Abstract
C19H17IN2, monoclinic, C2/c, a = 18.701(4) Å, b = 7.9230(16) Å, c = 24.069(6) Å, β = 111.168(2)°, V = 3325.6(13) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0201, wRref(F2) = 0.0462, T = 296(2) K.
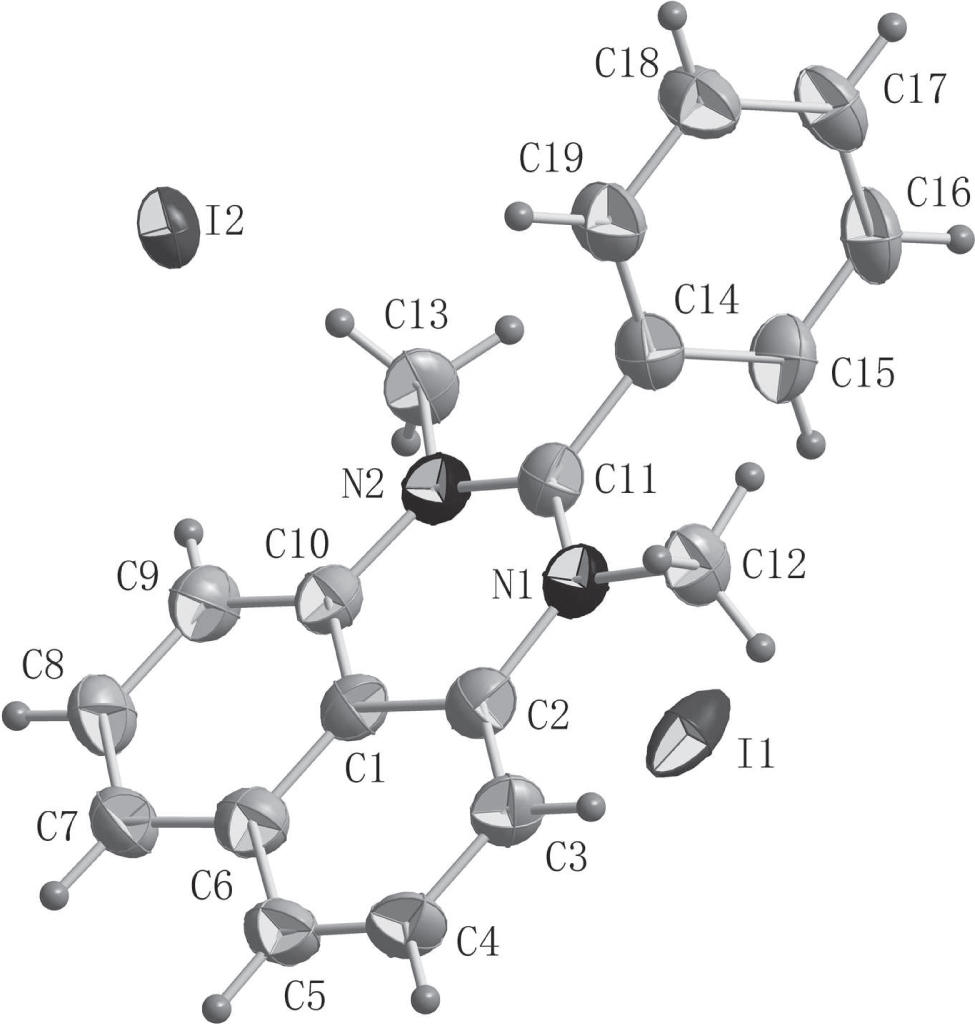
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.38 × 0.36 × 0.32 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 19.2 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 50°, 98.6% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 14906, 2887, 0.015 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2763 |
| N(param)refined: | 203 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2, 3] , PLATON [17] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 0.02337(10) | 0.0880(2) | 0.10919(7) | 0.0404(4) |
| N2 | 0.00485(9) | 0.3438(2) | 0.14921(7) | 0.0412(4) |
| C2 | −0.05664(12) | 0.0579(3) | 0.08300(9) | 0.0415(4) |
| C14 | 0.13526(12) | 0.2481(3) | 0.16972(10) | 0.0430(5) |
| C11 | 0.05110(11) | 0.2267(2) | 0.14101(9) | 0.0392(4) |
| C1 | −0.10546(11) | 0.1761(2) | 0.09493(8) | 0.0396(4) |
| C6 | −0.18568(12) | 0.1482(3) | 0.07256(9) | 0.0483(5) |
| C10 | −0.07554(11) | 0.3222(3) | 0.12880(9) | 0.0410(4) |
| C9 | −0.12331(14) | 0.4357(3) | 0.14080(11) | 0.0569(6) |
| H9 | −0.1035 | 0.5329 | 0.1626 | 0.068* |
| C16 | 0.25785(14) | 0.3241(3) | 0.16719(13) | 0.0608(6) |
| H16 | 0.2876 | 0.3660 | 0.1466 | 0.073* |
| C3 | −0.08599(14) | −0.0823(3) | 0.04876(11) | 0.0569(6) |
| H3 | −0.0537 | −0.1605 | 0.0410 | 0.068* |
| C17 | 0.29231(13) | 0.2778(3) | 0.22568(12) | 0.0583(6) |
| H17 | 0.3452 | 0.2870 | 0.2445 | 0.070* |
| C12 | 0.07474(14) | −0.0462(3) | 0.10397(12) | 0.0593(6) |
| H12A | 0.0642 | −0.1485 | 0.1210 | 0.089* |
| H12B | 0.1270 | −0.0134 | 0.1248 | 0.089* |
| H12C | 0.0666 | −0.0646 | 0.0627 | 0.089* |
| C15 | 0.17931(13) | 0.3095(3) | 0.13828(11) | 0.0539(5) |
| H15 | 0.1563 | 0.3402 | 0.0985 | 0.065* |
| C8 | −0.20211(15) | 0.4040(4) | 0.11994(12) | 0.0677(7) |
| H8 | −0.2342 | 0.4796 | 0.1292 | 0.081* |
| C19 | 0.17027(13) | 0.2034(3) | 0.22913(10) | 0.0535(6) |
| H19 | 0.1409 | 0.1638 | 0.2504 | 0.064* |
| C13 | 0.03612(15) | 0.5060(3) | 0.17746(13) | 0.0628(7) |
| H13A | 0.0310 | 0.5131 | 0.2157 | 0.094* |
| H13B | 0.0084 | 0.5970 | 0.1527 | 0.094* |
| H13C | 0.0893 | 0.5136 | 0.1825 | 0.094* |
| C18 | 0.24860(13) | 0.2178(3) | 0.25649(12) | 0.0599(6) |
| H18 | 0.2721 | 0.1865 | 0.2962 | 0.072* |
| C5 | −0.21444(14) | 0.0039(3) | 0.03718(11) | 0.0607(6) |
| H5 | −0.2670 | −0.0164 | 0.0217 | 0.073* |
| C7 | −0.23314(14) | 0.2659(4) | 0.08657(11) | 0.0615(6) |
| H7 | −0.2859 | 0.2488 | 0.0729 | 0.074* |
| C4 | −0.16575(16) | −0.1051(3) | 0.02568(12) | 0.0677(7) |
| H4 | −0.1859 | −0.1983 | 0.0016 | 0.081* |
| I2a | 0.0000 | 0.92943(3) | 0.2500 | 0.04629(7) |
| I1a | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.08320(11) |
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Source of material
Iodomethane (3.02 g, 0.021 mol) was added in one portion to a solution of 2-phenyl-1H-perimidine (2.44 g, 0.01 mol) in dimethylformamide (15 mL) at 373 K. The mixture was heated for 8 h, giving a yellow precipitate. After cooling, the yellow solid was filtered and dried under vacuum to give 1-methyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidine (1.83 g, 71%).
Iodomethane (3.02 g, 0.021 mol) was added dropwise to a solution of 1-methyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidine (2.58 g, 0.01 mol) in dimethylformamide (20 mL) at 373 K. The mixture was heated for 8 h, giving a yellow precipitate. After cooling, the yellow solid was filtered, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried under vacuum to give the desired salt 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide (3.04 g, 76%). A light yellow crystal was obtained by recrystallization from anhydrous ethanol.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were identified in difference Fourier syntheses. The methyl groups were idealized and refined using rigid groups allowed to rotate about the N—C bond (AFIX 137 option of the SHELXL-2013 program [2], [3]). The Uiso values of the hydrogen atoms of the methyl groups were set to 1.5Ueq(C) and the Uiso values of all other hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2 Ueq(C).
Comment
Perimidines have long attracted the attention of researchers because they exhibit a diverse range of biological activities [4], [5], [6], [7]. Perimidines can also be used as dyes and have a wide application in industrial field with solvent black 3 being a notable example 3 [8]. There are several preparative methods available for the synthesis of perimidine derivatives [9], [10], [11], [12], [13]. The most common method is the condensation reaction of 1,8-diaminonaphthalene with a carbonyl group [14], [15], [16]. Herein, a perimidine iodate was synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction [14, 15] . In the structure of the title compound, the bond angles N(1)—C(11)—N(2), N(1)—C(11)—C(14) and N(2)—C(11)—C(14) are 121.40(18), 119.33(18) and 119.23(17)°, respectively, indicative of the sp2 hybridization state of the C(11) atom. The newly-formed three-membered heterocyclic ring is essentially planar, as demonstrated by the fact that the angle between the naphthalene and N-heterocyclic rings is 4.065°. As revelaed by PLATON analysis [17], the maximum deviation from the least-squares plane through the 13 atoms of the perimidine ring is 0.060(2) Å. Two half-occupied iodide anions are present in the asymmetric unit and sit on special positions.
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (16B104), the Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Comprehensive Utilization of Advantage Plants Resources in Hunan South (XNZW16C01), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (2017JJ3093), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan University of Science and Engineering (16XKY063), and the Construct Program of the Key Discipline in Hunan University of Science and Engineering (2016).
References
1 Bruker: APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2013).Search in Google Scholar
2 Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
3 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar
4 Bu, X.; Deady, L. W.; Finlay, G. J.; Baguley, B. C.; Denny, W. A.: Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of 7-oxo-7H-dibenz[f,ij]isoquinoline and 7-oxo-7H-benzo[e]perimidine derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 44 (2001) 2004–2014.10.1021/jm010041lSearch in Google Scholar
5 Gong, X. W.; Li, X.; Li, W. L.; Gao, X.; Xu, W. F.; Zhai, H. M.: Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-4-(benzyloxy)-2-(cinnamoyl-oxy)-N,N,N-trimethyl-4-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride as a double-prodrug. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 27 (2008) 177–182.Search in Google Scholar
6 Ye, J.; Sun, X. X.; Qiu, S. Y.; Hu, A. X.: Synthesis, crystal structure and fungicidal activity of N-(4-tert-buty)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)thiazol-2-yl) propionamide. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 3 (2014)3 429–433.Search in Google Scholar
7 Fu, C. R.; Pei, J.; Ning, Y.; Liu, M.; Shan, P. C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Q.; Hu, F. Z.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Yang, H. Z.; Zou, X. M.: Synthesis and insecticidal activities of novel pyrazole oxime ether derivatives with different substituted pyridyl rings. Pest Manag. Sci. 70 (2013) 1207–1214.10.1002/ps.3672Search in Google Scholar
8 Hashim, J. A.; Kezhal, M. S.: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of 2-aryl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine. Res. Pharm. Biotech. 5 (2014) 1–6.Search in Google Scholar
9 Vanden, E. J. J.; Delfosse, F.; Mayence, A.; Haverbeke, Y. V.: Old reagents, new results-aromatization of Hantzsch 1,4-dihydropyridines with manganese-dioxide and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone. Tetrahedron 51 (1995) 5813–5818.10.1016/0040-4020(95)00318-3Search in Google Scholar
10 Hendrickson, J. B.; Hussoin, M. S.: Seeking the ideal dehydrating reagent. J. Org. Chem. 52 (1987) 4137–4139.10.1021/jo00227a041Search in Google Scholar
11 Deady, L. W.; Rodemann, T. J.: Synthesis of perimidine and fused perimidine derivatives from reaction of 1,8-naphthalenediamine with an iminoisocoumarin. Heterocycl. Chem. 35 (1998) 1417–1419.10.1002/jhet.5570350633Search in Google Scholar
12 Mueller-Westerhoff, U. T.; Vance, B.; Dong. I. Y.: The synthesis of dithiolene dyes with strong near-IR absorption. Tetrahedron 47 (1991) 909–932.10.1016/S0040-4020(01)80932-7Search in Google Scholar
13 Starshikov, M.; Pozharskii, F. T.: Synthesis of 2-(5-halogeno-2-f uryl)-2,3-dihydroperimidines. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 9 (1973) 922–924.10.1007/BF00471584Search in Google Scholar
14 Maslak, P.; Chopra, A.; Moylan, C. R.; Wortmann, R.; Lebus, S.; Rheingold, A. L.; Yap, G. P. A.: Optical properties of spiroconjugated charge-transfer dyes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (1996) 1471–1481.10.1021/ja9533003Search in Google Scholar
15 Starshikov, N. M.; Pozharskii, A. F.: Heterocyclic analogs of pleiadiene. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 10 (1978) 1413–1417.10.1007/BF00469962Search in Google Scholar
16 Sokolov, V. I.; Pozharskii, A. F.; Kashparov, I. S.; Ivanov, A. G.: Heterocyclic analogs of pleiadiene. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 4 (1974) 558–561.10.1007/BF00945648Search in Google Scholar
17 Spek, A. L.: Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D65 (2009) 148–155.10.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2017 Lin Yuan et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O

