Abstract
Norovirus is a prominent enteric virus responsible for severe acute gastroenteritis disease burden worldwide. In our current study, we analyzed 7,804 norovirus sequences of human and animals in China which were detected from 1980 to 2020 from GenBank. The GenBank database was searched up to May 2021 with the following search terms: “norovirus” or “norwalk virus” and “China.” The 7,804 norovirus sequences were collected and evaluated by phylogenetic analysis using MEGA X software package. The online typing tool (https://www.rivm.nl/mpf/typingtool/norovirus/) was used to confirm the genotypes. There were 36 norovirus genotypes prevailing in China. GII.4 was the most prevalent genotype, and GII.2, GII.3 and GII.17 also emerged during different time periods. Most sequences were detected in East China (41.72%, 3,256/7,804), but different norovirus genotypes were distributed widely across the country. A variety of norovirus genotypes, including GI, GII, GIII, GIV, GV, GVI, GVII and GX, were reported in different animals. Furthermore, a GI.3 sequence detected from animal had high identity with norovirus detected in human from the same region, indicating the potential norovirus zoonotic transmission in China. In conclusion, these results indicated that norovirus sequences with considerable genetic diversity distributed widely in China, with potential reverse zoonotic transmission from human to animals.
1 Introduction
Norovirus is a leading cause of epidemic and sporadic nonbacterial gastroenteritis of all age groups worldwide, with an estimated 684 million cases annually resulting in 212,000 deaths [1–3]. Its infection can be serious in young children, the elderly and immunocompromised individuals [4]. Norovirus is a single-stranded, positive sense RNA virus, which belongs to the Caliciviridae family [5]. Currently, it can be divided into at least ten genogroups (GI–GX) and 48 genotypes, of which GI, GII, GIV, GVIII and GIX infect humans [6]. Despite its high degree of diversity, GII.4 is the predominant genotype detected in norovirus outbreaks worldwide [7]. But other genotypes have emerged in some regions of the world [8,9]. It is reported that norovirus infection accounted for 32.21% of all-age patients with acute diarrhea conducted in China, playing a significant role in the etiology of diarrhea [10]. Therefore, it is essential to understand the genotype diversity, dominant variants and variant replacement patterns of norovirus in China, which is valuable for taking preventive measures.
Animal noroviruses have been found in a wide range of hosts, including pigs, cattle, dogs, cats foxes, raccoon dogs, yaks and so on [11–14]. The interspecies transmission of noroviruses is not well understood and the detection of human-like norovirus genotypes in some farm animals, wild animals and pets, indicating the possible zoonotic transmission [15]. Therefore, the virus diversity, geographic distribution and probability of interspecies transmission of norovirus infections of animals in China need to be investigated.
Some studies have been done to investigate the phylogeography of norovirus in China [16–19]. However, there has been no detailed report about the overall genotype diversity of norovirus of both human and animals and the possibility of zoonosis transmission in China during the past 20 years. In this study, we retrieved 7,673 human norovirus sequences and 131 animal norovirus sequences detected in China from GenBank. By analyzing these sequences, we aimed to summarize the molecular epidemiology of noroviruses in China, the geographical and temporal distribution of the different genotypes across the country and the potential interspecies transmission of norovirus.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Norovirus sequences search and retrieve strategy
The GenBank database was searched up to May 2021 with the following search terms: “norovirus” or “norwalk virus” and “China.” Sequences which contain the capsid region (ORF2) with isolation time and region were included. Other sequences were excluded. A total of 7,804 norovirus sequences including 7,673 human norovirus sequences and 131 animal norovirus sequences were retrieved. These sequences were detected in China from 1980 to 2020. Of all the 7,804 sequences, 166 sequences were complete genome sequences and 7,638 sequences were partial genome sequences (fragment sizes ranging from 218 to 7,238 bp). Of the 131 animal sequences, 71 were from cattle, 8 were from mouse, 2 were from rhesus monkey, 33 were from dog, 2 were from yak, 2 were from bat, 3 were from pig, 2 were from rat, 7 were from cat and 1 was from chimp.
The geographic regions were divided into East China, South China, North China, Southwest China, Northeast China, Central China and Northwest China. East China includes Shandong, Anhui, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Shanghai, Fujian and Taiwan; South China includes Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong and Macau; North China includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia; Southwest China includes Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan and Tibet; Northeast China includes Liaoning, Heilongjiang and Jilin; Central China includes Henan, Hubei and Hunan; Northwest China includes Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia and Xinjiang.
2.2 Sequence comparison and phylogenetic analysis
The online typing tool (https://www.rivm.nl/mpf/typingtool/norovirus/) was used to confirm the genotypes [20]. Nucleotide sequences were aligned and analyzed by the MEGA X software package (version X, www.megasoftware.net). The alignment of all sequences was performed by Clustal X of MEGA X software and then amended manually. The compatible nucleotide substitution model (GTR + I + G) was determined by Modeltest v. 3.7 [21]. The phylogenetic tree of animal norovirus sequences was constructed based on the partial ORF2 region (218 bp). Reference sequences belonging to different genotypes were obtained from previous reference for comparison in this study (Table S1) [6]. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the maximum likelihood method in MEGA X. One thousand bootstrap replicates were used to calculate the percentages of the branches obtained. Bootstrap values which were more than 70% were shown and were regarded as the evidence of a phylogenetic grouping. If more than two sequences which were published in the same study and classified into the same sub-genotypes, only one sequence was listed on the dendrogram in this study to make the data easier to recognize. After the lengths of the sequences were adjusted to the same, the nucleotide identity comparisons were performed by NCBI Blast website (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
3 Results
3.1 Phylogenetic analysis of human and animal norovirus sequences from China
The results showed that human norovirus sequences from China were all classified into GI (405 sequences), GII (7,259 sequences), GIX (8 sequences) and GIV (1 sequence) (Table 1). Among these, human norovirus sequences which belonged to GI can be further divided into GI.1, GI.2, GI.3, GI.4, GI.5, GI.6, GI.7, GI.8 and GI.9. Human norovirus sequences which belonged to GII can be further classified into GII.1, GII.2, GII.3, GII.4, GII.5, GII.6, GII.7, GII.8, GII.12, GII.13, GII.14, GII.16, GII.17, GII.20 and GII.21. GIV belonged to GIV.1 and GIX belonged to GIX.1.
Genotypes of human norovirus sequences from China
| Genotype (number) | Number of sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| GI (405) | GI.1 | 21 |
| GI.2 | 108 | |
| GI.3 | 84 | |
| GI.4 | 32 | |
| GI.5 | 41 | |
| GI.6 | 86 | |
| GI.7 | 9 | |
| GI.8 | 11 | |
| GI.9 | 13 | |
| GII (7,259) | GII.1 | 20 |
| GII.2 | 820 | |
| GII.3 | 821 | |
| GII.4 | 3,067 | |
| GII.5 | 10 | |
| GII.6 | 212 | |
| GII.7 | 18 | |
| GII.8 | 34 | |
| GII.12 | 143 | |
| GII.13 | 290 | |
| GII.14 | 24 | |
| GII.16 | 1 | |
| GII.17 | 1,364 | |
| GII.20 | 2 | |
| GII.21 | 433 | |
| GIV (1) | GIV.1 | 1 |
| GIX (8) | GIX.1 | 8 |
Based on the phylogenetic tree constructed, we found that norovirus detected in animals of China belonged to GI (1 sequence), GII (5 sequences), GIII (73 sequences), GIV (9 sequences), GV (10 sequences), GVI (28 sequences), GVII (3 sequences) and GX (2 sequences) (Figure 1). Of these sequences, GI can be divided into GI.3, GII can be divided into GII.17 and GII.11, GIII can be classified into GIII.1 and GIII.2, GIV belonged to GIV.2, GV can be divided into GV.1 and GV.2 and GVI can be classified into GVI.1 and GVI.2. GVII and GX can be divided into GVII.1 and GX.1, respectively. Cattle norovirus mainly belonged to GIII.1 and GIII.2, and yak norovirus were all classified into GIII.2. Mouse norovirus all belonged to GV.1 and rat norovirus all belonged to GV.2. Dog norovirus can be classified into GIV.2, GVI.1, GVI.2 and GVII.1. Cat norovirus all belonged to GIV.2. Monkey norovirus were divided into GII.17 and chimp norovirus was GI.3. Pig norovirus belonged to GII.11and bat norovirus belonged to GX.1.
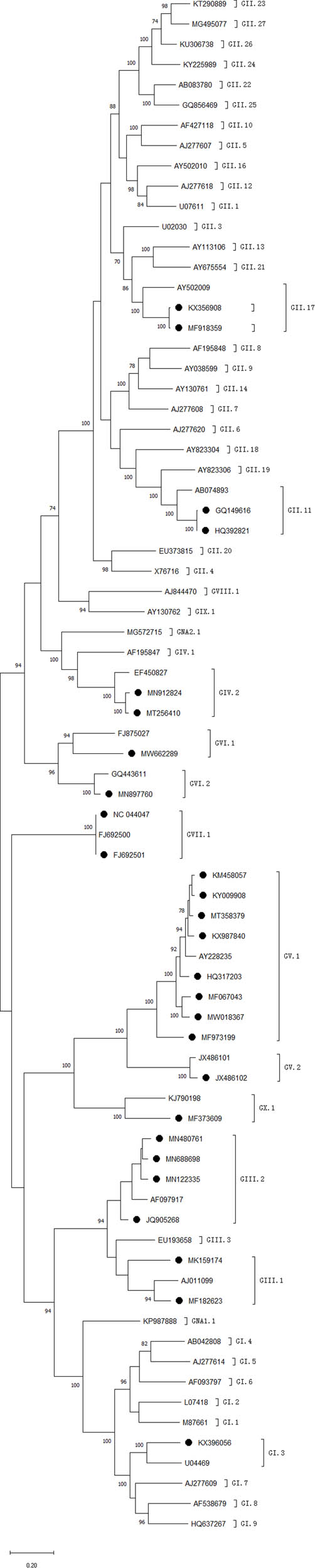
Phylogenetic trees representing animal norovirus genotypes. If more than two sequences which were published in the same study and classified into the same genotypes, only one sequence was listed on the dendrogram in this study. Bootstrap values which were less than 70% are not shown. The potential genotypic designations are shown outside of the square bars. ORF2 (capsid) regions of the sequences are compared and shown. ● represents the sequences from animals. The sequences without ● are the reference sequences.
3.2 Geographic and temporal distribution of norovirus genotypes in China
Norovirus genotypes are distributed widely in China (Table 2). Among all the norovirus sequences, most sequences were detected in East China (43.31%, 3,380/7,804), followed by South China (24.83%, 1,938/7,804) and North China (20.89%, 1,630/7,804). Most of GI and GII sequences were also detected in East China. GIV sequence was detected in North and Southwest China. GIX.1 sequences were detected in East China, Southwest China, South China and Central China. GIII sequences were mostly detected in Southwest China. Most of GV sequences were detected in North China and most of GVI sequences were detected in Southwest China. Some genotypes of norovirus were mainly confined to certain areas, such as GX.1 was only reported in East and Southwest China.
Norovirus genotypes geographic distribution in China
| Genotype (number) | Region (percentage) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North China (%) | Northeast China (%) | East China (%) | Central China (%) | South China (%) | Southwest China (%) | Northwest China (%) | |
| GI.1 (21) | — | — | 71.43 | — | 28.57 | — | — |
| GI.2 (108) | 20.37 | 12.96 | 39.81 | 2.78 | 12.96 | — | 11.11 |
| GI.3 (85) | 34.12 | — | 43.53 | 2.35 | 18.82 | 1.18 | — |
| GI.4 (32) | 18.75 | 3.13 | 56.25 | 6.25 | 12.50 | 3.13 | — |
| GI.5 (41) | 2.44 | — | 80.49 | — | 14.63 | 2.44 | — |
| GI.6 (86) | 4.65 | — | 76.74 | — | 16.28 | 2.33 | — |
| GI.7 (9) | — | 88.89 | — | 11.11 | — | — | |
| GI.8 (11) | 9.09 | — | 72.73 | — | 18.18 | — | — |
| GI.9 (13) | 38.46 | — | 46.15 | — | 15.38 | — | — |
| GII.1 (20) | 15.00 | — | 80.00 | — | 5.00 | — | — |
| GII.2 (820) | 11.34 | 0.37 | 35.37 | 18.29 | 23.78 | 8.17 | 3.05 |
| GII.3 (821) | 56.47 | 0.12 | 24.00 | 4.51 | 12.18 | 0.85 | — |
| GII.4 (3,067) | 24.36 | 1.96 | 38.93 | 1.27 | 31.92 | 2.87 | 0.65 |
| GII.5 (10) | 10.00 | — | 70.00 | — | 20.00 | — | — |
| GII.6 (212) | 12.26 | — | 58.96 | 6.13 | 12.26 | 4.25 | 6.13 |
| GII.7 (18) | 22.22 | — | 44.44 | 5.56 | 16.67 | 11.11 | — |
| GII.8 (34) | 2.94 | — | 11.76 | — | 85.29 | — | — |
| GII.11 (3) | 100 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| GII.12 (143) | 77.62 | — | 14.69 | 4.20 | 2.10 | 1.40 | — |
| GII.13 (290) | 4.14 | — | 38.62 | 0.69 | 4.14 | 52.41 | — |
| GII.14 (24) | 8.33 | — | 62.50 | 8.33 | 12.50 | 8.33 | — |
| GII.16 (1) | 100 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| GII.17 (1,366) | 2.12 | 1.76 | 55.86 | 5.93 | 36.02 | 0.07 | — |
| GII.20 (2) | 100 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| GII.21 (433) | 9.24 | — | 86.14 | — | 4.62 | — | — |
| GIII.1 (68) | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | — |
| GIII.2 (5) | 20.00 | — | — | 20.00 | — | 40.00 | 20.00 |
| GIV.1 (1) | 100 | — | |||||
| GIV.2 (9) | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | — |
| GV.1 (8) | 50.00 | — | 37.50 | — | 12.50 | — | — |
| GV.2 (2) | — | — | — | — | 100 | — | — |
| GVI.1 (2) | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | — |
| GVI.2 (26) | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | — |
| GVII.1 (3) | 100 | ||||||
| GIX.1 (8) | 37.50 | — | — | 25.00 | 12.50 | 25.00 | |
| GX.1 (2) | — | — | 50.00 | — | — | 50.00 | — |
Figure 2, Tables S2 and S3 show the dynamic temporal change of human norovirus genotypes. As time progressed, the diversity of norovirus genotypes expanded. In 1980 and 2002, the most prevalent genotypes were GII.20 (100%) and GI.4 (80.00%), respectively. GII.4 was the most prevalent genotype between 2004 and 2014. In 2015, 2016 and 2017, GII.17 (42.53%), GII.21 (25.33%) and GII.2 (56.72%) were the most predominant genotypes, respectively. In 2018 and 2019, GII.4 genotype was the most prevalent genotype. In 2020, GII.2 was the most prevalent genotype (85.11%).
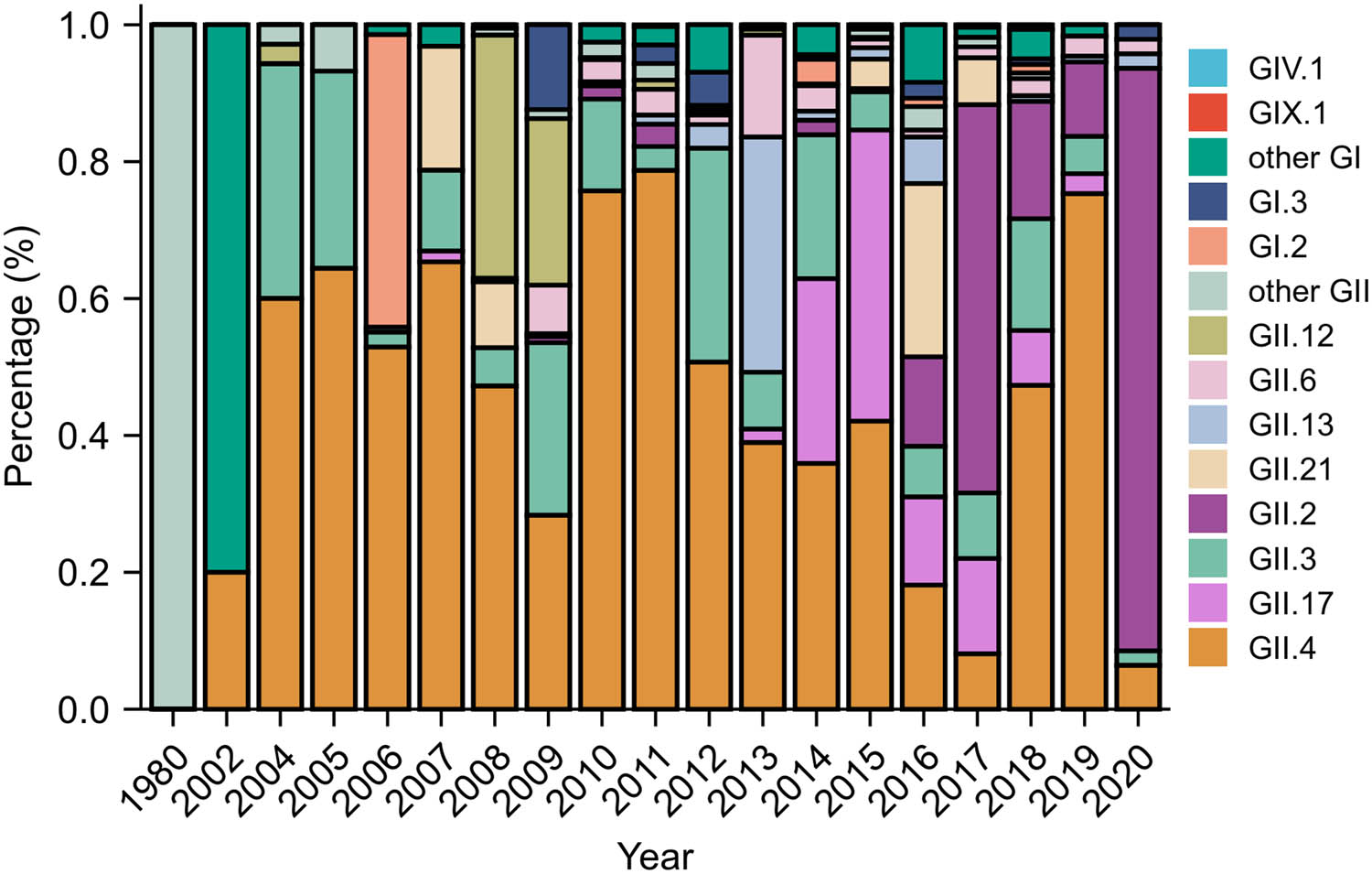
Temporal distribution of genotypes of human norovirus sequences in China. Different colors represent different genotypes of norovirus.
3.3 Potential norovirus zoonotic transmission in China
To investigate the potential zoonotic transmission of norovirus, we compared the identity of animal and human norovirus nucleotide sequences detected in the same geographical areas. The results showed that the chimp norovirus (KX396056) had the highest sequences/amino acid identity (84.7%) with the human GI.3 (KP753280), indicating the potential cross-species transmission between humans and animals in China.
4 Discussion
Norovirus outbreaks have been frequently reported in China and have caused a considerable disease burden [22]. Although there have been some studies about the phylogeography of norovirus in China [16–19], no study has summarized the overall genotype diversity of both human and animal norovirus and their potential zoonosis transmission in China during the past 20 years. Our study showed that the genotypes of norovirus in China included GI, GII, GIII, GIV, GV, GVI, GIX and GX. The percentages of GI, GII, GIII, GIV, GV, GVI, GIX and GX were 5.20% (406/7,804), 93.08% (7,264/7,804), 0.94% (73/7,804), 0.13% (10/7,804), 0.13% (10/7,804), 0.40% (31/7,804), 0.10% (8/7,804) and 0.03% (2/7,804), respectively, showing that GII was the most popular norovirus genotype in China. The results also showed that there were 36 genotypes throughout China. Among all genotypes, GII.4 (3,067/7,804, 39.30%), GII.17 (1,364/7,804, 17.48%), GII.2 (820/7,804, 10.51%) and GII.3 (821/7,804, 10.52%) were the predominant genotypes. This was in consistent with the global distribution of norovirus genotypes, whose predominant genotype is GII.4 and has been responsible for approximately 50% of outbreaks during the past several decades [23]. However, we found that GII.17, GII.2 and GII.3 also played an important role in the norovirus disease burden in China. Some studies predicted that these sequences may end the GII.4 era [24], but our study showed that GII.4 was still the most prevalent genotype and whether other genotypes can replace its predominance remains to be monitored.
In the present study, the results suggested that norovirus genotypes were detected in all seven regions of China, with most sequences detected in East China (43.31%, 3,380/7,804). This may be related with the local concerns, eating habits and geographic characteristics of East China. Among the predominant genotypes, most of GII.4 (38.93%), GII.2 (35.37%) and GII.17 (55.86%) were detected in East China and most of GII.3 (56.47%) were detected in North China, indicating that different predominant genotypes were circulating in different regions. This may be explained by the particularity of transmission of different genotypes and where the outbreaks occurred [25]. The temporal analysis of these human norovirus sequences suggested that the diversity of genotypes increased during the past 20 years. GII.4 has been particularly prevalent since 2002, and other genotypes (GII.17, GII.21 and GII.2) also became prevalent as time went by. The reason for the change of norovirus genotype among humans in China may be partly due to several outbreaks of different genotypes [26–29]. Although the sequences searched from GenBank in this study were affected by surveillance bias towards different regions, these results provided evidence that new norovirus genotypes continue to emerge and the differences in strain transmission remain unclear.
A variety of norovirus genotypes were obtained from animals in China, including cattle, mouse, rhesus monkey, dog, yak, bat, pig, rat, cat and chimp. GI and GII were mainly found in rhesus monkey, chimp and pig. GIII.1 and GIII.2 were all detected in cattle and yak. GIV was detected in dog and cat. GV.1 was detected in mouse and GV.2 was detected in rat. Both GVI.1 and GVI.2 were detected in dog. Besides, the norovirus sequences detected in bat all belonged to GX.1. We further aimed to investigate whether norovirus can jump the species barrier. The norovirus detected in chimps, which belonged to GI.3, showed high identity with human norovirus detected in the same regions, indicating the possibility of cross-species transmission. However, sequences detected in other animals, such as pigs, cattle, dogs and so on, did not show high identity with human norovirus in China. The norovirus sequence detected in chimps (GenBank No. KX396056) which belonged to GI.3 was detected from diarrheic chimps, indicating that human norovirus can cause symptoms in animals. Some phylogenetic analysis of noroviruses in animals showed that there may be an interspecies transmission of noroviruses [30]. To date, there is a lack of research on animal norovirus’s detection in human stool but it has been shown that human noroviruses could infect livestock animals such as pigs [31–34]. Our study indicated that human norovirus might be a reverse zoonosis pathogen, since the results showed that human noroviruses were detected in animals than the reverse. However, results in this study only indicated the zoonotic potential by comparing the identity of sequences and whether norovirus is a zoonotic or reverse zoonotic pathogen still remains to be further investigated.
In conclusion, human and animal noroviruses are widespread in China. This study has several limitations: (a) the sequences searched from GenBank were related with the local concern and number of studies, which cannot represent the whole temporal and geographical distribution of epidemic virology; (b) there is a possibility that there were missing sequences because their information did not contain the keywords. But this study still provided the genotype diversity of both human and animal noroviruses to some extent. The predominance of norovirus GII.4 is very clear, with a great diversity of genotypes circulating at a low frequency. Human norovirus might be a reverse zoonosis pathogen and the zoonosis still needs further investigation.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: M.L. and C.Z. conceived and designed the project. M.L. and K.L. collected the data. M.L. performed the interpretation of data. M.L., H.L., X.H. and Y.L. performed the statistical analysis. M.L. wrote the manuscript. C.Z. revised the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Ahmed SM, Hall AJ, Robinson AE, Verhoef L, Premkumar P, Parashar UD, et al. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(8):725–30.10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70767-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Fischer Walker CL, Perin J, Aryee MJ, Boschi-Pinto C, Black RE. Diarrhea incidence in low- and middle-income countries in 1990 and 2010: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:220.10.1186/1471-2458-12-220Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Pires SM, Fischer-Walker CL, Lanata CF, Devleesschauwer B, Hall AJ, Kirk MD, et al. Aetiology-specific estimates of the global and regional incidence and mortality of diarrhoeal diseases commonly transmitted through food. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0142927.10.1371/journal.pone.0142927Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Pearson JA, Tai N, Ekanayake-Alper DK, Peng J, Hu Y, Hager K, et al. Norovirus changes susceptibility to type 1 diabetes by altering intestinal microbiota and immune cell functions. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2654.10.3389/fimmu.2019.02654Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Randazzo W, D’Souza DH, Sanchez G. Norovirus: the burden of the unknown. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2018;86:13–53.10.1016/bs.afnr.2018.02.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Chhabra P, de Graaf M, Parra GI, Chan MC, Green K, Martella V, et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J Gen Virol. 2019;100(10):1393–406.10.1099/jgv.0.001318Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Zakikhany K, Allen DJ, Brown D, Iturriza-Gómara M. Molecular evolution of GII-4 norovirus strains. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41625.10.1371/journal.pone.0041625Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Thongprachum A, Okitsu S, Khamrin P, Maneekarn N, Hayakawa S, Ushijima H. Emergence of norovirus GII.2 and its novel recombination during the gastroenteritis outbreak in Japanese children in mid-2016. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;51:86–8.10.1016/j.meegid.2017.03.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Siebenga JJ, Vennema H, Zheng DP, Vinjé J, Lee BE, Pang XL, et al. Norovirus illness is a global problem: emergence and spread of norovirus GII.4 variants, 2001–2007. J Infect Dis. 2009;200(5):802–12.10.1086/605127Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Wang LP, Zhou SX, Wang X, Lu QB, Shi LS, Ren X, et al. Etiological, epidemiological, and clinical features of acute diarrhea in China. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2464.10.1038/s41467-021-22551-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Shi M, Lin XD, Chen X, Tian JH, Chen LJ, Li K, et al. The evolutionary history of vertebrate RNA viruses. Nature. 2018;556(7700):197–202.10.1038/s41586-018-0012-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Wang J, Li L, Xu Y, Mao T, Ma Y, Sun X, et al. Identification of a novel norovirus species in fox. Infect Genet Evol. 2022;98:105214.10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105214Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Li J, Liu W, Tian F, Tu Q, Xia X, Liu C, et al. First report of norovirus sequences isolated from raccoon dogs in mainland China. Virus Res. 2021;305:198546.10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198546Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Cui Y, Chen X, Yue H, Tang C. First detection and genomic characterization of bovine norovirus from yak. Pathogens. 2022;11(2):192.10.3390/pathogens11020192Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Villabruna N, Koopmans MPG, de Graaf M. Animals as reservoir for human norovirus. Viruses. 2019;11(5):478.10.3390/v11050478Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Qiao N, Ren H, Liu L. Genomic diversity and phylogeography of norovirus in China. BMC Med Genomics. 2017;10(Suppl 3):51.10.1186/s12920-017-0287-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Zhou H, Wang S, von Seidlein L, Wang X. The epidemiology of norovirus gastroenteritis in China: disease burden and distribution of genotypes. Front Med. 2020;14(1):1–7.10.1007/s11684-019-0733-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Wang JX, Zhou HL, Mo ZJ, Wang SM, Hao ZY, Li Y, et al. Burden of viral gastroenteritis in children living in rural China: population-based surveillance. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;90:151–60.10.1016/j.ijid.2019.10.029Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Wei N, Ge J, Tan C, Song Y, Wang S, Bao M, et al. Epidemiology and evolution of norovirus in China. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021;17(11):4553–66.10.1080/21645515.2021.1961465Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Kroneman A, Vega E, Vennema H, Vinjé J, White PA, Hansman G. Proposal for a unified norovirus nomenclature and genotyping. Arch Virol. 2013;158(10):2059–68.10.1007/s00705-013-1708-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Posada D, Crandall KA. MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics. 1998;14(9):817–8.10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Zhou HL, Zhen SS, Wang JX, Zhang CJ, Qiu C, Wang SM, et al. Burden of acute gastroenteritis caused by norovirus in China: a systematic review. J Infect. 2017;75(3):216–24.10.1016/j.jinf.2017.06.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] van Beek J, de Graaf M, Al-Hello H, Allen DJ, Ambert-Balay K, Botteldoorn N, et al. Molecular surveillance of norovirus, 2005–16: an epidemiological analysis of data collected from the NoroNet network. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(5):545–53.10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30059-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] de Graaf M, van Beek J, Vennema H, Podkolzin AT, Hewitt J, Bucardo F, et al. Emergence of a novel GII.17 norovirus – end of the GII.4 era? Euro Surveill. 2015;20(26):21178.10.2807/1560-7917.ES2015.20.26.21178Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Cates JE, Vinjé J, Parashar U, Hall AJ. Recent advances in human norovirus research and implications for candidate vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2020;19(6):539–48.10.1080/14760584.2020.1777860Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Chan MC, Lee N, Hung TN, Kwok K, Cheung K, Tin EK, et al. Rapid emergence and predominance of a broadly recognizing and fast-evolving norovirus GII.17 variant in late 2014. Nat Commun. 2015;6:10061.10.1038/ncomms10061Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Lu J, Sun L, Fang L, Yang F, Mo Y, Lao J, et al. Gastroenteritis outbreaks caused by norovirus GII.17, Guangdong Province, China, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(7):1240–2.10.3201/eid2107.150226Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Lu J, Fang L, Sun L, Zeng H, Li Y, Zheng H, et al. Association of GII.P16-GII.2 recombinant norovirus strain with increased norovirus outbreaks, Guangdong, China, 2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23(7):1188–90.10.3201/eid2307.170333Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Cheung SKC, Kwok K, Zhang LY, Mohammad KN, Lui GCY, Lee N, et al. Higher viral load of emerging norovirus GII.P16-GII.2 than pandemic GII.4 and epidemic GII.17, Hong Kong, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25(1):119–22.10.3201/eid2501.180395Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Villabruna N, Izquierdo Lara RW, Szarvas J, Koopmans MPG, Graaf M. Phylogenetic investigation of norovirus transmission between humans and animals. Viruses. 2020;12(11):1287.10.3390/v12111287Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Caddy SL, de Rougemont A, Emmott E, El-Attar L, Mitchell JA, Hollinshead M, et al. Evidence for human norovirus infection of dogs in the United kingdom. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(6):1873–83.10.1128/JCM.02778-14Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Mattison K, Shukla A, Cook A, Pollari F, Friendship R, Kelton D, et al. Human noroviruses in swine and cattle. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13(8):1184–8.10.3201/eid1308.070005Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Nakamura K, Saga Y, Iwai M, Obara M, Horimoto E, Hasegawa S, et al. Frequent detection of noroviruses and sapoviruses in swine and high genetic diversity of porcine sapovirus in Japan during fiscal year 2008. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(4):1215–22.10.1128/JCM.02130-09Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Sisay Z, Djikeng A, Berhe N, Belay G, Abegaz WE, Wang QH, et al. First detection and molecular characterization of sapoviruses and noroviruses with zoonotic potential in swine in Ethiopia. Arch Virol. 2016;161(10):2739–47.10.1007/s00705-016-2974-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 Manyu Li et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”

