Abstract
C18H18N2O4, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.2291(2) Å, b = 10.5932(4) Å, c = 15.3775(6) Å, β = 96.619(2)°, V = 846.13(6) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0479, wRref(F2) = 0.1438, T = 293(2) K.
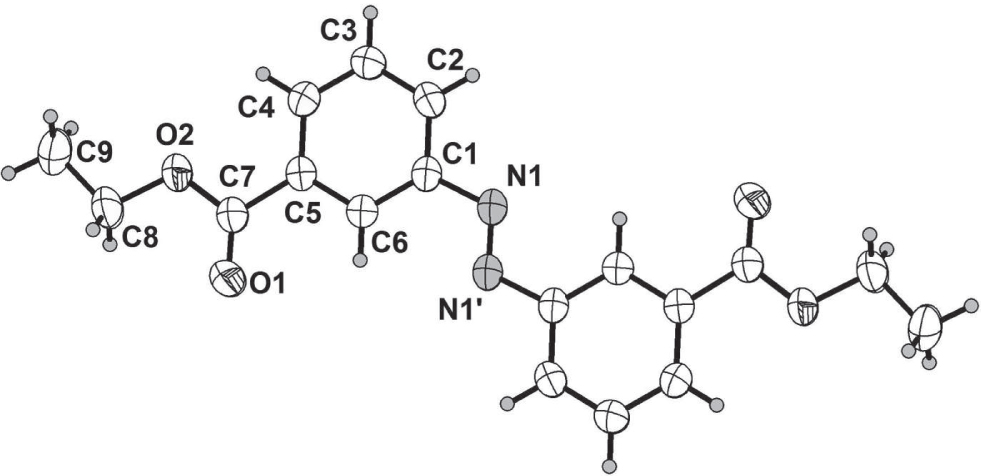
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in the figure (’ = 2−x, 2−y, 2−z). Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Orange block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.9 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 57°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 20762, 209, 0.022 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1866 |
| N(param)refined: | 110 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1, 2] , SHELX [3], DIAMOND [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | 0.10504(18) | 0.65799(9) | 0.85455(6) | 0.0555(3) |
| C6 | 0.6243(2) | 0.86064(10) | 0.94331(7) | 0.0418(3) |
| H6 | 0.6232 | 0.9208 | 0.8992 | 0.050* |
| C1 | 0.8062(2) | 0.86682(11) | 1.01687(7) | 0.0419(3) |
| C5 | 0.4449(2) | 0.76376(10) | 0.93660(7) | 0.0405(3) |
| C4 | 0.4443(2) | 0.67457(12) | 1.00307(8) | 0.0498(3) |
| H4 | 0.3222 | 0.6104 | 0.9986 | 0.060* |
| O1 | 0.2532(2) | 0.83270(11) | 0.79680(7) | 0.0799(4) |
| C2 | 0.8067(3) | 0.77771(13) | 1.08252(8) | 0.0538(3) |
| H2 | 0.9289 | 0.7822 | 1.1314 | 0.065* |
| C7 | 0.2592(2) | 0.75768(11) | 0.85532(8) | 0.0468(3) |
| C3 | 0.6257(3) | 0.68168(13) | 1.07583(9) | 0.0606(4) |
| H3 | 0.6262 | 0.6220 | 1.1202 | 0.073* |
| C8 | −0.0801(3) | 0.64201(16) | 0.77739(9) | 0.0657(4) |
| H8A | 0.0084 | 0.6303 | 0.7259 | 0.079* |
| H8B | −0.1891 | 0.7161 | 0.7685 | 0.079* |
| C9 | −0.2372(3) | 0.52945(14) | 0.79195(11) | 0.0662(4) |
| H9A | −0.1291 | 0.4560 | 0.7969 | 0.099* |
| H9B | −0.3687 | 0.5193 | 0.7435 | 0.099* |
| H9C | −0.3159 | 0.5401 | 0.8449 | 0.099* |
| N1 | 1.00062(18) | 0.96177(9) | 1.03032(6) | 0.0463(3) |
Source of material
All reagents and solvents were commercially available and used as received without further purification. Azobenzene-3,3′-dicarbonylchloride (3 mmol) was added to a solution of ethanol (25 mL) and 1,2-dichloroethane (15 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 3 h, then the solution was naturally cooled to room temperature. After filtration orange flakes of the title compound were obtained with 94.6% yield. Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution including 0.05 g of the product in methanol (5 mL) and chloroform (5 mL).
Experimental details
H atoms were subsequently treated as riding atoms with distances C—H = 0.96 (CH3), 0.97 (CH2), 0.93 Å (ArH) and O—H = 0.85 Å.
Comment
In recent years, the study of liquid crystalline materials has been of interest due to their potentially wide range of applications, such as in electrical [5], optical [6], and biological medical fields [7]. In this respect, the preparation of liquid crystalline materials containing azobenzene moieties appears to be very promising, because the photoinduced trans-cis isomerization of azobenzene chromophores can give rise to photochromic and optical dichroic effects [8]. Liquid crystalline polymers containing azobenzene derivatives have been widely investigated for the photo-controlled release of drugs [9], the preparation of holographic optical memories [10], and non-linear optical materials [11]. In order to enlarge the number of azobenzene derivatives, the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound was investigated.
The title crystal structure is centrosymmetric and contains one half of a title molecule in the asymmetric unit. Consequently the title molecule is located around an inversion center in the monoclinic space group P21/n (cf. the figure). Thus the intersection angle between two aryl rings is 0°, which is the same to that of azobenzene [12]. The crystal packing does not exhibit classical hydrogen bond interactions.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Foundation of Anyang Institute of Technology.
References
1 Bruker. APEX2. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2005.Search in Google Scholar
2 Bruker. SAINT-Plus. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2001.Search in Google Scholar
3 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4 Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 3.2i. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
5 Eich, M.; Wendorff, J. H.: Erasable holograms in polymeric liquid crystals. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 8 (1987) 467–471.10.1002/marc.1987.030080909Search in Google Scholar
6 Eich, M.; Wendorff, J. H.; Ringsdorf, H.; Schmidt, H. W.: Nonlinear optical self diffraction in a mesogenic side chain polymer. Makromol. Chem. 186 (1985) 2639–2647.10.1002/macp.1985.021861224Search in Google Scholar
7 Qiu, H.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Jing, F.; Zhou, E.: Synthesis and properties of two series of H-bonded and non-H-bonded thermotropic liquid crystal monomers. Liq. Cryst. 25 (1998) 419–425.10.1080/026782998206236Search in Google Scholar
8 Delaire, J. A.; Nakatani, K.: Linear and nonlinear optical properties of photochromic molecules and materials. Chem. Rev. 100 (2000) 1817–1846.10.1021/cr980078mSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
9 Xie, S.; Natansohn, A.; Rochon, P.: Microstructure of copolymers containing Disperse Red 1 and methyl methacrylate. Macromolecules 27 (1994) 1885–1890.10.1021/ma00085a034Search in Google Scholar
10 Altomare, A.; Ciardelli, F.; Marchini, M.; Solaro, R.: Polymeric dispersions of model azobenzene dyes. Polymer 46 (2005) 2086–2096.10.1016/j.polymer.2004.12.051Search in Google Scholar
11 Andruzzi, L.; Altomare, A.; Ciardelli, F.; Solaro, R.; Hvilsted, S.; Ramanujam, P. S.: Holographic gratings in azobenzene side-chain polymethacrylates. Macromolecules 32 (1999) 448–454.10.1021/ma980160jSearch in Google Scholar
12 Harada, J.; Ogawa, K.; Tomoda, S.: Molecular motion and conformational interconversion of azobenzenes in crystals as studied by X-ray diffraction. Acta. Crystallogr. B53 (1997) 662–672.10.1107/S0108768197002772Search in Google Scholar
©2017 Niu Yongsheng et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O

