Abstract
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is a common malignancy worldwide. LncRNA LINC00704 (mitotically associated long non-coding RNA) was reported as a crucial regulator in PTC. However, the biological mechanism of LINC00704 action remains unclear in PTC. The mRNA levels of LINC00704, miR-204-5p, and high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) were measured by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assay. HMGB1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and cyclin D1 protein levels were detected using the Western blot assay. The binding relationship between miR-204-5p and LINC00704 or HMGB1 was predicted by LncBase Predicted v.2 or TargetScan, respectively, and then validated by dual luciferase reporter assay. Cell viability, cell cycle, cell migration and invasion, and migration ratio were assessed by MTT, flow cytometry, transwell cell migration and invasion, and wound-healing assays, respectively. Results suggested that LINC00704 and HMGB1 were elevated and miR-204-5p decreased in PTC tissues and cells. Furthermore, rescue experiments demonstrated that the miR-204-5p inhibitor alleviated the inhibitory effects of LINC00704 knockdown on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion. Meanwhile, miR-204-5p overexpression repressed proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting HMGB1. Mechanical analysis discovered that LINC00704 could act as an miR-204-5p sponge to modulate HMGB1 expression. In conclusion, LINC00704 promoted PTC cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion by the miR-204-5p/HMGB1 axis, providing a novel therapeutic target for PTC patients.
1 Introduction
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is a common endocrine system tumor and accounts for 80–90% of thyroid cancer [1]. The morbidity of PTC has been increasing over the last two decades [2]. PTC easily metastasizes to the cervical lymph nodes, and this may be fatal for PTC patients [3]. Therefore, it is crucial to develop a new therapeutic target for PTC patients in the early stage of diagnosis.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs with more than 200 nucleotides (nts) in length and can regulate gene expression at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels [4]. LncRNA dysregulation has been reported in many cancer tissues, and their abnormal expression may relate to cancer progression. For instance, lncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) was dramatically increased in PTC tissues and cell lines, and its overexpression promoted cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and induced cell apoptosis; and the depletion of NEAT1 restrained xenograft tumor growth [5]. Previous studies documented that the level of LINC00704 was upregulated in PTC; LINC00704 knockdown restrained cell proliferation, migration, invasion, cell colony formation ability, and induced cell apoptosis in PTC [6]. However, the biological mechanism of LINC00704 action remains undefined in PTC.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of non-coding RNAs of about 22 nts in length, have been reported to function as messenger RNA (mRNA) inhibitors by downregulating mRNA translation or mediating mRNA degradation [7]. Also, the dysregulation of miRNA has been reported in many cancer processes such as cancer initiation, progression, and transition. For example, miR-23a was markedly reduced in PTC tissues and cells; the overexpression of miR-23a significantly impeded cell proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase, and promoted cell apoptosis, while an miR-23a inhibitor showed the opposite effects [8]. Another study in osteosarcoma demonstrated that miR-204-5p was conspicuously downregulated in osteosarcoma tissues and osteosarcoma cell lines; miR-204-5p overexpression promoted cell apoptosis and inhibited cell migration and invasion; and miR-204-5p mimics hampered the xenograft tumor growth in vivo [9]. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a ubiquitously expressed intracellular protein that binds DNA and transcription factors and regulates chromosomal structure and function [10]. HMGB1 has been identified as a crucial oncogene in several cancer types. HMGB1 was highly expressed in many cancer tissues and/or cells including prostate cancer [11], bladder cancer [12], human non-small cell lung cancer [13], gastric cancer [14], colon cancer [15], and also in PTC [16,17]. However, the biological mechanisms of miR-204-5p and HMGB1 action were still unclear in PTC.
In this study, we verified that LINC00704 and HMGB1 were distinctly upregulated, and miR-204-5p was drastically downregulated in PTC tissues and cells. Furthermore, we found that LINC00704 modulated HMGB1 to regulate cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in PTC by sponging miR-204-5p. This new regulatory pathway may provide a novel molecular target for early stage PTC diagnosis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Tissue samples
Fifty PTC tissues and the corresponding adjacent normal tissues were collected from the Quanzhou First Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University. All tissues were frozen at −80°C until further use.
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Quanzhou First Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University.
2.2 Cell culture and transfection
Four PTC cell lines (TPC-1, BCPAP, BHT101, and K1) and human thyroid epithelial cells (HTori-3) were purchased from Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockville, MD, USA) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen). The cells were cultivated in an incubator with the parameters of 37°C and 5% CO2. Small interfering RNA target for LINC00704 (si-LINC00704) and its matched control (si-NC); LINC00704 overexpression vector (LINC00704) and its matched control (vector); miR-204-5p mimic and miR-NC; miR-204-5p inhibitor and anti-miR-NC; and HMGB1 overexpression vector (HMGB1) and its matched control were obtained from Origene (Rockville, MD, USA). The transfection was conducted using Lipo-fectamine 2000 Reagent (Invitrogen) in accordance with the manual.
2.3 Quantitative reverse transcription- polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
The miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) was used to extract RNA from cells, and the RNA samples were reverse transcribed using Transcriptor First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche, Vilvoord, Brussel, Belgium). Quantitative PCR was conducted using FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master (Roche) by ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The data were calculated by using the 2−ΔΔCt method, normalizing with endogenous control glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and U6. All the primers were obtained from Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI, Shenzhen, China) and are listed as follows: LINC00704: forward 5′-TGCGTTCAGTAAAACGGGCA-3′, reverse 5′-TGTGGGAAATGCAGGGTTCT-3′; miR-204-5p: forward 5′-GACGCTTTCCCTTTGTCATCCT-3′, reverse 5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTC-3′; HMGB1: forward 5′-AGGATCCCAATGCACCCAAG-3′, reverse 5′-CGCAACATCACCAATGGACAG-3′; GAPDH: forward 5′-CGAGATCCCTCCAAAATCAA-3′, reverse 5′-TTCACACCCATGACGAACAT-3′; U6: forward 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′, reverse 5′-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′.
2.4 Western blot
Protein was extracted using a Protein Extraction Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China), and the sample concentration was detected using bicinchoninic acid (BCA) Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime). Following separation by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), the sample was transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA). Subsequently, the membrane was blocked in non-fat milk and incubated with primary antibody and secondary antibody in sequence. All antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA). The chemiluminescence intensity was assessed using eyoECL Plus Kit (Beyotime).
2.5 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay
For MTT assay, 5 × 103 cells were added into 96-well plates and cultivated for 24, 48, and 72 h. Then the cells were incubated with MTT for 3 h, and the formazan in the sample was dissolved by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 15 min at 37°C in the dark. The absorbance was detected at 570 nm using a spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
2.6 Cell cycle assay
In this assay, the transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells were trypsinized and washed with PBS, followed by fixation with 75% ethanol at 4°C overnight. Then the cells were centrifuged and resuspended in propidium iodide, followed by incubation for another 30 min. Thereafter, ModFit LT 3.0 for Windows (Verity Software House, Topsham, ME, USA) was applied to analyze the distribution of cells.
2.7 Transwell assay
For the migration assay, 500 µL of RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS was added to the lower chamber, while the cells suspended in serum-free medium were added to the upper chamber. After incubation, the cells in the lower chamber were stained with 0.1% crystal violet. Cell numbers in 10 fields were counted using a light microscope and calculated using Image Pro Plus (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD, USA). The protocol of invasion assay was similar to that of the migration assay, while the difference being that the upper chamber was covered with a matrigel matrix (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
2.8 Wound-healing assay
In this assay, the PTC cells (1 × 104 cells/well) were introduced into 96-well plates and then the starved monolayer cells were mounted on a reusable template to create a standard wound using a Wound Maker tool (Essen BioScience, Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Subsequently, an IncuCyte ZOOM Live-Cell Imaging System (Essen BioScience) was used to scan the plates at 0–24 h, and the IncuCyte ZOOM Software (Essen BioScience) was used to generate the quantified time-lapse curves in line with the operation manual.
2.9 Dual luciferase reporter assay
The interaction between LINC00704 and miR-204-5p was predicted by LncBase Predicted v.2 (http://carolina.imis.athena-innovation.gr), and the interaction between miR-204-5p and HMGB1 was predicted by TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org). LINC00704 and HMGB1-3′UTR or their corresponding mutant sequences were amplified and inserted into a psiCHECK2 plasmid (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), namely, LINC00704-WT, LINC00704-MUT, HMGB1-WT and HMGB1-MUT. Following the transfection of miR-204-5p mimics or miR-NC in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells with a luciferase reporter, the luciferase activity was assessed using a Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay Kit (Promega). Renilla luciferase activities were used as the internal reference to normalize the firefly luciferase activities.
2.10 Statistical analysis
In this study, all quantitative data were repeated at least three times and reported as mean ± standard deviation. The differences between two groups were analyzed using Student's t test, while the differences among more than three groups were assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). All data were calculated using GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA). A difference was considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 LINC00704 is upregulated in PTC tissues, cells, and correlated with the pathological characteristics of patients
To study the effects of LINC00704 on PTC, qRT-PCR was first conducted to detect the expression of LINC00704 in PTC tissues and cells. The results showed that the relative expression of LINC00704 was significantly increased in PTC tissues and cells (TPC-1, BCPAP, BHT101, and K1) compared with that in the corresponding adjacent normal tissues or human thyroid epithelial cells (HTori-3), respectively (Figure 1a and e). Then the correlation analysis measured the relation between the level of LINC00704 and the clinical and pathological characteristics of PTC patients. The chi-square test results indicated that the high level of LINC00704 was closely correlated with tumor size (P = 0.015), TNM stage (P = 0.005), and lymph node metastasis (P = 0.024) but not correlated with age or gender (Table 1). In addition, patients with higher expression of LINC00704 had lower survival rates and vice versa (Figure 1b). Taken together, the level of LINC00704 was dramatically elevated in PTC tissues and cells and correlated with the pathological characteristics of patients including tumor size, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis.

The relative expression of LINC00704 and miR-204-5p in PTC tissues and cells. The levels of LINC00704 (a and e) and miR-204-5p (c and f) were detected by qRT-PCR assay in PTC tissues and cells. (b) The overall survival ratio in high LINC00704 and low LINC00704 patients. (d) The correlation between miR-204-5p and LINC00704.
LINC00704 expression and clinicopathologic characteristics in PTC
| Parameters | Total | LINC00704 expression | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 25) | Low (n = 25) | |||
| Age | ||||
| <60 | 23 | 11 | 12 | 0.714 |
| ≥60 | 27 | 14 | 13 | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 17 | 10 | 7 | 0.413 |
| Female | 33 | 15 | 18 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | ||||
| <1 | 23 | 8 | 15 | 0.015* |
| ≥1 | 27 | 17 | 10 | |
| TNM stage | ||||
| I–II | 37 | 15 | 22 | 0.005* |
| III–IV | 13 | 10 | 3 | |
| Lymph node metastasis | ||||
| No | 29 | 12 | 17 | 0.024* |
| Yes | 21 | 13 | 8 | |
3.2 miR-204-5p is downregulated in PTC tissues, cells, and negatively linearly correlated with LINC00704
To study the roles of miR-204-5p in PTC, qRT-PCR was conducted to detect the expression of miR-204-5p in PTC tissues and cells. The results showed that miR-204-5p was remarkably downregulated in PTC tissues and cells in comparison with that in normal tissues and cells (Figure 1c and f). Additionally, the level of miR-204-5p was negatively linearly correlated with the level of LINC00704 (Figure 1d). These data revealed that miR-204-5p levels were reduced in PTC tissues and cells and negatively linearly correlated with LINC00704.
3.3 miR-204-5p is a target of LINC00704
To explore the biological role of LINC00704, LncBase Predicted v.2 online website was used to predict the targets of LINC00704. The results displayed that miR-204-5p shared complementary sequences with LINC00704 (Figure 2a). The dual luciferase reporter assay indicated that the transfection of miR-204-5p mimics lead to the apparent downregulation of the luciferase activity of LINC00704-WT but had no significant effect on the luciferase activity of LINC00704-MUT in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells (Figure 2b and c). Subsequently, the loss and gain assay indicated that the level of LINC00704 was conspicuously decreased and the level of miR-204-5p was notably elevated in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-LINC00704 and vice versa in the LINC00704 overexpressed group (Figure 2d–g). These results reveal that miR-204 negatively interacts with LINC00704.

miR-204-5p is a target of LINC00704. (a) The putative complementary sequences between miR-204-5p and LINC00704. The luciferase activity of LINC00704-WT or LINC00704-MUT reporter in TPC-1 (b) and BCPAP (c) cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics or miR-NC was assessed by dual luciferase reporter assay. The level of LINC00704 was detected by qRT-PCR in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-LINC00704 (d) or pcDNA-LINC00704 (e). The level of miR-204-5p was measured by qRT-PCR in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-LINC00704 (f) or pcDNA-LINC00704 (g).
3.4 miR-204-5p inhibitor alleviates the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion induced by LINC00704 depletion in PTC cells
To further investigate the interaction between LINC00704 and miR-204-5p, qRT-PCR was conducted to measure the level of miR-204-5p in PTC cells co-transfected with si-LINC00704 and miR-204-5p inhibitor. The results showed that miR-204-5p was distinctly upregulated in si-LINC00704-transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells, while a miR-204-5p inhibitor attenuated this upregulation (Figure 3a). Furthermore, the MTT assay showed that cell viability was strikingly reduced in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-LINC00704, but the miR-204-5p inhibitor reversed the trend (Figure 3b and c). Meanwhile, flow cytometry results suggested that more cells were in the G1 phase due to the knockdown of LINC00704, which was abrogated by transfection of an miR-204-5p inhibitor in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells (Figure 3d–g). Moreover, LINC00704 silencing repressed the protein levels of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA; proliferation marker) and cyclin D1 (cell cycle marker), while the downregulation of miR-204-5p mitigated the effects in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells (Figure 3h–k), supporting the effects of LINC00704 and miR-204-5p on cell proliferation and cell cycle. Apart from that, the transwell assay showed that the migrated cells and invading cells were all strikingly reduced in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-LINC00704 but the miR-204-5p inhibitor reversed the trend (Figure 3l–o). Simultaneously, the wound-healing assay also proved that miR-204-5p knockdown could abolish the suppressive action of si-LINC00704 on the migration ratio in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells (Figure 3p–s). These data suggest that an miR-204-5p inhibitor could mitigate the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion in PTC cells.

miR-204-5p is a target of LINC00704. (a) The level of miR-204-5p was measured by qRT-PCR in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-NC, si-LINC00704, si-LINC00704 + anti-miR-NC, or si-LINC00704 + miR-204-5p inhibitor. Cell viability (b and c), cell cycle (d-g), cell migration (l and m) and cell invasion (n and o) of transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells were assessed by MTT, flow cytometry, and transwell cell migration and invasion assays, respectively. (h–k) Protein levels of PCNA and cyclin D1 in transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells were assessed by Western blot assay. (p–s) Migration ratio was measured by wound-healing assay in transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells.
3.5 HMGB1 negatively interacts with miR-204-5p
To illustrate the biological mechanism of miR-204-5p, the putative target of miR-204-5p was identified with the TargetScan website. The search results suggested that miR-204-5p has complementary binding sites with the HMGB1 3′UTR (Figure 4a). The dual luciferase reporter assay indicated that miR-204-5p mimics significantly decreased the luciferase activity of HMGB1-3′UTR-WT related to that in miR-NC, while the luciferase activity of HMGB1-3′UTR-MUT was not obviously impaired in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells (Figure 4b and c). Furthermore, the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB1 both significantly decreased in TPC-1 and in BCPAP cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics compared with that in miR-NC (Figure 4d and f); while the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB1 showed the opposite trend in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with an miR-204-5p inhibitor (Figure 4e and g). In addition, HMGB1 was apparently upregulated in PTC tissues in comparison with that in adjacent normal tissues (Figure 4h). The scatter diagram indicated that the level of HMGB1 was negatively linearly correlated with the level of miR-204-5p (Figure 4i). Taken together, HMGB1 negatively interacts with miR-204-5p.

HMGB1 negatively interacts with miR-204-5p. (a) The putative complementary sequences between miR-204-5p and HMGB1 3′UTR. The luciferase activity of HMGB1-WT or HMGB1-MUT reporter in TPC-1 (b) and BCPAP (c) cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics or miR-NC was assessed by dual luciferase reporter assay. The level of HMGB1 was detected by qRT-PCR in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics (d) or miR-204-5p inhibitor (e). The protein level of miR-204-5p was measured by Western blot in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics (f) or miR-204-5p inhibitor (g). (h) The level of HMGB1 in PTC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. (i) The correlation between HMGB1 and miR-204-5p.
3.6 HMGB1 overexpression reverses inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion induced by miR-204-5p overexpression in PTC cells
To further research the interaction between miR-204-5p and HMGB1, miR-204-5p mimics and pcDNA-HMGB1 were co-transfected into TPC-1 and BCPAP cells. The qRT-PCR and Western blot assay results revealed that the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB1 were distinctly downregulated in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics, while the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB1 were oppositely affected in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells co-transfected with miR-204-5p mimics and pcDNA-HMGB1 in contrast to that in the corresponding matched controls (Figure 5a–c). Moreover, the MTT assay and flow cytometry assay results indicated that the overexpression of miR-204-5p inhibited cell viability and cell cycle in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells, whereas HMGB1 upregulation overturned these effects (Figure 5d–g). Furthermore, the changes in PCNA and cyclin D1 protein levels further demonstrated the regulatory effect of miR-204-5p and HMGB1 on cell proliferation and cell cycle (Figure 5h–k). Besides, the transwell assay indicated that migrated cells and invaded cells were greatly decreased in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with miR-204-5p mimics, while these inhibitory effects were mitigated by HMGB1 overexpression (Figure 5l and m). Synchronously, the migration ratio also showed a similar trend in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells (Figure 5n and o). These results demonstrated that HMGB1 overexpression weakened the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion induced by miR-204-5p overexpression in PTC cells.

HMGB1 overexpression reverses the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, cell migration and invasion induced by miR-204-5p overexpression in PTC cells. The relative mRNA (a) and protein (b and c) levels of HMGB1, cell viability (d and e), cell cycle (f and g), cell migration (l) and cell invasion (m), and migration ratio (n and o) in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with miR-NC, miR-204-5p mimics, miR-204-5p mimics + pcDNA or miR-204-5p mimics + pcDNA-HMGB1 were measured by qRT-PCR, Western blot, MTT, flow cytometry, transwell cell migration and invasion, and wound-healing assays, respectively. (h–k) Protein levels of PCNA and cyclin D1 in transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells were detected by Western blot assay.
3.7 LINC00704 silencing modulates HMGB1 low expression by sponging miR-204-5p in PTC cells
Based on the above results, we further explored the interaction among LINC00704, miR-204-5p, and HMGB1. The qRT-PCR and Western blot assays indicated that the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB1 were both notably downregulated in si-LINC00704-transfected TPC-1 and BCPAP cells, but an miR-204-5p inhibitor mitigated these inhibitory effects on the mRNA and protein levels of HMGB1 (Figure 6a–c). In addition, the scatter diagram shows that the level of HMGB1 was positively linearly correlated with the level of LINC00704 (Figure 6d). These data suggest that LINC00704 knockdown downregulates HMGB1 by targeting miR-204-5p in PTC cells.
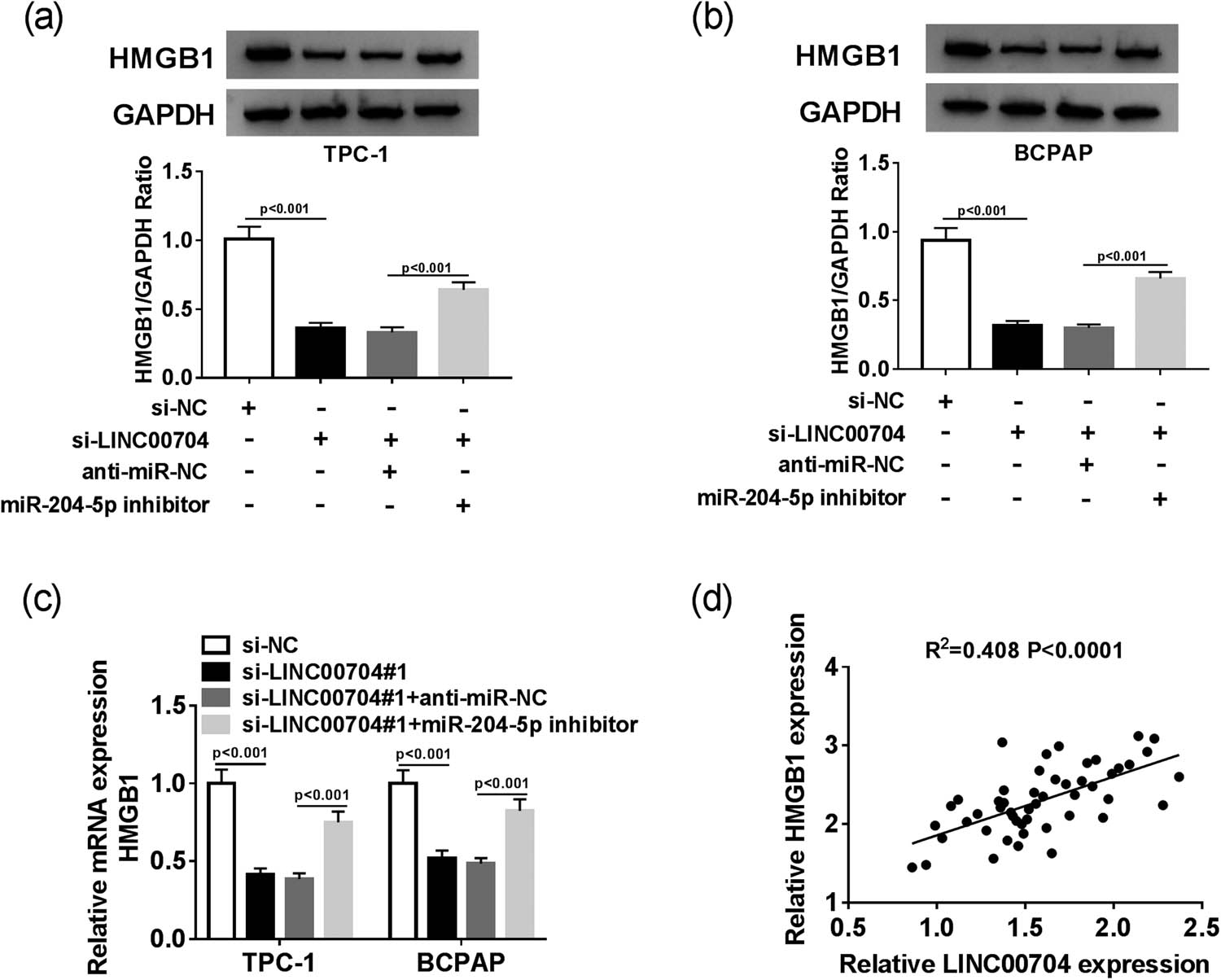
LINC00704 silencing modulates HMGB1 low expression by sponging miR-204-5p in PTC cells. The protein (a and b) and mRNA (c) levels of HMGB1 in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells transfected with si-NC, si-LINC00704, si-LINC00704 + anti-miR-NC, or si-LINC00704 + miR-204-5p inhibitor were detected by Western blot assay and qRT-PCR, respectively. (d) The correlation between HMGB1 and LINC00704. **P < 0.01.
4 Discussion
PTC is a common endocrine system tumor. LncRNAs have been documented to participate in several processes in tumor progression. In this study, we aimed to explore the biological mechanism of action of LINC00704 in PTC. Based on the above results, we found that LINC00704 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in PTC via the miR-204-5p/HMGB1 axis.
LINC00704 has been reported to dysregulate expression and associated tumor progression in many cancers including PTC. Tracy et al. reported that the level of LINC00704 (mitotically associated long non-coding RNA) was obviously elevated in breast cancer tissues and cells (MDA-MB-231); the depletion of LINC00704 dramatically reduced cell proliferation and viability [18]. In this study, we verified that LINC00704 was highly expressed in PTC tissues and cells. LINC00704 levels correlated with the pathological characteristics of patients including tumor size, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis. Moreover, LINC00704 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, invasion, and migration ratio in PTC cells. The above results are consistent with the previous study [6].
Recent studies demonstrated that miR-204-5p associates with cancer progression in many cancers. A report in breast cancer indicated that miR-204-5p was significantly downregulated in breast cancer tissues, and its overexpression repressed cell viability, proliferation, and migration capacity [19]. In fact, Liu et al. reported that the level of miR-204-5p was strikingly downregulated in PTC tissues and cell lines, and miR-204-5p overexpression restrained cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in PTC cells [20]. In the present study, we validated that the level of miR-204-5p was strikingly decreased in PTC tissues and cells. LncRNAs have been reported as competing endogenous RNAs that can affect the levels of miRNAs and contribute to abnormal target mRNA expression. In the present study, we validated that the level of miR-204-5p was strikingly decreased in PTC tissues and cells. A dual luciferase reporter assay indicated that miR-204-5p directly interacts with LINC00704. MiR-204-5p was remarkably upregulated in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells, while the transfection of miR-204-5p mitigated these effects. In addition, an miR-204-5p inhibitor alleviated the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion caused by si-LINC00704.
HMGB1 has been identified as an essential contributor towards the initiation and progression of many kinds of cancers. For example, HMGB1 was found to be obviously upregulated in gastric cancer cells; HMGB1 silencing inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, cell migration, and invasion and promoted cell apoptosis in vitro [21].
A study of PTC revealed that HMGB1 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and metastasis in PTC cells in vitro and restrained xenograft tumor growth in vivo [16]. In this study, HMGB1 was markedly upregulated in PTC tissues. HMGB1 3′UTR was predicted to have complementary sequences with miR-204-5p. Then the dual luciferase reporter assay validated that HMGB1 is a direct target of miR-204-5p. The level of HMGB1 was downregulated in PTC cells transfected with miR-204-5p and upregulated in PTC cells transfected with an miR-204-5p inhibitor. Moreover, HMGB1 overexpression relieved the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration and invasion in PTC cells induced by the miR-204-5p mimics. In addition, LINC00704 knockdown suppressed HMGB1 expression by sponging miR-204-5p.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, our results indicate that LINC00704 and HMGB1 were upregulated and miR-204-5p was downregulated in PTC tissues and cells. LINC00704 modulates HMGB1 to promote cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion in PTC by targeting miR-204-5p. The LINC00704/miR-204-5p/HMGB1 new regulatory pathway may provide a novel biomarker for PTC.
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Xing M, Haugen BR, Schlumberger M. Progress in molecular-based management of differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet. 2013;381(9871):1058–69.10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60109-9Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S, He J. Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer Res. 2015;27(1):2–12.10.1186/s40880-015-0001-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Perri F, Lorenzo G D, Scarpati G D, Buonerba C. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: a comprehensive review of current and future therapeutic options. World J Clin Oncol. 2011;2(3):150–7.10.5306/wjco.v2.i3.150Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Li T, Mo X, Fu L, Xiao B, Guo J. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs on gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(8):8601–12.10.18632/oncotarget.6926Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Zhang H, Cai Y, Zheng L, Zhang Z, Lin X, Jiang N. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 regulate papillary thyroid cancer progression by modulating miR-129-5p/KLK7 expression. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(10):6638–48.10.1002/jcp.26425Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Lu W, Xu Y, Xu J, Wang Z, Ye G. Identification of differential expressed lncRNAs in human thyroid cancer by a genome-wide analyses. Cancer Med. 2018;7(8):3935–44.10.1002/cam4.1627Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(12):861–74.10.1038/nrg3074Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Yin JJ, Cheng XY. MicroRNA-23a inhibits the growth of papillary thyroid carcinoma via regulating cyclin G1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(8):3431–9.Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Li M, Shen Y, Wang Q, Zhou X. MiR-204-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits migration of osteosarcoma via targeting EBF2. Biochimie. 2019;158:224–32.10.1016/j.biochi.2018.12.003Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Di X, He G, Chen H, Zhu C, Qin Q, Yan J, et al. High-mobility group box 1 protein modulated proliferation and radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(4):728–35.10.1111/jgh.14371Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Chang HY, Chen SY, Wu CH, Lu CC. Glycyrrhizin attenuates the process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by modulating HMGB1 initiated novel signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(12):3323–32.10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00251Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Jiang H, Hu X, Zhang H, Li W. Down-regulation of LncRNA TUG1 enhances radiosensitivity in bladder cancer via suppressing HMGB1 expression. Radiat Oncol. 2017;12(1):65.10.1186/s13014-017-0802-3Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Ma Y, Kang S, Wu X, Han B, Jin Z, Guo Z. Up-regulated HMGB1 in the pleural effusion of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients reduces the chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells. Tumori. 2018;104(5):338–43.10.5301/tj.5000656Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Wang S, Chen Y, Yu X, Lu Y, Wang H, Wu F, et al. miR-129-5p attenuates cell proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition via HMGB1 in gastric cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215(4):676–82.10.1016/j.prp.2018.12.024Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Wu Q, Meng WY, Jie Y, Zhao H. LncRNA MALAT1 induces colon cancer development by regulating miR-129-5p/HMGB1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6750–7.10.1002/jcp.26383Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Ding C, Yu H, Shi C, Shi T, Qin H, Cui Y. MiR-let-7e inhibits invasion and magration and regulates HMGB1 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:528–36.10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.057Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Guan X, Wang P, Chi J, Zhao S, Wang F. Relationships of BRAF mutation and HMGB1 to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;486(4):898–903.10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.117Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Tracy KM, Tye CE, Ghule PN, Malaby HLH, Stumpff J, Stein JL, et al. Mitotically-associated lncRNA (MANCR) affects genomic stability and cell division in aggressive breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16(4):587–98.10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0548Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Hong BS, Ryu HS, Kim N. Tumor suppressor miRNA-204-5p regulates growth, metastasis, and immune microenvironment remodeling in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79(7):1520–34.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0891Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Liu L, Wang J, Li X, Ma J, Shi C, Zhu H, et al. MiR-204-5p suppresses cell proliferation by inhibiting IGFBP5 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457(4):621–6.10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.037Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Tian L, Wang ZY, Hao J, Zhang XY. miR-505 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer progression through targeting HMGB1. J Cell Biochem. 2018;120(5):8044–52.10.1002/jcb.28082Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2020 Yihui Lin and Jianjia Jiang, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Plant Sciences
- Dependence of the heterosis effect on genetic distance, determined using various molecular markers
- Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) Regulated Phyto and Microbial Beneficial Protein Interactions
- Role of strigolactones: Signalling and crosstalk with other phytohormones
- An efficient protocol for regenerating shoots from paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera) leaf explants
- Functional divergence and adaptive selection of KNOX gene family in plants
- In silico identification of Capsicum type III polyketide synthase genes and expression patterns in Capsicum annuum
- In vitro induction and characterisation of tetraploid drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.)
- CRISPR/Cas9 or prime editing? – It depends on…
- Study on the optimal antagonistic effect of a bacterial complex against Monilinia fructicola in peach
- Natural variation in stress response induced by low CO2 in Arabidopsis thaliana
- The complete mitogenome sequence of the coral lily (Lilium pumilum) and the Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii) in China
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Use of phosphatase and dehydrogenase activities in the assessment of calcium peroxide and citric acid effects in soil contaminated with petrol
- Analysis of ethanol dehydration using membrane separation processes
- Activity of Vip3Aa1 against Periplaneta americana
- Thermostable cellulase biosynthesis from Paenibacillus alvei and its utilization in lactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
- Spatiotemporal dynamics of terrestrial invertebrate assemblages in the riparian zone of the Wewe river, Ashanti region, Ghana
- Antifungal activity of selected volatile essential oils against Penicillium sp.
- Toxic effect of three imidazole ionic liquids on two terrestrial plants
- Biosurfactant production by a Bacillus megaterium strain
- Distribution and density of Lutraria rhynchaena Jonas, 1844 relate to sediment while reproduction shows multiple peaks per year in Cat Ba-Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
- Biomedical Sciences
- Treatment of Epilepsy Associated with Common Chromosomal Developmental Diseases
- A Mouse Model for Studying Stem Cell Effects on Regeneration of Hair Follicle Outer Root Sheaths
- Morphine modulates hippocampal neurogenesis and contextual memory extinction via miR-34c/Notch1 pathway in male ICR mice
- Composition, Anticholinesterase and Antipedicular Activities of Satureja capitata L. Volatile Oil
- Weight loss may be unrelated to dietary intake in the imiquimod-induced plaque psoriasis mice model
- Construction of recombinant lentiviral vector containing human stem cell leukemia gene and its expression in interstitial cells of cajal
- Knockdown of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 inhibits glioma progression by regulating miR-338-3p/RRM2
- Protective effect of asiaticoside on radiation-induced proliferation inhibition and DNA damage of fibroblasts and mice death
- Prevalence of dyslipidemia in Tibetan monks from Gansu Province, Northwest China
- Sevoflurane inhibits proliferation, invasion, but enhances apoptosis of lung cancer cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling via regulating lncRNA PCAT6/ miR-326 axis
- MiR-542-3p suppresses neuroblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by downregulation of KDM1A and ZNF346
- Calcium Phosphate Cement Causes Nucleus Pulposus Cell Degeneration Through the ERK Signaling Pathway
- Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Exhibit Osteogenic Differentiation Potential
- MiR-489-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induces apoptosis, by targeting the BDNF-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway in glioblastoma
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown hinders the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by regulating the microRNA-34a-5p/NOTCH1 signaling pathway
- Large Brunner’s gland adenoma of the duodenum for almost 10 years
- Neurotrophin-3 accelerates reendothelialization through inducing EPC mobilization and homing
- Hepatoprotective effects of chamazulene against alcohol-induced liver damage by alleviation of oxidative stress in rat models
- FXYD6 overexpression in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis
- Risk factors for elevated serum colorectal cancer markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Effect of hepatic sympathetic nerve removal on energy metabolism in an animal model of cognitive impairment and its relationship to Glut2 expression
- Progress in research on the role of fibrinogen in lung cancer
- Advanced glycation end product levels were correlated with inflammation and carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes patients
- MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB
- Knockdown of DDX46 inhibits trophoblast cell proliferation and migration through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in preeclampsia
- Buformin suppresses osteosarcoma via targeting AMPK signaling pathway
- Effect of FibroScan test in antiviral therapy for HBV-infected patients with ALT <2 upper limit of normal
- LncRNA SNHG15 regulates osteosarcoma progression in vitro and in vivo via sponging miR-346 and regulating TRAF4 expression
- LINC00202 promotes retinoblastoma progression by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and aerobic glycolysis through miR-204-5p/HMGCR axis
- Coexisting flavonoids and administration route effect on pharmacokinetics of Puerarin in MCAO rats
- GeneXpert Technology for the diagnosis of HIV-associated tuberculosis: Is scale-up worth it?
- Circ_001569 regulates FLOT2 expression to promote the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of osteosarcoma cells through sponging miR-185-5p
- Lnc-PICSAR contributes to cisplatin resistance by miR-485-5p/REV3L axis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells
- MYL6B drives the capabilities of proliferation, invasion, and migration in rectal adenocarcinoma through the EMT process
- Inhibition of lncRNA LINC00461/miR-216a/aquaporin 4 pathway suppresses cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance in glioma
- Upregulation of miR-150-5p alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis of RAW264.7 macrophages by targeting Notch1
- Long non-coding RNA LINC00704 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma via miR-204-5p/HMGB1 axis
- Neuroanatomy of melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in the mouse brain
- Lipopolysaccharides promote pulmonary fibrosis in silicosis through the aggravation of apoptosis and inflammation in alveolar macrophages
- Influences of advanced glycosylation end products on the inner blood–retinal barrier in a co-culture cell model in vitro
- MiR-4328 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and induces apoptosis in keloid fibroblasts by targeting BCL2 expression
- Aberrant expression of microRNA-132-3p and microRNA-146a-5p in Parkinson’s disease patients
- Long non-coding RNA SNHG3 accelerates progression in glioma by modulating miR-384/HDGF axis
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediates MPTP/MPP+-induced apoptosis via regulating the miR-124/KLF4 axis in Parkinson’s disease
- PCR-detectable Candida DNA exists a short period in the blood of systemic candidiasis murine model
- CircHIPK3/miR-381-3p axis modulates proliferation, migration, and glycolysis of lung cancer cells by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Reversine and herbal Xiang–Sha–Liu–Jun–Zi decoction ameliorate thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury by regulating the RelA/NF-κB/caspase signaling pathway
- Therapeutic effects of coronary granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on rats with chronic ischemic heart disease
- The effects of yam gruel on lowering fasted blood glucose in T2DM rats
- Circ_0084043 promotes cell proliferation and glycolysis but blocks cell apoptosis in melanoma via circ_0084043-miR-31-KLF3 axis
- CircSAMD4A contributes to cell doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma by regulating the miR-218-5p/KLF8 axis
- Relationship of FTO gene variations with NAFLD risk in Chinese men
- The prognostic and predictive value of platelet parameters in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- LncRNA SNHG15 contributes to doxorubicin resistance of osteosarcoma cells through targeting the miR-381-3p/GFRA1 axis
- miR-339-3p regulated acute pancreatitis induced by caerulein through targeting TNF receptor-associated factor 3 in AR42J cells
- LncRNA RP1-85F18.6 affects osteoblast cells by regulating the cell cycle
- MiR-203-3p inhibits the oxidative stress, inflammatory responses and apoptosis of mice podocytes induced by high glucose through regulating Sema3A expression
- MiR-30c-5p/ROCK2 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and EMT via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in HG-induced HK-2 cells
- CTRP9 protects against MIA-induced inflammation and knee cartilage damage by deactivating the MAPK/NF-κB pathway in rats with osteoarthritis
- Relationship between hemodynamic parameters and portal venous pressure in cirrhosis patients with portal hypertension
- Long noncoding RNA FTX ameliorates hydrogen peroxide-induced cardiomyocyte injury by regulating the miR-150/KLF13 axis
- Ropivacaine inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion while inducing apoptosis of glioma cells by regulating the SNHG16/miR-424-5p axis
- CD11b is involved in coxsackievirus B3-induced viral myocarditis in mice by inducing Th17 cells
- Decitabine shows anti-acute myeloid leukemia potential via regulating the miR-212-5p/CCNT2 axis
- Testosterone aggravates cerebral vascular injury by reducing plasma HDL levels
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- PL/Vancomycin/Nano-hydroxyapatite Sustained-release Material to Treat Infectious Bone Defect
- The thickness of surface grafting layer on bio-materials directly mediates the immuno-reacitivity of macrophages in vitro
- Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation and biomedical applications
- Food Science
- Bread making potential of Triticum aestivum and Triticum spelta species
- Modeling the effect of heat treatment on fatty acid composition in home-made olive oil preparations
- Effect of addition of dried potato pulp on selected quality characteristics of shortcrust pastry cookies
- Preparation of konjac oligoglucomannans with different molecular weights and their in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities
- Animal Sciences
- Changes in the fecal microbiome of the Yangtze finless porpoise during a short-term therapeutic treatment
- Agriculture
- Influence of inoculation with Lactobacillus on fermentation, production of 1,2-propanediol and 1-propanol as well as Maize silage aerobic stability
- Application of extrusion-cooking technology in hatchery waste management
- In-field screening for host plant resistance to Delia radicum and Brevicoryne brassicae within selected rapeseed cultivars and new interspecific hybrids
- Studying of the promotion mechanism of Bacillus subtilis QM3 on wheat seed germination based on β-amylase
- Rapid visual detection of FecB gene expression in sheep
- Effects of Bacillus megaterium on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, antioxidant capacity, and immune function in suckling calves
- Effects of center pivot sprinkler fertigation on the yield of continuously cropped soybean
- Special Issue On New Approach To Obtain Bioactive Compounds And New Metabolites From Agro-Industrial By-Products
- Technological and antioxidant properties of proteins obtained from waste potato juice
- The aspects of microbial biomass use in the utilization of selected waste from the agro-food industry
- Special Issue on Computing and Artificial Techniques for Life Science Applications - Part I
- Automatic detection and segmentation of adenomatous colorectal polyps during colonoscopy using Mask R-CNN
- The impedance analysis of small intestine fusion by pulse source
- Errata
- Erratum to “Diagnostic performance of serum CK-MB, TNF-α and hs-CRP in children with viral myocarditis”
- Erratum to “MYL6B drives the capabilities of proliferation, invasion, and migration in rectal adenocarcinoma through the EMT process”
- Erratum to “Thermostable cellulase biosynthesis from Paenibacillus alvei and its utilization in lactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation”
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Plant Sciences
- Dependence of the heterosis effect on genetic distance, determined using various molecular markers
- Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) Regulated Phyto and Microbial Beneficial Protein Interactions
- Role of strigolactones: Signalling and crosstalk with other phytohormones
- An efficient protocol for regenerating shoots from paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera) leaf explants
- Functional divergence and adaptive selection of KNOX gene family in plants
- In silico identification of Capsicum type III polyketide synthase genes and expression patterns in Capsicum annuum
- In vitro induction and characterisation of tetraploid drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.)
- CRISPR/Cas9 or prime editing? – It depends on…
- Study on the optimal antagonistic effect of a bacterial complex against Monilinia fructicola in peach
- Natural variation in stress response induced by low CO2 in Arabidopsis thaliana
- The complete mitogenome sequence of the coral lily (Lilium pumilum) and the Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii) in China
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Use of phosphatase and dehydrogenase activities in the assessment of calcium peroxide and citric acid effects in soil contaminated with petrol
- Analysis of ethanol dehydration using membrane separation processes
- Activity of Vip3Aa1 against Periplaneta americana
- Thermostable cellulase biosynthesis from Paenibacillus alvei and its utilization in lactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
- Spatiotemporal dynamics of terrestrial invertebrate assemblages in the riparian zone of the Wewe river, Ashanti region, Ghana
- Antifungal activity of selected volatile essential oils against Penicillium sp.
- Toxic effect of three imidazole ionic liquids on two terrestrial plants
- Biosurfactant production by a Bacillus megaterium strain
- Distribution and density of Lutraria rhynchaena Jonas, 1844 relate to sediment while reproduction shows multiple peaks per year in Cat Ba-Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
- Biomedical Sciences
- Treatment of Epilepsy Associated with Common Chromosomal Developmental Diseases
- A Mouse Model for Studying Stem Cell Effects on Regeneration of Hair Follicle Outer Root Sheaths
- Morphine modulates hippocampal neurogenesis and contextual memory extinction via miR-34c/Notch1 pathway in male ICR mice
- Composition, Anticholinesterase and Antipedicular Activities of Satureja capitata L. Volatile Oil
- Weight loss may be unrelated to dietary intake in the imiquimod-induced plaque psoriasis mice model
- Construction of recombinant lentiviral vector containing human stem cell leukemia gene and its expression in interstitial cells of cajal
- Knockdown of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 inhibits glioma progression by regulating miR-338-3p/RRM2
- Protective effect of asiaticoside on radiation-induced proliferation inhibition and DNA damage of fibroblasts and mice death
- Prevalence of dyslipidemia in Tibetan monks from Gansu Province, Northwest China
- Sevoflurane inhibits proliferation, invasion, but enhances apoptosis of lung cancer cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling via regulating lncRNA PCAT6/ miR-326 axis
- MiR-542-3p suppresses neuroblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by downregulation of KDM1A and ZNF346
- Calcium Phosphate Cement Causes Nucleus Pulposus Cell Degeneration Through the ERK Signaling Pathway
- Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Exhibit Osteogenic Differentiation Potential
- MiR-489-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induces apoptosis, by targeting the BDNF-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway in glioblastoma
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown hinders the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by regulating the microRNA-34a-5p/NOTCH1 signaling pathway
- Large Brunner’s gland adenoma of the duodenum for almost 10 years
- Neurotrophin-3 accelerates reendothelialization through inducing EPC mobilization and homing
- Hepatoprotective effects of chamazulene against alcohol-induced liver damage by alleviation of oxidative stress in rat models
- FXYD6 overexpression in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis
- Risk factors for elevated serum colorectal cancer markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Effect of hepatic sympathetic nerve removal on energy metabolism in an animal model of cognitive impairment and its relationship to Glut2 expression
- Progress in research on the role of fibrinogen in lung cancer
- Advanced glycation end product levels were correlated with inflammation and carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes patients
- MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB
- Knockdown of DDX46 inhibits trophoblast cell proliferation and migration through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in preeclampsia
- Buformin suppresses osteosarcoma via targeting AMPK signaling pathway
- Effect of FibroScan test in antiviral therapy for HBV-infected patients with ALT <2 upper limit of normal
- LncRNA SNHG15 regulates osteosarcoma progression in vitro and in vivo via sponging miR-346 and regulating TRAF4 expression
- LINC00202 promotes retinoblastoma progression by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and aerobic glycolysis through miR-204-5p/HMGCR axis
- Coexisting flavonoids and administration route effect on pharmacokinetics of Puerarin in MCAO rats
- GeneXpert Technology for the diagnosis of HIV-associated tuberculosis: Is scale-up worth it?
- Circ_001569 regulates FLOT2 expression to promote the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of osteosarcoma cells through sponging miR-185-5p
- Lnc-PICSAR contributes to cisplatin resistance by miR-485-5p/REV3L axis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells
- MYL6B drives the capabilities of proliferation, invasion, and migration in rectal adenocarcinoma through the EMT process
- Inhibition of lncRNA LINC00461/miR-216a/aquaporin 4 pathway suppresses cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance in glioma
- Upregulation of miR-150-5p alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis of RAW264.7 macrophages by targeting Notch1
- Long non-coding RNA LINC00704 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma via miR-204-5p/HMGB1 axis
- Neuroanatomy of melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in the mouse brain
- Lipopolysaccharides promote pulmonary fibrosis in silicosis through the aggravation of apoptosis and inflammation in alveolar macrophages
- Influences of advanced glycosylation end products on the inner blood–retinal barrier in a co-culture cell model in vitro
- MiR-4328 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and induces apoptosis in keloid fibroblasts by targeting BCL2 expression
- Aberrant expression of microRNA-132-3p and microRNA-146a-5p in Parkinson’s disease patients
- Long non-coding RNA SNHG3 accelerates progression in glioma by modulating miR-384/HDGF axis
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediates MPTP/MPP+-induced apoptosis via regulating the miR-124/KLF4 axis in Parkinson’s disease
- PCR-detectable Candida DNA exists a short period in the blood of systemic candidiasis murine model
- CircHIPK3/miR-381-3p axis modulates proliferation, migration, and glycolysis of lung cancer cells by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Reversine and herbal Xiang–Sha–Liu–Jun–Zi decoction ameliorate thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury by regulating the RelA/NF-κB/caspase signaling pathway
- Therapeutic effects of coronary granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on rats with chronic ischemic heart disease
- The effects of yam gruel on lowering fasted blood glucose in T2DM rats
- Circ_0084043 promotes cell proliferation and glycolysis but blocks cell apoptosis in melanoma via circ_0084043-miR-31-KLF3 axis
- CircSAMD4A contributes to cell doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma by regulating the miR-218-5p/KLF8 axis
- Relationship of FTO gene variations with NAFLD risk in Chinese men
- The prognostic and predictive value of platelet parameters in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- LncRNA SNHG15 contributes to doxorubicin resistance of osteosarcoma cells through targeting the miR-381-3p/GFRA1 axis
- miR-339-3p regulated acute pancreatitis induced by caerulein through targeting TNF receptor-associated factor 3 in AR42J cells
- LncRNA RP1-85F18.6 affects osteoblast cells by regulating the cell cycle
- MiR-203-3p inhibits the oxidative stress, inflammatory responses and apoptosis of mice podocytes induced by high glucose through regulating Sema3A expression
- MiR-30c-5p/ROCK2 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and EMT via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in HG-induced HK-2 cells
- CTRP9 protects against MIA-induced inflammation and knee cartilage damage by deactivating the MAPK/NF-κB pathway in rats with osteoarthritis
- Relationship between hemodynamic parameters and portal venous pressure in cirrhosis patients with portal hypertension
- Long noncoding RNA FTX ameliorates hydrogen peroxide-induced cardiomyocyte injury by regulating the miR-150/KLF13 axis
- Ropivacaine inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion while inducing apoptosis of glioma cells by regulating the SNHG16/miR-424-5p axis
- CD11b is involved in coxsackievirus B3-induced viral myocarditis in mice by inducing Th17 cells
- Decitabine shows anti-acute myeloid leukemia potential via regulating the miR-212-5p/CCNT2 axis
- Testosterone aggravates cerebral vascular injury by reducing plasma HDL levels
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- PL/Vancomycin/Nano-hydroxyapatite Sustained-release Material to Treat Infectious Bone Defect
- The thickness of surface grafting layer on bio-materials directly mediates the immuno-reacitivity of macrophages in vitro
- Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation and biomedical applications
- Food Science
- Bread making potential of Triticum aestivum and Triticum spelta species
- Modeling the effect of heat treatment on fatty acid composition in home-made olive oil preparations
- Effect of addition of dried potato pulp on selected quality characteristics of shortcrust pastry cookies
- Preparation of konjac oligoglucomannans with different molecular weights and their in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities
- Animal Sciences
- Changes in the fecal microbiome of the Yangtze finless porpoise during a short-term therapeutic treatment
- Agriculture
- Influence of inoculation with Lactobacillus on fermentation, production of 1,2-propanediol and 1-propanol as well as Maize silage aerobic stability
- Application of extrusion-cooking technology in hatchery waste management
- In-field screening for host plant resistance to Delia radicum and Brevicoryne brassicae within selected rapeseed cultivars and new interspecific hybrids
- Studying of the promotion mechanism of Bacillus subtilis QM3 on wheat seed germination based on β-amylase
- Rapid visual detection of FecB gene expression in sheep
- Effects of Bacillus megaterium on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, antioxidant capacity, and immune function in suckling calves
- Effects of center pivot sprinkler fertigation on the yield of continuously cropped soybean
- Special Issue On New Approach To Obtain Bioactive Compounds And New Metabolites From Agro-Industrial By-Products
- Technological and antioxidant properties of proteins obtained from waste potato juice
- The aspects of microbial biomass use in the utilization of selected waste from the agro-food industry
- Special Issue on Computing and Artificial Techniques for Life Science Applications - Part I
- Automatic detection and segmentation of adenomatous colorectal polyps during colonoscopy using Mask R-CNN
- The impedance analysis of small intestine fusion by pulse source
- Errata
- Erratum to “Diagnostic performance of serum CK-MB, TNF-α and hs-CRP in children with viral myocarditis”
- Erratum to “MYL6B drives the capabilities of proliferation, invasion, and migration in rectal adenocarcinoma through the EMT process”
- Erratum to “Thermostable cellulase biosynthesis from Paenibacillus alvei and its utilization in lactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation”

