Abstract
C6H10AgBrN6O4, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 11.424(7) Å, b = 16.140(9) Å, c = 6.506(4) Å, β = 97.897(4)°, V =1188.73(12) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0473, wRref(F2) = 0.1177, T = 273(2) K.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.70 × 0.30 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 50.8 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku Mercury, ω-scans |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 50.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11275, 2166, 0.048 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1824 |
| N(param)refined: | 169 |
| Programs: | CrystalClear [1], SHELX [2] |
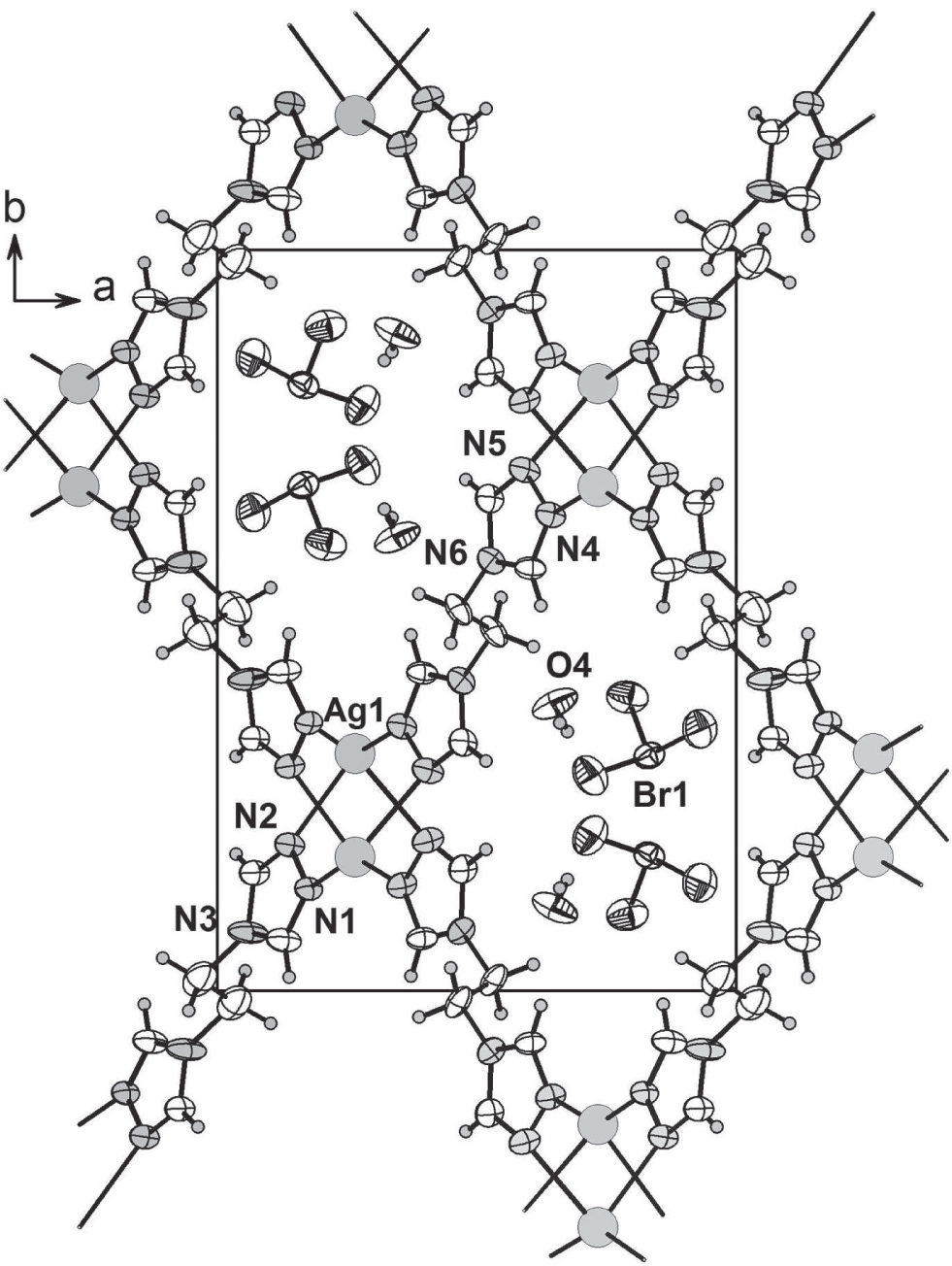
A part of the crystal structure is shown against the c-direction in the Figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag1 | 0.26545(5) | 0.31937(3) | 0.24161(7) | 0.0426(2) |
| Br1 | −0.16651(6) | 0.31749(4) | 0.00977(10) | 0.0435(2) |
| O1 | −0.2805(5) | 0.2904(4) | 0.1207(9) | 0.0716(16) |
| O2 | −0.0695(5) | 0.3542(4) | 0.1952(9) | 0.0750(16) |
| O3 | −0.2089(5) | 0.3970(3) | −0.1353(8) | 0.0687(15) |
| O4 | −0.3482(6) | 0.3879(3) | 0.4486(10) | 0.0816(19) |
| C1 | 0.0717(6) | 0.3410(4) | −0.3560(9) | 0.0403(15) |
| H1A | 0.0366 | 0.3161 | −0.4780 | 0.048* |
| C2 | 0.1284(6) | 0.4315(4) | −0.1237(9) | 0.0458(17) |
| H2A | 0.1397 | 0.4816 | −0.0532 | 0.055* |
| C3 | −0.0332(7) | 0.4839(5) | −0.4244(13) | 0.067(2) |
| H3A | −0.1040 | 0.4558 | −0.4881 | 0.081* |
| H3B | −0.0545 | 0.5269 | −0.3323 | 0.081* |
| C4 | 0.4744(6) | 0.3356(4) | 0.8287(10) | 0.0402(15) |
| H4A | 0.5191 | 0.3099 | 0.9411 | 0.048* |
| C5 | 0.3959(6) | 0.4294(3) | 0.6180(9) | 0.0375(14) |
| H5A | 0.3749 | 0.4803 | 0.5565 | 0.045* |
| C6 | 0.5339(6) | 0.4852(4) | 0.9194(10) | 0.0442(16) |
| H6A | 0.5481 | 0.5310 | 0.8294 | 0.053* |
| H6B | 0.6099 | 0.4645 | 0.9840 | 0.053* |
| N1 | 0.1763(4) | 0.3624(3) | −0.0599(7) | 0.0332(11) |
| N2 | 0.1397(5) | 0.3031(3) | −0.2081(7) | 0.0363(12) |
| N3 | 0.0595(6) | 0.4210(3) | −0.3073(9) | 0.0569(17) |
| N4 | 0.3568(5) | 0.3574(3) | 0.5453(7) | 0.0370(12) |
| N5 | 0.4070(5) | 0.2969(3) | 0.6827(7) | 0.0396(12) |
| N6 | 0.4709(4) | 0.4190(3) | 0.7951(7) | 0.0360(11) |
| H1W | −0.324(6) | 0.350(3) | 0.363(6) | 0.043* |
| H2W | −0.338(6) | 0.362(3) | 0.569(4) | 0.043* |
Source of material
A 5 mL aqueous solution of AgNO3 (0.2 mmol) and KBrO3 (0.2 mmol) was added to a tube. Then 5 mL 1:1 CH3CN/H2O solution (v/v) was slowly added. Finally a 5 mL CH3OH solution of 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane (btre) (0.1 mmol) was slowly added. Colorless crystals of the title compound (yield: 32% based on btre) were obtained after 1 weeks in a dark room at room temperature.
Experimental details
Carbon-bound hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Atomic coordinates of the hydrogen atoms of the water molecule were refined freely.
Discussion
The design of metal–organic coordination polymers are of current interest in the fields of supramolecular chemistry and crystal engineering not only because of their potential applications as functional materials but also due to their intriguing variety of topologies [3]. A successful strategy for construction of such networks is to employ appropriate ligands that can bond metal ions in different modes and provide a way to obtain new materials with intriguing architectures and excellent physical properties [4], [5], [6], [7]. Many factors such as the coordination geometry of the central atom, the structural characteristics of the ligands, the solvent system, and the counterions can play key roles in the construction of the coordination networks. The anions serve more than merely balancing the charges of a cationic complex and influence the structure of a supramolecular system through coordination to the metal. Silver coordination polymers have been widely studied not only for their applications as fluorescent materials, but also for their fascinating structures derived from variable coordination numbers from 2 to 6 of silver and different conformations around silver metal centers. Only a limited number of silver coordination polymers with the flexible 1-substituted 1,2,4-triazole ligands bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methane (btm) and 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)ethane (bte) [8], [9], [10] were synthesized and structurally characterized. The ligand 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane is a isomer of 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)ethane (bte). Liang and coworkers reported that the self-assembly reaction of flexible ligand 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane (btre) with Ag salt with BF4−, SO42−, NO3− and ClO4− gives novel coordination polymers with the anions playing an important role in the formation of coordination polymers [11]. On the other hand, a large number of mononuclear, oligonuclear, and polynuclear transition metal complexes of 1- and 4-substituted 1,2,4-triazole derivatives have been synthesized and characterized because of their unique properties and novel topologies. In order to continue to investigate the influence of the inorganic anions on the structures of silver coordination polymers with the flexible ligand btre, a new silver coordination polymer Ag(btre)BrO3⋅H2O was synthesized.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure consists of one Ag(I) ion, one 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane, one bromate counter anion and one water molecule. Each Ag(I) atom displays a distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry, coordinated by four triazole nitrogen atoms from four symmetry-related btre ligands, and form a three-dimensional microporous structure, while BrO3− anions and water molecules occupy the voids (cf. the figure).
The Ag—N bond lengths are in the range of 2.192(4) Å to 2.540(5) Å. The N—Ag—N bond angles are in the range of 96.24(17)° to 145.29(17)°. The Br—O bond lengths are in the range of 1.627(5)–1.633(5) Å. There are weak interactions between two oxygen atoms of adjacent BrO3− anion and hydrogen atom of H2O [H(1w)–O(4) 0.90(2) Å, H(2w)–O(4) 0.88(2) Å]. Each Ag(btre)4 unit is a four-connected mode. If a Ag(btre)4 unit is considered as one node and double btre as one building block, the two-dimensional network can be viewed as a simple two-dimensional (4,4) network. The distances between the Ag(I) atoms bridged by btre are 3.9492(19) Å to 6.6050(41) Å, along the b-axis and along the a-axis. So each silver(I) chain connects four adjacent btre ligand bridges, leading to a novel three-dimensional network. Though microporous voids exist, the interpenetrating network does not occur, while BrO3− anions and water molecules occupy the voids.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by grants from the Foundation of Qinghai institute of Salt Lakes (Y460091034).
References
1 Rigaku/MSC. CrystalClear. Rigaku/MSC Inc., The Woodlands, Texas, USA, (2006).Search in Google Scholar
2 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar
3 Hagrman, P. J.; Hagrmam, D.; Zubieta, J.: Organic-inorganic hybrid materials: from simple coordination polymers to organodiamine templated molybdenum oxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38 (1999) 2638–2684.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990917)38:18<2638::AID-ANIE2638>3.0.CO;2-4Search in Google Scholar
4 Eddaoudi, M.; Moler, D. B.; Li, H. L.; Chen, B. L.; Reineke, T. M.; Keeffe, M. O.; Yaghi, O. M.: Reticular chemistry: occurrence and taxonomy of nets and grammar for the design of frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 38 (2005) 176–182.10.1021/ar020022lSearch in Google Scholar
5 Zaworotko, M. J.: Superstructural diversity in two dimensions: crystal engineering of laminated solids. Chem. Commun. (2001) 1–9.10.1039/b007127gSearch in Google Scholar
6 Kuppler, R. J.; Timmons, D. J.; Fang, Q. R.; Li, J. R.; Makal, T. A.; Young, M. D.; Yuan, D. Q.; Zhao, D.; Zhuang, W. J.; Zhou, H. C.: Potential applications of metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 253 (2009) 3042–3066.10.1016/j.ccr.2009.05.019Search in Google Scholar
7 Lucia, C.; Gianfranco, C.; Davide, M.: Proserpio Borromean links and other non-conventional links in polycatenated coordination polymers: re-examination of some puzzling networks. CrystEngComm 5 (2003) 269–279.10.1039/B305246JSearch in Google Scholar
8 Qian, X.; Sun, P. P.; Ding, J. G.; Li, B. L.; Li, H. Y.: Syntheses, structures and properties of Mn(II), Zn(II) and Ag(I) coordination polymers with 2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)acetate. J. Mol. Struct. 1031 (2013) 175–179.10.1016/j.molstruc.2012.07.016Search in Google Scholar
9 Zhu, X.; Liu, X. G.; Li, B. L.; Zhang, Y.: Solvent–controlled assembly of supramolecular isomers: 2D (4,4) network, 1D ribbons of ring, and both 2D (4,4) networks and 1D ribbons of rings polycatenated in a 3D array. CrystEngComm 11 (2009) 997–1000.10.1039/b901780cSearch in Google Scholar
10 Zhu, X.; Ge, H. Y.; Zhang, Y. M.; Li, B. L.; Zhang, Y.: Self–assembly of five cobalt(II) coordination polymers from 1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)ethane. Polyhedron 25 (2006) 1875–1883.10.1016/j.poly.2005.07.042Search in Google Scholar
11 Liang, N.; Cui, Y. F.; Yuan, D. Y.; Li, B. L.; Li, H. Y.: Anion-controlled four silver coordination polymers with flexible bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane. Inorg. Chim. Acta 376 (2011) 612–618.10.1016/j.ica.2011.07.040Search in Google Scholar
©2017 Yanfeng Cui et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2) C42H40Cl2MnN6O10S2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-cyanophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H16F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of the first characterized polymeric copper and sodium complex diaqua-(tris-acetato-κO,O′)(μ2-acetato-κO′′)dinatrium copper(II) monohydrate, C8H18CuNa2O11
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-yl-methylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P,P′)silver(I) trifluorosulfonate–methanol (1:0.5), [Ag(C27H26P2)]SO3CF3⋅0.5CH3OH
- Crystal structure of μ-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphine)butane-2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′-bis(cyano-κC)dicopper(I)]-water, C58H56Cu2N6O2P2
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(1-hydrazinyl-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C15H23N7O4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H17IN2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(2,2′-(butane-1,4-diyl)-bis(5-carboxy-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato)-κ4O,O′,N,N′)cadmium(II) monohydrate, C14H18O11N4Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-3-(cyclopropylamino)-2-(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorobenzoyl) acrylate, C15H14Cl2FNO3
- Crystal structure of bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol-κ2O,O′)-(N,N-dimethylformamide)zinc(II), C43H31Cl2N5O5S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ3-2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethoxo)-tetrachloro-tetra-cobalt(II) methanol solvate, C17H44Cl4Co4N4O9
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-1-(4-bromophenyl)-9-methoxy-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-isopropyl-phenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-(4-methoxy phenyl)-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of monoaqua-[6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(1,2-phenylene bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-nitrophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)]zinc(II), C20H12Br2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of 11-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-17-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one – acetonitril (1/2), C33H41N3O2
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (phenylsulfinyl)carbamate, C11H15NO3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{diaqua-bis(3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)copper(II)} monohydrate, C18H18CuN6O7
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)benzoato-κN)cobalt(II), C18H20CoN6O8
- The crystal structure of 4-bromo-N-cyclopropyl-2,5-difluorobenzenesulfonamide, C9H8BrF2NO2S
- Crystal structure of ([3,3′-bipyridine]-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) dihydrate, C37H35Ag2N5O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid-κN]silver(I), C18H13AgN6O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C17H16O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C36H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of poly[1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′]silver(I) bromate monohydrate]silver(I), C6H10AgBrN6O4
- The crystal structure of 2,3,5-triphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-ium 2,3-dioxoindoline-5-sulfonate, C27H19N5O5S
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-amino-1,3-selenazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,3′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)(E)-dibenzoate, C18H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of cis-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methanol-κN,O)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)nickel(II), C18H16N6NiO2S2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole)boron – tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C36H37N4O6B
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-(μ3-1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)dysprosium(III)], C11H11DyN4O11
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-tris(dicyclo-hexylamido)hafnium(IV), C40H75HfN3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-[1-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)ethylidene]-2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazine, C28H20Cl2F2N8O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)benzoate, a Schiff base, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl)-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C17H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(pyrazin-2-ylthio)acetato-κ3N:O:S)silver(I)], C6H5AgN2O2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3-((E)-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C26H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-((((E)-1-(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl) oxime monohydrate, C17H20N2O7
- Crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid, C8H6ClNO4
- Crystal stucture of 4-((10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)methyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C27H31NOS
- The crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C13H10F3N3O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-tetraoxido-(μ2-5′-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H,2′H-3,3′-bi(1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)dimolybdenum(VI)], C8H6Mo2N8O6
- Crystal structure of (3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-bis(olato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′))-dizinc(II) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C42H38F12N8O4P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-2-acetylphenolato-κ3O:O,O′)trimanganese(II)], C48H42Mn3O12
- The crystal structure of 2,2-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,5-dihydro-[1,3,2]dioxaborinino[5,4-c]chromen-3-ium-2-uide, C11H6BF5O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboxylate, C13H19N3O3
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl 2,6-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5(4H)-carboxylate, C10H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-bis(η5-adamantylcyclopentadienyl)-3-phenyl-2-trimethylsilyl-2,3-dihydroisotitanazole, C42H55NSiTi
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C28H29N3O2
- Important impurity of Flupirtine – a single crystal study on ethyl (6-amino-5-((ethoxycarbonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl)(4-fluorobenzyl)carbamate, C18H21FN4O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C22H22N2O5
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,6-dihydroisoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate methanol solvate, C37H35N1O10
- The crystal structure of the inner salt of 2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]ethylcarbamic acid [systematic name: (2-((diaminomethylene)ammonio)ethyl)carbamate], C4H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinolinium) perchlorate – 8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline (1/1), C18H13ClN4O10
- The crystal structure of (5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)ferrocene, C13H12FeN2O
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-(fluorosulfonyl)ethyl)-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate, C9H13FO5S
- Crystal structure of the triclinic modification of 1-methyl-4-nitroimidzole, C4H5N3O2
- Corrigendum
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O

