Abstract
C11H14N2O3S, orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 10.1973(3) Å, b = 9.9487(4) Å, c = 23.1332(8) Å, V = 2346.86(14) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0527, wRref(F2) = 0.1407, T = 100 K.
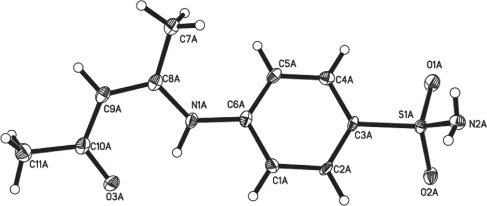
Tables 1–3 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless, plate, size 0.089×0.368×0.478 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.74 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω scans |
| 2θmax: | 49.98° |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique: | 21970, 2059 |
| N(param)refined: | 156 |
| Programs: | SHELX [14] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | Uiso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H(17) | 8c | −0.2775 | 0.4284 | −0.0090 | 0.017 |
| H(18) | 8c | −0.6073 | 0.1597 | −0.2580 | 0.017 |
| H(19) | 8c | −0.5368 | 0.2472 | −0.2726 | 0.017 |
| H(1) | 8c | −0.2720 | 0.4430 | −0.1086 | 0.017 |
| H(2) | 8c | −0.2971 | 0.3423 | −0.1981 | 0.016 |
| H(3) | 8c | −0.5016 | 0.0430 | −0.1234 | 0.017 |
| H(4) | 8c | −0.4749 | 0.1431 | −0.0342 | 0.018 |
| H(5) | 8c | −0.5989 | 0.3129 | 0.0114 | 0.028 |
| H(6) | 8c | −0.5944 | 0.3312 | 0.0786 | 0.028 |
| H(7) | 8c | −0.5268 | 0.2065 | 0.0499 | 0.028 |
| H(8) | 8c | −0.4344 | 0.4615 | 0.1173 | 0.018 |
| H(11A) | 8c | −0.1736 | 0.6917 | 0.1274 | 0.032 |
| H(11B) | 8c | −0.2184 | 0.5746 | 0.1682 | 0.032 |
| H(11C) | 8c | −0.3216 | 0.6780 | 0.1448 | 0.032 |
Fractional coordinates and atomic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S(1A) | 8c | −0.42093(6) | 0.10338(6) | −0.23726(3) | 0.0131(4) | 0.0107(4) | 0.0102(4) | 0.0015(2) | 0.0003(2) | −0.0015(2) |
| O(1A) | 8c | −0.4601(2) | −0.0326(2) | −0.22662(8) | 0.030(1) | 0.012(1) | 0.017(1) | 0.0000(8) | 0.0011(8) | −0.0011(8) |
| O(2A) | 8c | −0.3032(2) | 0.1289(2) | −0.26973(8) | 0.014(1) | 0.027(1) | 0.015(1) | 0.0015(9) | 0.0023(7) | −0.0057(8) |
| O(3A) | 8c | −0.1865(2) | 0.5425(2) | 0.04269(8) | 0.022(1) | 0.024(1) | 0.012(1) | −0.0040(8) | 0.0004(8) | 0.0023(8) |
| N(1A) | 8c | −0.3493(2) | 0.3724(2) | −0.00988(9) | 0.016(1) | 0.018(1) | 0.009(1) | 0.0001(9) | −0.0006(9) | −0.0014(9) |
| N(2A) | 8c | −0.5388(2) | 0.1725(2) | −0.27270(9) | 0.015(1) | 0.012(1) | 0.016(1) | 0.0002(9) | 0.0002(9) | −0.0001(9) |
| C(1A) | 8c | −0.3184(3) | 0.3628(3) | −0.1116(1) | 0.015(1) | 0.013(1) | 0.015(1) | −0.002(1) | 0.001(1) | −0.003(1) |
| C(2A) | 8c | −0.3329(2) | 0.3026(3) | −0.1653(1) | 0.016(1) | 0.017(1) | 0.008(1) | −0.000(1) | 0.005(1) | 0.000(1) |
| C(3A) | 8c | −0.4017(2) | 0.1820(3) | −0.1695(1) | 0.011(1) | 0.015(1) | 0.006(1) | 0.004(1) | −0.0013(9) | 0.001(1) |
| C(4A) | 8c | −0.4553(3) | 0.1232(3) | −0.1204(1) | 0.015(1) | 0.013(1) | 0.016(1) | 0.000(1) | −0.001(1) | 0.003(1) |
| C(5A) | 8c | −0.4399(3) | 0.1836(3) | −0.0670(1) | 0.017(1) | 0.017(1) | 0.010(1) | 0.003(1) | 0.001(1) | 0.005(1) |
| C(6A) | 8c | −0.3722(2) | 0.3052(3) | −0.0621(1) | 0.011(1) | 0.017(1) | 0.011(1) | 0.005(1) | −0.002(1) | −0.001(1) |
| C(7A) | 8c | −0.5467(3) | 0.3002(3) | 0.0455(1) | 0.019(1) | 0.022(2) | 0.015(2) | −0.000(1) | 0.003(1) | −0.003(1) |
| C(8A) | 8c | −0.4219(3) | 0.3783(3) | 0.0399(1) | 0.019(1) | 0.013(1) | 0.011(1) | 0.005(1) | −0.000(1) | 0.002(1) |
| C(9A) | 8c | −0.3822(3) | 0.4593(3) | 0.0843(1) | 0.018(1) | 0.017(1) | 0.010(1) | 0.004(1) | 0.000(1) | 0.002(1) |
| C(10A) | 8c | −0.2664(3) | 0.5412(3) | 0.0841(1) | 0.023(1) | 0.015(1) | 0.009(1) | 0.003(1) | −0.002(1) | 0.004(1) |
| C(11A) | 8c | −0.2429(3) | 0.6293(3) | 0.1358(1) | 0.027(2) | 0.019(2) | 0.018(2) | −0.001(1) | −0.003(1) | 0.001(1) |
Source of material
A solution of sulfanilamide (1.72 g, 0.01 mol) and acetylacetone (1.00 g, 0.01 mol) in methanol (10 mL) containing glacial acetic acid (1 mL) was refluxed for 8 h. The reaction mixture was filtered then, the filtered solid was crystallized from ethanol to give the title compound [13]. Yield: 91%; m.p. 206.9°C, IR, cm−1: 3361, 3283, 3193 (NH, NH2), 3091 (CH arom.); 2986, 2831 (CH aliph.), 1696 (C = O), 1376, 1165 (SO2). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, ppm): 2.0 [s, 3H, COCH3], 2.3 [s, 3H, CH3], 5.6 [s, 1H, CH], 6.5, 8.3 [2d, 4H, Ar—H, AB system, J = 7.3 Hz], 8.8 [s, 2H, NH, SO2NH2, D2O-exchangeable], 10.8 [s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchangeable]. 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, ppm): 18.6 (CH3), 26.3 (CH3C = O), 96.8 (CH), 113.7 (2), 129.8 (2), 131.6, 142.4, 160.7, 197.1 (C = O). Anal. calcd. for C11H14N2O3S (254.31): C, 51.95; H, 5.55; N, 11.02%; found: C, 51.72; H, 5.87; N, 10.77%.
Experimental details
Cell refinement and data reduction were carried out by Bruker SAINT [15]. The hydrogen atoms were placed on calculated positions with the help of the SHELX program (AFIX 3, 43 or 137 option) [14].
Discussion
Heterocyclic sulfonamide derivatives have shown good anticancer activity with variety of mechanisms including cell cycle perturbation at G1 phase, disruption of microtubules assembly and the well-known carbonic anhydrase inhibition activity with selectivity to the tumor associated isoforms hCA IX and hCA XII [1–5]. Combination of a 4-(4-oxopent-2-en-2-ylamino) scaffold with the biologically active sulfonamide moiety has received great attention as PI3 K inhibitor, which is an important enzyme controlling signal transduction [4, 6–8]. Recently, diaryl sulfone derivatives, that were synthesized from dapson have shown good cytotoxic activity on breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) [9]. As a continuation of our work to design and synthesize novel anticancer agents [6–12], we have designed and synthesized the title compound.
The aim of this work was to design and synthesize of (Z)-4-(4-oxopent-2-en-2-ylamino)benzenesulfonamide having a biologically active sulfonamide moiety. Thus, interaction of sulfanilamide with acetylacetone in absolute methanol and glacial acetic acid furnished the title compound. The structure of this compound was established on the basis of elemental analysis, IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR data and X-ray analysis.
The crystal structure of the title compound contains one molecule in the asymmetric unit (figure). In the title molecule C8A-C9A bond length is 1.367(4) Å, which is a typical C = C double bond. All geometric parameters are in the expected ranges. In the crystal structure the molecules are stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonds, of which O2A, O1A and N2A work as hydrogen bond acceptors and N2A and O1A work as hydrogen bond donors. These hydrogen bonding interactions lead to a layered structure parallel to the ab plane.
Funding source: King Saud University
Award Identifier / Grant number: RGP-VPP-302
Funding statement: The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding of this research through the Research Group Project no. RGP-VPP-302.
Acknowledgements:
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding of this research through the Research Group Project no. RGP-VPP-302.
References
1. Supuran, C. T.: Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 7 (2008) 168–181.10.1038/nrd2467Suche in Google Scholar
2. Supuran, C. T.; Scozzafava, A.: Carbonic anhydrases as targets for medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 (2007) 4336–4350.10.1016/j.bmc.2007.04.020Suche in Google Scholar
3. Supuran, C. T.; Scozzafava, A.; Casini, A.: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 23 (2003) 146–189.10.1002/med.10025Suche in Google Scholar
4. Knight, S. D.; Schmidt, S. J.: Smithkline Beecham Corporation, Quinoline derivatives as PI3 kinase inhibitors. US Patent: US 8138347, 2008.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Smart, B. E.: Fluorine substituent effects (on bioactivity). J. Fluor. Chem. 109 (2001) 3–11.10.1016/S0022-1139(01)00375-XSuche in Google Scholar
6. Al-Dosari, M. S.; Ghorab, M. M.; Alsaid, M. S.; Nissan, Y. M.: Discovering some novel 7-chloroquinolines carrying a biologically active benzenesulfonamide moiety as a new class of anticancer agents. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 61 (2013) 50–58.10.1248/cpb.c12-00812Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Al-Dosari, M. S.; Ghorab, M. M.; Alsaid, M. S.; Nissan, Y. M.; Ahmed, A. B.: Synthesis and anticancer activity of some novel trifluoromethylquinolines carrying a biologically active benzenesulfonamide moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 69 (2012) 373–383.10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.08.048Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Ghorab, M. M.; Ragab, F. A.; Heiba, H. I.; Nissan, Y. M.; Ghorab, W. M.: Novel brominated quinoline and pyrimidoquinoline derivatives as potential cytotoxic agents with synergistic effects of γ-radiation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35 (2012) 1335–1346.10.1007/s12272-012-0803-6Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Ghorab, M. M.; Alsaid, M. S.; Nissan, Y. M.: Dapson in heterocyclic chemistry, Part V: Synthesis, molecular docking and anticancer activity of some novel sulfonylbis-compounds carrying bologically active dihydropyridine, dihydroisoquinoline, 1,3-dithiolan, 1,3-dithian, acrylamide, pyrazole, pyrazolopyrimidine and benzochromene moieties. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 60 (2012) 1019–1028.10.1248/cpb.c12-00292Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Ghorab, M. M.; Ceruso, M.; Alsaid, M. S.; Nissan, Y. M.; Arafa, R. K.; Supuran, C. T.: Novel sulfonamides bearing pyrrole and pyrrolopyrimidine moieties as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: synthesis, cytotoxic activity and molecular modeling. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 87 (2014) 186–196.10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.09.059Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Ghorab, M. M.; Ceruso, M.; Alsaid, M. S.; Nissan, Y. M.; Supuran, C. T.: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: synthesis, molecular docking, cytotoxic and inhibition of the human carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II, IX, XII with novel benzenesulfonamides incorporating pyrrole, pyrrolopyrimidine and fused pyrrolopyrimidine moieties. Biooorg. Med. Chem. 22 (2014) 3684–3695.10.1016/j.bmc.2014.05.009Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Ghorab, M. M.; Alsaid, M. S.; Nissan, Y. M.: Anti-breast cancer of some novel pyrrole and pyrrolopyrimidine derivatives bearing a biologically active sulfonamide moiety. Life Sci. J. 10 (2013) 2170–2183.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Surjit, S. K.; Manojit, R.; Sachika, D. S.; Radhapiyari, D. W.; Singh, C. B.: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of in vitro antimicrobial activity of tri-n-butyltin (IV) complexes of para-azo-carboxylates derived from substituted anilines and 2,4-DNP. Main Group Chem. 14 (2015) 127–139.10.3233/MGC-140159Suche in Google Scholar
14. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
©2016 Mostafa M. Ghorab et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2,5-bis(4-pyridyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole-κ2N,N)(μ2-1,3-phenylenediacetato-κ3O,O′:O′′)cobalt(II)], C22H18CoN4O6
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(3-phenoxy-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(1-nitro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one)—acetonitrile (1:1), C6H5N11O6
- Crystal structure of potassium (E)-5-oxo-4-((5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4(5H)-yl)diazenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-1-ide – (E)-4,4-diazene-1,2-diylbis(2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one) – methanol (1/1/1), C9H11N16KO5
- Crystal structure of (N,N′-bis(2-(((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imino)methyl)phenyl)benzene-1,2-diamido-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)oxidovanadium(IV), C44H48N4OV
- Crystal structure of 5,5-bis(4-iodophenyl)-5H-cyclopenta[2,1-b:3,4-b′]dipyridine, C23H14I2N2
- Crystal structure of aquadichloridobis(1-((2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benotriazole-κN)mercury(II), C22H24Cl2HgN10O
- Crystal structure of 2-[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1H-benzimidazol-3-ium [2-(carboxymethyl)phenyl]acetate monohydrate, C26H24N4O5
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipiperidinium dichloride 0.12 hydrate, C10H22N2Cl2 · 0.12 H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua(μ2-4,4′(E)-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)nickel(II)] bis(6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-pyridine-4-carboxylate) pentahydrate, C26H42N4O15Ni
- Crystal structure of ethyl-5-amino-1-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C12H11N5O6
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(pyridin-2-olate-1-oxido-κ2O,O′)rhodium(I), C7H4NO4Rh
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea, C17H21ClN2S
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-chloropyridin-3-ylamino)methylene)malononitrile, C9H5ClN4
- Crystal structure of tetraaquabis(μ2-4-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O,O′)bis(4-chlorobenzoato-κO)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)distrontium(II), C52H40Cl4N4O12Sr2
- Crystal structure of 3-hydroxy-3-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one, C14H11NO2
- Crystal structures of bis(1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium) aquapentakis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)neodym(III) monohydrate, C24H22N9NdO17
- Crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1-tert-butyl 3-oxo-2-[phenyl(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)methyl]-1,2-pyrrolidinedicarboxylate, C24H34N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[diaquabis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato-κO1,κO2:κO3,κO4:κO5:κO6)-bis(μ2-4,4′-benzene-1,3-diylbis(4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)tricadmium(II)] tetrahydrate, C38H34Cd3N12O18
- Crystal structure of trans-dichlorido[1,3-bis(9-methyl-9H-fluoren-9-yl) benzimidazol-2-ylidene](pyridine)palladium(II) – a compound with anagostic CH–Pd interactions, C40H31Cl2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-5-(4-(tetrazol-1-id-5-yl)phenoxy)benzene-1,3-dicarboxyato-κ3O:O′:N)(4-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)propyl)pyridinium-κN)zinc(II)], C28H22ZnN6O5
- Crystal structure of 3,6-di-2-pyridinyl-4-pyridazine carbonitrile, C15H9N5
- Crystal structure of 5,5,9,13-tetramethyltetracyclo[10·2·1·01,10·04,9]pentadecane-3,7,14-triol, C20H34O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-7-methyl-5-oxo-4-phenyl-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C16H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of the poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)(μ3-carboxylatophenoxyacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′;O′′′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C21H16N2O6Pb
- Crystal structure of the poly[(μ4-biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) bis(μ3-8-(11-(oxysulfonyl)-4-silbenyl)-2-(oxysulfonyl)stilbene-κ4O:O′:O′′,O′′′) bis(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′) dipraseodymium(III)], C94H64N4O16Pr2S4
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-5-methoxy-7-(methoxymethoxy)-4-(3-methoxyphenoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C19H17IO7
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-carboxy-2,6-dimethylpyridinium-3-carboxylato-κO)tris(μ2-2,6-dimethylpyridinium-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)erbium(III)], C36H33ErN4O16
- This molecule targets at type 2 diabetes - a single crystal study on (2R,3S,5R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-5-[2-(methylsulfonyl)-2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazol-5(4H)-yl] tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-amine (Omarigliptin), C17H20F2N4O3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2,2′-benzene-1,2-diyldiacetato-κ2O:O′), (μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C22H19N5O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua(μ2-3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenoxy)benzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) dihydrate, C16H20O15Mn
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-sulfonyldipyridine, C10H8N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(E)-(2-chloro-6-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-1,2-dihydro-2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-one, C18H15ClFN3O
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O, O′)(triphenylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H19NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(2-(3-bromophenyl)-5-carboxy-1H-imidazol-4-carboxylato-κ2O,N) cobalt(II) trihydrate, C22H22Br2CoN4O13
- Crystal structure of 4-(pyridin-4-ylmethylsulfonyl)pyridine, C11H10N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolato-κ3S:S:N:N′)copper(I)], C2H3CuN4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaquabis(μ2-4,4′-sulfinyldipyridine-κ2N,N′)zinc(II)] diperchlorate dihydrate, C20H24N4O14S2Cl2Zn
- Crystal structure of (1-((1-benzylpyrrolidin-2-yl-κN)methyl)-3-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene–κC)dibromidopalladium(II), C18H25Br2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of pentacalcium tetranitridovanadate(V) mononitride based on a powder diffraction study, Ca5[VN4]N
- Crystal structure of ((1-((1-benzylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)-3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene)-κ2C,N)dichloridopalladium(II), C17H23Cl2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of 9-allyl-4,5-dichloro-12-cyano-9,10-dihydro-9,10-ethanoanthracen-12-yl acetate, C22H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(8-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenol, C18H19BrN2O5
- Crystal structure of 3-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-one, C11H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(3-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido-κ2N,N′)nickel(II) mono hydrate, C26H20Br4N8NiO3
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(2-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1-tert-butyl-2-((4-fluorophenyl)(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)methyl)-3-oxo-pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylate, C24H33FN2O7
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-fluorobenzoato-κ2O:O:O′) bis(μ2-2-fluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dinitrato-κ2O,O′ bis(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)diterbium(III), C52H32F4N6O14Tb2
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium 4-aminobenzenesulfonate 2/3 hydrate, C22H42N2O3S · 2/3 H2O
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium 4-aminobenzenesulfonate, C14H26N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(guanidinium) 3,3′-oxybis(6-carboxybenzoate), C18H20N6O9
- Crystal structure of N′-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C18H16N4O2
- Crystal structure of N′-(4-nitrobenzylidene)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C17H13N5O3
- Crystal structure of 5-((4-bromophenyl)(2-hydroxy-6-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl)methyl)-6-hydroxy-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C19H19BrN2O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(((cyclohexyl(phenyl)methylidene)amino)oxy)-2-hydroxy-N-(propan-2-yl)propan-1-aminium chloride, C19H31ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5-((2-hydroxy-6-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl)(phenyl)methyl)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C19H20N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4-bromophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9BrN2O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methylbenzoyl)pyrene, C24H16O
- Crystal structure of N-(5-bromo-4-(p-tolyl)thiazol-2-yl)-4-chlorobutanamide, C14H14BrClN2OS
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diphenylthiazol-2-amine, C15H12N2S
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-4-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ3N:O,O′)-lead(II)], C28H18O4N8Pb
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(4-oxopent-2-en-2-ylamino)benzenesulfonamide, C11H14N2O3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-methyl-1-(4-(2-methyl-2H-benzo[d] imidazol-1(7aH)-yl)butyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κ2N:N′)bis(μ3-5-tert-butylbenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)] tetrahydrate, C44H54Cd2N4O12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[aqua(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)bis(3′,5,5′-tricarboxybiphenyl-2-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)cadmium(II)], C42H28N2O17Cd
- Crystal structure of (2RS,3RS)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pentan-3-ol, C15H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of N′-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C19H19N5O
- Crystal structure of 3-(benzofuran-2-yl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1Hpyrazole-1-carbothioamide, C18H14FN3OS
- Crystal structure of ent-1β-acetoxy-7α,14α-di-hydroxy-7β,20-epoxykaur-16-en-15-one, C22H30O6
- Crystal structure of 1α,7β-dihydroxy-11β-acetoxy-ent-7β,20-epoxykaur-16-en-15-one, C22H30O6
- Crystal structure of 7β,14β,15β-trihydroxy-1α-acetoxy-7α,20-epoxy-ent-kaurane, C22H32O6
- Crystal structure of ent-1β,7α,11α-trihydroxy-7β,20-epoxykaur-16-en-15-one, C20H28O5
- Crystal structure of poly-[tetraaquabis(μ8-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-1κ3O4:O6:O8:2κ4O2:O2:O5:O5:3κ4O1:O3:O5:O7)(di-μ3-hydroxido)-pentazinc(II)] decahydrate, C20H34O32Zn5
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-methylthiazol-2-yl)-3-propylthiourea, C8H13N3S2
- Crystal structure of 2-((dimethylamino)methylene)-5,5-Dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione, C11H17NO2
- Crystal structure of poly[1,4-bis(2-methylbenzimidazol)butane-κ2N:N′)bis(4,4′-oxybis(benzoato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium] monohydrate, C48H38Cd2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(benzofuran-2-yl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)thiazole, C26H17ClFN3OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-isophthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)(μ2-1,4-\ bis((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II), C22H19N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(adipate-κ4O,O′:O′′, O′′′)(1,4-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II), C36H38N4O8Zn2
- Crystal structure of N-(2-(2-oxoindolin-4-yl)ethyl)-N-propylpropan-1-aminium tetraphenylborate, C40H45BN2O
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,3-dihydro-4-methyl-3-phenyl-2-thioxothiazol-5-yl)-1-ethanone, C12H11NOS2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-[(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-4-[(E)-(2,6-difluorobenzylidene)amino]-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C31H36F2N6S
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]-thiadiazole, C13H7ClN4S2
- Crystal structure of bis(ethanaminium) poly[bis(hexaselenido-κ2Se1,Se6)palladate(II)], C4H16N2PdSe12
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(benzofuran-2-yl)-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-4-phenylthiazole, C26H19N3OS
- Crystal structure of poly-[bis(μ3-5-hydroxyisophtalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)(μ2-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II)], C40H30N4O5Zn2
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ4-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetate-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)dizinc(II)], C44H38N4O8Zn2
- Crystal structure of 5,17-bis-cyano-25,26,27,28-tetrapropyloxy-calix[4]arene, C42H46N2O4
- Crystal structure of poly-[μ-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ3-5-hydroxyisophthalate(2–)-κ3O,O′:O′′)dicadmium(II)] monohydrate, C64H54N8O11Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly-[μ-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ4-4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)dicadmium(II)] monohydrate, C52H42N4O14Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly-[bis(μ4-adipato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-1,4-bis((2-ethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II)], C38H42N4O8Zn2
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-Bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C13H15BrO4
- Crystal structure of (2-(4-bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C13H17BrO3
- Crystal structure of 3-((1,3,5,7-tetraoxo-6-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-3,3a,4,4a,5,6,7,7a,8,8a-decahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindol-2(1H)-yl)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κN-trichloridocobalt(II) hemihydrate, C24H22Cl3CoN4O4.5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-4′,6′-dichloro-2,2′-[propane-1,3-diyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]-diphenol, C17H14Cl3N2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C17H13F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κO)bis(4,4′-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methylene)dibenzonitrile-κN)zinc(II), C48H32N10O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C10H8O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[aqua-(2-carboxy-5-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κO)(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C34H24N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C36H28N8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chloropropyl)piperidin-1-ium tetraphenylborate, C32H37BClN
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 5-(benzylamino)isophthalate, C17H17NO4
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 5-(dibenzylamino)isophthalate, C24H23NO4
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-phenylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C21H29N3S
- Crystal structure of (2,2′(cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(nitrilo(E)methylylidene))diphenolato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)dimethanolmanganese(III) bromide, C22H28BrMnN2O4
- Crystal structure of 3,5,7-tris(morpholinomethyl)tropolone·0.67 hydrate, C22H33N3O5·0.67H2O
- Crystal structure of biphenyl-2,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic acid – 4,4′-biphenyl-4,4′-diyldipyridine (3/2), C49H34N3O8
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-2,5-bis(4-pyridyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole-κ2N,N)(μ2-1,3-phenylenediacetato-κ3O,O′:O′′)cobalt(II)], C22H18CoN4O6
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(3-phenoxy-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(1-nitro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one)—acetonitrile (1:1), C6H5N11O6
- Crystal structure of potassium (E)-5-oxo-4-((5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4(5H)-yl)diazenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-1-ide – (E)-4,4-diazene-1,2-diylbis(2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one) – methanol (1/1/1), C9H11N16KO5
- Crystal structure of (N,N′-bis(2-(((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imino)methyl)phenyl)benzene-1,2-diamido-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)oxidovanadium(IV), C44H48N4OV
- Crystal structure of 5,5-bis(4-iodophenyl)-5H-cyclopenta[2,1-b:3,4-b′]dipyridine, C23H14I2N2
- Crystal structure of aquadichloridobis(1-((2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benotriazole-κN)mercury(II), C22H24Cl2HgN10O
- Crystal structure of 2-[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1H-benzimidazol-3-ium [2-(carboxymethyl)phenyl]acetate monohydrate, C26H24N4O5
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipiperidinium dichloride 0.12 hydrate, C10H22N2Cl2 · 0.12 H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua(μ2-4,4′(E)-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)nickel(II)] bis(6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-pyridine-4-carboxylate) pentahydrate, C26H42N4O15Ni
- Crystal structure of ethyl-5-amino-1-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C12H11N5O6
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(pyridin-2-olate-1-oxido-κ2O,O′)rhodium(I), C7H4NO4Rh
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea, C17H21ClN2S
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-chloropyridin-3-ylamino)methylene)malononitrile, C9H5ClN4
- Crystal structure of tetraaquabis(μ2-4-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O,O′)bis(4-chlorobenzoato-κO)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)distrontium(II), C52H40Cl4N4O12Sr2
- Crystal structure of 3-hydroxy-3-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one, C14H11NO2
- Crystal structures of bis(1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium) aquapentakis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)neodym(III) monohydrate, C24H22N9NdO17
- Crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1-tert-butyl 3-oxo-2-[phenyl(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)methyl]-1,2-pyrrolidinedicarboxylate, C24H34N2O7
- Crystal structure of poly[diaquabis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato-κO1,κO2:κO3,κO4:κO5:κO6)-bis(μ2-4,4′-benzene-1,3-diylbis(4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)tricadmium(II)] tetrahydrate, C38H34Cd3N12O18
- Crystal structure of trans-dichlorido[1,3-bis(9-methyl-9H-fluoren-9-yl) benzimidazol-2-ylidene](pyridine)palladium(II) – a compound with anagostic CH–Pd interactions, C40H31Cl2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-5-(4-(tetrazol-1-id-5-yl)phenoxy)benzene-1,3-dicarboxyato-κ3O:O′:N)(4-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)propyl)pyridinium-κN)zinc(II)], C28H22ZnN6O5
- Crystal structure of 3,6-di-2-pyridinyl-4-pyridazine carbonitrile, C15H9N5
- Crystal structure of 5,5,9,13-tetramethyltetracyclo[10·2·1·01,10·04,9]pentadecane-3,7,14-triol, C20H34O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-7-methyl-5-oxo-4-phenyl-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C16H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of the poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)(μ3-carboxylatophenoxyacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′;O′′′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C21H16N2O6Pb
- Crystal structure of the poly[(μ4-biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) bis(μ3-8-(11-(oxysulfonyl)-4-silbenyl)-2-(oxysulfonyl)stilbene-κ4O:O′:O′′,O′′′) bis(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′) dipraseodymium(III)], C94H64N4O16Pr2S4
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-5-methoxy-7-(methoxymethoxy)-4-(3-methoxyphenoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C19H17IO7
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-carboxy-2,6-dimethylpyridinium-3-carboxylato-κO)tris(μ2-2,6-dimethylpyridinium-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)erbium(III)], C36H33ErN4O16
- This molecule targets at type 2 diabetes - a single crystal study on (2R,3S,5R)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-5-[2-(methylsulfonyl)-2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazol-5(4H)-yl] tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-amine (Omarigliptin), C17H20F2N4O3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2,2′-benzene-1,2-diyldiacetato-κ2O:O′), (μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C22H19N5O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua(μ2-3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenoxy)benzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) dihydrate, C16H20O15Mn
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-sulfonyldipyridine, C10H8N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(E)-(2-chloro-6-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-1,2-dihydro-2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-one, C18H15ClFN3O
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O, O′)(triphenylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C24H19NO3PRh
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(2-(3-bromophenyl)-5-carboxy-1H-imidazol-4-carboxylato-κ2O,N) cobalt(II) trihydrate, C22H22Br2CoN4O13
- Crystal structure of 4-(pyridin-4-ylmethylsulfonyl)pyridine, C11H10N2O2S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolato-κ3S:S:N:N′)copper(I)], C2H3CuN4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaquabis(μ2-4,4′-sulfinyldipyridine-κ2N,N′)zinc(II)] diperchlorate dihydrate, C20H24N4O14S2Cl2Zn
- Crystal structure of (1-((1-benzylpyrrolidin-2-yl-κN)methyl)-3-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene–κC)dibromidopalladium(II), C18H25Br2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of pentacalcium tetranitridovanadate(V) mononitride based on a powder diffraction study, Ca5[VN4]N
- Crystal structure of ((1-((1-benzylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)-3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene)-κ2C,N)dichloridopalladium(II), C17H23Cl2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of 9-allyl-4,5-dichloro-12-cyano-9,10-dihydro-9,10-ethanoanthracen-12-yl acetate, C22H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(8-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenol, C18H19BrN2O5
- Crystal structure of 3-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-one, C11H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(3-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido-κ2N,N′)nickel(II) mono hydrate, C26H20Br4N8NiO3
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(2-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1-tert-butyl-2-((4-fluorophenyl)(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)methyl)-3-oxo-pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylate, C24H33FN2O7
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-fluorobenzoato-κ2O:O:O′) bis(μ2-2-fluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)dinitrato-κ2O,O′ bis(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)diterbium(III), C52H32F4N6O14Tb2
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium 4-aminobenzenesulfonate 2/3 hydrate, C22H42N2O3S · 2/3 H2O
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium 4-aminobenzenesulfonate, C14H26N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(guanidinium) 3,3′-oxybis(6-carboxybenzoate), C18H20N6O9
- Crystal structure of N′-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C18H16N4O2
- Crystal structure of N′-(4-nitrobenzylidene)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C17H13N5O3
- Crystal structure of 5-((4-bromophenyl)(2-hydroxy-6-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl)methyl)-6-hydroxy-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C19H19BrN2O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(((cyclohexyl(phenyl)methylidene)amino)oxy)-2-hydroxy-N-(propan-2-yl)propan-1-aminium chloride, C19H31ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5-((2-hydroxy-6-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl)(phenyl)methyl)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C19H20N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4-bromophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9BrN2O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methylbenzoyl)pyrene, C24H16O
- Crystal structure of N-(5-bromo-4-(p-tolyl)thiazol-2-yl)-4-chlorobutanamide, C14H14BrClN2OS
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diphenylthiazol-2-amine, C15H12N2S
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-4-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ3N:O,O′)-lead(II)], C28H18O4N8Pb
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(4-oxopent-2-en-2-ylamino)benzenesulfonamide, C11H14N2O3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-methyl-1-(4-(2-methyl-2H-benzo[d] imidazol-1(7aH)-yl)butyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κ2N:N′)bis(μ3-5-tert-butylbenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)] tetrahydrate, C44H54Cd2N4O12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[aqua(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)bis(3′,5,5′-tricarboxybiphenyl-2-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)cadmium(II)], C42H28N2O17Cd
- Crystal structure of (2RS,3RS)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pentan-3-ol, C15H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of N′-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C19H19N5O
- Crystal structure of 3-(benzofuran-2-yl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1Hpyrazole-1-carbothioamide, C18H14FN3OS
- Crystal structure of ent-1β-acetoxy-7α,14α-di-hydroxy-7β,20-epoxykaur-16-en-15-one, C22H30O6
- Crystal structure of 1α,7β-dihydroxy-11β-acetoxy-ent-7β,20-epoxykaur-16-en-15-one, C22H30O6
- Crystal structure of 7β,14β,15β-trihydroxy-1α-acetoxy-7α,20-epoxy-ent-kaurane, C22H32O6
- Crystal structure of ent-1β,7α,11α-trihydroxy-7β,20-epoxykaur-16-en-15-one, C20H28O5
- Crystal structure of poly-[tetraaquabis(μ8-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-1κ3O4:O6:O8:2κ4O2:O2:O5:O5:3κ4O1:O3:O5:O7)(di-μ3-hydroxido)-pentazinc(II)] decahydrate, C20H34O32Zn5
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-methylthiazol-2-yl)-3-propylthiourea, C8H13N3S2
- Crystal structure of 2-((dimethylamino)methylene)-5,5-Dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione, C11H17NO2
- Crystal structure of poly[1,4-bis(2-methylbenzimidazol)butane-κ2N:N′)bis(4,4′-oxybis(benzoato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium] monohydrate, C48H38Cd2N4O10
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(benzofuran-2-yl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)thiazole, C26H17ClFN3OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-isophthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)(μ2-1,4-\ bis((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II), C22H19N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(adipate-κ4O,O′:O′′, O′′′)(1,4-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II), C36H38N4O8Zn2
- Crystal structure of N-(2-(2-oxoindolin-4-yl)ethyl)-N-propylpropan-1-aminium tetraphenylborate, C40H45BN2O
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,3-dihydro-4-methyl-3-phenyl-2-thioxothiazol-5-yl)-1-ethanone, C12H11NOS2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-[(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-4-[(E)-(2,6-difluorobenzylidene)amino]-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C31H36F2N6S
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]-thiadiazole, C13H7ClN4S2
- Crystal structure of bis(ethanaminium) poly[bis(hexaselenido-κ2Se1,Se6)palladate(II)], C4H16N2PdSe12
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(benzofuran-2-yl)-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-4-phenylthiazole, C26H19N3OS
- Crystal structure of poly-[bis(μ3-5-hydroxyisophtalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)(μ2-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II)], C40H30N4O5Zn2
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ4-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetate-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)dizinc(II)], C44H38N4O8Zn2
- Crystal structure of 5,17-bis-cyano-25,26,27,28-tetrapropyloxy-calix[4]arene, C42H46N2O4
- Crystal structure of poly-[μ-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ3-5-hydroxyisophthalate(2–)-κ3O,O′:O′′)dicadmium(II)] monohydrate, C64H54N8O11Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly-[μ-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ4-4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)dicadmium(II)] monohydrate, C52H42N4O14Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly-[bis(μ4-adipato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-1,4-bis((2-ethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)dizinc(II)], C38H42N4O8Zn2
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-Bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C13H15BrO4
- Crystal structure of (2-(4-bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C13H17BrO3
- Crystal structure of 3-((1,3,5,7-tetraoxo-6-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-3,3a,4,4a,5,6,7,7a,8,8a-decahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindol-2(1H)-yl)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κN-trichloridocobalt(II) hemihydrate, C24H22Cl3CoN4O4.5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-4′,6′-dichloro-2,2′-[propane-1,3-diyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]-diphenol, C17H14Cl3N2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C17H13F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κO)bis(4,4′-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methylene)dibenzonitrile-κN)zinc(II), C48H32N10O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C10H8O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[aqua-(2-carboxy-5-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κO)(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C34H24N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C36H28N8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chloropropyl)piperidin-1-ium tetraphenylborate, C32H37BClN
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 5-(benzylamino)isophthalate, C17H17NO4
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 5-(dibenzylamino)isophthalate, C24H23NO4
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-phenylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C21H29N3S
- Crystal structure of (2,2′(cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(nitrilo(E)methylylidene))diphenolato-κ4O,O′,N,N′)dimethanolmanganese(III) bromide, C22H28BrMnN2O4
- Crystal structure of 3,5,7-tris(morpholinomethyl)tropolone·0.67 hydrate, C22H33N3O5·0.67H2O
- Crystal structure of biphenyl-2,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic acid – 4,4′-biphenyl-4,4′-diyldipyridine (3/2), C49H34N3O8


