-source data: A case study of Nanjing’s art institutions
- Study of pore-throat structure characteristics and fluid mobility of Chang 7 tight sandstone reservoir in Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin
- Study of fracturing fluid re-discharge based on percolation experiments and sampling tests – An example of Fuling shale gas Jiangdong block, China
- Impacts of marine cloud brightening scheme on climatic extremes in the Tibetan Plateau
- Ecological protection on the West Coast of Taiwan Strait under economic zone construction: A case study of land use in Yueqing
- The time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model of rock based on dynamic disturbance tests
- Evaluation of spatial form of rural ecological landscape and vulnerability of water ecological environment based on analytic hierarchy process
- Fingerprint of magma mixture in the leucogranites: Spectroscopic and petrochemical approach, Kalebalta-Central Anatolia, Türkiye
- Principles of self-calibration and visual effects for digital camera distortion
- UAV-based doline mapping in Brazilian karst: A cave heritage protection reconnaissance
- Evaluation and low carbon ecological urban–rural planning and construction based on energy planning mechanism
- Modified non-local means: A novel denoising approach to process gravity field data
- A novel travel route planning method based on an ant colony optimization algorithm
- Effect of time-variant NDVI on landside susceptibility: A case study in Quang Ngai province, Vietnam
- Regional tectonic uplift indicated by geomorphological parameters in the Bahe River Basin, central China
- Computer information technology-based green excavation of tunnels in complex strata and technical decision of deformation control
- Spatial evolution of coastal environmental enterprises: An exploration of driving factors in Jiangsu Province
- A comparative assessment and geospatial simulation of three hydrological models in urban basins
- Aquaculture industry under the blue transformation in Jiangsu, China: Structure evolution and spatial agglomeration
- Quantitative and qualitative interpretation of community partitions by map overlaying and calculating the distribution of related geographical features
- Numerical investigation of gravity-grouted soil-nail pullout capacity in sand
- Analysis of heavy pollution weather in Shenyang City and numerical simulation of main pollutants
- Road cut slope stability analysis for static and dynamic (pseudo-static analysis) loading conditions
- Forest biomass assessment combining field inventorying and remote sensing data
- Late Jurassic Haobugao granites from the southern Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Implications for postcollision extension of the Mongol–Okhotsk Ocean
- Petrogenesis of the Sukadana Basalt based on petrology and whole rock geochemistry, Lampung, Indonesia: Geodynamic significances
- Numerical study on the group wall effect of nodular diaphragm wall foundation in high-rise buildings
- Water resources utilization and tourism environment assessment based on water footprint
- Geochemical evaluation of the carbonaceous shale associated with the Permian Mikambeni Formation of the Tuli Basin for potential gas generation, South Africa
- Detection and characterization of lineaments using gravity data in the south-west Cameroon zone: Hydrogeological implications
- Study on spatial pattern of tourism landscape resources in county cities of Yangtze River Economic Belt
- The effect of weathering on drillability of dolomites
- Noise masking of near-surface scattering (heterogeneities) on subsurface seismic reflectivity
- Query optimization-oriented lateral expansion method of distributed geological borehole database
- Petrogenesis of the Morobe Granodiorite and their shoshonitic mafic microgranular enclaves in Maramuni arc, Papua New Guinea
- Environmental health risk assessment of urban water sources based on fuzzy set theory
- Spatial distribution of urban basic education resources in Shanghai: Accessibility and supply-demand matching evaluation
- Spatiotemporal changes in land use and residential satisfaction in the Huai River-Gaoyou Lake Rim area
- Walkaway vertical seismic profiling first-arrival traveltime tomography with velocity structure constraints
- Study on the evaluation system and risk factor traceability of receiving water body
- Predicting copper-polymetallic deposits in Kalatag using the weight of evidence model and novel data sources
- Temporal dynamics of green urban areas in Romania. A comparison between spatial and statistical data
- Passenger flow forecast of tourist attraction based on MACBL in LBS big data environment
- Varying particle size selectivity of soil erosion along a cultivated catena
- Relationship between annual soil erosion and surface runoff in Wadi Hanifa sub-basins
- Influence of nappe structure on the Carboniferous volcanic reservoir in the middle of the Hongche Fault Zone, Junggar Basin, China
- Dynamic analysis of MSE wall subjected to surface vibration loading
- Pre-collisional architecture of the European distal margin: Inferences from the high-pressure continental units of central Corsica (France)
- The interrelation of natural diversity with tourism in Kosovo
- Assessment of geosites as a basis for geotourism development: A case study of the Toplica District, Serbia
- IG-YOLOv5-based underwater biological recognition and detection for marine protection
- Monitoring drought dynamics using remote sensing-based combined drought index in Ergene Basin, Türkiye
- Review Articles
- The actual state of the geodetic and cartographic resources and legislation in Poland
- Evaluation studies of the new mining projects
- Comparison and significance of grain size parameters of the Menyuan loess calculated using different methods
- Scientometric analysis of flood forecasting for Asia region and discussion on machine learning methods
- Rainfall-induced transportation embankment failure: A review
- Rapid Communication
- Branch fault discovered in Tangshan fault zone on the Kaiping-Guye boundary, North China
- Technical Note
- Introducing an intelligent multi-level retrieval method for mineral resource potential evaluation result data
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Forest cover assessment using remote-sensing techniques in Crete Island, Greece”
- Addendum
- The relationship between heat flow and seismicity in global tectonically active zones
- Commentary
- Improved entropy weight methods and their comparisons in evaluating the high-quality development of Qinghai, China
- Special Issue: Geoethics 2022 - Part II
- Loess and geotourism potential of the Braničevo District (NE Serbia): From overexploitation to paleoclimate interpretation

