Abstract
C9H8BrF2NO2S, triclinic, P1̅ (no. 2), a = 7.5277(6) Å, b = 8.3730(7) Å, c = 9.8785(9) Å, α = 92.637(3)°, β = 111.201°, γ = 105.856(2)°, V = 551.08(8) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0330, wRref(F2) = 0.0787, T = 273 K.
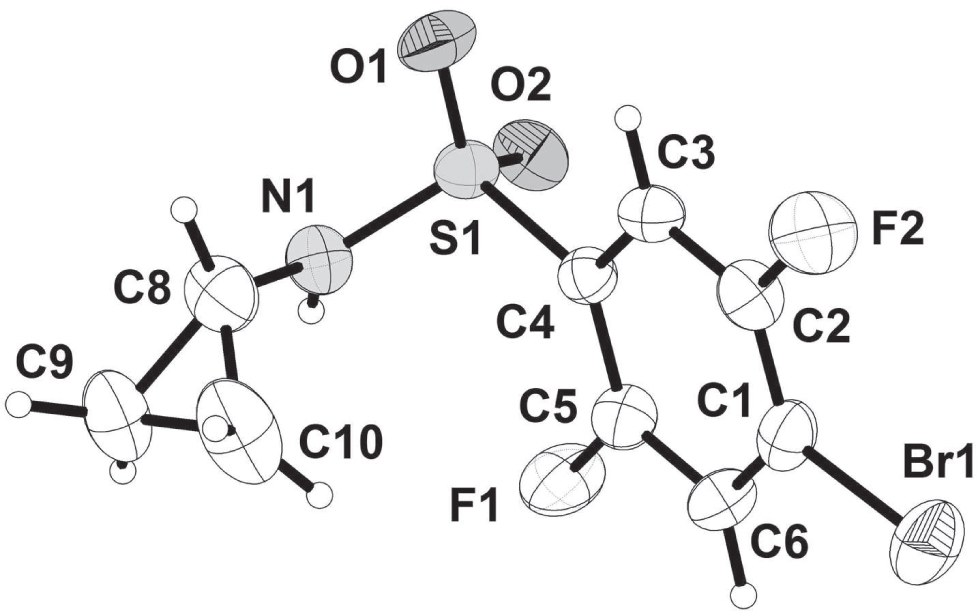
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 39.3 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker CCD, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 50.2°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 3574, 1940, 0.020 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1580 |
| N(param)refined: | 149 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1N | 0.657(5) | 0.053(4) | 0.430(3) | 0.030(9)* |
| Br1 | 0.05704(5) | 0.39942(5) | −0.18303(4) | 0.05545(17) |
| C1 | 0.2215(4) | 0.3637(4) | 0.0009(4) | 0.0380(8) |
| C2 | 0.3573(5) | 0.4963(4) | 0.1075(4) | 0.0383(8) |
| C3 | 0.4746(5) | 0.4730(4) | 0.2439(3) | 0.0348(7) |
| H3 | 0.5662 | 0.5647 | 0.3145 | 0.042* |
| C4 | 0.4544(4) | 0.3107(4) | 0.2745(3) | 0.0298(7) |
| C5 | 0.3187(4) | 0.1787(4) | 0.1658(4) | 0.0351(7) |
| C6 | 0.2025(4) | 0.2011(4) | 0.0290(4) | 0.0391(8) |
| H6 | 0.1136 | 0.1095 | −0.0428 | 0.047* |
| N1 | 0.7084(4) | 0.1475(4) | 0.4356(3) | 0.0372(7) |
| C8 | 0.8632(5) | 0.1845(4) | 0.3784(4) | 0.0478(9) |
| H8 | 0.9786 | 0.2844 | 0.4309 | 0.057* |
| C9 | 0.9092(6) | 0.0406(5) | 0.3220(4) | 0.0568(10) |
| H9A | 0.8276 | −0.0718 | 0.3207 | 0.068* |
| H9B | 1.0486 | 0.0525 | 0.3421 | 0.068* |
| C10 | 0.8129(7) | 0.1440(6) | 0.2191(5) | 0.0738(14) |
| H10A | 0.8935 | 0.2190 | 0.1765 | 0.089* |
| H10B | 0.6726 | 0.0946 | 0.1550 | 0.089* |
| O1 | 0.7408(3) | 0.4390(3) | 0.5240(2) | 0.0443(6) |
| O2 | 0.4574(3) | 0.1985(3) | 0.5154(3) | 0.0425(5) |
| F1 | 0.2979(3) | 0.0193(2) | 0.1936(2) | 0.0539(5) |
| F2 | 0.3769(3) | 0.6550(2) | 0.0794(2) | 0.0594(6) |
| S1 | 0.59626(11) | 0.27917(9) | 0.45233(8) | 0.0328(2) |
Source of material
All chemicals, reagents and solvents are of analytical grade and are commercially available. Preparation of 4-bromo-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonyl chloride: 2-bromo-1,4-difluorobenzene (10.00 g, 52 mmol) was dissolved in 100 mL CH2Cl2. To this solution, chlorosulfonic acid (30.18 g, 260 mmol) was added over a period of 20 min at 0 °C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 h. The reaction mixture was poured into 60 g ice water, and then extracted with dichloromethane. The organic phase was dehydrated with anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated at reduced pressure to afford a light yellow powder (14.05 g, 93%). Preparation of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide: A mixture of 4-bromo-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonyl chloride (12.00 g, 41 mmol), cyclopropylamine (2.80 g, 49 mmol), and triethylamine (8.30 g, 82 mmol) in 100 mL dichloromethane was stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The mixture was concentrated at reduced pressure, and the residue was washed with 60 mL water and crystallized from n-hexane to afford pure product (11.60 g, 91%).
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions. The Uiso values of the hydrogen atoms of methyl groups were set to 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl) and the Uiso values of all other hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Discussion
The hepatitis C virus is a leading cause of liver disease and represents a serious health concern [3]. The treatment with non-nucleoside thumb pocket 2 HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors has made a great progress [4]. Phenyl sulfonamide and its derivatives can be used as an important intermediate in the synthesis of non-nucleoside thumb pocket 2 HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors. In addition, it has been reported that phenyl sulfonamides can also be used to synthesize the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which shows anti-cancer effect [5].
All bond lengths and angles are in the expected ranges. Particularly, the bond length of C—Br bond is 1.884 Å. In addition, the bond length of C2–F5 and C5–F1 are 1.349 Å and 1.353 Å, respectively. The angle of C4S1N1 is 108.55° due to the steric stabilization. Title molecules are pairwise connected by classical N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The molecules packing in the crystal structure is additionally stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Cooperation Program of Guizhou Province (LH20157647).
References
1 Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Brucker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2009).Suche in Google Scholar
2 Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3 Lavanchy, D.: Evolving epidemiology of hepatitis C virus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 17 (2011) 107–115.10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03432.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
4 Stammers, T. A.; Coulombe, R.; Rancourt, J.; Thavonekham, B.; Fazal, G.; Goulet, S.; Jakalian, A.; Wernic, D.; Tsantrizos, Y.; Poupart, M. A.; Bös, M.; McKercher, G.; Thauvette, L.; Kukolj, G.; Beaulieu, P. L.: Discovery of a novel series of non-nucleoside thumb pocket 2 HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23 (2013) 2585–2589.10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.110Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5 Ali, A. M.; Gómez-Biagi, R. F.; Rosa, D. A.; Lai, P. S.; Heaton, W. L.; Park, J. S.; Eiring, A. M.; Vellore, N. A.; de Araujo, E. D.; Ball, D. P.: Shouksmith, A. E.; Patel, A. B.; Deininger, M. W.; O’Hare. T.; Gunning, P. T.: Disarming an electrophilic warhead: retaining potency in tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-resistant CML lines while circumventing pharmacokinetic liabilities. Chem. Med. Chem. 11 (2016) 850–861.10.1002/cmdc.201600021Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2017 Li Liu et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O

