Abstract
C13H14N2O2S, triclinic, P1̅ (no. 2), a = 4.8885(2) Å, b = 10.3414(5) Å, c = 12.6056(6) Å, α = 95.162(2)°, β = 97.487(1)°, γ = 101.494°, V = 614.73(5) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0507, wRref(F2) = 0.1149, T = 100 K.
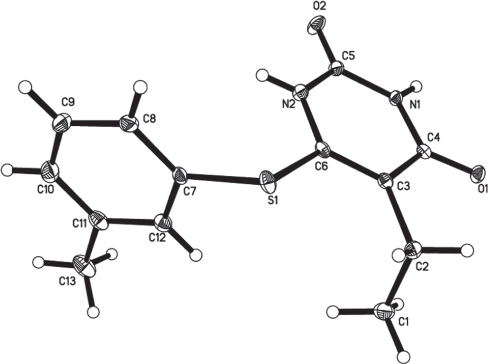
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1–3 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless, needle, size 0.041×0.125×0.789 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.58 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II D8 venture, φ and ω scans |
| 2θmax: | 66.39° |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique: | 34863, 4704 |
| N(param)refined: | 173 |
| Programs: | SHELX [16], Bruker programs [17] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | Uiso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H(1A) | 2i | 0.7206 | 0.0336 | 0.8976 | 0.030 |
| H(1B) | 2i | 0.4402 | 0.0635 | 0.8329 | 0.030 |
| H(1C) | 2i | 0.7034 | 0.1830 | 0.8788 | 0.030 |
| H(2A) | 2i | 0.9739 | 0.1015 | 0.7559 | 0.017 |
| H(2B) | 2i | 0.7174 | −0.0221 | 0.7119 | 0.017 |
| H(8A) | 2i | 1.3085 | 0.6147 | 0.6737 | 0.021 |
| H(9A) | 2i | 1.2738 | 0.8305 | 0.7354 | 0.027 |
| H(10A) | 2i | 1.0003 | 0.8643 | 0.8680 | 0.027 |
| H(12A) | 2i | 0.7837 | 0.4677 | 0.8797 | 0.019 |
| H(13A) | 2i | 0.7400 | 0.6462 | 1.0358 | 0.038 |
| H(13B) | 2i | 0.4861 | 0.6583 | 0.9459 | 0.038 |
| H(13C) | 2i | 0.7178 | 0.7881 | 0.9984 | 0.038 |
| H(1N2) | 2i | 0.703(5) | 0.439(2) | 0.575(2) | 0.037(6) |
| H(1N1) | 2i | 0.108(5) | 0.135(2) | 0.484(2) | 0.029(5) |
Fractional coordinates and atomic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S(1) | 2i | 1.09014(7) | 0.35958(4) | 0.72973(3) | 0.0096(2) | 0.0150(2) | 0.0179(2) | 0.0024(1) | −0.0026(1) | −0.0043(1) |
| O(1) | 2i | 0.2631(2) | −0.02499(9) | 0.59015(8) | 0.0144(5) | 0.0105(5) | 0.0172(5) | 0.0003(4) | 0.0004(4) | 0.0015(4) |
| O(2) | 2i | 0.2623(2) | 0.3684(1) | 0.45650(9) | 0.0206(5) | 0.0151(5) | 0.0220(6) | −0.0023(4) | −0.0079(4) | 0.0081(4) |
| N(1) | 2i | 0.2697(2) | 0.1718(1) | 0.52333(9) | 0.0104(5) | 0.0106(5) | 0.0119(5) | −0.0002(4) | −0.0021(4) | 0.0000(4) |
| N(2) | 2i | 0.6357(2) | 0.3547(1) | 0.5810(1) | 0.0103(5) | 0.0111(5) | 0.0145(6) | −0.0014(4) | −0.0010(4) | 0.0019(4) |
| C(1) | 2i | 0.6468(3) | 0.0898(2) | 0.8472(1) | 0.0233(8) | 0.0224(7) | 0.0150(7) | 0.0070(6) | 0.0019(6) | 0.0036(6) |
| C(2) | 2i | 0.7655(3) | 0.0729(1) | 0.7416(1) | 0.0141(6) | 0.0142(6) | 0.0155(6) | 0.0056(5) | 0.0002(5) | 0.0019(5) |
| C(3) | 2i | 0.6476(3) | 0.1537(1) | 0.6602(1) | 0.0097(6) | 0.0129(6) | 0.0107(6) | 0.0028(5) | 0.0006(4) | −0.0006(5) |
| C(4) | 2i | 0.3855(3) | 0.0920(1) | 0.5902(1) | 0.0108(6) | 0.0122(6) | 0.0097(6) | 0.0027(5) | 0.0014(4) | −0.0007(5) |
| C(5) | 2i | 0.3814(3) | 0.3033(1) | 0.5164(1) | 0.0124(6) | 0.0126(6) | 0.0119(6) | −0.0011(5) | −0.0002(5) | 0.0017(5) |
| C(6) | 2i | 0.7613(3) | 0.2828(1) | 0.6525(1) | 0.0087(5) | 0.0132(6) | 0.0105(6) | 0.0020(5) | 0.0003(4) | −0.0020(5) |
| C(7) | 2i | 1.0460(3) | 0.5220(1) | 0.7706(1) | 0.0130(6) | 0.0123(6) | 0.0117(6) | 0.0016(5) | −0.0026(5) | −0.0012(5) |
| C(8) | 2i | 1.1950(3) | 0.6289(2) | 0.7276(1) | 0.0180(7) | 0.0190(7) | 0.0127(6) | −0.0012(5) | −0.0009(5) | 0.0029(5) |
| C(9) | 2i | 1.1750(4) | 0.7565(2) | 0.7645(1) | 0.0272(8) | 0.0170(7) | 0.0199(7) | −0.0014(6) | −0.0034(6) | 0.0066(6) |
| C(10) | 2i | 1.0114(3) | 0.7762(2) | 0.8435(1) | 0.0254(8) | 0.0155(7) | 0.0234(8) | 0.0061(6) | −0.0059(6) | 0.0014(6) |
| C(11) | 2i | 0.8622(3) | 0.6705(2) | 0.8882(1) | 0.0150(6) | 0.0236(7) | 0.0153(7) | 0.0068(6) | −0.0033(5) | −0.0019(6) |
| C(12) | 2i | 0.8821(3) | 0.5417(2) | 0.8506(1) | 0.0123(6) | 0.0177(7) | 0.0147(6) | 0.0014(5) | 0.0003(5) | 0.0004(5) |
| C(13) | 2i | 0.6862(4) | 0.6927(2) | 0.9746(1) | 0.0228(8) | 0.0336(9) | 0.0208(8) | 0.0119(7) | 0.0011(6) | −0.0056(7) |
Source of material
6-Chloro-5-ethyluracil (1.75 g, 0.01 mol) and m-thiocresol (1.24 g, 0.01 mol) were added to a solution of potassium hydroxide (0.56 g, 0.01 mol), in ethanol (50 mL), and the mixture was heated under reflux for four hours. The solvent was then evaporated in vaccuo and the residue was treated with water (200 mL), filtered, washed with cold water, dried and crystallized from aqueous ethanol to yield 1.99 g (76%) of the title compound as colourless needles. M.P.: 452–454 K. Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanolic solution at room temperature. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 250 MHz): δ 0.95 (t, 3H, CH2CH3, J = 7.4 Hz), 2.31 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.45 (q, 2H, CH2CH3, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.23–7.48 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 10.82 (s, 1H, NH), 11.22 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 62.9 MHz): δ 13.61 (CH2CH3), 19.74 (CH2CH3), 20.73 (CH3), 118.63 (Pyrimidine C-5), 126.97, 127.52, 128.20, 129.16, 130.66, 138.82 (Ar—C), 142.83 (Pyrimidine C-2), 150.48 (Pyrimidine C-6), 163.03 (Pyrimidine C-4). ESI-MS, m/z: 261.2 (M-H)−.
Experimental details
Cell refinement and data reduction were carried out by Bruker SAINT and SHELXS-97 [16, 17]. The nitrogen bonded hydrogen atoms were refined freely; all others were idealizes and refined using a riding model (AFIX43, AFIX23 or AFIX137 option of the SHELX program [16].
Discussion
The pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H-dione (uracil) nucleus is a major pharmacophore in many chemotherapeutic agents. The chemotherapeutic efficacy of pyrimidine-related derivatives is related to their ability to inhibit vital enzymes responsible for DNA biosynthesis including dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), thymidylate synthetase (TSase), thymidine phosphorylase (TPase) and reverse transcriptase (RTase). 1-[2-(Hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6-(phenylthio)thymine (HEPT) and its derivatives have long been known for their potent activity against human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) [1–7]. In addition, numerous pyrimidine-related derivatives displayed marked activities against herpes simplex viruses (HSV) [8], and hepatitis B viruses (HBV) [9]. Moreover, potent anticancer [10, 11] and antimicrobial activities [12–15] were observed among several pyrimidine-2,4-dione derivatives. In the present investigation, we report the crystal structure of the title compound, which was proved to exhibit marked anti-HIV-1 activity [7].
The asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of title compound contains one molecule. There are two aromatic ring systems in title molecule: the tolyl ring (C7—C12) and the pyrimidine ring (C3/C4/N1/C5/N2/C6) attached to the sulphur atoms. The of these rings planes are almost perpendicular and make a dihedral angle of 88.94(3)°. The molecules packing in the crystal structure is stabilized via three intermolecular hydrogen bonds, of which the O1 and O2 act as hydrogen bond acceptors and N1, N2 and C9 act as hydrogen bond donors. The distance of the interactions between the N2—H1N2⋯O2i, N1—H1N1⋯O1ii and C9—H9A⋯O1iii are 2.04(2), 2.00(2) and 2.47 Å, respectively, and the angles are 163(2), 169.7(19) and 146.0°, respectively. Symmetry codes: (i) -x+1, -y+1, -z+1; (ii) -x, -y, -z+1; (iii) x+1, y+1, z.
Acknowledgment:
This research project was supported by a grant from the `Research Center of the Female Scientific and Medical Colleges', Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University.
References
1. Hopkins, A. L.; Ren, J.; Esnouf, R. M.; Willcox, B. E.; Jones, E. Y.; Ross, C.; Miyasaka, T.; Walker, R. T.; Tanaka, H.; Stammers, D. K.; Staurt, D. I.: Complexes of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with Inhibitors of the HEPT Series reveal conformational changes relevant to the design of potent non-nucleoside inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 39 (1996) 1589–1600.10.1021/jm960056xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
2. Miyasaka, T.; Tanaka, H.; Baba, M.; Hayakawa, H.; Walker, R. T.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E.: A novel lead for specific anti-HIV-1 agents 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6-(phenylthio)thymine. J. Med. Chem. 32 (1989) 2507–2509.10.1021/jm00132a002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Pontikis, R.; Benhida, R.; Aubertin, A. H.; Grieson, D. S.; Monneret, C.: Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of novel N-1 side chain-modified analogs of 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6-(phenylthio)thymine (HEPT). J. Med. Chem. 40 (1997) 1845–1854.10.1021/jm960765aSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.: The design and synthesis of N-1-alkylated-5-aminoaryalkylsubstituted-6-methyluracils as potential non-nucleoside HIV-1 RT inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 (2007) 7399–7407.10.1016/j.bmc.2007.07.058Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Artico, M.; Massa, S.; Mai, A.; Marongiu, M. E.; Piras, G.; Tramontino, E.; La Colla, P.: 3,4-Dihydro-2-alkyloxy-6-benzyl-4-oxoypyrimidines (DABOs): a new class of specific inhibitors of human immunodeficiency vitus type 1. Antiviral Chem. Chemother. 4 (1993) 361–368.10.1177/095632029300400608Suche in Google Scholar
6. El-Emam, A. A.; Massoud, M. A.; El-Bendary, E. R.; El-Sayed, M. A.: Synthesis of certain 6-substituted uracils and related derivatives as potential antiviral agents. Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. 25 (2004) 991–996.10.5012/bkcs.2004.25.7.991Suche in Google Scholar
7. El-Emam, A. A.; Nasr, M. N. A.; Pedersen, E. B.; Fouad, T.; Nielsen, C.: Synthesis of certain 6-(arylthio)uracils as potential antiviral agents. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 174 (2001) 25–35.10.1080/10426500108040231Suche in Google Scholar
8. Russ, P.; Schelling, P.; Scapozza, L.; Folkers, G.; De Clercq, E.; Marquez, V. E.: Synthesis and biological evaluation of 5-substituted derivatives of the potent antiherpes agent (north)-methanocarbathymine. J. Med. Chem. 46 (2003) 5045–5054.10.1021/jm030241sSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Semaine, W.; Johar, M., Tyrrell, D. L. J.; Kumar, R.; Agrawal, B.: Inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication by pyrimidines bearing an acyclic moiety:Effect on wild-type and mutant HBV. J. Med. Chem. 49 (2006) 2049–2054.10.1021/jm058271dSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Al-Safarjalani, O. N.; Zhou, X.; Rais, R. H.; Shi, J.; Schinazi, R. F.; Naguib, F. N. M.; El Kouni, M. H.: 5-(Phenylthio)acyclouridine: a powerful enhancer of oral uridine bioavailability: relevance to chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and other uridine rescue regimens. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 55 (2005) 541–551.10.1007/s00280-004-0967-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S. T.: An alternative molecular mechanism of action of 5-fluorouracil, a potent anticancer drug. Biochem. Pharmacol. 53 (1997) 1569–1575.10.1016/S0006-2952(97)00040-3Suche in Google Scholar
12. Periti, P.: Evolution of bacterial dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 36 (1995) 887–890.10.1093/jac/36.6.887Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Sincak, C. A.: Iclaprim, a novel diaminopyrimidine for the treatment of resistant Gram-positive infections. Ann Pharmacother. 43 (2009) 1107–1114.10.1345/aph.1L167Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Al-Abdullah, E. S.; Al-Obaid, A. M.; Al-Deeb, O. A.; Habib, E. E.; El-Emam, A. A.: Synthesis of novel 6-phenyl-2,4-disubstituted pyrimidine-5-carbonitriles as potential antimicrobial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 (2011) 4642–4647.10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.08.003Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Al-Deeb, O. A.; Al-Turkistani, A. A.; Al-Abdullah, E. S.; El-Brollosy, N. R.; Habib, E. E.; El-Emam, A. A.: Pyrimidine-5-carbonitriles – part III: Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of novel 6-(2-substituted propyl)-2,4-disubstituted pyrimidine-5-carbonitriles. Heterocycl. Commun. 19 (2013) 411–419.10.1515/hc-2013-0139Suche in Google Scholar
16. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
17. Brucker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Brucker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
©2016 Reem I. Al-Wabli et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of fac-hexacarbonylbisμ2-(3-carboxy-3′-carboxylato-2,2′-bipyridine)-κ3N,N′:O-dirhenium(I) tetrahydrate, C30H22N4O18Re2
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)methane, C25H36N4
- Crystal structure of bis(triphenylphosphine-κP)bis(μ2-1H,1′H-2,2′-biimidazole-κ3N,N′:N′)disilver(I) bis(tetrafluoroborate), C48H42Ag2B2F8N8P2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2-pyrazinecarboxamido)-benzene, C16H12N6O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromobenzoic acid, C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of bis(ethyltriphenylphos-phonium) tetrabromidocuprate(II), (C20H20P)2[CuBr4]
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C19H17BrN2
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(3-(pyrazin-2-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ2N,N′)-cobalt(II),C22H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamanganese(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MnN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of butyl 2-(3,5-dimethyl-1,1-dioxido-2H-1,2,6-thiadiazin-4-yl)benzoate, C16H20N2O4S
- Crystal structure of hexaaquabis(μ2-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)bis(μ3-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)tetra-manganese(II) dihydrate, C48H40Mn4N24O16
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmate(II)] bis(2-aminoisonicotinate) tetrahydrate, C38H50CdN8O10
- Crystal structure of succinic acid — 4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanylpyridine (1/1), C15H16N2O4S
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanyl)pyridine-κN)dicopper(II), C30H32N4O8S2Cu2
- Crystal structure of 1-((2R,3S)-2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl)-2-phenoxyethan-1-one, C18H19NO3
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium sulfanilate, C10H18N2O3S
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium 2′-carboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate, C20H25NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-acetyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-5,6-dichloro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H13Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ3-2-methyl-6-oxidopyridinium-4-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)neodymium(III) chloride, C14H16ClN2O8Nd
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-4-methyl-2-(2-methylbenzyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, C12H15N3O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl)ethanone
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(4-(diethylamino)phenyl)diazen-1-ium-1-yl)benzenesulfonate monohydrate
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[(1E)-prop-1-ene-1,2-diyldisulfanediyl]bis(5-methyl-2,5-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazole, C9H10N4S4
- Crystal structure of poly [μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)cerium(III)] monohydrate (C10H13O9Ce)
- Crystal structure of tris((2-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)phenoxy)ethyl)amine, C36H27N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-bis((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)] dinitrate, C20H24CuN18O8
- Crystal structure of (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoic acid-κN) (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I), C20H15N4O4Ag
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(3,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C18H15F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol hemihydrate, C13H17ClO3 · 0.5 H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κN)(m2-2-(1H-1,2,4-trizol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-3,1-benzimidazol-3-ium-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] dihydrate, C30H30N10O12Zn
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-((((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy-κ2O,O′))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ2O′′,O′′′]zinc(II), C28H22N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenyl) terephthalate C20H10F2N2O8
- Crystal structure of catena-[aqua((4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κO)(μ2-(4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κN)manganese(II)], C42H36N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of N′-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbohydrazide, C14H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of bis(8-ethyl-5-oxo-2-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-5,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate dihydrate, C36H42CuN10O12
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)bis(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylato)zinc(II), C60H56N6Zn2O16F2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13FN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexaqua(μ2-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-1κ2O,O′;2κO′)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κO)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) octahydrate, C60H76Gd2N18O32
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl bis(μ2-2-methoxybenzenethiolato-κ2S)pyridine(triphenylphosphane)dirhenium(I), C43H34NO8PS2Re2
- Crystal structure of 14-((1-(benzyloxycarbonyl-amino)-2-methylpropan-2-yl)sulfanyl)acetate Mutilin, C34H49NO6S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-6-(((2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d] imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol — ethanol (1/1), C24H25N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenylbutane-1,3-dione, C13H14O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenyl-3-(2-phenylhydrazono)butan-1-one, C19H20N2OS2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)aniline-κ2N,N′)zinc(II)
- Crystal structure of bis(1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolato)mercury(II)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-styryl-1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C24H19FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of aquabis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate trihydrate, [Cu(C17H18N3FO3)2(H2O)](C6H2SO4)·3(H2O)
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazatetracyclo[5·5·0·05·9·03·11]dodecane 1/3 hydrate, C6H8N12O13
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C25H20AsN2O3Rh
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-chlorophenyl)ethanone, C14H10Cl2O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-2-(2-(6-(4-methoxybenzyl)-7-oxo-7H-thiazolo[3,3-b][1,2,4]triazin-3-yl)phenoxy)acetamide, C25H26N4O4S
- Crystal structure of tetraqua((E)-4,4′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-1-ide)-κ2N:O)barium(II), C4H10N8O6Ba
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of diethylammonium 5-((4-fluorophenyl)(6-hydroxy-1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-4-olate, C23H30FN5O6
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluoro-phenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12F2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tris(N-nitroso-N-oxyanilino-κ2O, O′) oxidoniobium(V), C18H15N6O7Nb
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-benzoyl-4-methyl-2-(phenylamino)thiophen-3-yl)ethan-1-one, a structure with Z′ = 6, C20H17NO2S
- Crystal structure of diethyl-3-methyl-4-phenylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate, C19H18O4S2
- Crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate — benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid (1/1), C24H22N2O12
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1,3,2λ3,4-diazaphosphasiletidine
- Crystal structure of hexaquamanganese(II) bis(hexaborato-κ3O,O′,O′′)manganese(II) dihydrate, B12H28Mn2O34
- Crystal structure of 1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium pentaborate, [C7H13N2][B5O6(OH)4]
- Crystal structure of 13-(4-fluorophenyl)-11,13-dihydro-1H-benzo[h]indazolo[6,7-b] [1, 6]naphthyridin-12(6H)-one — dimethylformamide — water (1/2/1), C29H31FN6O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-ol, C14H12ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-((2-bromo-1-phenylvinyl)oxy)benzonitrile, C15H10BrNO
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido(1E,1′E)-N,N′-((1,4-phenylenebis(propane-2,2-diyl))bis(4,1-phenylene))bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)methanimine-κN)dizinc(II), C36H34N4Zn2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(3-methylpyridinyl)hexahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo-[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetrone, C24H20N4O4
- Crystal structure of trans-bis(2-methylmaleato-κ2O,O′) bis(piperazinium-κN) cobalt(II) trihydrate, C18H36CoN4O11
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)benzohydrazide, C18H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of 3,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-9H-carbazole, C18H13N5
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-pyridinyl)-1-naphthoic acid, C16H11NO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-diformyl-4,4′-(6H,12H-5,11-methano-dibenzo[b,f][11,5]diazocine-2,8-diyl)dibenzene, C29H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N′-(adamantan-2-ylidene)pyridine-3-carbohydrazide, C16H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbaldehyde), C14H18N4O2
- Crystal structure of methyl 8-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-5a,8-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,5a,6,7,8,10a,10b-decahydrocyclohepta[e]indene-3a(1H)-carboxylate, C21H34O3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-propyl-2-(propylthio)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C11H15N3OS
- Crystal structure of poly[diacetato(μ2-1,4-bis(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)nickel(II)], C26H22N8NiO4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,4-dibromo-6-{(E)[(4-fluorobenzyl)imino]methyl}phenolato-κ2N,O) copper(II), C28H18Br4F2N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-phenylthiourea, C17H22N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-(6-(5-amino-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridin-2-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine – dioxan (2/1), C25H23N7O
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-6-[(3-methylphenyl)sulfanyl]pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C13H14N2O2S
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-(cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)amide-κ2N′′,N′′′)manganese(II), C44H54N4Mn
- Crystal structure of prop-2-en-1-yl 2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxylate, C13H10O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-((3-methylphenyl)imino)methylphenolato-κ2N,O:O)hexacarbonyldimanganese(I), C34H24Mn2N2O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxybut-2-en-1-one C9H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[pentane-1,5-diylbis(oxy)]dibenzaldehyde, C19H20O4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-benzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C16H13NO2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)methanimine, C13H9Cl2N
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-5-bromothiazole-4-carboxylate, C6H7BrN2O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzylisothiouronium tetraphenylborate, C32H31BN2S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C24H16CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium(III)dichloride (THF), C14H23Cl2OTi
- Crystal structure of 3-ferrocenylsulfonyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C23H19FeN3O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C18H11FN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,6-ditosyl-1,6-diazecane, C22H30N2O4S2
- Crystal structure of N-phenyl-2-(pyridin-4-ylcarbonyl)hydrazinecarboxamide with Z′ = 4, C13H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)cyclohexylamine, C30H31NP2
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-N-phenylpropanamide, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 6-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-[1,2,4]-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole, C15H9FN4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(dicyanoazanido-2κN-μ2-dicyanoazanido-1κN:2κN′)(μ2-2-methoxy-6-(((2-((3-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)ethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-1κ2N,N′,2κ2O,O′,1κ2O′′,O′′′:2κ2O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)copper(II)], C22H20CdCuN8O5
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of fac-hexacarbonylbisμ2-(3-carboxy-3′-carboxylato-2,2′-bipyridine)-κ3N,N′:O-dirhenium(I) tetrahydrate, C30H22N4O18Re2
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)methane, C25H36N4
- Crystal structure of bis(triphenylphosphine-κP)bis(μ2-1H,1′H-2,2′-biimidazole-κ3N,N′:N′)disilver(I) bis(tetrafluoroborate), C48H42Ag2B2F8N8P2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2-pyrazinecarboxamido)-benzene, C16H12N6O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromobenzoic acid, C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of bis(ethyltriphenylphos-phonium) tetrabromidocuprate(II), (C20H20P)2[CuBr4]
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C19H17BrN2
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(3-(pyrazin-2-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ2N,N′)-cobalt(II),C22H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamanganese(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MnN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of butyl 2-(3,5-dimethyl-1,1-dioxido-2H-1,2,6-thiadiazin-4-yl)benzoate, C16H20N2O4S
- Crystal structure of hexaaquabis(μ2-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)bis(μ3-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)tetra-manganese(II) dihydrate, C48H40Mn4N24O16
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmate(II)] bis(2-aminoisonicotinate) tetrahydrate, C38H50CdN8O10
- Crystal structure of succinic acid — 4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanylpyridine (1/1), C15H16N2O4S
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanyl)pyridine-κN)dicopper(II), C30H32N4O8S2Cu2
- Crystal structure of 1-((2R,3S)-2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl)-2-phenoxyethan-1-one, C18H19NO3
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium sulfanilate, C10H18N2O3S
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium 2′-carboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate, C20H25NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-acetyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-5,6-dichloro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H13Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ3-2-methyl-6-oxidopyridinium-4-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)neodymium(III) chloride, C14H16ClN2O8Nd
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-4-methyl-2-(2-methylbenzyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, C12H15N3O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl)ethanone
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(4-(diethylamino)phenyl)diazen-1-ium-1-yl)benzenesulfonate monohydrate
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[(1E)-prop-1-ene-1,2-diyldisulfanediyl]bis(5-methyl-2,5-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazole, C9H10N4S4
- Crystal structure of poly [μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)cerium(III)] monohydrate (C10H13O9Ce)
- Crystal structure of tris((2-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)phenoxy)ethyl)amine, C36H27N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-bis((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)] dinitrate, C20H24CuN18O8
- Crystal structure of (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoic acid-κN) (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I), C20H15N4O4Ag
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(3,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C18H15F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol hemihydrate, C13H17ClO3 · 0.5 H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κN)(m2-2-(1H-1,2,4-trizol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-3,1-benzimidazol-3-ium-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] dihydrate, C30H30N10O12Zn
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-((((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy-κ2O,O′))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ2O′′,O′′′]zinc(II), C28H22N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenyl) terephthalate C20H10F2N2O8
- Crystal structure of catena-[aqua((4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κO)(μ2-(4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κN)manganese(II)], C42H36N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of N′-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbohydrazide, C14H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of bis(8-ethyl-5-oxo-2-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-5,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate dihydrate, C36H42CuN10O12
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)bis(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylato)zinc(II), C60H56N6Zn2O16F2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13FN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexaqua(μ2-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-1κ2O,O′;2κO′)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κO)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) octahydrate, C60H76Gd2N18O32
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl bis(μ2-2-methoxybenzenethiolato-κ2S)pyridine(triphenylphosphane)dirhenium(I), C43H34NO8PS2Re2
- Crystal structure of 14-((1-(benzyloxycarbonyl-amino)-2-methylpropan-2-yl)sulfanyl)acetate Mutilin, C34H49NO6S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-6-(((2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d] imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol — ethanol (1/1), C24H25N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenylbutane-1,3-dione, C13H14O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenyl-3-(2-phenylhydrazono)butan-1-one, C19H20N2OS2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)aniline-κ2N,N′)zinc(II)
- Crystal structure of bis(1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolato)mercury(II)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-styryl-1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C24H19FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of aquabis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate trihydrate, [Cu(C17H18N3FO3)2(H2O)](C6H2SO4)·3(H2O)
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazatetracyclo[5·5·0·05·9·03·11]dodecane 1/3 hydrate, C6H8N12O13
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C25H20AsN2O3Rh
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-chlorophenyl)ethanone, C14H10Cl2O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-2-(2-(6-(4-methoxybenzyl)-7-oxo-7H-thiazolo[3,3-b][1,2,4]triazin-3-yl)phenoxy)acetamide, C25H26N4O4S
- Crystal structure of tetraqua((E)-4,4′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-1-ide)-κ2N:O)barium(II), C4H10N8O6Ba
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of diethylammonium 5-((4-fluorophenyl)(6-hydroxy-1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-4-olate, C23H30FN5O6
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluoro-phenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12F2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tris(N-nitroso-N-oxyanilino-κ2O, O′) oxidoniobium(V), C18H15N6O7Nb
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-benzoyl-4-methyl-2-(phenylamino)thiophen-3-yl)ethan-1-one, a structure with Z′ = 6, C20H17NO2S
- Crystal structure of diethyl-3-methyl-4-phenylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate, C19H18O4S2
- Crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate — benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid (1/1), C24H22N2O12
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1,3,2λ3,4-diazaphosphasiletidine
- Crystal structure of hexaquamanganese(II) bis(hexaborato-κ3O,O′,O′′)manganese(II) dihydrate, B12H28Mn2O34
- Crystal structure of 1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium pentaborate, [C7H13N2][B5O6(OH)4]
- Crystal structure of 13-(4-fluorophenyl)-11,13-dihydro-1H-benzo[h]indazolo[6,7-b] [1, 6]naphthyridin-12(6H)-one — dimethylformamide — water (1/2/1), C29H31FN6O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-ol, C14H12ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-((2-bromo-1-phenylvinyl)oxy)benzonitrile, C15H10BrNO
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido(1E,1′E)-N,N′-((1,4-phenylenebis(propane-2,2-diyl))bis(4,1-phenylene))bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)methanimine-κN)dizinc(II), C36H34N4Zn2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(3-methylpyridinyl)hexahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo-[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetrone, C24H20N4O4
- Crystal structure of trans-bis(2-methylmaleato-κ2O,O′) bis(piperazinium-κN) cobalt(II) trihydrate, C18H36CoN4O11
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)benzohydrazide, C18H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of 3,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-9H-carbazole, C18H13N5
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-pyridinyl)-1-naphthoic acid, C16H11NO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-diformyl-4,4′-(6H,12H-5,11-methano-dibenzo[b,f][11,5]diazocine-2,8-diyl)dibenzene, C29H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N′-(adamantan-2-ylidene)pyridine-3-carbohydrazide, C16H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbaldehyde), C14H18N4O2
- Crystal structure of methyl 8-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-5a,8-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,5a,6,7,8,10a,10b-decahydrocyclohepta[e]indene-3a(1H)-carboxylate, C21H34O3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-propyl-2-(propylthio)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C11H15N3OS
- Crystal structure of poly[diacetato(μ2-1,4-bis(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)nickel(II)], C26H22N8NiO4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,4-dibromo-6-{(E)[(4-fluorobenzyl)imino]methyl}phenolato-κ2N,O) copper(II), C28H18Br4F2N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-phenylthiourea, C17H22N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-(6-(5-amino-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridin-2-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine – dioxan (2/1), C25H23N7O
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-6-[(3-methylphenyl)sulfanyl]pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C13H14N2O2S
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-(cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)amide-κ2N′′,N′′′)manganese(II), C44H54N4Mn
- Crystal structure of prop-2-en-1-yl 2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxylate, C13H10O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-((3-methylphenyl)imino)methylphenolato-κ2N,O:O)hexacarbonyldimanganese(I), C34H24Mn2N2O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxybut-2-en-1-one C9H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[pentane-1,5-diylbis(oxy)]dibenzaldehyde, C19H20O4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-benzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C16H13NO2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)methanimine, C13H9Cl2N
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-5-bromothiazole-4-carboxylate, C6H7BrN2O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzylisothiouronium tetraphenylborate, C32H31BN2S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C24H16CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium(III)dichloride (THF), C14H23Cl2OTi
- Crystal structure of 3-ferrocenylsulfonyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C23H19FeN3O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C18H11FN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,6-ditosyl-1,6-diazecane, C22H30N2O4S2
- Crystal structure of N-phenyl-2-(pyridin-4-ylcarbonyl)hydrazinecarboxamide with Z′ = 4, C13H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)cyclohexylamine, C30H31NP2
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-N-phenylpropanamide, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 6-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-[1,2,4]-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole, C15H9FN4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(dicyanoazanido-2κN-μ2-dicyanoazanido-1κN:2κN′)(μ2-2-methoxy-6-(((2-((3-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)ethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-1κ2N,N′,2κ2O,O′,1κ2O′′,O′′′:2κ2O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)copper(II)], C22H20CdCuN8O5

