Abstract
Babesia microti is an obligate intra-erythrocytic parasite transmitted by infected ticks. B. microti is a eukaryote much larger than prokaryotic microbes and more similar to human hosts in their biochemistry and metabolism. Moreover, Babesia spp. possess various immune evasion mechanisms leading to persistent and sometimes life-threatening diseases in immunocompromised hosts. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most prevalent adult B-cell malignancy, and a small percentage of CLL transforms into aggressive lymphomas. CLL also causes immune dysfunction due to the over-expansion of immature and ineffective B-cells. When our patient with indolent CLL presented with anemia, pancytopenia, and splenomegaly, all his healthcare providers presumptively assumed a malignant transformation of CLL. However, these are also the signs and symptoms of babesiosis. Herein, we report a case where B. microti infection was presumed as a malignant transformation of CLL and narrowly avoided a devastating outcome. Although the patient developed fulminant sepsis, he finally received the correct diagnosis and treatment. Unfortunately, the disease recrudesced twice. Each time, it became more difficult to control the infection. We describe the clinical course of the case and discuss the case-specific literature review. This report highlights the importance of differential diagnoses ruling out infections which include babesiosis, prior to initiating the treatment of B-cell malignancy.
1 Introduction
Human babesiosis is a zoonotic infection caused by Babesia spp. transmitted by Ixodid ticks [1]. Babesia spp. are obligate intraerythrocytic parasites belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa, which have the unique ability to penetrate and lyse human erythrocytes [2]. Single-cell eukaryotes are five to seven orders of magnitude larger than average prokaryotes [3] and are biochemically, metabolically, and genetically more similar to their human hosts than prokaryotes. For these reasons, once they infect a host, they are difficult to eradicate without harming the host [4,5]. They also have sophisticated organelles and various immune evasion mechanisms leading to persistent and sometimes life-threatening diseases in immunocompromised hosts [6,7]. Another reason for their persistence is that they develop resistance to the drugs used to treat the disease [4]. Also, gene mutations in the parasite can cause treatment failure [8,9]. We have illustrated the location of these eukaryotic protists in the evolutionary ladder (Figure S1).
Pathogenesis requires several vectors and steps which have been described in numerous previous reviews [10,11]. Once inside the human body, the motile spore-like sporozoites invade the erythrocytes using the apical complex. Babesia multiplies inside erythrocytes asexually, with each Babesia budding into two to four daughter cells (merozoites) and continuing to infect adjacent erythrocytes using their gliding ability [7]. Eventually, infected erythrocytes lyse and cause symptoms such as hemolytic anemia, hemoglobinuria, and jaundice [12]. These symptoms are often misdiagnosed as hematologic malignancies [13,14].
Symptoms of babesiosis range from asymptomatic (about 20% of the cases) or mild, while others may develop a severe or even fatal course of disease depending on the hosts’ immune status [15]. Although early babesiosis symptoms are non-specific, with fever and malaise, severe cases may present dyspnea, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly (or both), anemia, jaundice, hemoglobinuria, hypotension, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia [12]. Of note, splenomegaly, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and many of its physical symptoms are similar to those of stage 4 chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Thus, it is important to differentiate babesiosis from the advanced stages of CLL.
CLL is the most prevalent adult B-cell malignancy, representing 30% of all adult leukemias [16]. The progression of CLL is heterogeneous. In some patients, it remains indolent through their life expectancy, while in others, it can exacerbate acute aggressive forms easily reaching stages 3 or 4 in Rai’s staging system [17]. The signs and symptoms of advanced CLL are very similar to those of babesiosis. These include malaise, fever, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and/or pain in the upper left abdomen due to splenomegaly [18]. Although babesiosis and advanced CLL present similar signs and symptoms, these two diseases require diametrically different treatments [19]. CLL requires immune-suppressive anti-neoplastic therapy, while babesiosis requires immune-enhancing anti-infective treatment. Thus, it is of utmost importance to differentiate babesiosis from advanced CLL.
History of tick bite or residing in or traveling to endemic areas may give clues for potential risks of babesiosis, but a more specific diagnosis of babesiosis is necessary. When parasitemia is high, the diagnosis will be made by peripheral blood smears [12] demonstrating common intra-erythrocytic ring forms of the parasite (red arrow, Figure 1) or rarely by a pathognomonic tetrad configuration of merozoites resembling a Maltese cross [10] (black arrow, Figure 1). The diagnosis can be confirmed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR), targeting the 18 S rRNA gene of Babesia microti from whole blood, as described in the reference [20].
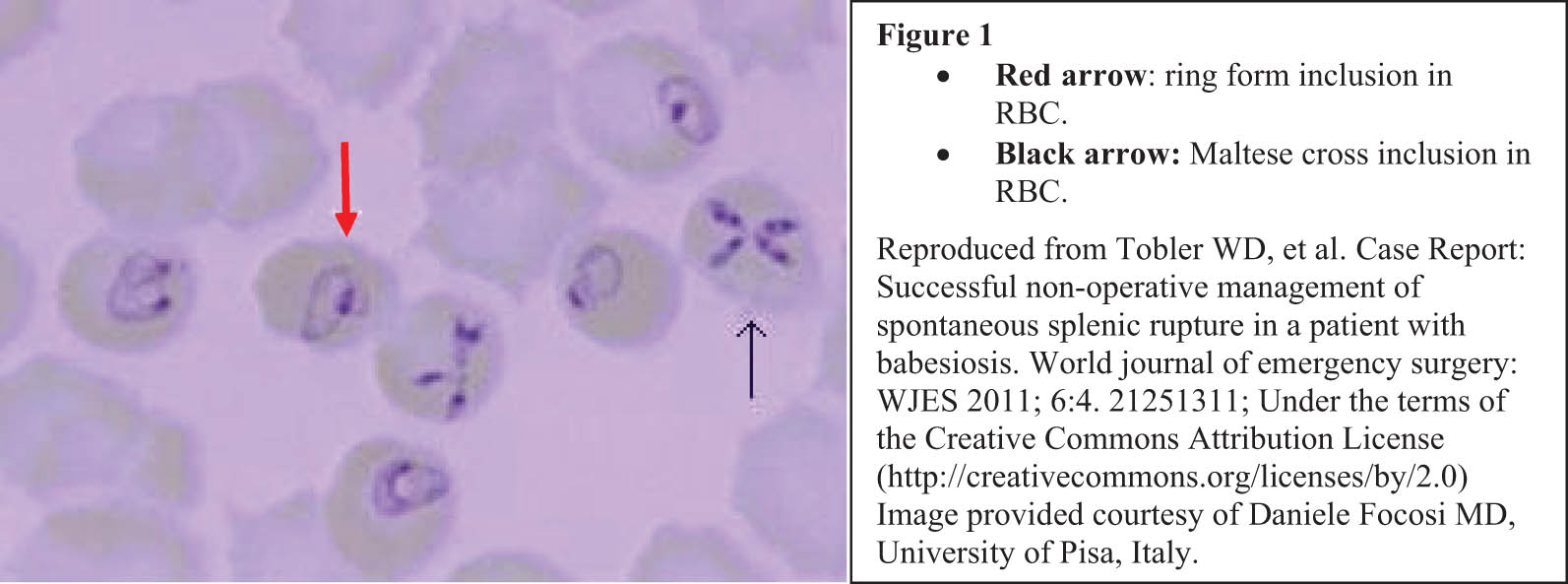
Ring forms and Maltese cross inclusions in erythrocytes.
1.1 Epidemiology of babesiosis
The most predominant species identified in the eastern and midwestern United States is B. microti, while B. divergens is common in Europe. In recent years, B. duncani was identified in the western United States [21,22]. More than 100 Babesia spp. have been identified, and different geographic regions and varied animal host different Babesia species [1]. These geography-specific Babesia species were reported in detail in previous publications [10,11].
The most common mode of infection is through the bites of infected ticks, but often patients do not recall the incidences of tick bites [12]. Less commonly, babesiosis can be transmitted through blood transfusions. Although the incidence is low, transfusion-transmitted babesiosis is much more dangerous because these patients commonly have serious comorbidities requiring transfusion. Very rarely an infected mother can transmit babesia to the newborn [12].
The incidence of babesiosis has been steadily increasing in the United States. The cumulative incidence of babesiosis in the United States between 2011 and 2015 was 7,612 cases (6,277 confirmed and 1,335 probable) [23]. Of these, 7,194 cases (94.5%) occurred in seven states: Connecticut, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin [23]. The risk factors for severe babesiosis are extremely young or old age; immunosuppression due to malignancy, organ transplantation, or splenectomy; and persons with chronic heart, liver, or kidney diseases [11]. Our patient is old, has heart disease, has malignancy, and resides in one of the seven states of the United States where babesiosis is endemic.
Between 1983 and 1994 in Wisconsin, three fatalities occurred (30%) among ten reported cases. All three deaths occurred in patients who were immunocompromised by asplenia or receiving high-dose steroids [24]. Thus, among the immunocompromised hosts, babesiosis should be recognized as a serious health threat [23].
1.2 Clinical course of the case
In late October 2019, a 76-year-old male with a history of indolent CLL and heart failure (HF) presented at a cardiology annual checkup. The cardiologist noticed anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia. Suspecting a malignant transformation of CLL, the cardiologist recommended an oncology consult. Patient’s leukocyte count was 2,000/µL (reference range: 4,000–10,500/µL), erythrocyte count was 3 × 106/µL (reference range: 4.7–6.0 × 106/µL), and platelet count was 43 × 103/µL (reference range: 150–450 × 103/µL). He had lost about 6.2 kg in the previous month. He had never smoked, never used any recreational drugs, and did not drink any alcohol.
His past medical history was notable with paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation leading to bundle branch block and heart failure in 2007, which was treated with medical management and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) implantation. These interventions resulted in an excellent outcome with no physical limitation (NYHA category 1). During the heart failure diagnosis, CLL was identified incidentally but did not require any treatment for the past 15 years. His lymphocyte count fluctuated between 23,000 and 50,000/µL (normal range: 720–4,100/µL) without any other symptoms.
In early November 2019, the patient sought oncology consult where a computerized axial tomography (CT) scan revealed massive splenomegaly with dimensions of 22 cm × 10.5 cm × 20 cm, (normal spleen size: 12 cm × 5 cm × 7 cm; Figure 2), mediastinal lymphadenopathy, but no significant atherosclerotic changes or cardiomegaly were observed. However, serum immunoglobulins, albumin, and total protein were all low. Hypogammaglobulinemia is one of the criteria for malignant transformation of CLL [25]. His oncologist’s diagnosis was a malignant transformation to lymphoma, and he recommended immunotherapy with rituximab and ibrutinib. This is particularly important because advanced CLL is usually treated with corticosteroids, rituximab, or ibrutinib. With occult babesiosis in the background, these treatments could have been deadly as has been reported previously [24].
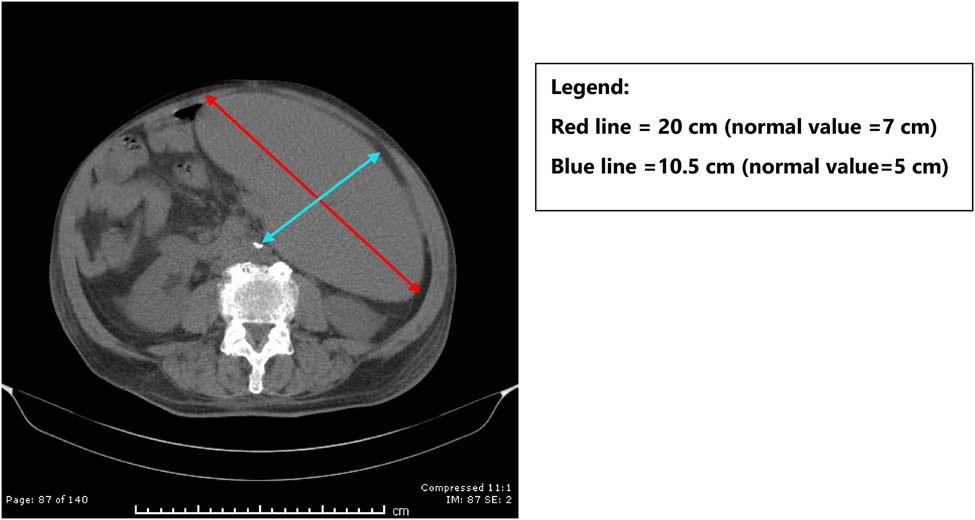
CT scan showing massive splenomegaly.
Serendipitously, the patient was aware of the serious adverse effects associated with the drugs of choice for CLL, ibrutinib [26,27,28] and rituximab [29,30,31], and he opted for an antioxidant resveratrol supplementation instead. Resveratrol induces apoptosis of malignant lymphocytes in vitro [32] and in vivo [33] Antioxidant supplementation started at the beginning of January 2020, generating one week of symptomatic relief, but by the second week, the patient’s symptoms had progressively worsened with severe pallor, dyspnea, and muscle weakness. For the next 3 weeks, the patient was too weak to get out of bed.
In the middle of February 2020, the patient developed shaking chills, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and delirium. He was transferred to the emergency department (ED) at the local hospital. At the ED, his temperature was 38·7°C, BP was 80/43 mmHg, pulse 124 beats per minute, breathing 20 breaths per minute, and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score was 8. The SOFA score ≥8 is associated with a 21% hospital mortality rate [34].
ED physician’s diagnosis was sepsis. His laboratory findings at the ED are presented in Table 1. Immediately, supportive care to manage sepsis was initiated, including fluid resuscitation, controlling fever, and supplementing oxygen. Simultaneously, several diagnostic tests to determine the cause of sepsis were undertaken. The tests for pneumonia, pancreatitis, pyelonephritis, hepatitis, and acute decompensated heart failure were carried out, and none were significant. CT scan without contrast showed the same massive splenomegaly as was observed at the oncology visit. Urinalysis and urine culture were negative, and the ICD and its wires were in a good position. The ED physician noted unusual intracellular inclusions in the RBCs of the peripheral blood smear and consulted the infection specialist. After examining the specimen, the infection specialist (HC) determined that the inclusion bodies were the ring-form intraerythrocytic parasites (Figure 1) and made a diagnosis of babesiosis. The attending pathologist concurred with the diagnosis. Additionally, real-time PCR with an FDA-approved and clinically validated assay (Quest Diagnostics) confirmed the diagnosis by the presence of B. microti DNA in the blood. Tests for Ehrlichia muris-like, Ehrlichia ewingii/canis, Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella, and Lyme antibody were all negative.
Laboratory test results of the patient at the emergency department
| Patient’s value | Reference range | |
|---|---|---|
| WBC (per μL) | 900 | 4,000–10,500 |
| Differential (count) | ||
| Neutrophils | 500 | 1,800–7,800 |
| Lymphocytes | 300 | 1,000–3,200 |
| RBC (per μL) | 2.54 × 106 | 4.7–6.0 × 106 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.7 | 13.5–18.0 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 24.8 | 40–54 |
| Platelets (per μL) | 21 × 103 | 150–450 × 103 |
| MPV (fL) | 13.2 | 7.4–11.4 |
| Amylase (U/L) | 32 | 29–103 |
| Lipase (U/L) | 31 | 11–82 |
| BNP (pg/mL) | 23 | 0–100 |
| Troponin (ng/mL) | 0.03 | <0.04 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.3 | 0.5–2.2 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 2.3 | 0.3–1.0 |
| Bilirubin, direct (mg/dL) | 0.5 | 0.0–0.2 |
| AST (SGOT) (U/L) | 35 | 5–40 |
| ALT (SGPT) (U/L) | 24 | 7–52 |
| LDH (U/L) | 235 | 125–220 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 78 | 34–104 |
| Smear interpretation | Rare intracellular inclusion in RBC observed | Consulted infectious disease specialist |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 65 | 9–20 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.7 | 0.7–1.3 |
| Glomerular filtration rate (mL/min) | 39.4 | >60.0 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 7.4 | 8.4–10.2 |
fL, Femtoliter (10−15); BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide.
Once the diagnosis was made, aggressive anti-parasitic and antibiotic treatments were initiated by establishing a central venous catheter. The patient received a standard regimen for babesiosis treatment, a 10-day course of atovaquone 750 mg b.i.d. and concurrent azithromycin 500 mg q12 h. Also, he received an RBC-replacement transfusion. The patient was well-recovered and discharged after 4 days in the hospital. He completed the 10-day course of atovaquone and azithromycin treatment at home. The patient was able to do all his normal physical activities for the next 2 months.
Unfortunately, babesiosis recurred twice after the first discharge from the hospital, and the patient was re-admitted with a second severe sepsis. Although the patient is still taking the medications after 14 months after the second admission, he can do most of his physical activities. The recrudescent part of babesiosis will be detailed in our next report.
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the author’s institutional review board or equivalent committee.
2 Discussion
This case clearly illustrates that eukaryotic infections such as babesiosis can become life-threatening illnesses in immunocompromised patients. It should be noted that his comorbid CLL involves B-cell defects resulting in impaired immunity, which increases the threat of severe babesiosis and recrudescence. Furthermore, babesiosis and advanced CLL symptoms are extremely similar, both presenting anemia, pancytopenia, and splenomegaly. Therefore, careful differential diagnosis is crucial.
The postulated causes for recrudescence are Babesia spp. express variant erythrocyte surface antigen1, which facilitates their adhesion to other cells [29] and forms a cluster with other RBCs [35]. These clusters can resist the hydrodynamic force of the bloodstream [35] and escape the splenic elimination of Babesia spp. [36,37]. These RBC clusters localize in the microvasculature [35], and Babesia spp. may avoid detection using PCR test. However, B. microti-specific clusters were not observed in the previous autopsy study [38]. We are not certain whether this autopsy study examined microvasculature. Future studies inspecting microvasculature are warranted.
Additionally, PCR has excellent sensitivity (96.2%) but poor to moderate specificity (70.5%), which carries approximately 30% false negative rates [39]. Although the negative PCR tests indicate the absence of detectable babesia DNA in the blood of approximately 70% (specificity) of the tested, the other 30% could have parasitemia that is below the detection levels of PCR [39]. This patient had negative PCR tests continuously since the first discharge. Nevertheless, babesiosis recrudesced twice. A marker of true negativity of babesia infection is desperately needed. One group used haptoglobin levels as a marker for the true negativity of babesia infection [9]. This test is based on the principle that highly oxidative-free hemoglobin originating from RBC lysis forms a haptoglobin–hemoglobin (Hp–Hb) complex, thereby avoiding oxidative tissue damage [40]. Hp–Hb complex lowers the serum haptoglobin levels, and the complex is eliminated by CD163-mediated endocytosis by macrophages through the spleen or other organs in the reticuloendothelial system [41]. This patient’s haptoglobin level was below the lowest detectable level for nearly 2 years. Additionally, the differential diagnosis should consider a history of Lyme disease, malaria, acute anemia, Colorado tick fever, Ehrlichiosis, typhoid fever, and CLL.
2.1 Differentiating CLL and babesiosis
As we described in the introduction, advanced CLL presents many symptoms of severe babesiosis and differential diagnosis becomes difficult when two pathologies coincide. Furthermore, the treatment modalities are diametrically different [17]. According to the 2018 International Workshop on CLL (IWCLL), guidelines recommend starting CLL therapy [42] if any one of the following criteria is satisfied: (a) hemoglobin <10 g/dL or platelet count of <100 × 109/L; (b) massive (≥6 cm below the left costal margin) splenomegaly; (c) symptomatic splenomegaly; (d) presence of disease-related symptoms such as unintentional weight loss of ≥10% within the previous 6 months, or significant fatigue [42]. This patient’s initial hemoglobin level was 9·7 g/dL, platelet count was 45 × 109/L, and he had massive splenomegaly. Thus, this patient satisfied the IWCLL criterion for CLL treatment. IWCLL criterion for treatment appears too non-specific and overly lenient. This patient could have received CLL treatment which might have generated disastrous consequences.
2.2 Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
In immunocompetent patients, several cases of HLH following B. microti infection have been reported [43,44]. HLH is an aggressive and life-threatening syndrome of excessive immune activation. HLH can be categorized as primary and secondary. Primary HLH is a genetics-derived pathology usually occurring in children [45]. Secondary HLH is a rare but potentially lethal complication following severe infections or malignancies with high mortality [46]. B-cell malignancies, including CLL, are less prone to develop HLH [47,48] compared with the patients who have T- or natural killer cell-associated lymphoma [47].
2.3 Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) following babesiosis
Babesiosis can cause non-immune hemolytic anemia due to the lysis of RBC by the parasite, as well as hemolytic anemia via autoimmunity [49]. AIHA is defined as the “destruction of RBCs through autoimmune mechanisms mediated by autoantibodies against erythrocyte surface antigens” [50]. Several studies reported post babesiosis (PB)-related AIHA, which occurred predominantly in asplenic patients [51,52]. Narurkar et al. stated that post-babesia AIHA is different from other types of AIHA because non-PB-related AIHAs are usually treated with splenectomy, but PB-associated AIHAs occur among asplenic patients [53]. Because PB-associated AIHAs occurred all in asplenic patients, [49] and asplenia increases autoimmune reactions, [54,55] asplenia may be the driver of AIHA. In pathological stress conditions such as asplenia, the liver takes over the removal of effete RBCs with monocytes acting as transient macrophages [56]. Further research on PB-associated AIHA is needed to elucidate whether post-babesiosis immune activation induces autoimmune reaction or asplenia triggers autoimmune hemolysis to remove senescent erythrocytes.
2.4 Cancer immunotherapy and eukaryotic infections
Ibrutinib and rituximab are the drugs of choice for the treatment of CLL. These drugs revolutionized CLL treatment with less toxicity than chemotherapy, but they suppress inflammatory pathways, which impair immune defense and can induce eukaryotic infections [57]. The patients who received Rituximab experienced relapses and persistent babesia infection [29]. Ibrutinib, which irreversibly inhibits Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, induces immune dysfunction and can cause serious fungal infections [27,58]. Immune suppression due to heavy corticosteroid usage has increased the risk of eukaryotic infections, Mucormycosis, after COVID-19 infection [59].
2.5 Resveratrol and immune suppression
It is highly likely that the resveratrol our patient took might have blunted the immune responses to babesiosis and contributed to severe sepsis. The innate immune system expresses TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β to defend the host from invading pathogens. Resveratrol suppresses NF-kB, TNF-α, and MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) [27,58,60,61], and suppresses inflammatory responses against pathogens [62,63]. Resveratrol supplementation has resulted in mortalities among multiple myeloma patients in phase II clinical trial [64], and antioxidants supplementation was associated with poor survival among cancer patients [65].
3 Conclusions
When CLL patients present with anemia, pancytopenia, and splenomegaly, a careful differential diagnosis should be made to rule out the infectious origin of symptoms such as babesiosis before proceeding to anti-CLL treatment. First, a blood smear should rule out the presence of babesia parasites in the blood and then confirm the results with rt-PCR. We hope our patient’s journey will offer an opportunity for a better understanding of the complexities of eukaryotic infections such as babesiosis and the difficulties in treating them in immunocompromised hosts.
Acknowledgment
We thank our patient for allowing us to use his clinical data in this manuscript. The authors acknowledge the efforts of Annie Ren, PhD, at the University of Toronto for creating the Figure of the evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding is involved.
-
Conflict of interest: All the authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript except Eleftherios P. Diamandis, who holds consultant roles with Abbott Diagnostics and Imaware Diagnostics.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Mylonakis E. When to suspect and how to monitor babesiosis. Am Family Phys. 2001;63(10):1969–74.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Jacot D, Tosetti N, Pires I, Stock J, Graindorge A, Hung YF, et al. An apicomplexan actin-binding protein serves as a connector and lipid sensor to coordinate motility and invasion. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;20(6):731–43. 10.1016/j.chom.2016.10.020.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Lynch M. The origins of eukaryotic gene structure. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;23(2):450–68. 10.1093/molbev/msj050. Epub 2005 Nov 9.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Fairlamb AH, Gow NA, Matthews KR, Waters AP. Drug resistance in eukaryotic microorganisms. Nat Microbiol. 2016;1(7):16092. 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.92.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Janket S-J, Conte HA, Diamandis EP. Do Prevotella copri and Blastocystis promote euglycaemia? Lancet Microbe. 2021;2(11):e565–6.10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00215-9Search in Google Scholar
[6] Morrissette NS, Sibley LD. Cytoskeleton of apicomplexan parasites. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002;66(1):21–38. 10.1128/MMBR.66.1.21-38.2002.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Frénal K, Dubremetz JF, Lebrun M, Soldati-Favre D. Gliding motility powers invasion and egress in Apicomplexa. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(11):645–60. 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.86.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Capela R, Moreira R, Lopes F. An overview of drug resistance in protozoal diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5748. 10.3390/ijms20225748.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Simon MS, Westblade LF, Dziedziech A, Visone JE, Furman RR, Jenkins SG, et al. Clinical and molecular evidence of atovaquone and azithromycin resistance in relapsed babesia microti infection associated with rituximab and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Infect Dis: An Off Publ Infect Diseases Soc Am. 2017;65(7):1222–5.10.1093/cid/cix477Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Krause PJ. Human babesiosis. Int J Parasitol. 2019;49(2):165–74.10.1016/j.ijpara.2018.11.007Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Vannier E, Krause PJ. Human babesiosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(25):2397–407.10.1056/NEJMra1202018Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] CDC. Parasite – Babesiosis Atlanta. Georgia: HHS; 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/babesiosis/disease.html.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Akel T, Mobarakai N. Hematologic manifestations of babesiosis. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2017;16(1):6.10.1186/s12941-017-0179-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Bläckberg J, Lazarevic VL, Hunfeld KP, Persson KEM. Low-virulent Babesia venatorum infection masquerading as hemophagocytic syndrome. Ann Hematol. 2018;97(4):731–3.10.1007/s00277-017-3220-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Vannier E, Krause PJ. Update on babesiosis. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2009;2009:984568. 10.1155/2009/984568 Epub 2009 Aug 27.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Knittel G, Liedgens P, Reinhardt HC. Targeting ATM-deficient CLL through interference with DNA repair pathways. Front Genet. 2015;6:207.10.3389/fgene.2015.00207Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Rozovski U, Hazan-Halevy I, Keating MJ, Estrov Z. Personalized medicine in CLL: Current status and future perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2014;352(1):4–14.10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.013Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Hallek M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(9):946–65.10.1002/ajh.24826Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Bucktrout SL, Bluestone JA, Ramsdell F. Recent advances in immunotherapies: From infection and autoimmunity, to cancer, and back again. Genome Med. 2018;10(1):79.10.1186/s13073-018-0588-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Krause PJ, Telford S 3rd, Spielman A, Ryan R, Magera J, Rajan TV, et al. Comparison of PCR with blood smear and inoculation of small animals for diagnosis of Babesia microti parasitemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34(11):2791–4. 10.1128/jcm.34.11.2791-4.1996.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Herwaldt BL, Linden JV, Bosserman E, Young C, Olkowska D, Wilson M. Transfusion-associated babesiosis in the United States: A description of cases. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):509–19.10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00362Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Karkoska K, Louie J, Appiah-Kubi AO, Wolfe L, Rubin L, Rajan S, et al. Transfusion-transmitted babesiosis leading to severe hemolysis in two patients with sickle cell anemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018;65(1). 10.1002/pbc.26734. Epub 2017 Aug 2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Gray EB, Herwaldt BL. Babesiosis surveillance – united states, 2011-2015. Morbidity Mortal Wkly Rep Surveill Summaries (Washington, DC: 2002). 2019;68(6):1–11.10.15585/mmwr.ss6806a1Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Herwaldt BL, Springs FE, Roberts PP, Eberhard ML, Case K, Persing DH, et al. Babesiosis in Wisconsin: A potentially fatal disease. Am J Tropical Med Hyg. 1995;53(2):146–51.10.4269/ajtmh.1995.53.146Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Pangalis GA, Angelopoulou MK, Vassilakopoulos TP, Siakantaris MP, Kittas C. B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic lymphoma, and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, including Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia: A clinical, morphologic, and biologic spectrum of similar disorders. Sem Hematol. 1999;36(2):104–14.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Mato AR, Nabhan C, Thompson MC, Lamanna N, Brander DM, Hill B, et al. Toxicities and outcomes of 616 ibrutinib-treated patients in the United States: A real-world analysis. Haematologica. 2018;103(5):874–9.10.3324/haematol.2017.182907Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Chamilos G, Lionakis MS, Kontoyiannis DP. Call for action: Invasive fungal infections associated with ibrutinib and other small molecule kinase inhibitors targeting immune signaling pathways. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;66(1):140–8.10.1093/cid/cix687Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Salem JE, Manouchehri A, Bretagne M, Lebrun-Vignes B, Groarke JD, Johnson DB, et al. Cardiovascular toxicities associated with ibrutinib. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(13):1667–78. 10.016/j.jacc.2019.07.056.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Krause PJ, Gewurz BE, Hill D, Marty FM, Vannier E, Foppa IM, et al. Persistent and relapsing babesiosis in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(3):370–6. 10.1086/525852.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Norris LB, Georgantopoulos P, Rao GA, Haddock KS, Bennett CL, Dorn WJB. Association between rituximab use and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy among non-HIV, non-Hodgkin lymphoma Veteran’s Administration patients. ASCO Annu Meet J Clin Oncol. 2014;e19540.10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.e19540Search in Google Scholar
[31] Roberts DM, Jones RB, Smith RM, Alberici F, Kumaratne DS, Burns S, et al. Rituximab-associated hypogammaglobulinemia: Incidence, predictors and outcomes in patients with multi-system autoimmune disease. J Autoimmunity. 2015;57:60–5.10.1016/j.jaut.2014.11.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Billard C, Izard JC, Roman V, Kern C, Mathiot C, Mentz F, et al. Comparative antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of resveratrol, epsilon-viniferin and vine-shots derived polyphenols (vineatrols) on chronic B lymphocytic leukemia cells and normal human lymphocytes. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43(10):1991–2002. 10.1080/1042819021000015952.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Tomic J, McCaw L, Li Y, Hough MR, Ben-David Y, Moffat J, et al. Resveratrol has anti-leukemic activity associated with decreased O-GlcNAcylated proteins. Exp Hematol. 2013;41(8):675–86. 10.1016/j.exphem.2013.04.004. Epub Apr 15.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Jones AE, Trzeciak S, Kline JA. The sequential organ failure assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(5):1649–54.10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819def97Search in Google Scholar
[35] Schetters T. Mechanisms involved in the persistence of babesia canis infection in dogs. Pathog (Basel, Switz). 2019;8(3):94.10.3390/pathogens8030094Search in Google Scholar
[36] Allred DR. Babesiosis: Persistence in the face of adversity. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19(2):51–5.10.1016/S1471-4922(02)00065-XSearch in Google Scholar
[37] Krause PJ, Daily J, Telford SR, Vannier E, Lantos P, Spielman A. Shared features in the pathobiology of babesiosis and malaria. Trends Parasitol. 2007;23(12):605–10.10.1016/j.pt.2007.09.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[38] Clark IA, Budd AC, Hsue G, Haymore BR, Joyce AJ, Thorner R, et al. Absence of erythrocyte sequestration in a case of babesiosis in a splenectomized human patient. Malar J. 2006;5:69. 10.1186/475-2875-5-69.Search in Google Scholar
[39] Akoolo L, Schlachter S, Khan R, Alter L, Rojtman AD, Gedroic K, et al. A novel quantitative PCR detects Babesia infection in patients not identified by currently available non-nucleic acid amplification tests. BMC Microbiol. 2017;17(1):16. 10.1186/s12866-017-0929-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Nantasenamat C, Prachayasittikul V, Bulow L. Molecular modeling of the human hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex sheds light on the protective mechanisms of haptoglobin. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62996.10.1371/journal.pone.0062996Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Schaer DJ, Vinchi F, Ingoglia G, Tolosano E, Buehler PW. Haptoglobin, hemopexin, and related defense pathways-basic science, clinical perspectives, and drug development. Front Physiol. 2014;5:415.10.3389/fphys.2014.00415Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Döhner H, et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood. 2018;131(25):2745–60.10.1182/blood-2017-09-806398Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Go SA, Phuoc VH, Eichenberg SE, Temesgen Z, Beckman TJ. Babesia microti infection and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in an immunocompetent patient. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;65:72–4.10.1016/j.ijid.2017.09.026Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[44] Kennedy-Snodgrass C, Obayomi M, Muddasani R, Slonim LB, Braunstein M. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to Babesia in an immunocompetent adult. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(3):379–83.10.1002/ajh.25364Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[45] Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatric Blood Cancer. 2007;48(2):124–31.10.1002/pbc.21039Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[46] Fisman DN. Hemophagocytic syndromes and infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6(6):601–8.10.3201/eid0606.000608Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Han AR, Lee HR, Park BB, Hwang IG, Park S, Lee SC, et al. Lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: Clinical features and treatment outcome. Ann Hematol. 2007;86(7):493–8. 10.1007/s00277-007-0278-6. Epub 2007 Mar 9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Tiong IS, Lau MB, Toumoua S, Chiruka S. A case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia after treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab chemotherapy, with autopsy findings. Case Rep Hematol. 2012;2012:326053. 10.1155/2012/326053 Epub 2012 Dec 17.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Rajapakse P, Bakirhan K. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia associated with human babesiosis. J Hematol. 2021;10(2):41–5. 10.14740/jh820 Epub 2021 Apr 27.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Berentsen S, Barcellini W. Autoimmune hemolytic anemias. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(15):1407–19. 10.056/NEJMra2033982 Search in Google Scholar
[51] Santos MA, Tierney LM Jr, Manesh R. Babesiosis-associated warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(3):928–9.10.1007/s11606-019-05506-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Woolley AE, Montgomery MW, Savage WJ, Achebe MO, Dunford K, Villeda S, et al. Post-babesiosis warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(10):939–46.10.1056/NEJMoa1612165Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Narurkar R, Mamorska-Dyga A, Nelson JC, Liu D. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia associated with babesiosis. Biomarker Res. 2017;5:14.10.1186/s40364-017-0095-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Di Sabatino A, Rosado MM, Cazzola P, Riboni R, Biagi F, Carsetti R, et al. Splenic hypofunction and the spectrum of autoimmune and malignant complications in celiac disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4(2):179–86.10.1016/S1542-3565(05)00982-1Search in Google Scholar
[55] Giuffrida P, Aronico N, Rosselli M, Lenti MV, Cococcia S, Roccarina D, et al. Defective spleen function in autoimmune gastrointestinal disorders. Intern Emerg Med. 2020;15(2):225–9.10.1007/s11739-019-02129-wSearch in Google Scholar
[56] Theurl I, Hilgendorf I, Nairz M, Tymoszuk P, Haschka D, Asshoff M, et al. On-demand erythrocyte disposal and iron recycling requires transient macrophages in the liver. Nat Med. 2016;22(8):945–51.10.1038/nm.4146Search in Google Scholar
[57] Reynolds KL, Sullivan RJ, Fintelmann FJ, Mansour MK, England J. Case 9-2020: A 64-Year-Old man with shortness of breath, cough, and hypoxemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(12):1150–9.10.1056/NEJMcpc1909621Search in Google Scholar
[58] Ghez D, Calleja A, Protin C, Baron M, Ledoux MP, Damaj G, et al. Early-onset invasive aspergillosis and other fungal infections in patients treated with ibrutinib. Blood. 2018;131(17):1955–9.10.1182/blood-2017-11-818286Search in Google Scholar
[59] Stone N, Gupta N, Schwartz I. Mucormycosis: time to address this deadly fungal infection. Lancet Microbe. 2021;2(8):e343–e4.10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00148-8Search in Google Scholar
[60] Ruchlemer R, Ben-Ami R, Bar-Meir M, Brown JR, Malphettes M, Mous R, et al. Ibrutinib-associated invasive fungal diseases in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: An observational study. Mycoses. 2019;62(12):1140–7.10.1111/myc.13001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[61] Varughese T, Taur Y, Cohen N, Palomba ML, Seo SK, Hohl TM, et al. Serious infections in patients receiving ibrutinib for treatment of lymphoid cancer. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67(5):687–92.10.1093/cid/ciy175Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[62] Tian Y, Ma J, Wang W, Zhang L, Xu J, Wang K, et al. Resveratrol supplement inhibited the NF-κB inflammation pathway through activating AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway in mice with fatty liver. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016;422(1–2):75–84. 10.1007/s11010-016-2807-x Epub 2016 Sep 9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Feng M, Zhang Q, Wu W, Chen L, Gu S, Ye Y, et al. Inducible Guanylate-Binding Protein 7 Facilitates Influenza A Virus Replication by Suppressing Innate Immunity via NF-κB and JAK-STAT Signaling Pathways. J Virol. 2021;95(6):e02038–20. 10.1128/JVI.-20. Print 2021 Feb 24.Search in Google Scholar
[64] Popat R, Plesner T, Davies F, Cook G, Cook M, Elliott P, et al. A phase 2 study of SRT501 (resveratrol) with bortezomib for patients with relapsed and or refractory multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2013;160(5):714–7.10.1111/bjh.12154Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[65] Ambrosone CB, Zirpoli GR, Hutson AD, McCann WE, McCann SE, Barlow WE, et al. Dietary supplement use during chemotherapy and survival outcomes of patients with breast cancer enrolled in a cooperative group clinical trial (SWOG S0221). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(8):804–14.10.1200/JCO.19.01203Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2022 Harry A. Conte et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”

