Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a type of main microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus (DM) and an important factor that causes blindness in adults. SOX4 is a transcription factor expressed in the pancreas and is essential for normal endocrine pancreatic development. However, the effect and the regulatory mechanism of SOX4 on DR have not been reported. In the present study, upregulation of SOX4 was found in DM patients, particularly in DR patients and mice models. The in vitro experiments showed that SOX4 depletion increased the viability and inhibited the inflammation level of human retinal endothelial cells (HRCECs) induced by high glucose. Besides, SOX4 knockdown inhibited the migration and angiogenesis of HRCECs upon high glucose treatment. Mechanically, depletion of SOX4 inhibited the NF-κB pathway. Therefore, SOX4 could serve as a promising target for DR treatment.
1 Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the main microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus (DM) and is a leading factor that causes blindness [1,2]. The main pathological changes of DR include retinal cell apoptosis and angiogenesis [3]. Previous studies demonstrated that the progression of DR was accompanied by oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation [2,4,5,6]. Because the highly complex pathogenesis of DR has not been fully elucidated, it is thus necessary to study and search for new therapeutic targets. In particular, inflammation and angiogenesis are two critical factors affecting DR progression.
The SOX family on the Y chromosome is an important set of transcriptional regulators involved in many developmental processes, including the endocrine pancreas development [7,8]. SOX4 is a transcription factor expressed in the pancreas and is essential for normal endocrine pancreatic development [9,10]. Studies have found that overexpression of SOX4 regulates the CXCL12 promoter in liver cancer cells to enhance tumor-induced angiogenesis, which contributes to distant tumor metastasis and causes poor prognosis in liver cancer patients [11]. Other studies have reported that SOX4 can be upregulated explicitly by retinoic acid and interleukin (IL)-1 treatment, a key transcription factor related to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis [12]. In addition, increased SOX4 expression inhibits insulin secretion by upregulation of STXBP6 and increases the risk of diabetes [13]. The role of SOX4 in metabolism and immunity has also been further studied. For example, SOX4 represses host innate immunity to facilitate pathogen infection by hijacking the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling networks [14]. However, its effects on DR have not been reported.
Inflammation is the main pathological feature of DR, and inhibition of inflammation has been found to significantly alleviate the development of DR [15]. The transcription factor NF-κB is responsible for expressing a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines and plays an important role in causing inflammation in many diseases [16]. It has been reported that Erianin could reduce microglia-induced retinal inflammation and DR by inhibiting the hyperglycemia-mediated ERK1/ERK 2-NF-κB axis [17]. In addition, it has been reported that SOX4 can promote the migration and invasion of melanoma cells by activating the NF-κB pathway [18]. Here, this study aimed to clarify the mechanism underlying SOX4-mediated NF-κB pathway in the DR model.
A series of experiments on high-glucose-induced human retinal endothelial cell (HRCEC) injury were performed to verify it. The results showed that the depletion of SOX4 could reduce the inflammatory level and inhibit the angiogenesis of HRCECs via targeting the NF-κB pathway.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Samples
The peripheral blood of healthy people, DR patients, and treatment groups from our hospital was collected to detect the mRNA level of SOX4. The patient has signed informed consent; 8-week-old female STZ-induced DB model mice (with and without retinopathy) were purchased from the Beijing weitonglihua company. The expression level of SOX4 protein was detected using immunoblot after the mouse eyeball was taken out.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animal use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals.
2.2 Antibodies
SOX4 antibody (1:500 dilutions, ab243739, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody (1:1,000 dilution, ab32152, Abcam), p65 antibody (1:500 dilution, ab32536, Abcam), p-p65 antibody (1:500 dilution, ab76302, Abcam), IκBα antibody (1:1,000 dilution, #9242, Cell signaling, USA), p- IκBα antibody (1:500 dilution, #2859, Cell signaling, USA), GAPDH antibody (1:2,000 dilution, ab8245, Abcam).
2.3 Cell culture, high glucose treatment, and transfection
HRCECs were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. HRCECs were treated with 33 mM glucose for 24 h. The siRNAs were from RioBio and transfected into cells by Lipofectamine 2000 (11668019; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). For siRNA transfection, 10 μL of siRNAs of SOX4 was added into 200 μL of OPTI medium for 5 min; 5 μL of lipofectamine was then added into 500 μL of OPTI-MEM for 5 min, mixed for 20 min, and added into cells. After 24 h, the subsequent assays were performed.
2.4 Immunoblot assay
Cell samples were lysed with lysis buffer (60 mM Tris–HCl; pH, 6.8; 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS]; 20% glycerol; 0.25% bromophenol blue; 1.25% 2-mercaptoethanol; and protease inhibitor cocktail, Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing, China). Total protein was separated using 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and sequentially transferred onto poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes (IPSN07852; EMD Millipore Corp, Billerica, MA, USA). The PVDF membranes were then blocked with 5% dry milk at room temperature for 2 h in tris-buffered saline with Tween (TBST) and subsequently incubated with the primary antibodies in TBST buffer for 1.5 h. Finally, the membranes were maintained with horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated antibodies for another 1 h. Signals were then visualized using the enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) kit.
2.5 Quantitative PCR (qPCR) assays
Trizol (15596026; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) served as an isolation kit to extract RNAs from cells. Then, the RNAs were reverse-transcribed using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Total mRNA was then reversely transcribed using a cDNA synthesis system. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was performed using an SYBR Ex Taq kit (Takara, Japan). The following thermocycling conditions were used: initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 58°C for 30 s, and extension at 72°C for 30 s. The 2−ΔΔCq method was used to quantify the results. Subsequently, the mRNA level was normalized to GAPDH. The primer sequences were as follows: tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α: 5′-ATGAGCACTGAAAGCATGATC-3′ and 5′-TCACAGGGCAATGATCCCAAAGTAGACCTGCCC-3′, IL-6: 5′-ATGAACTCCTTCTCCACAAGC-3′ and 5′-CTACATTTGCCGAAGAGCCCTCAGGCTGGACTG-3′, IL-8: 5′-ATGACTTCCAAGCTGGCCGTG-3′ and 5′-TTATGAATTCTCAGCCCTCTTCAAAAACTTCTC-3′.
2.6 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay
After transfection for 48 h, HRCECs were maintained for 48 h and then treated with MTT (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing, China) for 3 h and washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cells were then extracted using 150 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide, and the absorbance value at a wavelength of 570 nm was measured and finally analyzed using a Multifunctional enzyme marker (Thermo Fisher, San Jose, CA, USA).
2.7 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) assay
HRCECs were lysed with PBS and minced with magnetic beads, and lysates were collected and centrifuged. Concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in HRCECs were measured using ELISA kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). In brief, the sample was added to the reaction well (100 µL per well). At the end of incubation, the reagent was poured out of the reaction well, added 250 µL of 1× PBST buffer, then quickly poured it out, and repeated it twice. Next, an enzyme-labeled antibody was added, incubated for 2 h at 100 µL per well, and finally washed on the plate.
2.8 Transwell assay
Cells were resuspended in serum-free medium and were plated into the upper chambers to induce the migration toward the place containing the complete medium. After 24 h, cells in the top were removed, and the remaining cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min and stained with crystal violet (0.2%). The number of invasion cells was counted.
2.9 Tube formation assay
Each well of the 24-well plate was coated with 100 µL of matrigel and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Cells were then laid with 10,000 cells per well, cultured for 4 h, and observed under a microscope.
2.10 Statistics
GraphPad 7.0 was used for performing statistical analysis. Data were represented as mean ± SEM. Student’s t-test was used for statistical comparisons, and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 SOX4 was upregulated in DB model mice, and its depletion rescued the viability of HRCECs caused by high glucose
To uncover the possible effects of SOX4 on the progression of DR, the mRNA level of SOX4 was detected in the peripheral blood monocytes of patients. qPCR assays showed an increased SOX4 mRNA level in patients with DR, whereas it was decreased in the DR-treatment group (Figure 1a). The diabetic mice model was induced by STZ, and the expression of SOX4 increased, while it was aggravated in STZ-induced mice with retinopathy (Figure 1b). A DR cell model was constructed by administering high glucose (33 mM) into HRCECs for 24 h. Immunoblot assays showed the upregulation of SOX4 in high-glucose-induced HRCECs, compared to the normal group (Figure 1c). Subsequently, a siRNA of SOX4 was transfected into high-glucose-induced HRCECs to deplete its expression, and obviously decreased SOX4 expression was noticed (Figure 1c). MTT assay showed that high glucose treatment suppressed the viability of HRCECs, and SOX4 depletion increased the viability of HRCECs upon high glucose treatment (Figure 1d). Therefore, SOX4 was upregulated in DB samples, and its depletion rescued the viability of HRCECs caused by high glucose treatment.
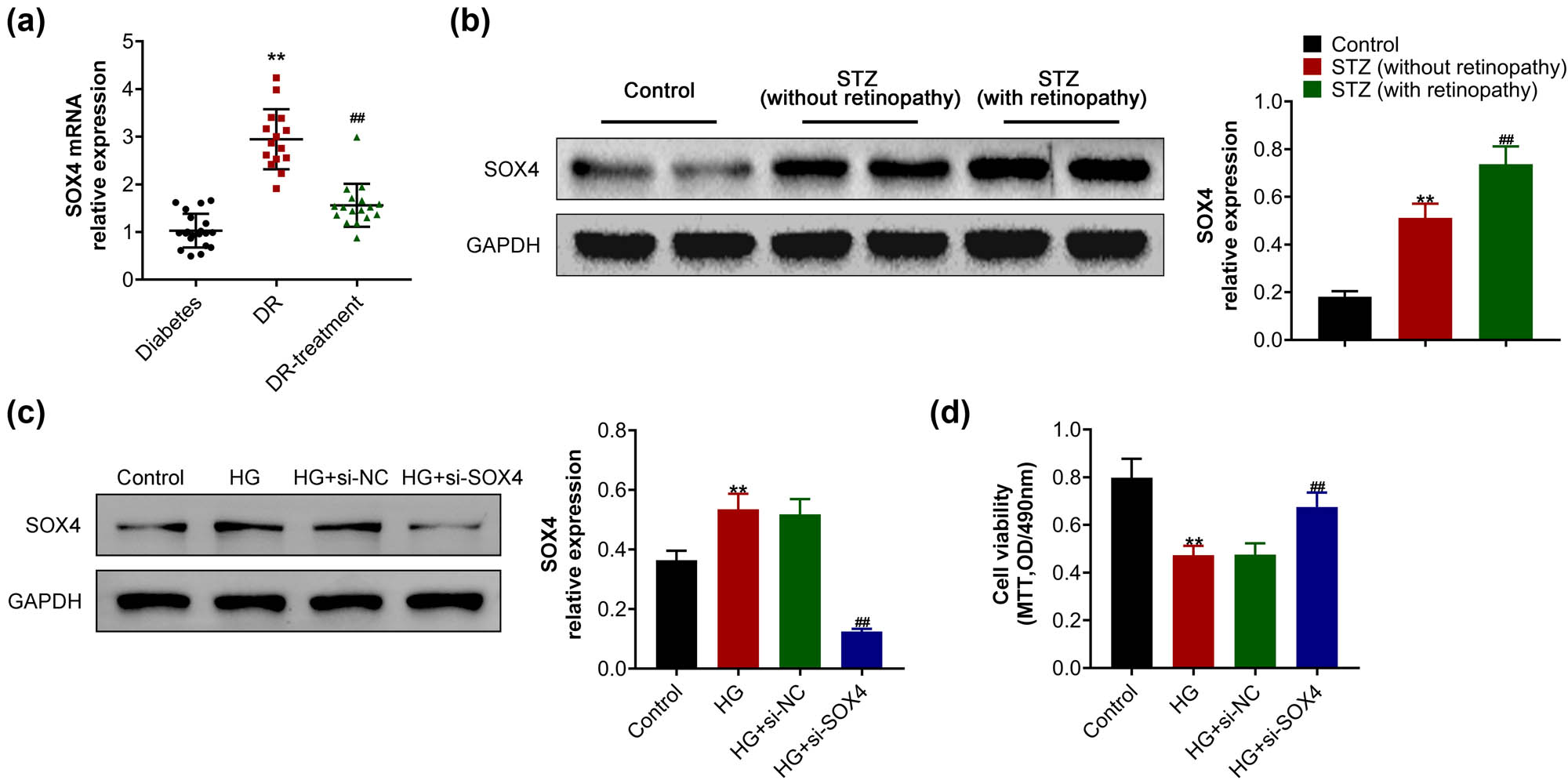
SOX4 was upregulated in DB samples, and its depletion suppressed the viability of high-glucose-induced HRCECs. (a) qPCR assays showed the mRNA level of SOX4 in the peripheral blood monocytes from patients with diabetes, DR, and DR-treatment group. (b) Immunoblot assay showed the expression of SOX4 in mice upon treatment of control, STZ (without retinopathy), and STZ (with retinopathy). (c) Immunoblot assay showed the expression of SOX4 in HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. (d) MTT assay showed the viability of HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, HG versus control, **p < 0.01, HG + siSOX4 versus HG + siNC, ## p < 0.01. HG, high glucose, NC, negative control.
3.2 SOX4 depletion restrained the high-glucose-induced inflammatory response in HRCECs
The following studies were then performed to detect the effects of SOX4 on the inflammatory response of HRCECs. qPCR assays showed that high glucose treatment increased the mRNA levels of inflammatory factors, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in HRCECs (Figure 2a). In addition, SOX4 depletion suppressed the mRNA levels of these inflammatory factors, suggesting the inhibition of inflammatory response caused by SOX4 depletion (Figure 2a). Similarly, ELISA showed that high glucose treatment increased the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in HRCECs (Figure 2b), whereas SOX4 ablation suppressed the secretion of these inflammatory factors (Figure 2b). Therefore, SOX4 depletion restrained the high-glucose-induced inflammatory response in HRCECs.
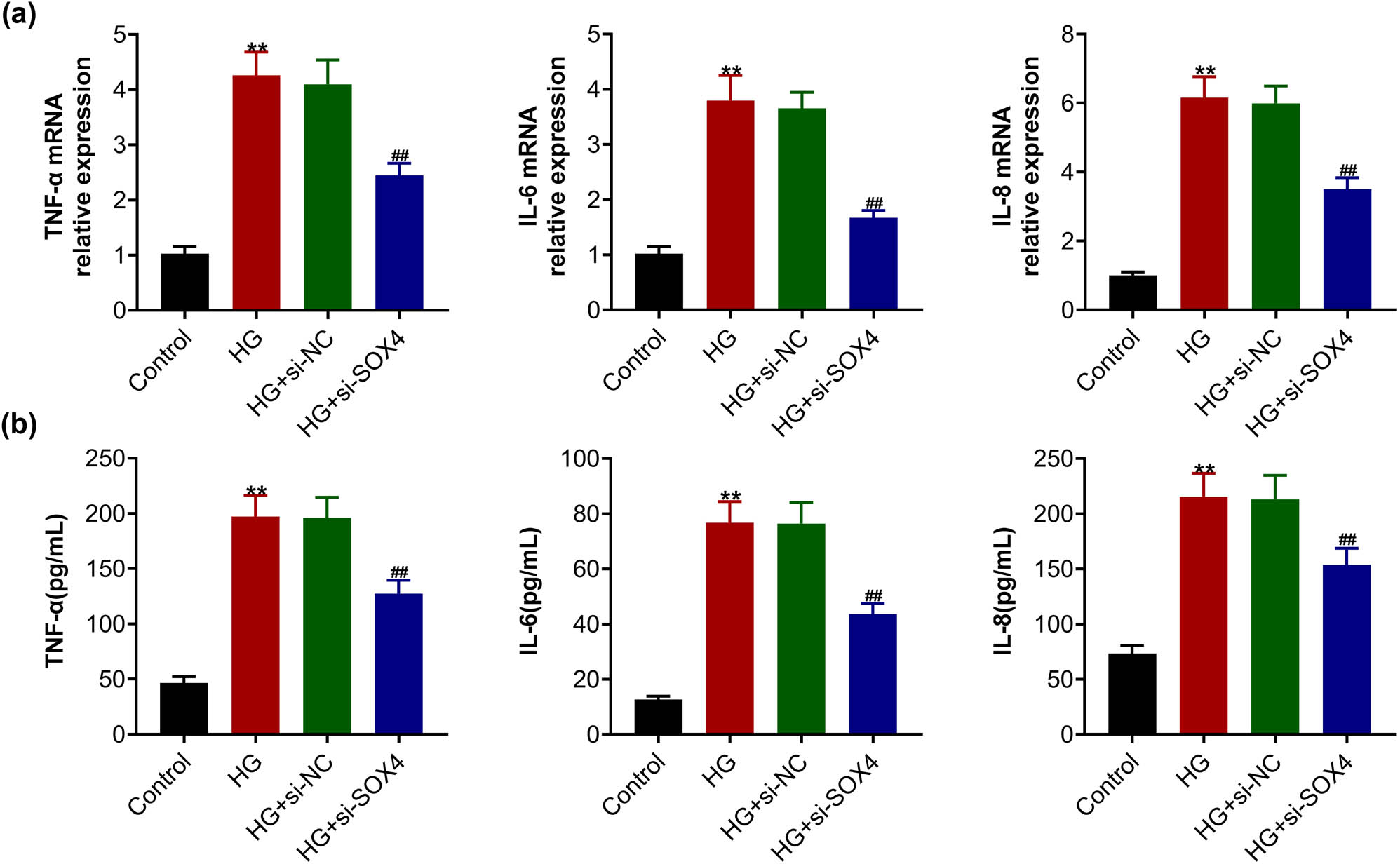
SOX4 depletion restrained the high-glucose-induced inflammatory response in HRCECs. (a) qPCR assay showed the mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. (b) ELISA assay showed the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, HG versus control, **p < 0.01, HG + siSOX4 versus HG + siNC, ## p < 0.01. HG, high glucose, NC, negative control.
3.3 SOX4 depletion suppressed the high-glucose-induced migration and angiogenesis in HRCECs
Subsequently, the present study detected the effects of SOX4 on the migration and angiogenesis of HRCECs upon high glucose treatment. Transwell assay showed that high glucose treatment promoted the migration of HRCECs, whereas the ablation of SOX4 suppressed the migration of HRCECs upon high glucose treatment (Figures 3a and b). The tube formation in vitro assay showed that high glucose treatment stimulated the tube formation of HRCECs, whereas the depletion of SOX4 suppressed the angiogenesis of HRCECs induced by high glucose (Figure 3c). In addition, the immunoblot assay showed that high glucose increased the expression of VEGF, whereas knockdown of SOX4 suppressed VEGF expression in HRCECs caused by high glucose (Figure 3d). Taken together, SOX4 depletion suppressed the high-glucose-induced migration and angiogenesis in HRCECs.
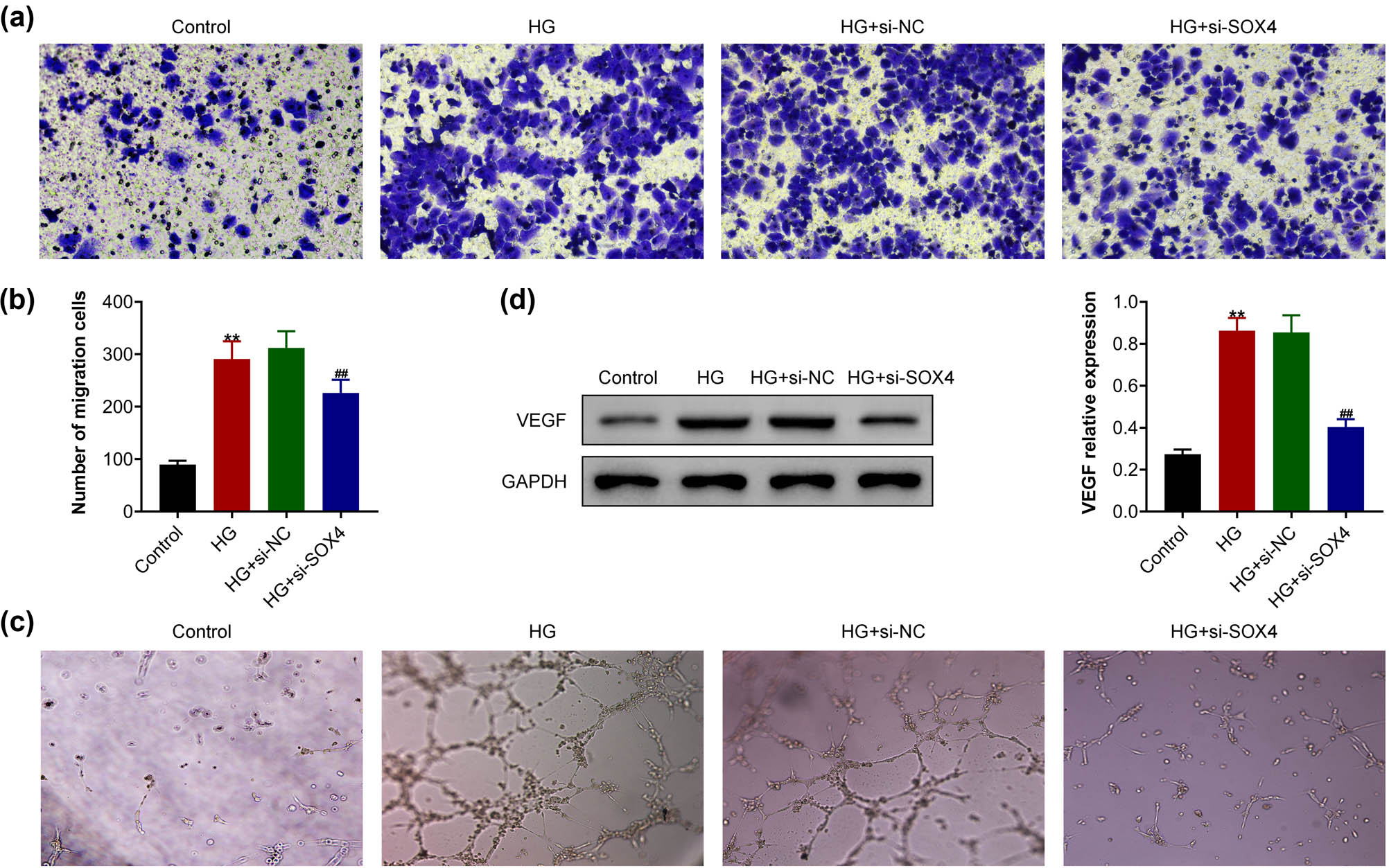
SOX4 depletion suppressed the high-glucose-induced migration and angiogenesis of HRCECs. (a) Transwell assay showed the migration of HRCEC upon the indicated treatment, and (b) the migratory cell numbers were counted. (c) Tube formation assay showed the angiogenesis of HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. (d) Immunoblot assay showed VEGF expression in HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, HG versus control, **p < 0.01, HG + siSOX4 versus HG + siNC, ## p < 0.01. HG, high glucose, NC, negative control.
3.4 SOX4 ablation inhibited the high-glucose-induced NF-κB signaling pathway in HRCECs
Further studies were performed to explore the possible mechanism. A previous study showed the effects of SOX4 on the NF-κB signaling pathway, which could affect cell viability, inflammation, and angiogenesis [19]. Therefore, the effects of SOX4 on the NF-κB signaling pathway were explored in high-glucose-induced HRCECs. Immunoblot assay showed that high glucose treatment increased the phosphorylation levels of p65 and IκBα in HRCECs (Figure 4). Importantly, depletion of SOX4 suppressed the phosphorylation levels of p65 and IκBα in HRCECs induced by high glucose (Figure 4). Taken together, SOX4 ablation inhibited NF-κB signaling pathway in HRCECs induced by high glucose.
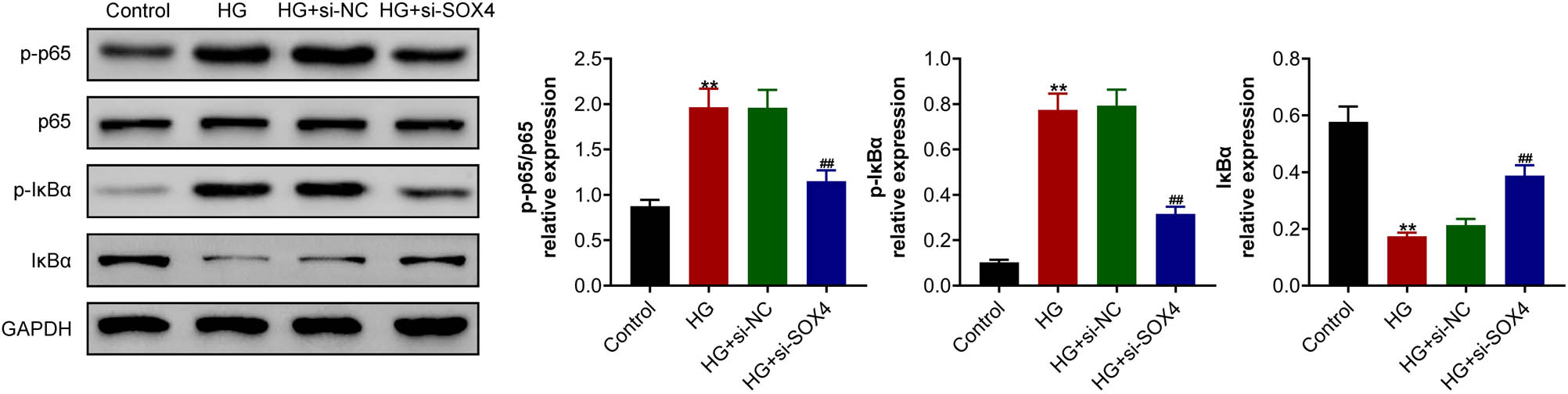
SOX4 ablation inhibited the high-glucose-induced NF-κB signaling pathway in HRCECs. Immunoblot assay showed the expressions of the phosphorylation levels of p65 and IκBα in HRCECs upon the indicated treatment. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, HG versus control, **p < 0.01, HG + siSOX4 versus HG + siNC, ## p < 0.01. HG, high glucose, NC, negative control.
4 Discussion
DR is the most important manifestation of diabetic microangiopathy, a kind of fundus lesion with specific changes, and is one of the serious complications of diabetes [20]. Vitrectomy should be performed as early as possible in patients with severe proliferative DR, such as repeated massive fundus hemorrhage, large fibrous proliferative membrane, and retinal detachment [21]. To further improve the cure rate of DR, new and more effective treatment drugs still need to be developed. Also, it is urgently needed to clarify the pathogenesis of DR and identify the key regulatory proteins [22]. Interestingly, this study identified a protein, SOX4, that could promote high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells, serving as a promising target for DR.
MTT assay showed the stimulative effects of SOX4 on the viability of high-glucose-induced HRCECs. qPCR and ELISA assays further confirmed the regulatory effects of SOX4 on the inflammatory response of high-glucose-induced HRCECs. Transwell, tube formation, and immunoblot assays were further performed and confirmed the regulatory effects of SOX4 on the migration and angiogenesis of high glucose-induced HRCECs. SOX4, well-known as a transcription factor, was expressed in the pancreas and is essential for normal endocrine pancreatic development [23]. Also, SOX4 was involved in regulating multiple cellular processes, such as tumorigenesis [10]. SOX4-induced ARHGAP9 overexpression also promoted the progression of acute myeloid leukemia [24]. Azilsartan could prevent AGE-induced inflammatory response in human chondrocytes through inhibition of SOX4 [25]. Our data, therefore, showed the potential of SOX4 as a target for DR treatment.
A previous study indicated that SOX4 could promote melanoma cell migration and invasion by activating the NF-κB pathway [19]. In this study, SOX4 was involved in the high-glucose-induced injury of HRCECs by regulating the NF-κB pathway. The pathway affected multiple downstream cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, motility, apoptosis, and angiogenesis, thus contributing to the progression of DR [17]. Besides, multiple proteins or drugs affected the progression and development of DR via the NF-κB pathway [2]. For example, nimbolide could ameliorate the STZ-induced DR in rats through the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway [26]. In addition, asiatic acid attenuated DR through NF-κB p65-mediated modulation of microglia polarization [27]. CD146 pathway was a novel biomarker of angiogenesis and inflammation in DR progression [27]. Similarly, SOX4 affected angiogenesis and inflammation in high-glucose-induced HRCECs.
Notably, overexpression of SOX4-mediated CXCL12 promoter in HCC cells enhanced tumor-induced angiogenesis, contributing to distant tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients [11]. In this study, the effects of SOX4 on the angiogenesis of HRCECs were determined. However, the precise mechanism underlying the effects of SOX4 on angiogenesis via the NF-κB pathway needs further study.
In conclusion, SOX4 depletion increased the viability, inhibited the inflammation level, and suppressed the migration and angiogenesis in high-glucose-induced HRCECs. The underlying mechanism was via the NF-κB pathway. SOX4 was therefore served as a promising target for DR treatment.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding is involved.
-
Author contributions: Haifeng Wei and Quan Gu designed the study, supervised the data collection, analyzed the data, interpreted the data, prepared the manuscript for publication, and reviewed the draft manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Ma Y, Li S, Zhang A, Ma Y, Wan Y, Han J, et al. Association between red blood cell distribution width and diabetic retinopathy: a 5-year retrospective case-control study. J Ophthalmol. 2021;2021:6653969. 10.1155/2021/6653969. PMID: 34327012.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Forrester JV, Kuffova L, Delibegovic M. The role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Front Immunol. 2020;11:583687. 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583687. PMID: 33240272.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Jin Q, Hao XF, Xie LK, Xu J, Sun M, Yuan H, et al. A network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:8878569. 10.1155/2020/8878569. PMID: 33204295.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Valle MS, Russo C, Malaguarnera L. Protective role of vitamin D against oxidative stress in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021;37(8):e3447. 10.1002/dmrr.3447. PMID: 33760363.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Bek T. Mitochondrial dysfunction and diabetic retinopathy. Mitochondrion. 2017;36:4–6. 10.1016/j.mito.2016.07.011. PMID: 27456429.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Luan Y, Luan Y, Feng Q, Chen X, Ren KD, Yang Y. Emerging role of mitophagy in the heart: therapeutic potentials to modulate mitophagy in cardiac diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:3259963. 10.1155/2021/3259963. PMID: 34603595.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Wilson M, Koopman P, Matching SOX. partner proteins and co-factors of the SOX family of transcriptional regulators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12(4):441–6. 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00323-4. PMID: 12100890.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Weider M, Reiprich S, Wegner M. Sox appeal – Sox10 attracts epigenetic and transcriptional regulators in myelinating glia. Biol Chem. 2013;394(12):1583–93. 10.1515/hsz-2013-0146. PMID: 23729567.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Huang HY, Cheng YY, Liao WC, Tien YW, Yang CH, Hsu SM, et al. SOX4 transcriptionally regulates multiple SEMA3/plexin family members and promotes tumor growth in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e48637. 10.1371/journal.pone.0048637. PMID: 23251334.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Xu X, Zong K, Wang X, Dou D, Lv P, Zhang Z, et al. miR-30d suppresses proliferation and invasiveness of pancreatic cancer by targeting the SOX4/PI3K-AKT axis and predicts poor outcome. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):350. 10.1038/s41419-021-03576-0. PMID: 33824274.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Tsai CN, Yu SC, Lee CW, Pang JS, Wu CH, Lin SE, et al. SOX4 activates CXCL12 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells to modulate endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis in vivo. Oncogene. 2020;39(24):4695–710. 10.1038/s41388-020-1319-z. PMID: 32404985.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Zhu YJ, Jiang DM. LncRNA PART1 modulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-373-3p/SOX4 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(19):8175–85. 10.26355/eurrev_201910_19124. PMID: 31646607.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Collins SC, Do HW, Hastoy B, Hugill A, Adam J, Chibalina MV, et al. Increased expression of the diabetes gene SOX4 reduces insulin secretion by impaired fusion pore expansion. Diabetes. 2016;65(7):1952–61. 10.2337/db15-1489. PMID: 26993066.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Shang J, Zheng Y, Mo J, Wang W, Luo Z, Li Y, et al. Sox4 represses host innate immunity to facilitate pathogen infection by hijacking the TLR signaling networks. Virulence. 2021;12(1):704–22. 10.1080/21505594.2021.1882775. PMID: 33517839.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Tu Y, Song E, Wang Z, Ji N, Zhu L, Wang K, et al. Melatonin attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation of Muller cells in diabetic retinopathy via activating the Sirt1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111274. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111274. PMID: 33517190.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Shih RH, Wang CY, Yang CM. NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015;8:77. 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077. PMID: 26733801.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Zhang T, Ouyang H, Mei X, Lu B, Yu Z, Chen K, et al. Erianin alleviates diabetic retinopathy by reducing retinal inflammation initiated by microglial cells via inhibiting hyperglycemia-mediated ERK1/2-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2019;33(11):11776–90. 10.1096/fj.201802614RRR. PMID: 31365278.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Cheng Q, Du J, Xie L, Liu X, Li Z, Zuo F, et al. Inhibition of SOX4 induces melanoma cell apoptosis via downregulation of NF-kappaB p65 signaling. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(1):369–76. 10.3892/or.2018.6443. PMID: 29767266.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Cheng Q, Wu J, Zhang Y, Liu X, Xu N, Zuo F, et al. SOX4 promotes melanoma cell migration and invasion though the activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(2):447–53. 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3030. PMID: 28627651.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Thumshirn M, Berger W. A case from practice (311). Sensorimotor polyneuropathy and autonomous neuropathy with increased sweating in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus II – diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy and microangiopathy. Praxis (Bern 1994). 1994;83(45):1272–3. PMID: 7973288.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Glassman AR, Beaulieu WT, Maguire MG, Antoszyk AN, Chow CC, Elman MJ, et al. Visual acuity, vitreous hemorrhage, and other ocular outcomes after vitrectomy vs aflibercept for vitreous hemorrhage due to diabetic retinopathy: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021;139(7):725–33. 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.1110. PMID: 33956075.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Majidi SP, Rajagopal R. Photoreceptor responses to light in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Vis Neurosci. 2020;37:E007. 10.1017/S0952523820000061. PMID: 32921331.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Xu EE, Krentz NA, Tan S, Chow SZ, Tang M, Nian C, et al. SOX4 cooperates with neurogenin 3 to regulate endocrine pancreas formation in mouse models. Diabetologia. 2015;58(5):1013–23. 10.1007/s00125-015-3507-x. PMID: 25652387.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] He X, Zou H, Wang F. SOX4-induced upregulation of ARHGAP9 promotes the progression of acute myeloid leukemia. Drug Dev Res. 2021;82(8):1227–34. 10.1002/ddr.21837. PMID: 34159626.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Lei J, He M, Xu L, He C, Li J, Wang W. Azilsartan prevented AGE-induced inflammatory response and degradation of aggrecan in human chondrocytes through inhibition of Sox4. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(8):e22827. 10.1002/jbt.22827. PMID: 34051020.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Shu X, Hu Y, Huang C, Wei N. Nimbolide ameliorates the streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy in rats through the inhibition of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(8):4255–62. 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.039. PMID: 34354407.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Fang M, Wan W, Li Q, Wan W, Long Y, Liu H, et al. Asiatic acid attenuates diabetic retinopathy through TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB p65 mediated modulation of microglia polarization. Life Sci. 2021;277:119567. 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119567. PMID: 33965378.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 Haifeng Wei and Quan Gu, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”

