Abstract
This study assessed the prevalence of plague bacterium (Yersinia pestis) among rodents captured in Umzingwane and Nkayi districts, south-western Zimbabwe. A total of 44 rodents were captured on three consecutive days per trapping session in the study sites using a removal trapping method in April 2018. Captured rodents were euthanized, and blood samples were collected. The Giemsa stain method was used to detect plague bacteria. The trapping success was not significantly different (χ² = 1.50, df = 1, P = 0.221), 8.5% for the Nkayi district, while in the Umzingwane district, it was 8%. Overall, only one rodent species, i.e., Mastomys natalensis, tested positive for Y. pestis in the Umzingwane district, thus yielding a prevalence rate of 2.3% for the entire study area. This was the most important finding of a Y. pestis-positive rodent in a non-endemic wild area in the Umzingwane district. These results point to a low prevalence of Y. pestis in the study area and the importance of an active plague disease surveillance and monitoring system.
1 Introduction
Plague, a disease caused by the bacilli bacterium, Yersinia pestis, primarily affects rodents, mainly transmitted from one host to another through bites of infective fleas [1]. However, there are alternative transmission routes, such as inhalation and direct contact, which do not normally play a role in the maintenance of plague bacterium in the animal reservoirs [2]. Fleas are generalists in their feeding behavior; thus, in the absence of rodents, they seek alternative hosts, such as wild and domestic animals, as well as people [3]. Thus, some flea species, for instance, Xenopsylla brasiliensis, are implicated as effective plague transmitters [4]. Alternatively, humans can acquire plague by handling infected rodents or by droplet infection, although humans do not play a role in the long-term survival of the plague bacterium [2]. In most cases, a plague outbreak causes a great population decrease in rodents of some species within their local and established ranges (Barnes, 1993, cited in Thiagarajan et al. [5]). However, some rodent hosts act as reservoirs of the disease in the enzootic environment allowing low levels of the pathogen circulation [3].
The first cases of human plague in Zimbabwe were recorded in 1974. The cases showed a complicated combination of plagues [6]. From then up to 1985, there were 89 cases noted, of which 23 deaths occurred [7]. Subsequent plague human cases were recorded in 1994 and 1997, where the highest cases of plague were noted, with about 400 cases and 30 deaths confirmed in Nkayi and Lupane districts, Matabeleland North [7,8]. In 2012 (latest information), plague was detected in Zimbabwe, but there was no full report of the disease [6]. Unavailability of active plague surveillance may have adverse repercussions, as an epidemic can occur undetected [9]. Plague foci are dynamic and keep on emerging and re-emerging [10], hence the importance of research to establish any potential new plague foci.
Plague bacterium can be hosted by a number of rodents. It was detected in multimammate mouse (Mastomys natalensis) and Gerbilliscus species in Tanzania [11]. Furthermore, small mammals, such as rabbits (Sylvilagus floridanus), marmots (Marmota), and chipmunks (Eutamias spp.), were shown to maintain plague in the wilderness [3]. Surveying diseases among free ranging wild animal populations may provide an early warning system for the presence of a disease. There is generally less active plague surveillance in Zimbabwe [4], except the few publications on rodents and fleas which largely focus on rodent and flea species diversity [12,13]. Therefore, this study aims to fill the gap in knowledge on plague prevalence in Zimbabwe by assessing the prevalence of plague bacteria among rodent species in Nkayi and Umzingwane districts. These two districts are in the same agro-ecological zone but differ in their plague occurrence: one is plague endemic (Nkayi district) while the other is plague non-endemic (Umzingwane district) [6,7].
2 Materials and methods
The study was conducted in south-western Zimbabwe in Nkayi and Umzingwane districts’ located in natural region IV (Figure 1). Nkayi district has deep Kalahari sands occupying 60% of the area whereas Umzingwane district’s soils are derived from granite rocks being coarse, sandy, and low in fertility [14]. The most common type of vegetation in Nkayi district is broad leafed woodlands, teak (Baikiaea plurijuga), and Brachystegia spp. [15]. Umzingwane district is characterized by three types of vegetation, which are bushveld, mainly covered with Acacia ranging between 1 and 5 m high, wooded grassland, and woodland covered by Terminalia and Combretum genus trees. The grasslands are the main source of grazing land [14].
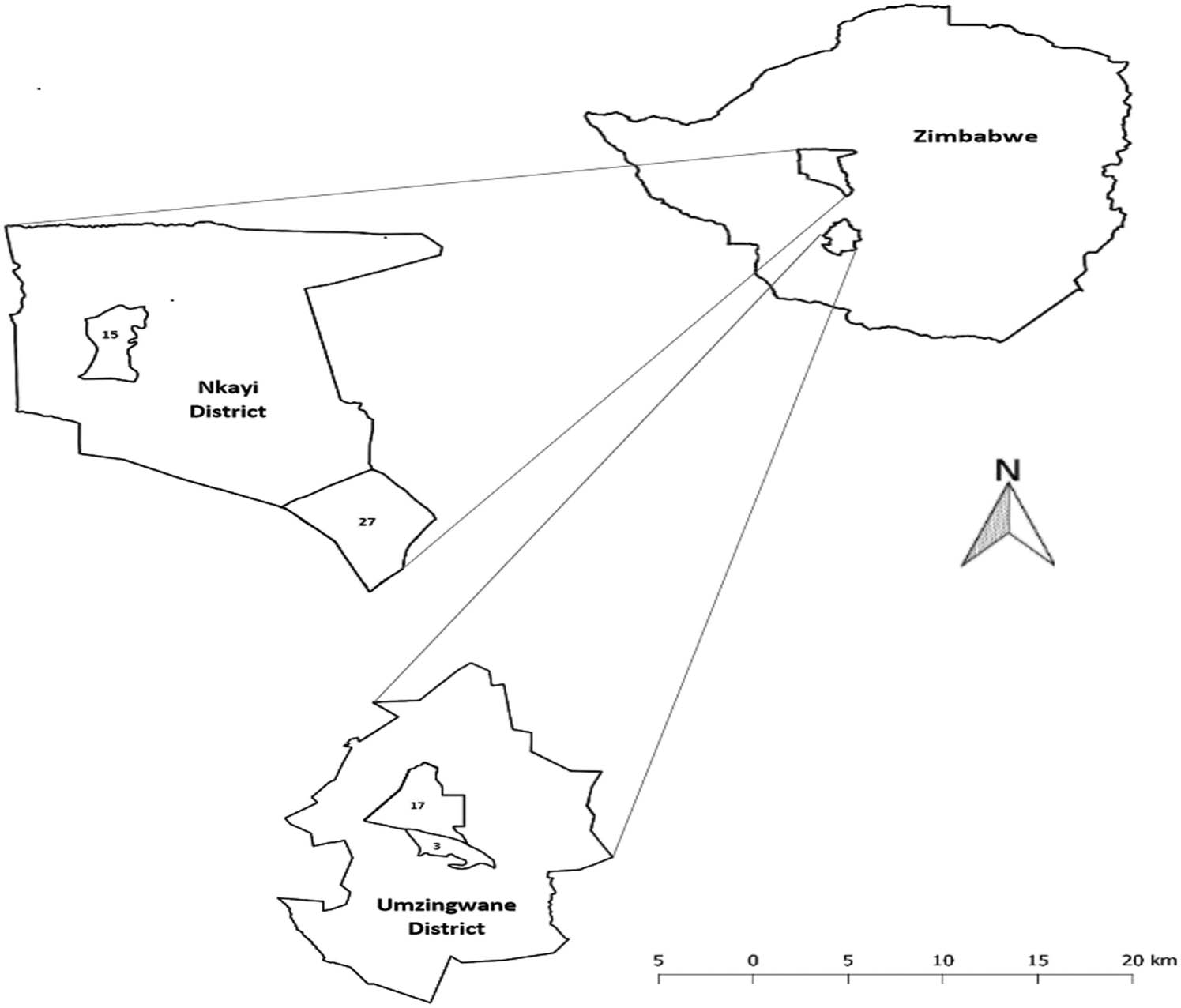
Location of Nkayi and Umzingwane Districts in south-western Zimbabwe. Notes: 15, 27, 3, and 17 represent Monki, Mathoba, Nhlekiyane, and Crocodile wards, respectively.
In the Nkayi district, most of the local rural community members are engaged in extensive livestock production and cultivation of some drought-tolerant crops, such as sorghum (Sorghum vulgare), finger millet (Eleusine coracana) and pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum). However, farmers do sometimes grow some short-season maize (Zea mays) varieties. Nkayi district’s population was reported to be 109,135 people, while the Umzingwane district had 62,990 people in 2012 [16].
This study followed a quasi-experimental design comprising two strata, i.e., districts and then two villages in each district. In the Nkayi district, the two villages studied were Mathoba and Monki villages while in the Umzingwane district were Crocodile and Nhlekiyane villages. All the trapping procedures and further processing of rodents were carried out following Dennis et al. [7], except that traps were placed 10 m apart.
Rodent trapping was conducted in April 2018 by first observing rodent activity, such as maize cob consumption and/or clearly constructed tracks and warrens. Rodents were captured in villages, i.e., bushes habitats using 15 Sherman live traps placed about 10 m apart in transects [17]. Three transects were placed in uncultivated places near fields in each study village. On the first day of sampling, traps were set late afternoon and inspected the following morning between 6 am and 7 am before it was too hot to reduce stress in captured rodents. Traps were left open for three consecutive days per village, i.e., 45 traps.
Productive traps were replaced in the morning following Kimaro et al. [17]. Traps with captures were taken to a central processing point in each study village, in an open area, for euthanization of rodents using chloroform, species identification and blood sample collection. Rodents were identified according to the illustrations and descriptions by du Plessis et al. [18]. Rodents identified were confirmed with the Natural History Museum, Bulawayo, Zimbabwe. Rodents’ cadavers were buried in a pit of about 50 cm deep.
After about 2–3 min after introducing the rodent to chloroform, blood was collected from the euthanized rodent using a hypodermic needle with a connected syringe. Blood was collected from the heart blood on which blood smears were made. Slides with Giemsa stain were examined at ×1,000 for 5–10 min, searching for bipolar coccobacilli [19] in the Wildlife Laboratory at Chinhoyi University of Technology, Chinhoyi, Zimbabwe.
2.1 Data analysis
Trapping success was calculated as the number of animals caught divided by the trapping period divided by the number of traps set per period multiplied by 100 (7). The Chi-square (χ²) test of independence or cross-tabulation was used to determine if there were differences among the trapping success in STATISTICA version 10 for Windows [20]. Diversity of rodents in each district was calculated following the Shannon–Wiener (H′) index measure of diversity [21]. The prevalence of Y. pestis in rodents’ blood samples was calculated as the number of Y. pestis-positive rodent individuals divided by the total number of rodents examined multiplied by 100.
3 Results
A total of 44 rodents were captured in the two study districts, i.e., Nkayi (H′ = 0.89) and Umzingwane (H′ = 0.62). There was no significant difference in the trapping success between the study districts, i.e., Nkayi (8.5%) and Umzingwane (8%) (Table 1) (χ² = 1.50, df = 1, P = 0.221). Twenty-three (23) rodents were caught in the Nkayi district and 21 in the Umzingwane district, i.e., 17 M. natalensis (Smith, 1834), 6 Gerbilliscus brantsi (Smith, 1836), 4 Gerbilliscus leucogaster (Peters, 1852), and 17 Saccostomys campestris (Peters, 1846). Only one rodent, i.e., M. natalensis, caught in the Umzingwane district tested positive for the plague bacterial, indicating an overall prevalence of plague of 2.4% in the study area (Table 2).
Rodents trapping success in the study area
| Variable | Nkayi district | Umzingwane district | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mathoba | Monki | Crocodile | Nhlekiyane | |
| No. rodents per site | 10 | 13 | 13 | 8 |
| Trapping success (%) | 7 | 10 | 10 | 6 |
| Mean trapping success (%) | 8.50 | 8.00 | ||
Rodents captured species diversity and prevalence of bacterial plague in the study area
| Rodent species | Nkayi district | Umzingwane district | Overall prevalence (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of rodents captured | # of rodents that are positive for Y. pestis | Prevalence (%) | # of rodents captured | # of rodents that positive for Y. pestis | Prevalence (%) | ||
| M. natalensis | 0 | 0 | 17 | 1 | 5.9 | 5.9 | |
| S. campestris | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| G. brantsi | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| G. leucogaster | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Species diversity (H′) | 0.89 | — | — | 0.62 | — | — | — |
| Total/average (%) | 23 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 1 | 4.8 | 2.4 |
Note: – denotes not applicable; # – denotes number.
4 Discussion
This study is the first to report the presence of plague bacteria among rodents in Umzingwane district, even though a low prevalence of plague disease exists in the study area. Elsewhere, plague bacteria were reported as being difficult to detect in rodents and fleas associated with prairie dog colonies (Cynomys) at Thunder Basin National Grassland in Wyoming, USA [5]. Thus, it was suggested that where possible plague determination investigations could be conducted in places where there are noticeable rodent die-offs [5]. Since time immemorial M. natalensis was observed not to easily succumb to plague bacteria, thus termed an enzootic host [11,22]. Thus, some of the caught species may not be ideal host for Y. pestis, for instance T. leucogaster was observed to easily succumb to Y. pestis closely related bacilli Y. pestis tuberculosis subspecies pestis [23].
Since no die-offs were observed during the sampling time, it may imply that an inter-epizootic period could have existed during which Y. pestis cannot be recovered from fleas, rodents, or any other host [1]. Instead, it was proposed in Iran and Madagascar that the bacteria could remain in existence in the soil. However, one study recommended that the transmission route by exposure of susceptible mice to Y. pestis-contaminated soil seems doubtful under natural conditions because the infectious period was short-lived and the transmission efficiency was low [24]. Thus, during plague quiescent times, it is likely that detecting Y. pestis is by mere chance.
In northern Tanzania, 517 wild, peri-domestic, and small commensal mammals, including rodents and wild carnivores, were captured, but only three tested positive for Y. pestis. This is an indication for the need for large samples to fully get a good picture of the infection status of a rodent population [11]. There can, however, be possibilities that Y. pestis is concentrated on certain rodent body organs as was reported in a study in Mongolia, where Y. pestis was detected in spleen samples, while liver samples from rodents tested negative using Polymerase Chain Reaction [25]. This therefore points to the importance of a large sample associated with diversified samples from the rodent body parts to enhance the chances of detection of the representative infection status of populations.
5 Conclusion
The study provides the first evidence of plague bacteria infection in a rodent species in Umzingwane district, a non-endemic region for the plague disease. It is recommended that future studies on plague bacteria assessment should involve a larger sample both for rodent populations and areas covering endemic and non-endemic regions, cover a longer sampling timeframe, and take samples from other body parts of rodents (liver and spleen) for testing beyond the blood.
Acknowledgments
Our sincere gratitude goes to the following village heads, Mr. R. Ncube and Mr. R. Tshuma (Umzingwane district) and Mr. A Mlotshwa and Mr. J. M. Gwayi (Nkayi district) for permission to conduct the study in their areas of jurisdiction. We are also indebted to Nkayi Principal Environmental Health Technician, Mr. J. Sibanda, and the Health Technicians, Mr. G. Mabhena and Mr. N. Ncube, for providing us with plague historical information.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Annabel Banda conceived and designed the experiments, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools, prepared figures and/or tables, authored or reviewed drafts of the manuscript, and approved the final draft. Edson Gandiwa conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed the data, contributed analysis tools, authored or reviewed drafts of the manuscript, and approved the final draft. Never Muboko and Victor K. Muposhi authored or reviewed drafts of the manuscript, and approved the final draft.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Rivière-Cinnamond A, Santandreu A, Luján A, Mertens F, Espinoza JO, Carpio Y, et al. Identifying the social and environmental determinants of plague endemicity in Peru: Insights from a case study in Ascope, la Libertad. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):1–11.10.1186/s12889-018-5062-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Perry RD, Fetherston JD. Yersinia pestis – Etiologic agent of plague. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997;10(1):35–66.10.1128/CMR.10.1.35Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Gage KL, Kosoy MY. Natural history of plague: Perspectives from more than a century of research. Annu Rev Entomol. 2005;50:505–28.10.1146/annurev.ento.50.071803.130337Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Chikwenhere G. Rodents and human diseases in Zimbabwe. In: Rats and human health in Africa: Proceedings of an international workshop on rodent-borne diseases and the RatZooMan research project. Malelane, Republic of South Africa: Natural Resources Institute of the University of Greenwich; 2006. p. 1–46.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Thiagarajan B, Bal Y, Gage KL, Cully JF. Prevalence of Yersinia pestis in rodents and fleas associated with black-tailed prairie dogs (Cynomys ludovicianus) at Thunder Basin National Grassland, Wyoming. J Wildl Dis. 2008;44(3):731–6.10.7589/0090-3558-44.3.731Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Munyenyiwa A, Zimba M, Nhiwatiwa T, Barson M. Plague in Zimbabwe from 1974 to 2018: A review article. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(11):1–17.10.1371/journal.pntd.0007761Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Dennis DT, Gage KL, Gratz N, Poland JD, Tikhomirov E. Plague manual-epidemiology, distribution, surveillance and control. In: Plague manual: Epidemiology, distribution, surveillance and control; Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 1999. p. 447.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Manungo P, Peterson D, Todd C, Mthamo N, Pazvakavambwa B. Risk factors for contracting plague in Nkayi district, Zimbabwe. Cent Afr J Med. 1998;44:173–6.Search in Google Scholar
[9] WHO. Plague around the world, 2010–2015. Wkly Epidemiol Rec/Heal Sect Secr Leag Nations. 2016;91(8):89–93. https://www.who.int/wer/2016/wer9108.pdf?ua=1.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Andrianaivoarimanana V, Kreppel K, Elissa N, Duplantier JM, Carniel E, Rajerison M, et al. Understanding the persistence of plague foci in madagascar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(11):1–8.10.1371/journal.pntd.0002382Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Ziwa MH, Matee MI, Hang’Ombe BM, Lyamuya EF, Kilonzo BS. Plague in Tanzania: An overview. Tanzan J Health Res. 2013;15(4):252–8.10.4314/thrb.v15i4.7Search in Google Scholar
[12] Zimba M, Pfukenyi D, Mukaratirwa S. Seasonal abundance of plague vector xenopsylla brasiliensis from rodents captured in three habitat types of periurban suburbs of harare, Zimbabwe. J Vec-Bor and Zoon Dis. 2010;11(8):1187–92.10.1089/vbz.2010.0095Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Zimba M, Loveridge J, Pfukenyi DM, Mukaratirwa S. Seasonal abundance and epidemiological indices of potential plague vectors dinopsyllus lypusus (Siphonaptera: Hystrichopsyllidae) and ctenophthalmus calceatus (Siphonaptera: Ctenophthalmidae) on rodents captured from three habitat types of Hatcliffe and Dzivarasekwa suburbs of Harare, Zimbabwe. J Med Entomol. 2012;49(6):1453–9.10.1603/ME11231Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Renaudin B, Patinet J. Environmental impact assessment (EIA)-ACF Zimbabwe. La Fontaine des Marins; 2010.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Dube T, Homann-Kee Tui S, Van Rooyen AF, Rodriguez D. Baseline and situation analysis report: Integrating crop and livestock production for improved food security and livelihoods in rural Zimbabwe. ICRISAT – Socioecon Discuss Pap Ser. 2014;29:8–9.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Zimstat C. Census 2012: Preliminary report. 2013. p. 123.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Kimaro DN, Msanya BM, Meliyo J, Hieronimo P, Mwango S, Kihupi NI, et al. Anthropogenic soils and land use patterns in relation to small mammal and flea abundance in plague endemic area of Western Usambara Mountains, Tanzania. Tanzan J Health Res. 2014;16(3):1–12.10.4314/thrb.v16i3.9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] du Plessis J, Swanepoel L, McDonough M, Schoeman C. A conservation assessment of Gerbilliscus leucogaster. South Africa: The Red list of Mammals of South Africa, Swaziland and Lesotho; 2016.Search in Google Scholar
[19] WHO. Interregional meeting on prevention and control of plague. In: Antananarivo, Madagascar 1–11 April 2006. Antananarivo: World Health Organisation; 2008. p. 1–65. http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/WHO_HSE_EPR_2008_3/en/.Search in Google Scholar
[20] StatSoft. STATISTICA for Windows. 2300 Tulsa: StaSoft Inc; 2010.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Krebs CJ. Ecology: The experimental analysis of distribution. 4th edn. New York, USA: HarperCollins College; 1994. p. 801.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Neerinckx SB, Peterson AT, Gulinck H, Deckers J, Leirs H. Geographic distribution and ecological niche of plague in sub-Saharan Africa. Int J Health Geogr. 2008;7:54.10.1186/1476-072X-7-54Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Isaacson M, Taylor P, Arntzen L. Ecology of plague in Africa: Response of indigenous wild rodents to experimental plague infection. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(2):339–44.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Boegler KA, Graham CB, Montenieri JA, McMillan K, Holmes JL, Petersen JM, et al. Evaluation of the infectiousness to mice of soil contaminated with yersinia pestis-infected blood. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012;12(11):948–52.10.1089/vbz.2012.1031Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Riehm JM, Tserennorov D, Kiefer D, Stuermer IW, Tomaso H, Zöller L, et al. Yersinia pestis in small rodents, Mongolia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(7):1320–2.10.3201/eid1707.100740Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2022 Annabel Banda et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”

