Abstract
Long-term fertilization will affect the above-ground vegetation, but we have little understanding of soil bacterial community structure and diversity so far. This study aims to study the effect of organic fertilization on the soil bacterial community structure and diversity of protected long-term continuous tomato cropping by using high-throughput sequencing technology. Results show that (1) fertilization application (chemical fertilizer [CF] and vermicompost [VM]) significantly changed the soil physico-chemistry properties, such as soil pH decreased compared with control treatment and increased the soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and total potassium (TK) contents; (2) VM increased the Shannon index of soil bacteria but decreased the soil Chao1 index; and (3) soil Proteobacteria and Actinomycetes were dominant taxa and the relative abundance of Actinobacteria increased by 36.40–44.27 and 25.80–29.35%, with CF and VM, respectively, compared with the control. Pearson correlation analysis showed that soil pH, SOC, TN, TP, and TK were the main environmental factors that affected the diversity and richness of soil bacterial communities. Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that the SOC and TN play important roles in the composition of soil bacterial communities. In summary, the effect of VM on the soil bacterial community structure of continuous tomato cropping is better than that of CF, which should be used in the sustainable production of facility tomatoes.
1 Introduction
Microorganisms are a key component of the soil ecological chain. They play important roles in soil nutrient cycling, organic matter (OM) formation and decomposition, soil-borne disease occurrence and prevention, and crop growth and development. Additionally, soil microorganisms are crucial for maintaining soil ecological balance and fertility [1,2]. Therefore, maintaining high soil microbial activity and diversity is fundamental for current soil quality management practices.
Continuous protected tomato cropping is common in southern China. The continuous cropping of a single species often leads to an imbalance in the soil microbial flora, which manifests as a decrease in microbial diversity, an increase in pathogenic bacteria, and a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria [3,4]. Furthermore, tomato production is often accompanied by excessive application of chemical fertilizers (CFs). This practice affects crop yield, soil physical and chemical characteristics, and quality and directly changes the structure of the soil microbial community [5,6]. Studies have shown that the long-term application of CFs can significantly reduce soil pH and microorganism number and diversity [6].
The use of organic materials (including livestock and poultry manure and straw) to fertilize continuous cropping soils in facilities has a high application value; it can also replace CFs and, therefore, reduce the volume used in facility agricultural production. The input of organic materials can effectively improve the structure of continuous cropping soil aggregates, increase the OM content, and reduce the salt content. Ding et al. [7] performed field experiments showing that long-term combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers increased the diversity of soil bacteria and fungi and promoted the growth of beneficial bacteria; conversely, single application of CFs promoted fungi growth. Long-term use of organic manure and straw returning in the field can also increase the abundance of flora such as growth-promoting bacteria (plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, which promote plant growth and many microbial products that stimulate plant growth) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, which promote soil health [8,9]. However, it is still unknown whether the input of organic materials can significantly enhance the structure of the bacterial community in continuous cropping soil.
China produces billions of tons of organic solid waste every year, including agricultural waste (e.g., straw), which has surpassed 800 million tons produced yearly. A large amount of straw is burned or discarded, polluting the environment and wasting resources [10]. As of 2010, the total amount of livestock and poultry manure emissions in China has reached 1.9 billion tons, 227 million of which have not been properly treated to prevent environmental pollution [11]. This solid waste is rich in nutrients and OM needed for crop growth and development [12,13]. After being composted or adequately processed, organic solid waste can be used for fertilization in agricultural production, promoting sustainable development and reducing environmental pollution [13,14]. Therefore, in this study, we used high-throughput sequencing technology to analyze the effects of composting or earthworm treatment of livestock and poultry manure (vermicompost, VM) and CF on the composition and diversity of soil bacterial communities in facility tomato continuous cropping. We analyzed the feasibility of applying VM and CF in the sustainable production of facility agriculture and provided a theoretical basis for the rational fertilization of facility agriculture.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental design
The experiments were performed in a greenhouse in the Suzhou Polytechnic Institute of Agriculture (120.64 E, 31.43 N), Jiangsu, China, from March to June 2020. The greenhouse had natural light exposure, and the day and night temperature was controlled to be within 15–35°C.
This study used a completely random design. The fertilization treatments tested were VM, CF, and the control (CK) without fertilization. There were three treatments in total, and each was repeated five times. The total amount of N, P2O5, and K2O was equal in all fertilization treatments. To achieve the local general fertilization amount desired, the N, P2O5, and K2O dosages were set to 0.45, 0.20, and 0.40 g kg−1 soil, respectively (approximately 850 kg N hm−2, 552 kg P2O5 hm−2, and 850 kg K2O hm−2). The soil’s total nitrogen (TN), total phosphor (TP), and total potassium (TK) were detected by a soil elemental analyzer (FlashSmart, ThermoFisher). The soil moisture content was 43%.
The amount of VM applied was 13.10 g kg−1 soil (approximately 30 t hm−2), and the amount of RS was 45.52 g kg−1 soil (approximately 95 t hm−2) (Table 1). Additional fertilizers (urea, superphosphate, and potassium sulfate) were added to VM and RS to achieve the same N, P2O5, and K2O content as the CF treatment. We added the total contents of urea, superphosphate, and potassium sulfate of 50, 35, and 30 kg, respectively. The nutrient contents of the fertilizers used are shown in Table 1.
The properties of VM and rice straw
| Treatment | pH | SOC (g kg) | TN (g kg) | TP (g kg) | TK (g kg) | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VM | 6.38 | 2,035 | 46.8 | 17.85 | 4.65 | 7.4 |
| RS | 5.92 | 5,830 | 450.5 | 8.35 | 6.53 | 52.69 |
Note: VM: vermicompost; RS: rice straw; SOC: soil organic carbon; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TK: total potassium; C/N: soil organic carbon/total nitrogen.
All fertilizers were applied as a base fertilizer simultaneously to thoroughly mix the soil and fertilizer. No top dressing was performed during the tomato growth period.
2.2 Soil characteristics
The soil used in this study was utilized for 5 years of continuous tomato cropping in the greenhouse. Soil pH (soil/water = 1/5) and electrical conductivity (EC, soil/water = 1/5) were measured with a pH meter (INESA, Shanghai, China) and a DDS-307 conductivity meter (Shanghai Precise Science Instrument Co., China), respectively. The OM content was estimated by the potassium dichromate dilution calorimetry method [15]. Soil’s total carbon (TC) and TN were measured using a Vario EL III element analyzer (Elementar Co., Germany) [16]. Soil TK was detected by a soil elemental analyzer (FlashSmart, ThermoFisher).
The pH value and EC of the tested soil were 6.17 and 490 μS cm−1, respectively, and the available nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium contents were 206.9, 374.0, and 564.6 mg kg−1, respectively. The soil organic carbon (SOC) and TN content were 46.63 and 3.07 g kg−1, respectively, and the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio was 8.93. The tomato plants were cultivated in polyethylene pots (30 cm × 28 cm). After the air-dried soil was sieved with a 1 cm mesh, each pot was packed with 15 kg of soil with a bulk density of approximately 1.30 g cm−3.
The RS used in the experiment was collected from the experimental rice base of the Suzhou Polytechnic Institute of Agriculture, air-dried, and crushed to 2–3 cm before use.
On March 12, 2020, seedlings (with 3–4 true leaves) that grew sturdily, neatly, moderately, and relatively uniformly were selected and transplanted into pots. The irrigation was maintained during the growth period at 70% of the field water holding capacity and 80% of conventional field management. The test tomato variety used was “Zhongyan No. 988,” cultivated by the Beijing ZhongYanYiNong Seedling Co., Ltd. The entire growth period was 108 days.
2.3 Sample collection and measurement methods
Soil samples were collected during the tomato full fruit period (75 days). The soil samples were collected using a soil auger (8 cm in diameter). The soils were collected from 5 to 10 points along an S-shaped path within each treatment and mixed for a sample to ensure the representativeness of soil samples for each treatment, and immediately sent to the laboratory for analysis. A part of the fresh soil was passed through a 10-mesh sieve, and the root residues were removed and stored at −80°C for soil bacterial community and diversity analysis. Another part of fresh soil was air-dried and passed through 20- and 100-mesh sieves to determine the soil physical and chemical properties.
The total deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of each soil sample (0.5 g) was extracted using a Fast DNA SPIN Kit for Soil (MP Bio, USA), and the DNA was pre-checked with 1% agarose gel to assure purity. Next, the concentration and quality were tested by a NanoDrop 2000 UV spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA); the qualified products were sent to Zoonbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd, to determine the composition of the soil microbial communities. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and product purification were performed using diluted genomic DNA.
The HiFi Hotstar ReadMix PCR kit high-fidelity enzyme (KAPA Biosystems, USA) was used for PCR. PCR products were detected with 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, purified by gel extraction, and analyzed with a NanoDrop 2000 UV micro-spectrophotometer and 2% agarose gel electrophoresis to inspect the library quality. Products that passed the quality inspection were quantified with a Qubit (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA) and mixed in the corresponding proportions according to the data volume requirements of each sample.
The V3–V4 region, a highly variable region of ribosomal genes, was used for bacterial 16S rDNA amplification, and the universal primers used were F341 (5′-ACTCCTAGGGRSGCAGCAG-3′) and R806 (5′-GGACTACVVGGTATCTA-3). The index and linker sequences suitable for HiSeq2500 PE250 sequencing were added to the 5′-end of the universal primers. Amplified fragments of approximately 425 and 320 bp were obtained. After adding adapters, the products were sequenced using the HiSeq platform Illumina Miseq PE300 to obtain 2 × 300 bp Paired-End data, which was used to analyze the soil bacterial community. The Project accession number for raw data is SUB10527892.
2.4 Data analysis
QIIME (Version 1.7.0) was used to aggregate the 16S sequence data, and the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) method was used for species clustering (similarity: 97%). Mothur software was used to analyze the bacterial diversity and richness index. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) was used in R to indicate the beta diversity of the soil bacterial community. Adonis analysis was used in R to indicate the soil bacterial community similarity. The Adonis analysis was performed by using the R software vegan package at the operational taxonomic unit (OTU) level. The OTU was used to determine significant differences between different fertilization treatments (P < 0.05); the data were used to construct a PCoA by using an R software vegan package at the OTU level. The Canoco 4.5 data package was used for redundancy analysis (RDA).
SPSS 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for one-way analysis of variance and Pearson’s correlation analysis. The differences between treatments were tested with the Duncan test. The data in the graphs are all averages of five biological replicates.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Soil physical and chemical properties
The pH of the soil treated with fertilization was significantly lower than that of CK (pH 7.20), with the most significant decrease occurring with CF (pH 4.54) and the minor decrease occurring with VM (pH 5.35) (Table 2). Compared with CK, fertilization treatments significantly increased the soil TN (6.01–26.61 g kg), SOC (10.03–15.88 g kg), TP (8.28–9.54 g kg), and TK (5.25–6.35 g kg) contents (Table 2).
Soil physico-chemistry properties under different treatments
| Treatment | pH | SOC (g kg) | TN (g kg) | TP (g kg) | TK (g kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.20 ± 0.01a | 160.03 ± 6.21 | 20.20 ± 5.35a | 8.28 ± 3.28b | 5.25 ± 2.10c |
| CF | 5.35 ± 0.02b | 510.50 ± 40.85 | 22.35 ± 5.14a | 15.35 ± 2.54a | 8.78 ± 1.55a |
| VM | 4.54 ± 0.01c | 230.30 ± 5.85 | 22.41 ± 4.81a | 9.54 ± 3.25b | 6.35 ± 1.55b |
CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost; SOC: soil organic carbon; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TK: total potassium; Lowercase letter indicates the Duncan test at the P < 0.05 level. The table content indicates mean ± standard deviations. All values are the mean values from three replicates.
3.2 Relative abundance of soil bacterial groups at different taxonomic levels
The 3153–3649 OTUs of the treated soil samples belonged to 35 phyla, 92 classes, 160 orders, 329 families, and 687 genera. At the level of bacterial phylum classification, the dominant phyla were Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Firmicutes, Gemmatimonadetes, Bacteroides, Candidatus Saccharibacteria, Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobia, and Cyanobacteria (relative abundance >1%) (Figure 1). The relative abundance of the dominant bacteria groups, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria, increased significantly after the application of organic materials (to 36.40–44.27% and 25.80–29.35%) compared with CK (35.88 and 23.10%); the relative abundance of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes also increased significantly, but the relative abundance of Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobiobio, Cyrobiobiosella, and Cyanobacteria was significantly reduced. CF treatments had the opposite effect on organic materials, leading to lower Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria abundances (23.46 and 19.13%). Proteobacteria had the highest abundance ratio in the CK treatment (44.27%), and the treatment with the highest abundance of Actinobacteria was VM (29.35%). These results show that the application of organic materials can increase the relative content of phylum-level dominant flora in the soil and decrease the abundance of other microbial flora to varying degrees.
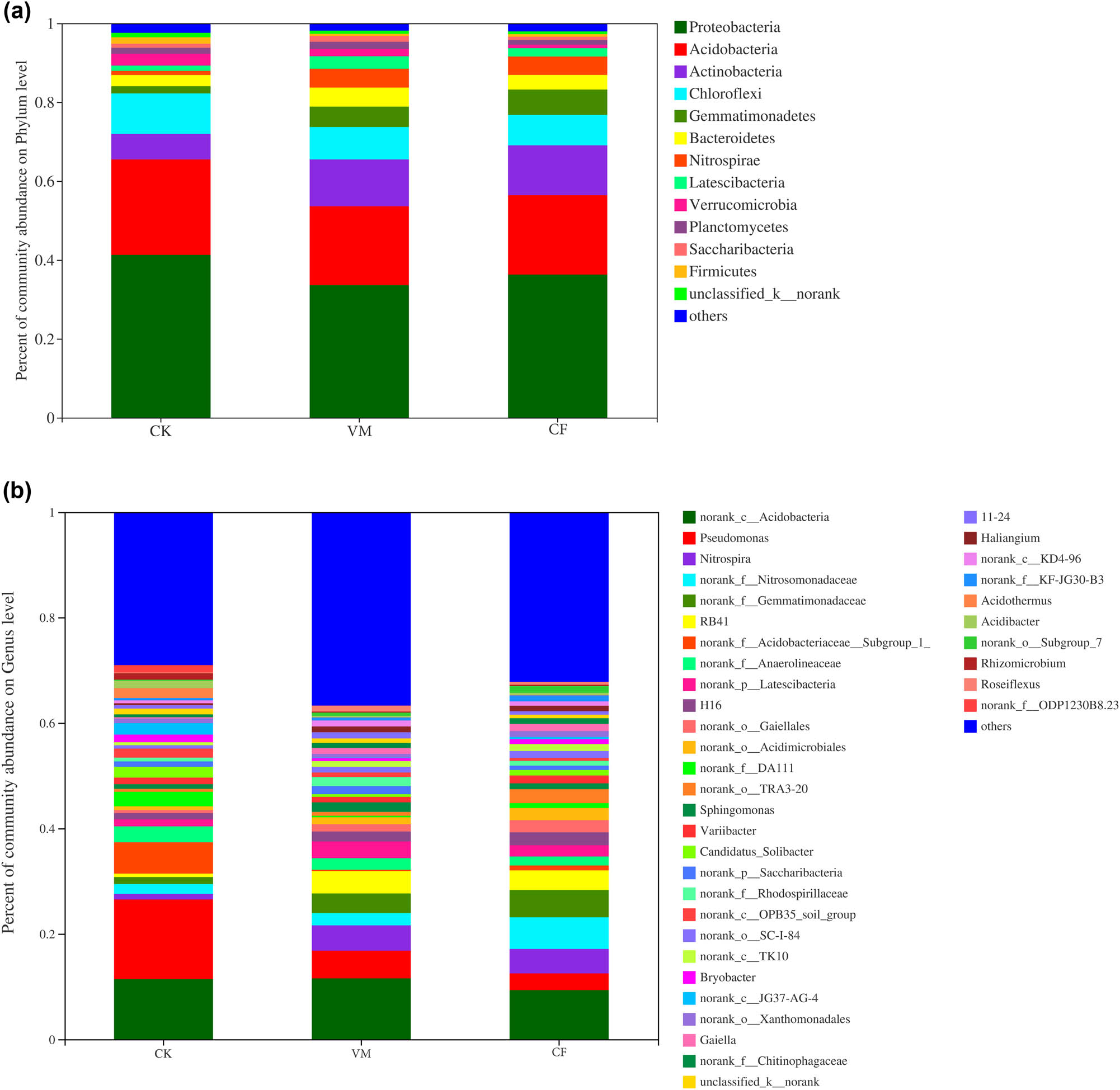
Relative abundance of soil bacterial phyla (a) and genera (b) in different treatments.
Figure 1 shows the relative abundance of the bacterial genus in different treatments, in which the parts with an average abundance level lower than 0.5% are merged. They are insignificant in the CF (2.42%) treatment, compared with CK (3.65%) and VM (3.86%), slightly increasing the relative abundance of these bacteria. Gemmatimonas represented 4.72% of CM and 4.71% of VM; in CF, this dominant flora in the soil significantly reduced its relative abundance (3.29%). Gp6, Gp16, and Gp4 belong to the acid phylum (Acidobacteria), and their relative abundance is the highest in the CF treatments (8.0, 6.87, and 4.10%, respectively), followed by CK (6.33, 3.25, and 4.06%, respectively). Hence, the application of organic materials reduced the relative abundance of Gp6, Gp16, and Gp4 compared to CF and CK. Gaiella had the highest relative abundance in the VM treatment (3.78%) and the lowest in CF (2.45%). There were also several genera that changed significantly differed in abundance between different treatments. For example, Bacillus and Streptomyces had the highest abundance in CF and the lowest in VM. CK had the lowest. Porphyrobacter was significantly more abundant in VM than in CK and CF, with increases ranging 1.08–1.61 times. The relative abundance of Hyphomicrobium was the highest in VM and the lowest in CF.
The heatmap based on species showed the bacterial composition of different treatments (Figure A1). From Figure A3, we could infer that the bacterial compositions of VM and CF were more similar compared to that of CK, indicating that the fertilization treatment significantly changed the soil bacterial composition. Based on Figure A1, the g_staphylococcus was dominant in the VM and CF, whereas f_Peptostreptococcaceae and f_Pseudonocardiaceae were dominant in VM and CK, respectively.
3.3 Changes in soil bacterial community structure
The bacterial communities were analyzed by 16S rDNA sequencing of 18 soil samples obtained from 54,249 to 64,915 high-quality sequences and from 42,661 to 54,118 effective sequences (74–90% of high-quality sequences).
The average read length was 414.37 bp. The sequencing coverage rate was 97%, and a total of 3,153–3,649 OTUs were obtained, which shows that the gene sequences in the soil samples reflect the true soil bacterial community status.
The rarefaction curve indicates the sample sequencing depth and can be used to evaluate whether the sequencing volume is sufficient to cover all groups. Figure A2 shows the rarefaction curve for all samples in this test under the condition of similarity of 0.97. As shown in Figure 1, all soil sample dilution curves tended to flatten, indicating that sampling was reasonable, and the confidence in the bacterial community structure in the actual environment was high, which could reflect the bacterial community of a soil sample in a relatively realistic way (Table 3).
Soil bacterial alpha diversity in different treatments
| Treatments | Chao1 | Shannon–weiner | Simpson | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2455.45 ± 20.32b | 6.54 ± 0.12b | 0.005 ± 0.0001 | 0.99 ± 0.001a |
| CF | 2354.20 ± 35.21b | 6.32 ± 0.18b | 0.008 ± 0.0002 | 0.98 ± 0.005a |
| VM | 2741.35 ± 45.40a | 7.86 ± 0.54a | 0.009 ± 0.0001 | 0.99 ± 0.003a |
Lowercase indicates the Duncan test at the P < 0.05 level. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost; SOC: soil organic carbon; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TK: total potassium. The table content indicates mean ± standard deviations. All values are the mean values from three replicates.
The soil Chao1 and Shannon and Simpson indices differed significantly (P < 0.05) between the six treatments. The Chaol index of the different fertilization modes ranked CK > VM > CF in our analyses; VM and CF treatments led to values significantly lower than CK, whereas there was no significant difference between other treatments and CK. The Shannon and Simpson indices were the highest for VM and the lowest for CF; they were significantly higher for VM than for CF treatment. The Chaol index was significantly negatively correlated with
Pearson correlation of soil alpha bacterial diversities and soil physico-chemistry properties
| pH | SOC | TN | TP | TK | C/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | 0.385 | −0.104 | −0.105 | −0.845 | 0.286 | −0.82 |
| Shannon–Weiner | 0.865* | 0.885* | 0.203 | −0.204 | 0.308 | 0.12 |
| Simpson | 0.102 | 0.910* | 0.154 | 0.53 | 0.341 | 0.897* |
The table content indicates the correlation coefficent by Pearson’s correlation analysis. *P < 0.05.
PCoA was used to show the soil bacterial beta diversity (Figure 2). The results showed that among all the treatments, the soil bacterial community compositions of VM and CF were the most similar.
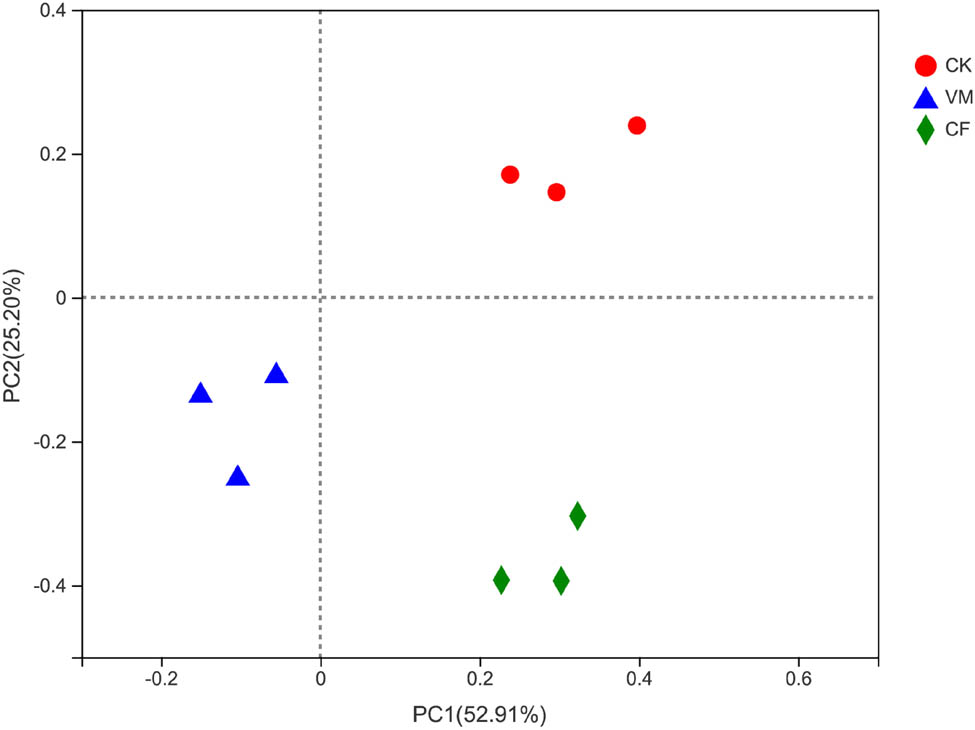
PCoA analysis of bacterial community structure in different fertilization treatments. Note: The β-diversity (changes in community structures) was calculated at the OTU level (97%) based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity index. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost.
The results showed that the first (PCoA1) and the second (PCoA2) principal component axis contributed, respectively, 18.91 and 13.81% to the difference between fertilization treatments. The distances between CF and VM were the closest, indicating that the soil OTU composition of the three was the most similar. This indicates that fertilization changed the composition of the bacterial community in continuous cropping soil, especially for the organic fertilizer treatment. The Adonis results indicate that the soil bacterial structure was significantly changed among CK, CF, and VM (Adonis P < 0.05, Figure A3).
A Venn diagram illustrates the number of common and unique OTUs in three treatments, as shown in Figure A4. In total, 2,126 OTUs were detected, of which 1,238 (58.23%) were shared among the CK, CF, and VM soils (Figure A4). There were only 320 OTUs found in CK, accounting for 15.05% of the total. CF soils produced 110 OTUs, accounting for (5.17%), and the OTUs specific for VM were 9, accounting for 0.04%.
3.4 Correlation between soil bacterial groups and chemical properties
To clarify the environmental factors that change the structure of the soil microbial community, we analyzed the correlation between the dominant flora at the bacterial phylum and the genus level and the soil chemical properties (Table 5 and Figure 3). At the phylum classification level, Actinomycetes were negatively correlated with EC and significantly positively correlated with
Pearson correlation of relative abundance of soil bacterial at phyla level and soil physico-chemistry properties
| pH | SOC | TN | TP | TK | C/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | −0.214 | 0.803* | 0.215 | 0.072 | 0.305 | 0.264 |
| Acidobacteria | 0.154 | −0.735* | −0.284 | −0.183 | −0.528* | 0.969* |
| Actinobacteiria | −0.228 | 0.864* | 0.891* | 0.314 | 0.872* | −0.454* |
| Chloroflexi | 0.084 | −0.682* | 0.23 | 0.022 | −0.402* | −0.204 |
| Gemmatimonadetes | 0.286 | 0.430* | 0.136 | 0.801* | 0.785* | 0.343 |
| Bacteroidetes | −0.028 | 0.785* | 0.24 | 0.892 | 0.234 | 0.787* |
*P < 0.05. The table content indicates the correlation coefficent by Pearson’s correlation analysis. *P < 0.05.
SOC: soil organic carbon; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TK: total potassium; C/N: soil organic carbon/total nitrogen.
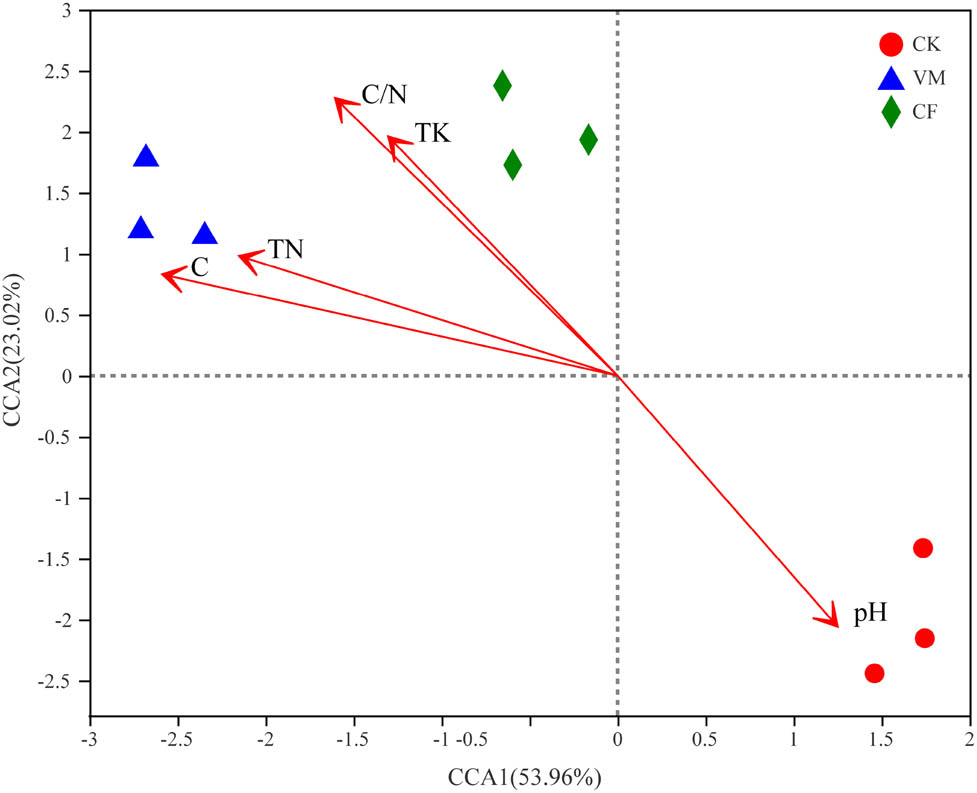
RDA of soil physico-chemistry properties and bacterial at OTU level. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost.
RDA results showed that the first and second ordination axes explained 56.0 and 8.6% of the bacterial community changes, respectively, and the two together explained 64.6% of the bacterial community changes (Figure 3). On the first sorting axis, the bacterial communities of organic material treatment (VM) were significantly changed compared with those of CF and CK, and they were distributed on both sides of the first axis. The overall degree of explanation of soil chemical properties for changes in bacterial community structure was 75.2%, of which
4 Discussion
Soil microbial diversity is an important factor in maintaining soil health [17]. Studies have shown that continuous cropping reduces the microbial diversity around the rhizosphere and increases the abundance of pathogens, leading to the occurrence of root diseases [18]. For example, Li et al. [19] analyzed the microbial communities in rhizosphere soil samples of healthy tomatoes and diseased tomatoes suffering from bacterial wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum) that were grown continuously for 3 years and showed that the soil microbial diversity was higher in healthy tomato than in diseased tomato. Therefore, improving the diversity of soil microorganisms is key to alleviating soil-borne diseases in continuous cropping soil. This study showed that after fertilization with VM and CM, the soil bacterial alpha diversity increased in continuous tomato cropping and decreased after applying CFs. That might be because the application of VM improved the soil aggregate structure and chemical properties (such as pH and EC value), improving soil microbial diversity [20]. Furthermore, the increase in soil nutrients through the application of VM, especially the increase of OM (Table 2), can promote the growth of soil microorganisms [21]. Considering the chemical properties of the soil, the application of VM can significantly increase the EC value, and there is a risk of secondary soil salinization after long-term application. Hence, fertilization with earthworm manure might be a more appropriate alternative. Similar to our results, Khan et al. [22] compared the effects of long-term application of VM and inorganic fertilizer to soil used for cucumber cultivation and found that the soil microbial diversity treated was the highest with VM treatments. VM is the product of semi-decomposed agricultural or food waste that has been processed by the earthworm intestinal system. Its microbial diversity and aggregate structure are better than traditional compost [23,24]. Soils with high bacterial community diversity have functional redundancy among the communities, and the fluctuation of certain microbial groups has little effect on the overall function of soil microorganisms. Therefore, increasing bacterial community diversity can effectively maintain soil ecological functions and health [17]. The application of VM can increase the diversity of the bacterial community in the continuous cropping soil of facility-grown tomatoes, thereby improving soil disease resistance.
Ai et al. [25] found that soil disease resistance is positively correlated with the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Actinomycota in rhizosphere soil. In rhizosphere soils with low plant incidence, the total number of these microorganisms is higher than in rhizosphere soil with high plant incidence. This may be due to the strong disease resistance of some unique microorganisms belonging to these categories [26]. We found that the relative abundances of Actinomycetes, Firmicutes, and Bacteroides were significantly increased after applying organic materials, especially VM (Figure 2), which contrasts with the results obtained by Arjun et al. [27]. This indicates that the application of VM has the potential to improve the resistance to soil pathogens. It is generally believed that the phylum Proteobacteria, which includes trophic bacteria [28], can use complex OM and plant residues as carbon and nitrogen sources [29]. Here, the content of nutrients (
5 Conclusion
VM application has greater advantages than CF, RS, and conventional compost by adjusting soil pH and maintaining low soil salinity. In addition, the rich nutrient content and better soil aggregate structure in the soil VM fertilization can significantly improve the soil microbial environment and diversity, especially by increasing the abundance of some microorganisms that have an anti-pathogenic effect, which is useful to overcome the limitations of continuous cropping.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Chengzhong Wang from Suzhou Polytechnic Institute of Agriculture, Suzhou, for providing assistance.
-
Funding information: The work was financially supported by the Basic Research on Suzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (SNG2020062) and SZAI Science and Technology Incubation Project (PY2104).
-
Author contributions: Jun Chen, Yichun Du and Wei Zhu designed and did the experiment and prepared this manuscript. Xin Pan helped to finish the bioinformatic analysis. Zhen Wang revised this manuscript and languageediting. All coauthors contributed to manuscript editing.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Appendix
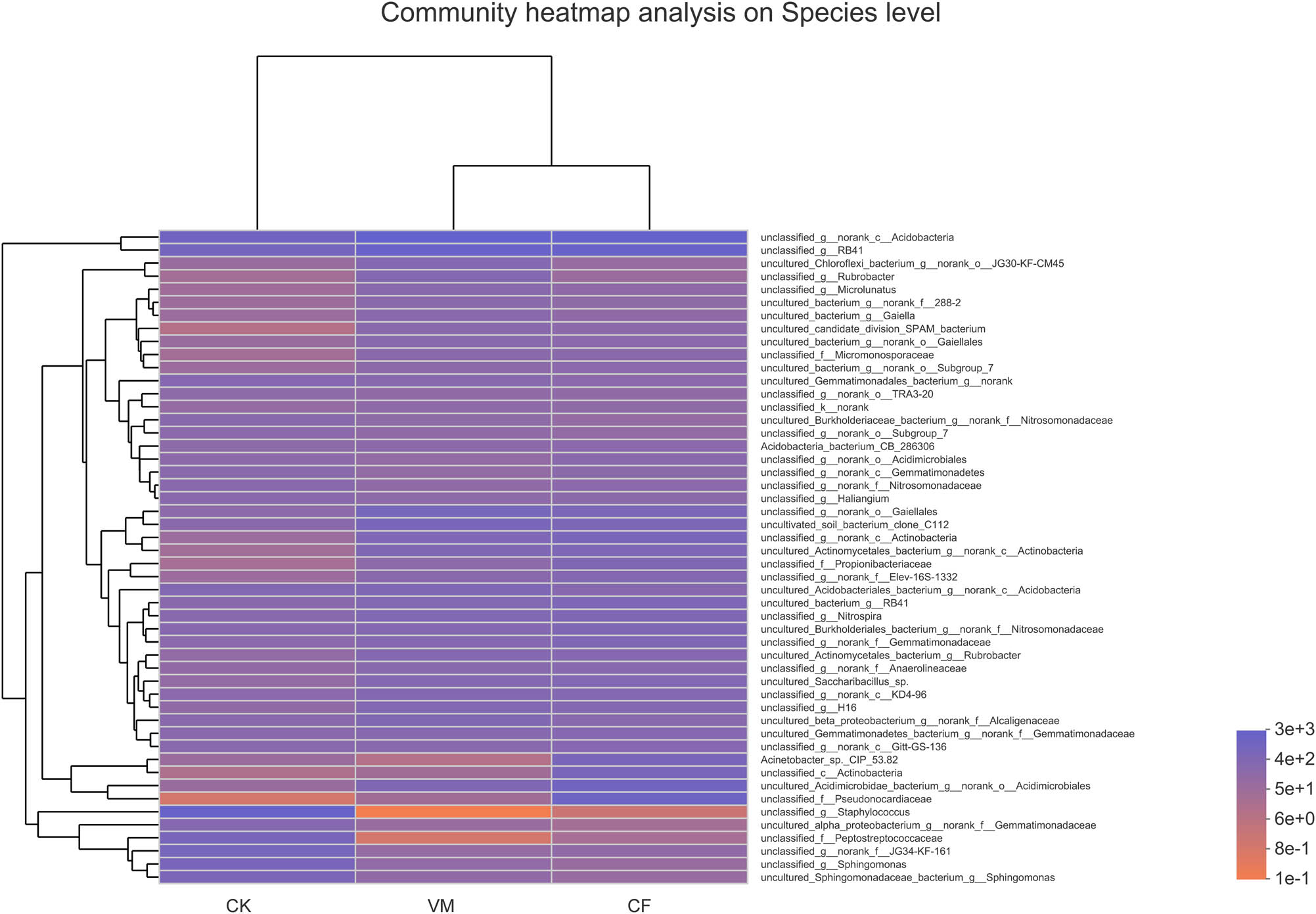
Heatmap diagram based on specie level of bacteria from the different soil samples. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost.
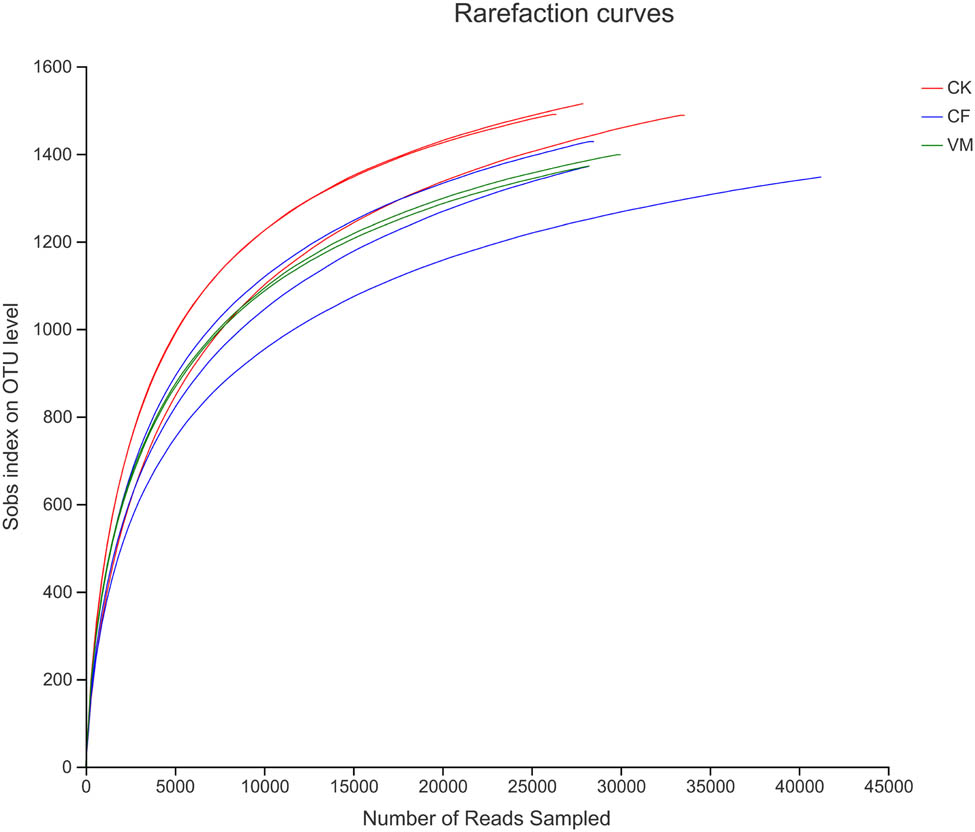
Rarefraction diagram of soil bacteria from the different soil samples. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost.
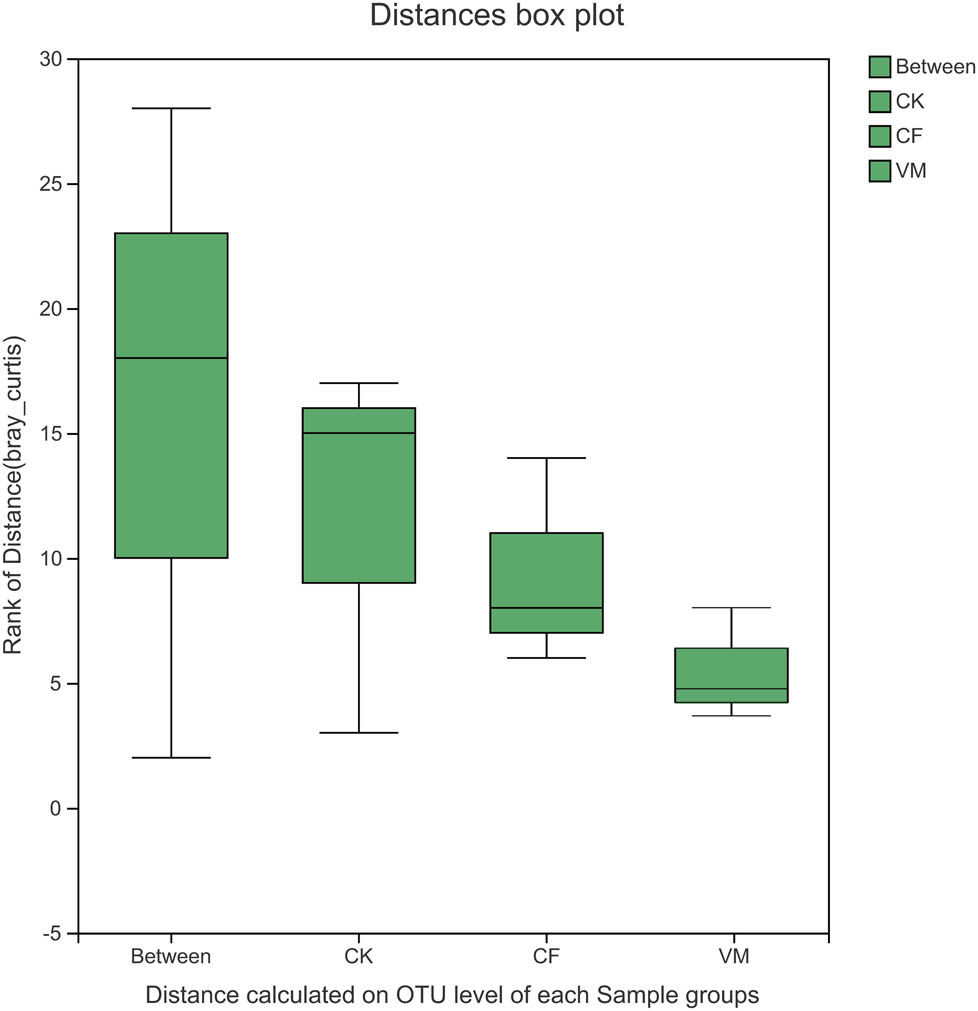
Distance box plot of soil bacteria from the different soil samples based on Adonis analysis. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost.
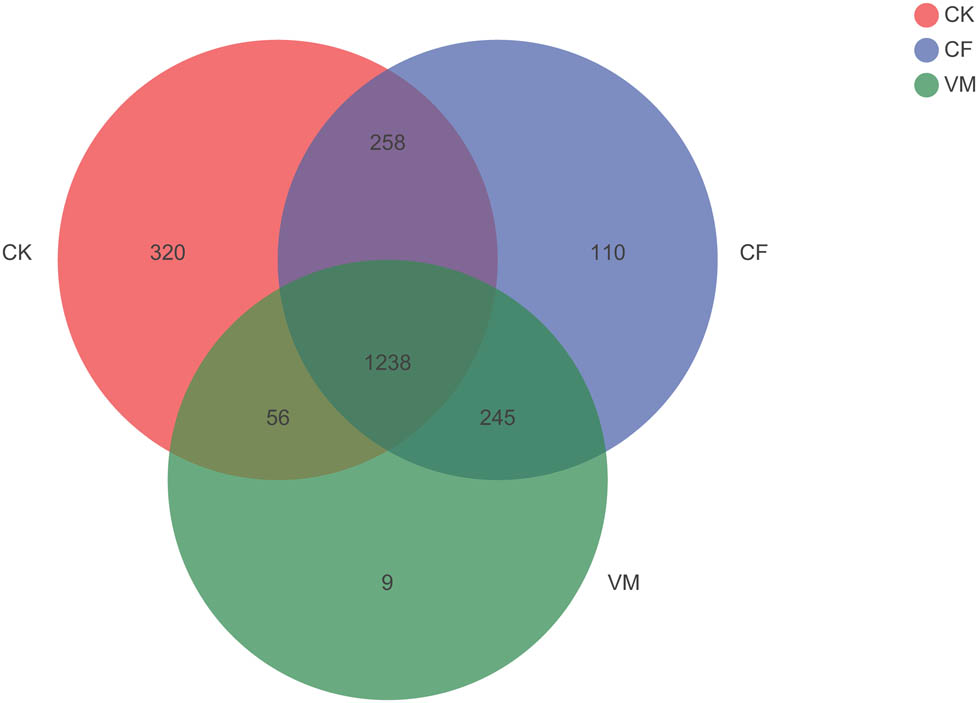
Venn diagram showing the numbers of shared and exclusive OTUs of bacteria from the different soil samples. CK: control; CF: chemical fertilizer; VM: vermicompost.
References
[1] Zak DR, Holmes WE, White DC, Peacock AD, Tilman D. Plant diversity, soil microbial communities, and ecosystem function: are there any link. Ecology. 2003;84:2042–50.10.1890/02-0433Search in Google Scholar
[2] Jacobsen CS, Hjelms MH. Agricultural soils, pesticides and microbial diversity. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2014;27:15–20.10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.003Search in Google Scholar
[3] Li JG, Ren GD, Jia ZJ, Dong YH. Composition and activity of rhizosphere microbial communities associated with healthy and diseased greenhouse tomatoes. Plant Soil. 2014;380(1–2):337–47.10.1007/s11104-014-2097-6Search in Google Scholar
[4] Fu HD, Zhang GX, Fan Z, Sun ZP, Geng GM, Li TL, et al. Effects of continuous tomato monoculture on soil microbial properties and enzyme activities in a solar greenhouse. Sustainability. 2017;9:317.10.3390/su9020317Search in Google Scholar
[5] Zhong WH, Gu T, Wang W, Zhang B, Lin XG, Huang QR, et al. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant and Soil. 2010;326(s1–2):511–22.10.1007/s11104-009-9988-ySearch in Google Scholar
[6] Hu XJ, Liu JJ, Wei D, Zhu P, Cui XA, Zhou BK, et al. Soil bacterial communities under different long-term fertilization regimes in three locations across the black soil region of northeast china. Pedosphere. 2018;28(5):751–63.10.1016/S1002-0160(18)60040-2Search in Google Scholar
[7] Ding JL, Jiang X, Guan DW, Ma MC, Zhao BS, Zhou BK, et al. Responses of micropopulation in black soil of northeast china to long-term fertilization and crops. Sci Agric Sin. 2016;22:4408–18.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Zhu F, Hou JT, Xue SG, Wu C, Wang QL, Hartley W. Vermicompost and gypsum amendments improve aggregate formation in bauxite residue. Land Degrad Dev. 2017;28(7):2109–20.10.1002/ldr.2737Search in Google Scholar
[9] Wang JY, Yan XY, Gong W. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil productivity on the north China plain. Pedosphere. 2015;25(3):450–8.10.1016/S1002-0160(15)30012-6Search in Google Scholar
[10] Zwieten LV, Kimber S, Morris S, Chan KY, Downie A, Rust J, et al. Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil. 2010;327(1/2):235–46.10.1007/s11104-009-0050-xSearch in Google Scholar
[11] Fischer G, Ermolieva T, Sun LX. Environmental pressure from intensification of livestock and crop production in China: plausible trends towards 2030. Amsterdam: CATSEI; 2010. p. 1–29.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Bierman P, Metzger JD, Lucht C. Effects of vermicomposts produced from cattle manure, food waste and paper waste on the growth and yield of peppers in the field. Pedobiologia. 2005;49(4):297–306.10.1016/j.pedobi.2005.02.001Search in Google Scholar
[13] Zhao J, Ni T, Li J, Lu Q, Fang ZY, Huang QW, et al. Effects of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice-wheat cropping system. Appl Soil Ecol. 2016;99:1–12.10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.11.006Search in Google Scholar
[14] Lazcano C, Arnold J, Zaller JG, Tato A, Domínguez J. Compost and vermicompost as nursery pot components: effects on tomato plant growth and morphology. Span J Agric Res. 2009;7:944–51.10.5424/sjar/2009074-1107Search in Google Scholar
[15] Li YJ, Wang H, Zhao JN. Effects of tillage methods on soil physicochemical properties and biological characteristics in farmland: a review. Chin J Appl Ecol. 2015;26:939–48.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Xu F, Zhang T, Huai BD, Sui WZ, Yang X. Effects of land use changes on soil fungal community structure and function in the riparian wetland along the downstream of the songhua river. Environ Sci. 2021;2021(42):2531–40.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Reich PB, Jeffries TC, Gaitan JJ, Encinar D, et al. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10541.10.1038/ncomms10541Search in Google Scholar
[18] Mareque C, Cecilia T, Beracochea M, Battistoni F. Isolation, characterization and plant growth promotion effects of putative bacterial endophytes associated with sweet sorghum (sorghum bicolor (l) moench). Ann Microbiol. 2015;65:1057–67.10.1007/s13213-014-0951-7Search in Google Scholar
[19] Li JG, Ren GD, Jia ZJ, Dong YH. Composition and activity of rhizosphere microbial communities associated with healthy and diseased greenhouse tomatoes. Plant Soil. 2014;380(1–2):337–47.10.1007/s11104-014-2097-6Search in Google Scholar
[20] Six J, Elliott ET, Paustian K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: a mechanism for c sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol Biochem. 2000;32(14):2099–103.10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00179-6Search in Google Scholar
[21] Qian YL, Liang ZT, Cao Q, Yang XL, ShenYY, Wang XZ. Effects of grass-planting on soil bacterial community composition of apple orchard in longdong arid region. Chin J Ecol. 2018;37(10):3010–7.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Khan MA, Shampa SA, Hossain MB. Effects of irrigation, fertilizer and manure on pore-water nutrient availability, yield and change of soil chemical properties with rice-rice cropping. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2021;4:1–12.10.1080/00103624.2021.1953057Search in Google Scholar
[23] Vivas A, Moreno B, Garcia-Rodriguez S, Benitez E. Assessing the impact of composting and vermicomposting on bacterial community size and structure, and microbial functional diversity of an olive-mill waste. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100(3):1319–26.10.1016/j.biortech.2008.08.014Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Li FS, Li TL, Chang Q, Zhao FY, Yang LY. Effects of vermicomposts on tomato yield and quality and soil fertility in greenhouse under different sol water regimes. Agric Water Manag. 2015;160:98–105.10.1016/j.agwat.2015.07.002Search in Google Scholar
[25] Ai C, Liang GQ, Sun JW, He P, Tang SH, Yang SH, et al. The alleviation of acid soil stress in rice by inorganic or organic ameliorants is associated with changes in soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition. Biol Fertil Soils. 2015;51(4):465–77.10.1007/s00374-015-0994-3Search in Google Scholar
[26] Tamura M, Tharayil N. Plant litter chemistry and microbial priming regulate the accrual, composition and stability of soil carbon in invaded ecosystems. New Phytol. 2014;203(1):110–24.10.1111/nph.12795Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Arjun S, Prasanna SD, Rameshwar T, Kanika K, Vir SR, Surender S, et al. Taxonomic and functional annotation of gut bacterial communities of eisenia foetida and perionyx excavatus. Microbiol Res. 2015;175:48–56.10.1016/j.micres.2015.03.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Ng EL, Bandow C, Proença DN, Santos S, Guilherme R, Morais PV, et al. Does altered rainfall regime change pesticide effects in soil? a terrestrial model ecosystem study from mediterranean portugal on the effects of pyrimethanil to soil microbial communities under extremes in rainfall. Appl Soil Ecol. 2014;84:245–53.10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.08.006Search in Google Scholar
[29] Spain AM, Krumholz LR, Elshahed MS. Abundance, composition, diversity and novelty of soil proteobacteria. ISME J. 2009;3(8):992–1000.10.1038/ismej.2009.43Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Chodak M, Gołębiewski M, Morawska-Płoskonka J, Kuduk K, Niklińska M. Soil chemical properties affect the reaction of forest soil bacteria to drought and rewetting stress. Ann Microbiol. 2015;65(3):1627–37.10.1007/s13213-014-1002-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Borrero C, Ordovás J, Trillas MI, Avilés M. Tomato fusarium wilt suppressiveness. the relationship between the organic plant growth media and their microbial communities as characterised by biolog. Soil Biol Biochem. 2006;38(7):1631–7.10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.11.017Search in Google Scholar
[32] Hertweck C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:26.10.1002/anie.200806121Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Gopal M, Gupta A, Sunil E, Thomas GV. Amplification of plant beneficial microbial communities during conversion of coconut leaf substrate to vermicompost by eudrilus sp. Curr Microbiol. 2009;59(1):15–20.10.1007/s00284-009-9388-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 Jun Chen et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”

