Abstract
C7H5BrO2, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.9992(4) Å, b = 4.7064(4) Å, c = 25.149(2) Å, b = 92.283(4)°, V = 709.51(10) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0363, wRref(F2) = 0.0857, T = 200 K.
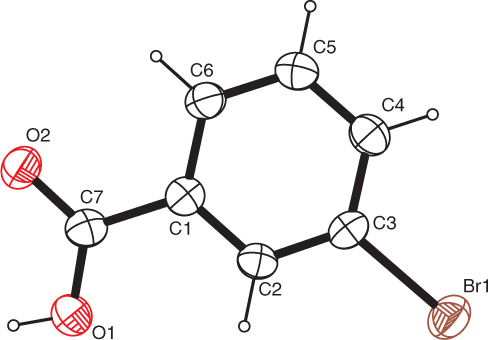
The crystal structure is shown in the figure, Tables 1–3 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless, needle, size 0.087×0.143×0.447 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 57.21 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II CCD, φ and ω scans |
| 2θmax: | 56.76° |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique: | 6657, 1772 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1299 |
| N(param)refined: | 92 |
| Programs: | SHELX [14], WinGX [15], Mercury [16], Platon [17] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | Uiso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H(1) | 4e | −0.1170 | 0.0563 | 0.0324 | 0.060 |
| H(2) | 4e | −0.0844 | 0.4964 | 0.1344 | 0.035 |
| H(4) | 4e | 0.4000 | 1.0471 | 0.1840 | 0.042 |
| H(5) | 4e | 0.6150 | 0.9074 | 0.1132 | 0.045 |
| H(6) | 4e | 0.4837 | 0.5686 | 0.0531 | 0.041 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br(1) | 4e | −0.04126(5) | 0.91383(9) | 0.22006(1) | 0.0417(2) | 0.0508(2) | 0.0339(2) | 0.0028(2) | 0.0084(1) | −0.0056(2) |
| O(1) | 4e | −0.0839(4) | 0.1697(5) | 0.0573(1) | 0.042(1) | 0.034(2) | 0.045(1) | −0.009(1) | 0.007(1) | −0.007(1) |
| O(2) | 4e | 0.2195(4) | 0.2219(6) | 0.01020(9) | 0.053(1) | 0.041(2) | 0.040(1) | −0.010(1) | 0.016(1) | −0.009(1) |
| C(1) | 4e | 0.1866(5) | 0.4995(7) | 0.0878(1) | 0.033(2) | 0.022(2) | 0.030(2) | 0.003(1) | 0.002(1) | 0.006(1) |
| C(2) | 4e | 0.0573(5) | 0.5810(7) | 0.1298(1) | 0.028(1) | 0.026(2) | 0.033(2) | −0.001(1) | 0.001(1) | 0.005(1) |
| C(3) | 4e | 0.1372(5) | 0.7853(7) | 0.1646(1) | 0.030(2) | 0.032(2) | 0.025(1) | 0.006(1) | 0.004(1) | 0.006(1) |
| C(4) | 4e | 0.3457(5) | 0.9083(8) | 0.1593(1) | 0.034(2) | 0.036(2) | 0.035(2) | −0.002(2) | −0.004(1) | −0.001(2) |
| C(5) | 4e | 0.4724(5) | 0.8246(8) | 0.1174(1) | 0.030(2) | 0.041(2) | 0.043(2) | −0.004(1) | 0.003(1) | −0.001(2) |
| C(6) | 4e | 0.3950(5) | 0.6235(7) | 0.0819(1) | 0.031(2) | 0.035(2) | 0.037(2) | −0.001(1) | 0.006(1) | −0.001(1) |
| C(7) | 4e | 0.1027(5) | 0.2834(7) | 0.0492(1) | 0.034(2) | 0.025(2) | 0.034(2) | 0.000(1) | 0.004(1) | 0.007(1) |
Source of material
The compound was obtained commercially (Aldrich). Crystals suitable for the diffraction study were obtained upon recrystallization from boiling water.
Discussion
Benzoic acid has found widespread use as a ligand in coordination chemistry for a variety of transition metals and elements from the s- and p-block of the periodic system of the elements. It can act as a neutral or – upon deprotonation – an anionic ligand and serve as mono- or bidentate ligand. By varying the substituents on the phenyl moiety, the acidity of the carboxylic acid group can be fine-tuned. Particular interest rests in benzoic acid derivatives showing an asymmetric pattern of substituents on the aromatic moiety due to different possible orientations of the ligand in coordination compounds and the possible formation of stereoisomeric products. The crystal and molecular structures of all possible monohalogenated benzoic acids bearing the halogen substituent in ortho, meta and para position to the carboxylic group have been reported for fluorine [1], chlorine [2–4], bromine [5–7] and iodine [8–10]. However, for 3-bromobenzoic acid [6], no coordinates of hydrogen atoms have been taken into account during the refinement of the structure. To rationalize the coordination behaviour of various benzoic acid derivatives towards a number of transition metals in dependence of the pH value of the reaction batches it seemed interesting to redetermine the crystal structure of the title compound including hydrogen positions.
The title compound is a monobrominated derivative of benzoic acid bearing the halogen substituent in meta position to the carboxylic group. Intracyclic C—C—C angles cover a range from 118.6(3)–121.6(3)° with the smallest angle on the carbon atom in para position to the carbon atom bearing the carboxylic acid group and the largest angle on the carbon atom bonded to the bromine substituent. The C—Br bond length was measured at 1.892(3) Å. In comparison to other compounds featuring a brominated phenyl group whose metrical parameters have been deposited with the Cambridge Structural Database [11], the latter value is among the most common ones reported. The range as well as the position of the angles found in the current study differ from the ones reported earlier [6]. The least-squares planes of the phenyl group and the carboxylic group enclose an angle of 2.9(6)°. In the crystal, hydrogen bonds of the O—H⋯O type can be observed to form acid dimers (graph set descriptor: R22(8) [12, 13]). The shortest intercentroid distance between two centers of gravity is measured at 4.706(2) Å which corresponds to the length of axis b of the unit cell.
Acknowledgements:
The authors thank Mr Brian Zacharias for helpful discussions.
References
1. Hathwar, V. R.; Thakur, T. S.; Dubey, R.; Pavan, M. A.; Row, T. N. G.; Desiraju, G. R.: Extending the supramolecular synthon based fragment approach (SBFA) for transferability of multipole charge density parameters to monofluorobenzoic acids and their cocrystals with isonicotinamide: importance of C—H⋯O, C—H⋯F, and F⋯F intermolecular regions. J. Phys. Chem. A 115 (2011) 12852–12863.10.1021/jp2039866Search in Google Scholar PubMed
2. Polito, M.; D'Oria, E.; Maini, L.; Karamertzanis, P. G.; Grepioni, F.; Braga, D.; Price, S.: The crystal structures of chloro and methyl ortho-benzoic acids and their co-crystal: rationalizing similarities and differences. CrystEngComm 10 (2008) 1848–1854.10.1039/b811438bSearch in Google Scholar
3. Gougoutas, J. Z.; Lessinger, L.: Solid state chemistry of organic polyvalent iodine compounds. IV. Topotactic transformations of 2-iodo-3π′-chlorodibenzoyl peroxide and the crystal structure of m-chlorobenzoic acid. J. Solid State Chem. 12 (1975) 51–62.10.1016/0022-4596(75)90177-2Search in Google Scholar
4. Wilson, C. C.; Xu, X.; Florence, A. J.; Shankland, N.: Temperature dependence of proton transfer in 4-chlorobenzoic acid. New J. Chem. 30 (2006) 979–981.10.1039/b601123cSearch in Google Scholar
5. Kowalska, K.; Trzybinski, D.; Sikorski, A.: Crystal structure of 2-bromobenzoic acid at 120 K: a redetermination. Acta Crystallogr. E70 (2014) o1139–o1140.10.1107/S160053681402087XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Tanaka, N.; Ashida, T.; Sasada, Y.; Kakudo, M.: The crystal structure of m-bromobenzoic acid. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 40 (1967) 2717.10.1246/bcsj.40.2717Search in Google Scholar
7. Ohkura, K.; Kashino, S.; Haisa, M.: The crystal and molecular structure of p-bromobenzoic acid. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 45 (1972) 2651–2652.10.1246/bcsj.45.2651Search in Google Scholar
8. Liwporncharoenvong, T.; Luck, R. L.: The effects, assessed by electrochemical techniques and single crystal structures, of ortho substitution on benzoate ligands supporting the quadruply-bonded dimolybdenum bond. Inorg. Chim. Acta 340 (2002) 147–154.10.1016/S0020-1693(02)01095-2Search in Google Scholar
9. Patil, A. A.; Curtin, D. Y.; Paul, I. C.: Effect of molecular symmetry and intermolecular halogen-halogen interactions on the crystal structures of halogen-substituted benzoic acids. X-ray crystal structure of m-iodobenzoic acid. Isr. J. Chem. 25 (1985) 320–326.10.1002/ijch.198500052Search in Google Scholar
10. Nygren, C. L.; Wilson, C. C.; Turner, J. F. C.: On the solid state structure of 4-iodobenzoic acid. J. Phys. Chem. A 109 (2005) 2586–2593.10.1021/jp047189bSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Allen, F. H.: The Cambridge structural database: a quarter of a million crystal structures and rising. Acta Crystallogr. B58 (2002) 380–388.10.1107/S0108768102003890Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Bernstein, J.; Davis, R. E.; Shimoni, L.; Chang, N.-L.: Patterns in hydrogen bonding: functionality and graph set analysis in crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34 (1995) 1555–1573.10.1002/anie.199515551Search in Google Scholar
13. Etter, M. C.; MacDonald, J. C.; Bernstein, J.: Graph-set analysis of hydrogen-bond patterns in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. B46 (1990) 256–262.10.1107/S0108768189012929Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
16. Macrae, C. F.; Bruno, I. J.; Chisholm, J. A.; Edgington, P. R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P. A.: Mercury CSD 2.0 – new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41 (2008) 466–470.10.1107/S0021889807067908Search in Google Scholar
17. Spek, A. L.: Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D65 (2009) 148–155.10.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2016 Lubabalo Ndima et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of fac-hexacarbonylbisμ2-(3-carboxy-3′-carboxylato-2,2′-bipyridine)-κ3N,N′:O-dirhenium(I) tetrahydrate, C30H22N4O18Re2
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)methane, C25H36N4
- Crystal structure of bis(triphenylphosphine-κP)bis(μ2-1H,1′H-2,2′-biimidazole-κ3N,N′:N′)disilver(I) bis(tetrafluoroborate), C48H42Ag2B2F8N8P2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2-pyrazinecarboxamido)-benzene, C16H12N6O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromobenzoic acid, C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of bis(ethyltriphenylphos-phonium) tetrabromidocuprate(II), (C20H20P)2[CuBr4]
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C19H17BrN2
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(3-(pyrazin-2-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ2N,N′)-cobalt(II),C22H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamanganese(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MnN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of butyl 2-(3,5-dimethyl-1,1-dioxido-2H-1,2,6-thiadiazin-4-yl)benzoate, C16H20N2O4S
- Crystal structure of hexaaquabis(μ2-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)bis(μ3-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)tetra-manganese(II) dihydrate, C48H40Mn4N24O16
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmate(II)] bis(2-aminoisonicotinate) tetrahydrate, C38H50CdN8O10
- Crystal structure of succinic acid — 4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanylpyridine (1/1), C15H16N2O4S
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanyl)pyridine-κN)dicopper(II), C30H32N4O8S2Cu2
- Crystal structure of 1-((2R,3S)-2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl)-2-phenoxyethan-1-one, C18H19NO3
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium sulfanilate, C10H18N2O3S
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium 2′-carboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate, C20H25NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-acetyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-5,6-dichloro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H13Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ3-2-methyl-6-oxidopyridinium-4-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)neodymium(III) chloride, C14H16ClN2O8Nd
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-4-methyl-2-(2-methylbenzyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, C12H15N3O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl)ethanone
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(4-(diethylamino)phenyl)diazen-1-ium-1-yl)benzenesulfonate monohydrate
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[(1E)-prop-1-ene-1,2-diyldisulfanediyl]bis(5-methyl-2,5-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazole, C9H10N4S4
- Crystal structure of poly [μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)cerium(III)] monohydrate (C10H13O9Ce)
- Crystal structure of tris((2-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)phenoxy)ethyl)amine, C36H27N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-bis((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)] dinitrate, C20H24CuN18O8
- Crystal structure of (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoic acid-κN) (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I), C20H15N4O4Ag
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(3,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C18H15F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol hemihydrate, C13H17ClO3 · 0.5 H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κN)(m2-2-(1H-1,2,4-trizol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-3,1-benzimidazol-3-ium-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] dihydrate, C30H30N10O12Zn
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-((((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy-κ2O,O′))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ2O′′,O′′′]zinc(II), C28H22N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenyl) terephthalate C20H10F2N2O8
- Crystal structure of catena-[aqua((4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κO)(μ2-(4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κN)manganese(II)], C42H36N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of N′-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbohydrazide, C14H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of bis(8-ethyl-5-oxo-2-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-5,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate dihydrate, C36H42CuN10O12
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)bis(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylato)zinc(II), C60H56N6Zn2O16F2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13FN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexaqua(μ2-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-1κ2O,O′;2κO′)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κO)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) octahydrate, C60H76Gd2N18O32
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl bis(μ2-2-methoxybenzenethiolato-κ2S)pyridine(triphenylphosphane)dirhenium(I), C43H34NO8PS2Re2
- Crystal structure of 14-((1-(benzyloxycarbonyl-amino)-2-methylpropan-2-yl)sulfanyl)acetate Mutilin, C34H49NO6S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-6-(((2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d] imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol — ethanol (1/1), C24H25N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenylbutane-1,3-dione, C13H14O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenyl-3-(2-phenylhydrazono)butan-1-one, C19H20N2OS2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)aniline-κ2N,N′)zinc(II)
- Crystal structure of bis(1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolato)mercury(II)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-styryl-1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C24H19FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of aquabis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate trihydrate, [Cu(C17H18N3FO3)2(H2O)](C6H2SO4)·3(H2O)
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazatetracyclo[5·5·0·05·9·03·11]dodecane 1/3 hydrate, C6H8N12O13
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C25H20AsN2O3Rh
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-chlorophenyl)ethanone, C14H10Cl2O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-2-(2-(6-(4-methoxybenzyl)-7-oxo-7H-thiazolo[3,3-b][1,2,4]triazin-3-yl)phenoxy)acetamide, C25H26N4O4S
- Crystal structure of tetraqua((E)-4,4′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-1-ide)-κ2N:O)barium(II), C4H10N8O6Ba
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of diethylammonium 5-((4-fluorophenyl)(6-hydroxy-1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-4-olate, C23H30FN5O6
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluoro-phenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12F2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tris(N-nitroso-N-oxyanilino-κ2O, O′) oxidoniobium(V), C18H15N6O7Nb
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-benzoyl-4-methyl-2-(phenylamino)thiophen-3-yl)ethan-1-one, a structure with Z′ = 6, C20H17NO2S
- Crystal structure of diethyl-3-methyl-4-phenylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate, C19H18O4S2
- Crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate — benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid (1/1), C24H22N2O12
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1,3,2λ3,4-diazaphosphasiletidine
- Crystal structure of hexaquamanganese(II) bis(hexaborato-κ3O,O′,O′′)manganese(II) dihydrate, B12H28Mn2O34
- Crystal structure of 1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium pentaborate, [C7H13N2][B5O6(OH)4]
- Crystal structure of 13-(4-fluorophenyl)-11,13-dihydro-1H-benzo[h]indazolo[6,7-b] [1, 6]naphthyridin-12(6H)-one — dimethylformamide — water (1/2/1), C29H31FN6O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-ol, C14H12ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-((2-bromo-1-phenylvinyl)oxy)benzonitrile, C15H10BrNO
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido(1E,1′E)-N,N′-((1,4-phenylenebis(propane-2,2-diyl))bis(4,1-phenylene))bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)methanimine-κN)dizinc(II), C36H34N4Zn2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(3-methylpyridinyl)hexahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo-[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetrone, C24H20N4O4
- Crystal structure of trans-bis(2-methylmaleato-κ2O,O′) bis(piperazinium-κN) cobalt(II) trihydrate, C18H36CoN4O11
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)benzohydrazide, C18H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of 3,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-9H-carbazole, C18H13N5
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-pyridinyl)-1-naphthoic acid, C16H11NO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-diformyl-4,4′-(6H,12H-5,11-methano-dibenzo[b,f][11,5]diazocine-2,8-diyl)dibenzene, C29H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N′-(adamantan-2-ylidene)pyridine-3-carbohydrazide, C16H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbaldehyde), C14H18N4O2
- Crystal structure of methyl 8-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-5a,8-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,5a,6,7,8,10a,10b-decahydrocyclohepta[e]indene-3a(1H)-carboxylate, C21H34O3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-propyl-2-(propylthio)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C11H15N3OS
- Crystal structure of poly[diacetato(μ2-1,4-bis(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)nickel(II)], C26H22N8NiO4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,4-dibromo-6-{(E)[(4-fluorobenzyl)imino]methyl}phenolato-κ2N,O) copper(II), C28H18Br4F2N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-phenylthiourea, C17H22N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-(6-(5-amino-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridin-2-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine – dioxan (2/1), C25H23N7O
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-6-[(3-methylphenyl)sulfanyl]pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C13H14N2O2S
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-(cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)amide-κ2N′′,N′′′)manganese(II), C44H54N4Mn
- Crystal structure of prop-2-en-1-yl 2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxylate, C13H10O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-((3-methylphenyl)imino)methylphenolato-κ2N,O:O)hexacarbonyldimanganese(I), C34H24Mn2N2O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxybut-2-en-1-one C9H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[pentane-1,5-diylbis(oxy)]dibenzaldehyde, C19H20O4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-benzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C16H13NO2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)methanimine, C13H9Cl2N
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-5-bromothiazole-4-carboxylate, C6H7BrN2O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzylisothiouronium tetraphenylborate, C32H31BN2S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C24H16CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium(III)dichloride (THF), C14H23Cl2OTi
- Crystal structure of 3-ferrocenylsulfonyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C23H19FeN3O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C18H11FN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,6-ditosyl-1,6-diazecane, C22H30N2O4S2
- Crystal structure of N-phenyl-2-(pyridin-4-ylcarbonyl)hydrazinecarboxamide with Z′ = 4, C13H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)cyclohexylamine, C30H31NP2
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-N-phenylpropanamide, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 6-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-[1,2,4]-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole, C15H9FN4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(dicyanoazanido-2κN-μ2-dicyanoazanido-1κN:2κN′)(μ2-2-methoxy-6-(((2-((3-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)ethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-1κ2N,N′,2κ2O,O′,1κ2O′′,O′′′:2κ2O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)copper(II)], C22H20CdCuN8O5
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of fac-hexacarbonylbisμ2-(3-carboxy-3′-carboxylato-2,2′-bipyridine)-κ3N,N′:O-dirhenium(I) tetrahydrate, C30H22N4O18Re2
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)methane, C25H36N4
- Crystal structure of bis(triphenylphosphine-κP)bis(μ2-1H,1′H-2,2′-biimidazole-κ3N,N′:N′)disilver(I) bis(tetrafluoroborate), C48H42Ag2B2F8N8P2
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2-pyrazinecarboxamido)-benzene, C16H12N6O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromobenzoic acid, C7H5BrO2
- Crystal structure of bis(ethyltriphenylphos-phonium) tetrabromidocuprate(II), (C20H20P)2[CuBr4]
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C19H17BrN2
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(3-(pyrazin-2-yl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ2N,N′)-cobalt(II),C22H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamanganese(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MnN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of butyl 2-(3,5-dimethyl-1,1-dioxido-2H-1,2,6-thiadiazin-4-yl)benzoate, C16H20N2O4S
- Crystal structure of hexaaquabis(μ2-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)bis(μ3-3-(6-carboxylatopyridin-2-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido)tetra-manganese(II) dihydrate, C48H40Mn4N24O16
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cadmate(II)] bis(2-aminoisonicotinate) tetrahydrate, C38H50CdN8O10
- Crystal structure of succinic acid — 4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanylpyridine (1/1), C15H16N2O4S
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfanyl)pyridine-κN)dicopper(II), C30H32N4O8S2Cu2
- Crystal structure of 1-((2R,3S)-2,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl)-2-phenoxyethan-1-one, C18H19NO3
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium sulfanilate, C10H18N2O3S
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium 2′-carboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate, C20H25NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-acetyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-5,6-dichloro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H13Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ3-2-methyl-6-oxidopyridinium-4-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O′′)neodymium(III) chloride, C14H16ClN2O8Nd
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-4-methyl-2-(2-methylbenzyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, C12H15N3O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl)ethanone
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(4-(diethylamino)phenyl)diazen-1-ium-1-yl)benzenesulfonate monohydrate
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[(1E)-prop-1-ene-1,2-diyldisulfanediyl]bis(5-methyl-2,5-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazole, C9H10N4S4
- Crystal structure of poly [μ2-acetato-κ3-O,O′:O′)diaqua(μ3-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)cerium(III)] monohydrate (C10H13O9Ce)
- Crystal structure of tris((2-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)phenoxy)ethyl)amine, C36H27N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-bis((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)] dinitrate, C20H24CuN18O8
- Crystal structure of (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoic acid-κN) (4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)benzoato-κN)silver(I), C20H15N4O4Ag
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(3,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C18H15F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol hemihydrate, C13H17ClO3 · 0.5 H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κN)(m2-2-(1H-1,2,4-trizol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-3,1-benzimidazol-3-ium-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] dihydrate, C30H30N10O12Zn
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-((((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy-κ2O,O′))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ2O′′,O′′′]zinc(II), C28H22N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenyl) terephthalate C20H10F2N2O8
- Crystal structure of catena-[aqua((4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κO)(μ2-(4-carboxyphenyl)acetato-κ2O:O′)bis(4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κN)manganese(II)], C42H36N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of N′-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbohydrazide, C14H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of bis(8-ethyl-5-oxo-2-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-5,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate dihydrate, C36H42CuN10O12
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)bis(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylato)zinc(II), C60H56N6Zn2O16F2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13FN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexaqua(μ2-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-1κ2O,O′;2κO′)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κO)(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κ2O,O′)digadolinium(III) octahydrate, C60H76Gd2N18O32
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl bis(μ2-2-methoxybenzenethiolato-κ2S)pyridine(triphenylphosphane)dirhenium(I), C43H34NO8PS2Re2
- Crystal structure of 14-((1-(benzyloxycarbonyl-amino)-2-methylpropan-2-yl)sulfanyl)acetate Mutilin, C34H49NO6S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-6-(((2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d] imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol — ethanol (1/1), C24H25N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenylbutane-1,3-dione, C13H14O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(bis(methylthio)methylene)-1-phenyl-3-(2-phenylhydrazono)butan-1-one, C19H20N2OS2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(2-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)aniline-κ2N,N′)zinc(II)
- Crystal structure of bis(1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiolato)mercury(II)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-styryl-1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C24H19FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of aquabis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate trihydrate, [Cu(C17H18N3FO3)2(H2O)](C6H2SO4)·3(H2O)
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazatetracyclo[5·5·0·05·9·03·11]dodecane 1/3 hydrate, C6H8N12O13
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C25H20AsN2O3Rh
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-chlorophenyl)ethanone, C14H10Cl2O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-2-(2-(6-(4-methoxybenzyl)-7-oxo-7H-thiazolo[3,3-b][1,2,4]triazin-3-yl)phenoxy)acetamide, C25H26N4O4S
- Crystal structure of tetraqua((E)-4,4′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazol-1-ide)-κ2N:O)barium(II), C4H10N8O6Ba
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-phenoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C22H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of diethylammonium 5-((4-fluorophenyl)(6-hydroxy-1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-yl)methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-4-olate, C23H30FN5O6
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluoro-phenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12F2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tris(N-nitroso-N-oxyanilino-κ2O, O′) oxidoniobium(V), C18H15N6O7Nb
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-benzoyl-4-methyl-2-(phenylamino)thiophen-3-yl)ethan-1-one, a structure with Z′ = 6, C20H17NO2S
- Crystal structure of diethyl-3-methyl-4-phenylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylate, C19H18O4S2
- Crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate — benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid (1/1), C24H22N2O12
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-1,3-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1,3,2λ3,4-diazaphosphasiletidine
- Crystal structure of hexaquamanganese(II) bis(hexaborato-κ3O,O′,O′′)manganese(II) dihydrate, B12H28Mn2O34
- Crystal structure of 1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium pentaborate, [C7H13N2][B5O6(OH)4]
- Crystal structure of 13-(4-fluorophenyl)-11,13-dihydro-1H-benzo[h]indazolo[6,7-b] [1, 6]naphthyridin-12(6H)-one — dimethylformamide — water (1/2/1), C29H31FN6O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-ol, C14H12ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-((2-bromo-1-phenylvinyl)oxy)benzonitrile, C15H10BrNO
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido(1E,1′E)-N,N′-((1,4-phenylenebis(propane-2,2-diyl))bis(4,1-phenylene))bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)methanimine-κN)dizinc(II), C36H34N4Zn2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(3-methylpyridinyl)hexahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo-[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetrone, C24H20N4O4
- Crystal structure of trans-bis(2-methylmaleato-κ2O,O′) bis(piperazinium-κN) cobalt(II) trihydrate, C18H36CoN4O11
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)benzohydrazide, C18H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of 3,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-9H-carbazole, C18H13N5
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-pyridinyl)-1-naphthoic acid, C16H11NO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-diformyl-4,4′-(6H,12H-5,11-methano-dibenzo[b,f][11,5]diazocine-2,8-diyl)dibenzene, C29H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N′-(adamantan-2-ylidene)pyridine-3-carbohydrazide, C16H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbaldehyde), C14H18N4O2
- Crystal structure of methyl 8-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-5a,8-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,5a,6,7,8,10a,10b-decahydrocyclohepta[e]indene-3a(1H)-carboxylate, C21H34O3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-propyl-2-(propylthio)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C11H15N3OS
- Crystal structure of poly[diacetato(μ2-1,4-bis(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)nickel(II)], C26H22N8NiO4
- Crystal structure of bis(2,4-dibromo-6-{(E)[(4-fluorobenzyl)imino]methyl}phenolato-κ2N,O) copper(II), C28H18Br4F2N2O2Cu
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-phenylthiourea, C17H22N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-(6-(5-amino-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridin-2-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine – dioxan (2/1), C25H23N7O
- Crystal structure of 5-ethyl-6-[(3-methylphenyl)sulfanyl]pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C13H14N2O2S
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-(cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene-κ2N,N′))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis((2,6-diisopropylphenyl)amide-κ2N′′,N′′′)manganese(II), C44H54N4Mn
- Crystal structure of prop-2-en-1-yl 2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxylate, C13H10O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-((3-methylphenyl)imino)methylphenolato-κ2N,O:O)hexacarbonyldimanganese(I), C34H24Mn2N2O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxybut-2-en-1-one C9H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[pentane-1,5-diylbis(oxy)]dibenzaldehyde, C19H20O4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-benzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C16H13NO2S
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)methanimine, C13H9Cl2N
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-5-bromothiazole-4-carboxylate, C6H7BrN2O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzylisothiouronium tetraphenylborate, C32H31BN2S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C24H16CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium(III)dichloride (THF), C14H23Cl2OTi
- Crystal structure of 3-ferrocenylsulfonyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C23H19FeN3O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C18H11FN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,6-ditosyl-1,6-diazecane, C22H30N2O4S2
- Crystal structure of N-phenyl-2-(pyridin-4-ylcarbonyl)hydrazinecarboxamide with Z′ = 4, C13H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of N,N-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)cyclohexylamine, C30H31NP2
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-N-phenylpropanamide, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 6-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-[1,2,4]-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole, C15H9FN4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(dicyanoazanido-2κN-μ2-dicyanoazanido-1κN:2κN′)(μ2-2-methoxy-6-(((2-((3-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)ethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-1κ2N,N′,2κ2O,O′,1κ2O′′,O′′′:2κ2O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)copper(II)], C22H20CdCuN8O5


