Abstract
Expansive soil is a type of unsaturated soil that develops fissures within its body due to dry and wet cycles. These fissures are the primary factor contributing to slope instability in expansive soil regions. In this study, we conducted research on the impact of herbaceous plant root systems on soil properties in the Shangluo area of Shaanxi. This area is known for its distribution of expansive soils. We achieved this by planting three types of commonly used slope protection plants. The results revealed significant differences in root system characteristics among the three herbaceous plants: Lolium perenne, Cynodon dactylon, and Medicago. Particularly, Lolium perenne exhibited a well-developed and heterogeneous root system with a substantial number of roots. These roots were primarily concentrated within the interval of 0 < L ≤ 0.5 mm. The specific gravity of soil tended to decrease after herbaceous plant roots were planted. The growth of herbaceous plants greatly increased the soil’s ability to hold water. The presence of herbaceous root systems significantly improved the soil consolidation effect. The entanglement and interpenetration effects of the plant root system had a significant influence on the dispersion of soil macroaggregates and the formation of soil fabrics. The colloid content of the soil increased with the growth of the plant root system. Additionally, the root system of herbaceous plants greatly enhanced the angle of internal friction and cohesion of soil. The growth of herbal plants significantly enhanced the properties of expansive soils by improving the soil structure, increasing the nutrient richness, enhancing soil water retention, and augmenting both soil agglomeration and internal friction angles, thereby improving the soil’s solid capacity. This study elucidates the mechanisms by which herbaceous plants exert long-term beneficial effects on expansive soil areas, contributing to the prevention and control of regional ecological security.
1 Introduction
Expanded soil is a type of unsaturated soil composed mainly of clay minerals, such as montmorillonite and illite, which have high affinity for water [1]. When absorbing water, expansive soil undergoes significant expansion, and when losing water it experiences significant contraction. This cyclic wet and dry process leads to the formation of numerous random cracks within the soil, which greatly compromises its structural integrity. These cracks are a major contributing factor to slope instability in areas with expansive soil [2]. In recent years, numerous scholars have extensively researched slope protection, focusing primarily on various engineering measures such as concrete, slurry masonry retaining walls, retaining walls, and anti-slip piles [3,4]. However, these engineering measures often prioritize strength and efficacy, disregarding the ecological aspect and resulting in poor landscape effects [5]. Over time, the surfaces of concrete, slurry masonry schist, and retaining walls are prone to weathering and damage, rendering the effectiveness of such engineering measures in slope protection unsustainable [6]. In recent years, there have been scholars conducting research on vegetation slope protection [7]. However, due to the limited effectiveness and quantification challenges of vegetation slope protection measures on thick soil layers, engineering measures are often combined with vegetation slope protection methods in practical engineering to ensure slope protection [8]. Herbaceous plant slope protection is a technology that utilizes the root system of plants to retain water, stabilize soil, and also provides environmental benefits [9]. Plant roots play a crucial role in reinforcing, anchoring, and preventing runoff, which effectively strengthens the soil, enhances the slope stability, and reduces the soil erosion [10]. The consolidation effect of the plant root system on soil can be attributed to two main factors: the chemical effect of the root system and the mechanical effect of the root system itself. The interaction between the plant’s root system and the soil forms a composite stress structure, which enhances the soil’s resistance to shear, seepage, and erosion caused by water flow on the slope [11].
A number of scholars have conducted studies on the reinforcement of soil by plant roots and have explored the relationship between plant roots and soil shear strength [12]. The findings indicate that herbaceous soil complexes can enhance the shear strength of the system [13]. Certain researchers have demonstrated a positive correlation between soil shear strength and the root content, particularly when the soil water content and moisture density are at specific levels [14]. It has also been observed that herbaceous plant roots enhance the soil shear strength when the soil has a high water content, with root action potentially exceeding 1.0 under high saturation conditions [15,16]. Some scholars have analyzed the cellulose and lignin contents in the plant root system and found that herbaceous root systems exhibit a higher cellulose content compared to the lignin content [17]. This characteristic of herbaceous plants is manifested as higher tensile properties in their mechanical properties. The contribution of herbaceous crop root systems to the shear strength of the soil body primarily depends on the average tensile strength of the root body, as well as the number and area of all functioning roots on the shear plane [18,19,20]. Herbaceous plant root systems can be utilized as flexible reinforcing materials for slope protection [21]. Studies have demonstrated that the plant root system significantly enhances soil shear strength, and the effect of the root system on soil shear strength varies significantly with different soil moisture contents [22,23,24].
In summary, the impact of herbaceous plant root systems on soil shear strength has been investigated through laboratory simulation experiments [25]. It has been found that using the herbaceous plant root system as a flexible reinforcing material can effectively enhance the tensile strength of soil [26]. However, previous studies have primarily focused on laboratory experiments where quantitative plant root systems were added to simulate the reinforcing effect of herbaceous plants on soil [27,28,29,30]. The influence of herbaceous plants on soil consolidation and properties under real field conditions has not been extensively studied. To further investigate the effects of herbaceous plants on the stability of expansive soils, it is essential to examine the growth characteristics of the root systems of these plants within the soil of typical expansive soil regions, as well as their influence on the soil at the project site. This study focuses on the typical expansive soil areas in Shaanxi, where field test sites were established to plant three common herbaceous plants used for slope protection. It is expected to reveal the effect and mechanism of herbaceous plants on soil consolidation in expansive soil areas from the changes in soil characteristics and plant root structure. It provides theoretical support and guidance for the practice of vegetation slope protection engineering.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
This study was conducted in Shangluo City, southern Shaanxi Province, which is known for its distribution of expansive soils. The test field was located in Waishang Town, Shangzhou District, Shangluo City, Shaanxi Province. The test field was a natural soil slope with a 35° inclination and a height of 3 m. The main test plants selected were Lolium perenne, Cynodon dactylon, and Medicago, which are commonly found in the local area. Control treatment experiments were also conducted, with each plot measuring 6 m × 4 m and three replicates in each experimental area. The layout of the test field is shown in Figure 1.
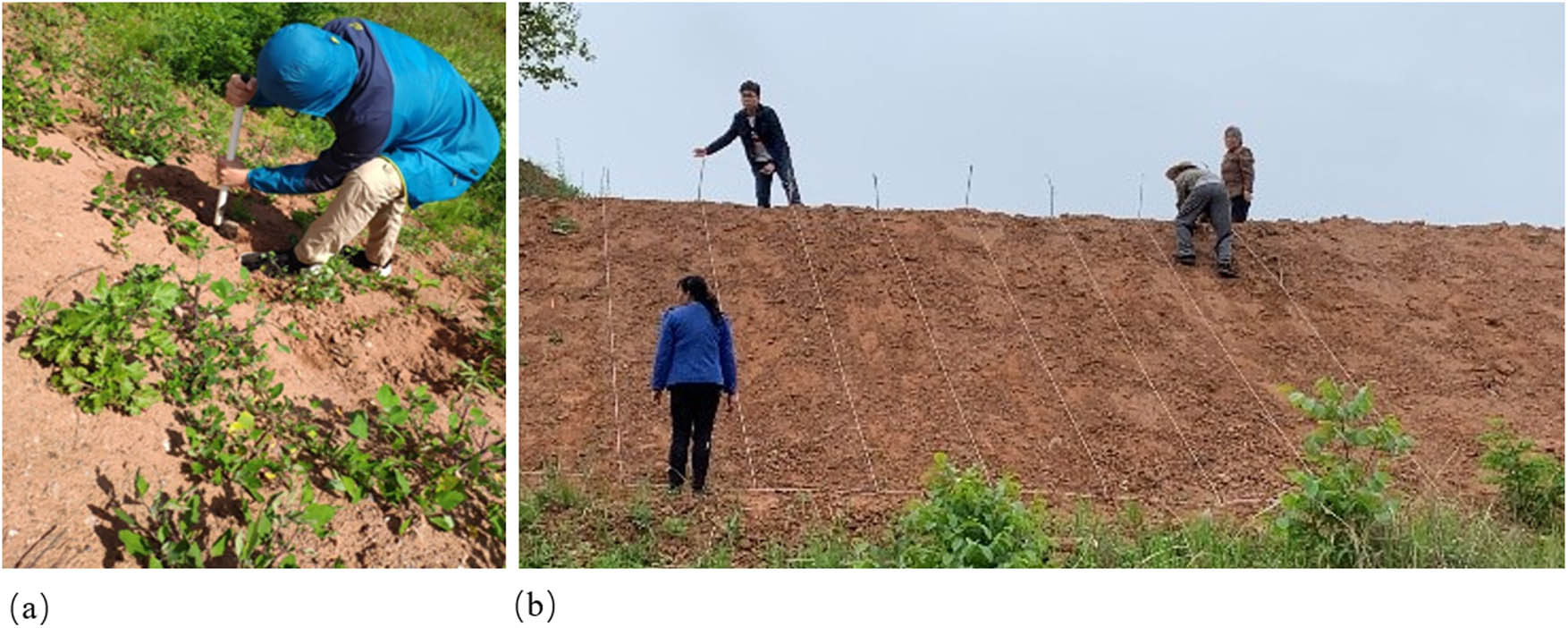

Experimental field set up with real scenes. (a) Original slope appearance. (b) Test plots laid out in different areas.
Before the construction of the experimental field, the composition of soil particles and the microstructure of the test site were analyzed. According to the criteria for classifying expansive soil, the content of particles smaller than 0.005 mm in this trial area was found to be 38.4%, indicating that it is classified as moderate expansive soil. The microstructure of this soil exhibits a sheet-like structure, with fine scaly morphology. This structure is a significant representation of the microstructure of montmorillonite (Figure 2).
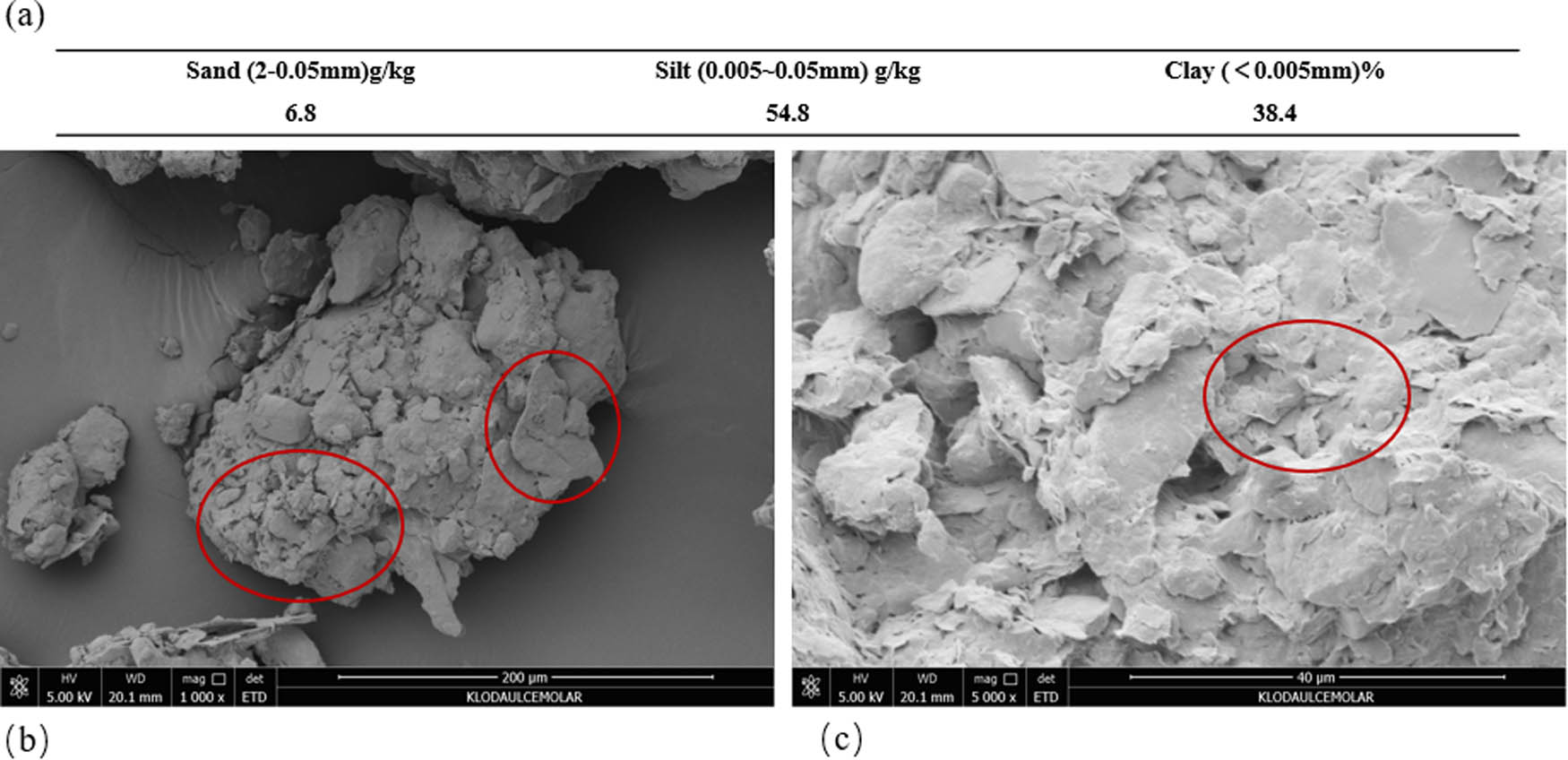

Composition and microstructure of undisturbed soil particles. (a) Composition of undisturbed soil particles. (b) SEM image of undisturbed soil (200 µm). (c) SEM image of undisturbed soil (40 µm).
Herbaceous plants were planted in April 2021 after the experimental field was set up. Sampling and analyses were carried out in September 2022, completing a crop growth cycle of one and a half years.
2.2 Sample collection and analysis
Sampling was conducted at the peak of plant biomass, and three entire plants were randomly selected for observation of root morphology. Each sample plot was arranged in an S-shaped curve to remove the above-ground portion of the plant. The center of the plant was chosen such that the center of the ring blade circle aligned with the central point. Soil samples were collected from the ring blade in a downward direction along the vertical axis of the plant. The collected soil samples were pre-treated based on the requirements of different testing indexes and then subjected to testing.
2.3 Test method
The soil sample was stripped and rinsed with water multiple times to extract the plant root system. The root system was then placed in a root tray and carefully unfolded using tweezers for root measurements [31]. A root scanning and analysis system (WinRHIZ0) was used to determine the root parameters [25]. The shear force of the soil was tested using a three-head shear tester, Model 14.10 Pocket Vane Tester, while consolidation experiments were conducted using a KTG fully automatic pneumatic consolidator [32]. The in situ soil was dried, sprayed with gold, and coated before being observed and analyzed for its micro-morphology under a scanning electron microscope [33]. Soil specific gravity was determined using the drainage method, soil moisture content was determined using the weighing method, and soil texture was determined using the densitometer method [28].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Study of root characteristics of different herbaceous plant root systems
The morphology and scanned images of the root systems of three herbaceous plants are presented in Figures 3 and 4, respectively. The root systems of these plants exhibit distinct morphological characteristics. Lolium perenne, a tufted plant, possesses a well-developed and fast-growing root system with numerous tillers. Its rhizome is short, and its fibrous roots are primarily distributed in the surface soil at a depth of 15–20 cm. The root system of Lolium perenne is lengthy and slender, making it difficult to separate individual roots due to intertwining. Cynodon dactylon has rhizomes and stolons, resulting in a developed root system. Its fibrous roots are fine and tough, exhibiting strong branching strength and a large branching angle. Medicago has a very long main root with no branching. It possesses few capillary fibrous roots and a relatively simple root structure, which is influenced by slope planting. Upon scanning the root system of these plants, it was observed that the root system of Lolium perenne is slender and long, whereas the root system of Cynodon dactylon is thicker and tougher. Medicago has a lesser lateral root system.
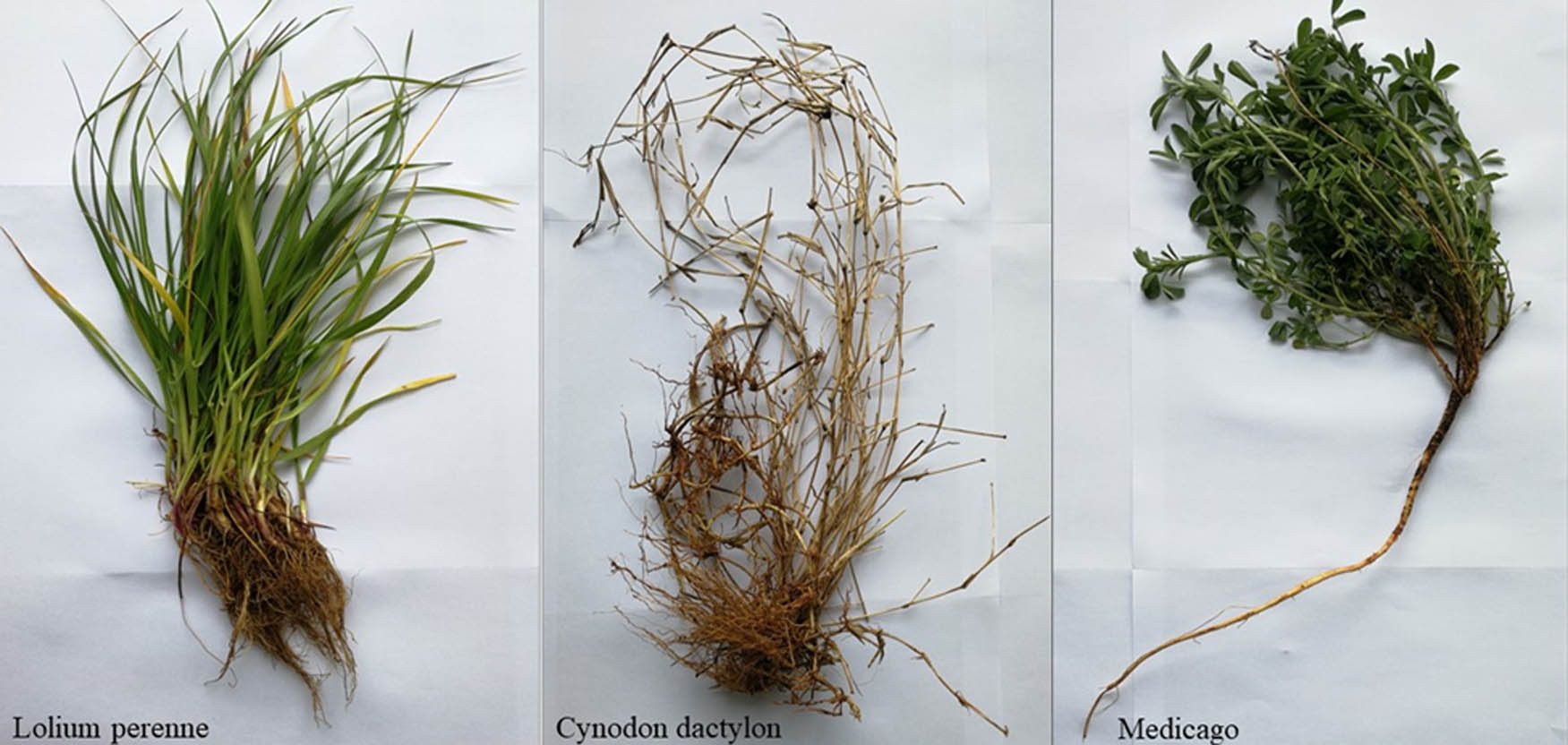

Overall image of the root system of three herbaceous plants.
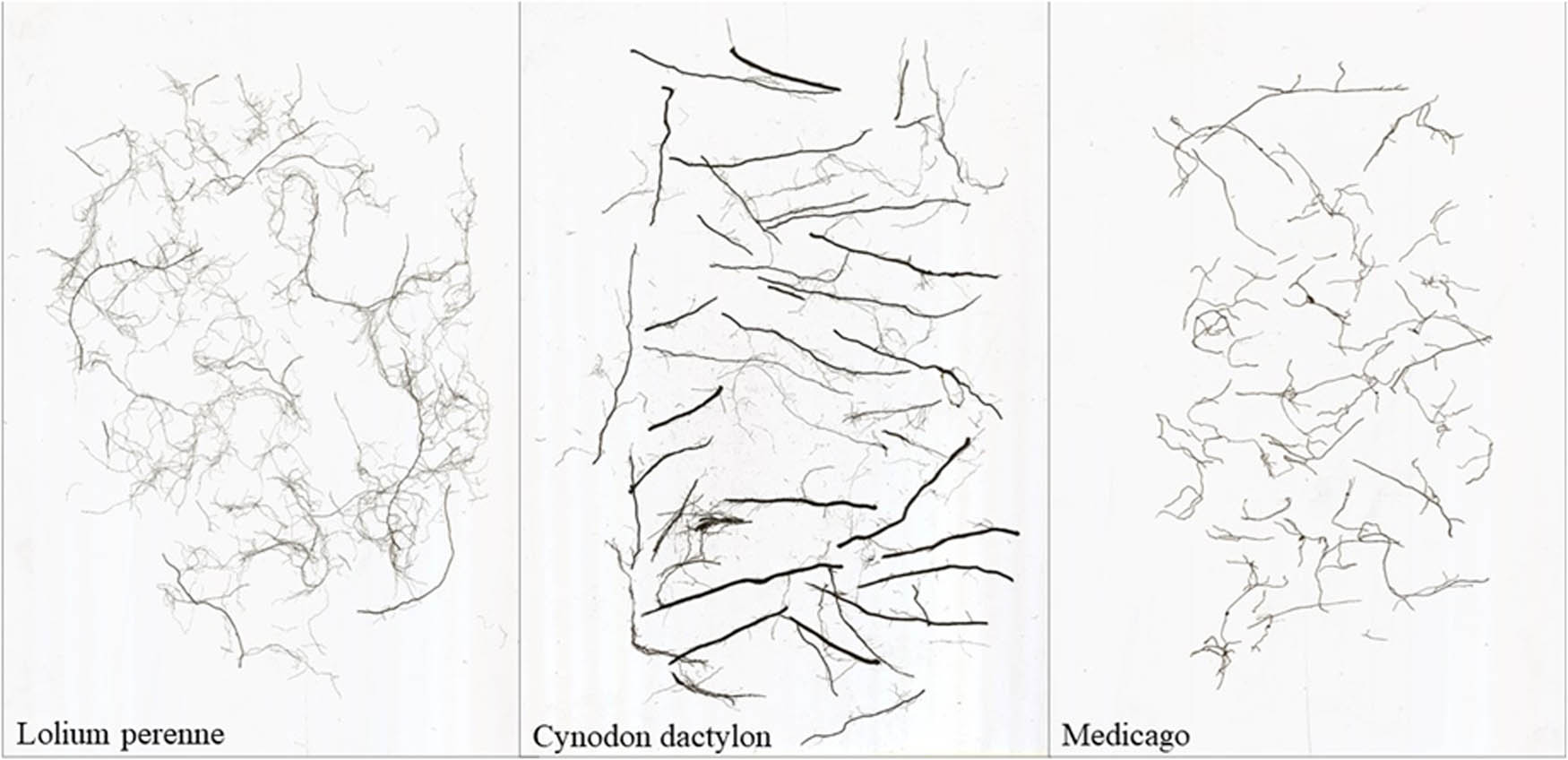
Scanned images of root systems of three herbaceous plants.
In order to quantify the length of the root system of three herbaceous plants, the root system was classified into six intervals. The intervals were defined as follows: 0 < L ≤ 0.5 mm, 0.5 < L ≤ 1.0 mm, 1.0 < L ≤ 1.5 mm, 1.5 < L ≤ 2.0 mm, 2.0 < L ≤ 2.5 mm, and 2.5 < L ≤ 3.0 mm. Figure 5 shows that the root system of Lolium perenne was mainly concentrated in the 0 < L ≤ 0.5 mm interval. Similarly, the root system of Cynodon dactylon was also mainly concentrated in the same interval, but it also had a significant distribution in the 0.5 < L ≤ 1.5 mm interval. On the other hand, the root system of Medicago fibrous was mainly concentrated in the 0 < L ≤ 0.5 mm interval, but it was also found in the 2.5 < L ≤ 3.0 mm interval. Furthermore, Medicago fibrous had the longest root length in the 2.5 < L ≤ 3.0 mm diameter range, while Cynodon dactylon and Lolium perenne had almost no root system in this diameter range.
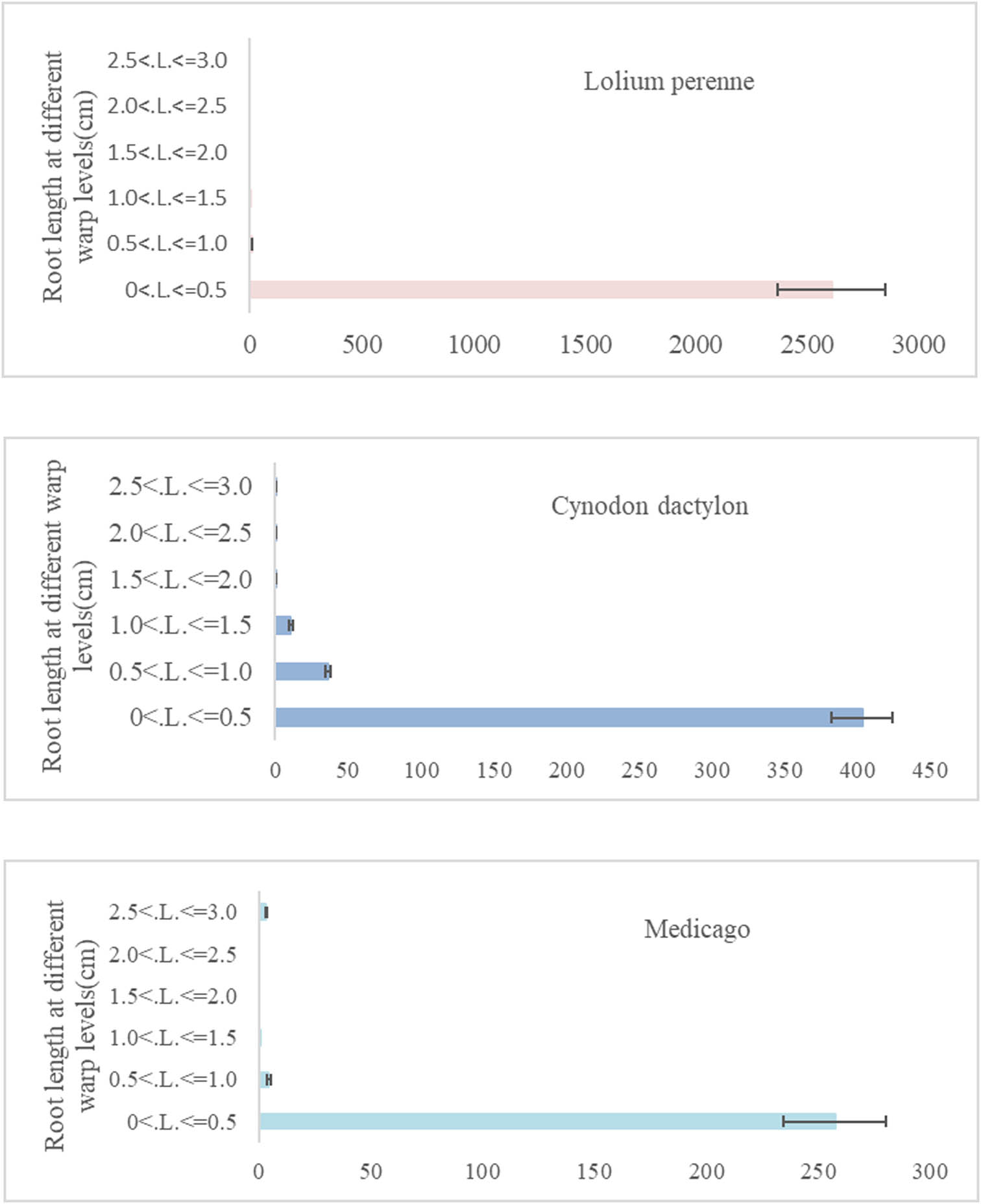
Root length of the herbaceous root system in different diameter ranges.
3.2 Research on the effect of different herbaceous plant root systems on soil specific gravity
The impact of herbaceous root systems on soil specific gravity is illustrated in Figure 6. It is evident that herbaceous root systems have a significant effect on soil specific gravity, and the magnitude of this effect varies depending on the characteristics of roots. Generally, the soil specific gravity tends to decrease after the implementation of herbaceous root systems. For instance, in the Medicago treatment, the soil specific gravity decreased by 0.051 g/cm3 compared to the Control treatment. Similarly, in the Lolium perenne treatment, the soil specific gravity decreased significantly by 0.16 g/cm3 compared to the Control treatment. Moreover, the Cynodon dactylon treatment resulted in a soil specific gravity decrease of 0.5 g/cm3 compared to the Control treatment. Interestingly, the soil weight under the Lolium perenne treatment was 0.109 g/cm3 lower than the Medicago treatment and 0.06 g/cm3 lower than the Cynodon dactylon treatment when considering all three herbaceous plants.
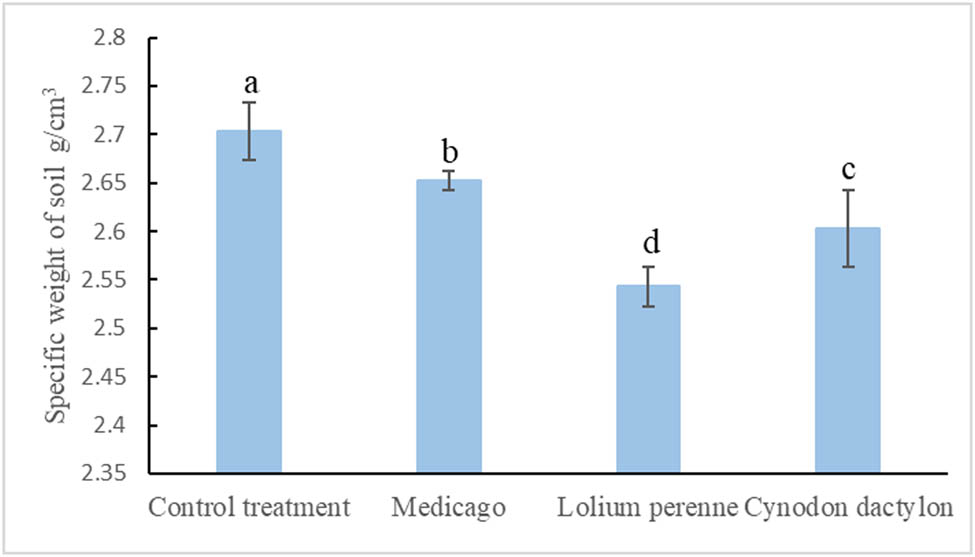
Soil specific gravity under the influence of different herbaceous plants.
The differences in root characteristics of the three herbaceous plants are important factors contributing to the observed results. This is because the root system of Lolium perenne is large and redundant, leading to entanglement and interpenetration of the roots, which in turn increase the soil pore space [28]. As a result, the soil weight decreased the most compared to the Control treatment. Cynodon dactylon has a longer stolon length, stronger branching strength, and a greater branching angle. Its root system depth is not as deep as Lolium perenne and Medicago, and its influence on soil porosity per unit area is not as high as that of Lolium perenne. Consequently, the rate of decrease in soil specific gravity under Cynodon dactylon treatment is not as high as that under Lolium perenne treatment. Medicago, being a taproot plant with a long main root and fewer capillary fibrous roots, has a weaker effect on soil pore space and the smallest effect on soil specific gravity compared to the Control treatment.
3.3 Study of the effect of different herbaceous root systems on soil water content
Different herbaceous plant root systems had varying effects on soil water content. As shown in Figure 7, under the Lolium perenne treatment, the soil water content was significantly higher by 6.08% compared to the Control treatment. Similarly, under the Medicago treatment, the soil water content was significantly higher by 3.70% compared to the Control treatment. The Cynodon dactylon treatment also resulted in a significantly higher soil water content by 2.77% compared to the Control treatment. However, there was no significant difference in soil water content between the Medicago and Cynodon dactylon treatments. The data analysis revealed that all three herbaceous plant root systems could significantly improve the soil’s water holding capacity.
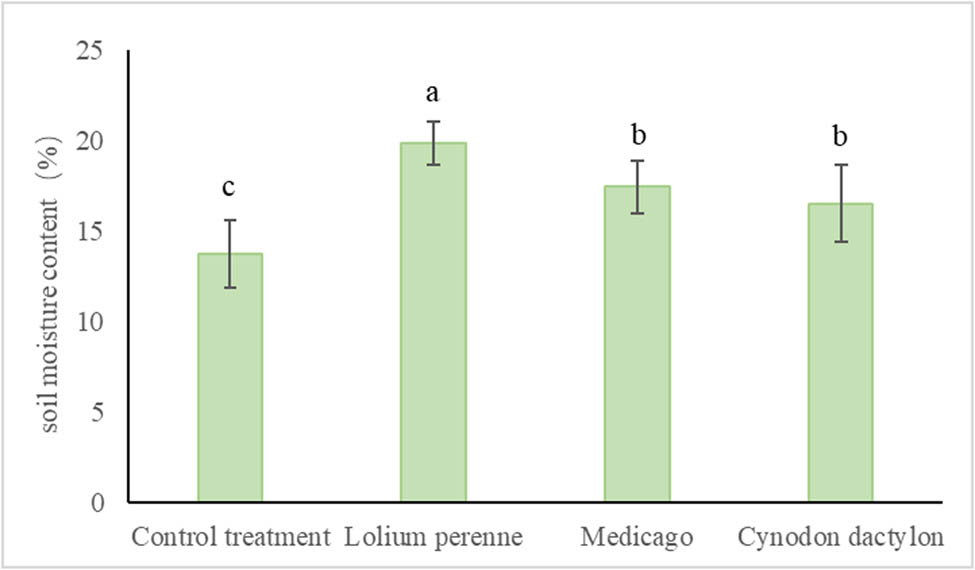
Soil water content under the influence of different herbaceous plants.
Among them, Lolium perenne had the highest water holding capacity due to its larger root volume, while Medicago and Cynodon dactylon did not have the same capacity as Lolium perenne due to their small root volume per unit area. The improvement in soil water holding capacity by herbaceous plants was primarily attributed to the storage of water by their root systems and the shading effect of their above-ground parts, which reduced water evaporation from the soil surface.
3.4 Study on the effect of different herbaceous plant root systems on soil consolidation effect
The experimental results of soil consolidation under three herbaceous plant treatments are shown in Figure 8. The soil was compacted and deformed, resulting in reduced pore ratios under applied loads while increasing the soil strength. At the same pressure, Lolium perenne treatment had the largest pore ratio, while the Control treatment had the smallest pore ratio. At an applied load of 50 kPa, the pore ratio (e) was 0.87 for Lolium perenne, 0.82 for Medicago, and 0.78 for Cynodon dactylon. As the applied load increased, the soil pore ratios of the three herbaceous treatments decreased with increasing pressure values. Particularly, the soil pore ratios of the Cynodon dactylon treatments decreased significantly with the pressure values. The Cynodon dactylon treatment exhibited the highest reduction in soil porosity ratio with increasing pressure values, reaching a similar pore ratio as the Control treatment at 200 kPa. In contrast, the pore ratio of Lolium perenne treatment and Medicago treatment decreased at a slower rate compared to Cynodon dactylon with increasing imposed load. However, Lolium perenne treatment showed the slowest decrease in the soil pore ratio. When the applied load reached 1,600 kPa, the soil pore ratios under various treatments were approximately the same. These findings suggest that the herbaceous root system no longer had a significant effect on the soil porosity ratio at the ultimate pressure.
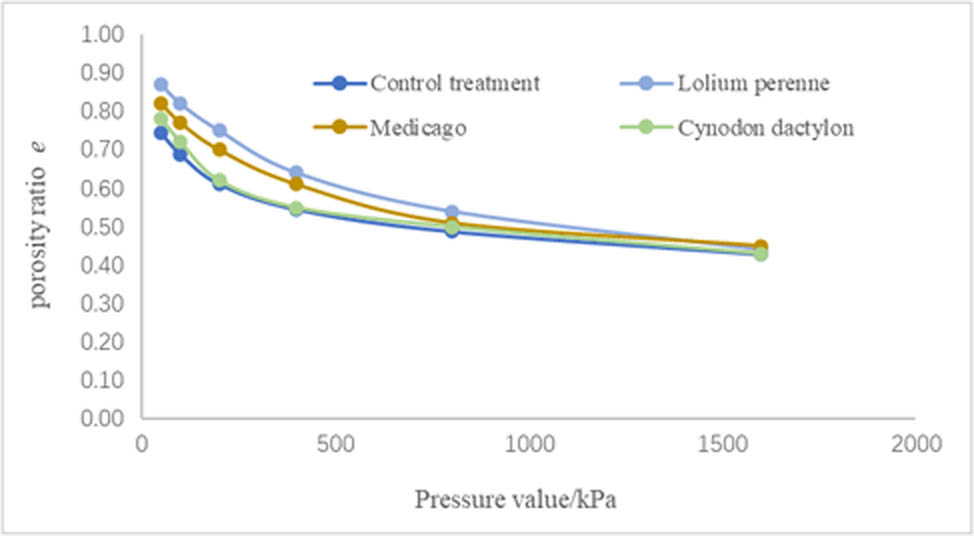
Soil consolidation effect under the influence of different herbaceous plants.
The different root morphology of herbaceous plants contributed to the observed results. Cynodon dactylon had a weak root consolidation capacity due to its low root volume per unit area. The consolidation effect of the Cynodon dactylon root system disappeared after the external load increased. Lolium perenne exhibited the best soil consolidation among the three herbaceous plant types. This can be attributed to its well-developed and heterogeneous root characteristics, as well as its large root volume per unit area [29]. Among the three herbaceous plant types, Medicago showed the best soil consolidation due to its thick primary root system, although it had a low lateral root volume. In summary, Lolium perenne had the most effective soil consolidation due to its large root system per unit area, while Medicago had an intermediate consolidation effect due to its strong primary root system but a small lateral root system. The presence of herbaceous root systems can effectively improve clayey soils with small inter-particle pores, poor aeration and permeability, and poor drainage [30].
3.5 Study of the effect of different herbaceous root systems on soil mechanical properties
The direct shear test of soil under three herbaceous treatments is shown in Figure 9. The cohesion of soil increased significantly under the planting of herbaceous crops compared to the Control treatment. The highest increase in cohesion was observed in Lolium perenne, which showed a 38.93% increase in cohesion compared to the Control treatment. Medicago and Cynodon dactylon treatments also showed a significant increase in soil cohesion compared to the Control treatment, with Medicago showing a 14.92% increase and Cynodon dactylon showing a 10.02% increase. However, there was no significant difference between Medicago and Cynodon dactylon treatments. The angle of internal friction of soil also changed significantly due to the influence of herbaceous roots. Under Lolium perenne treatment, the angle of internal friction increased by 93.44% compared to the Control treatment, while under Medicago treatment it increased by 63.11%. The angle of internal friction of soil under Cynodon dactylon treatment increased by 45.90% compared to the Control treatment. Overall, the presence of herbaceous plant roots significantly increased both the soil’s internal friction angle and cohesion.
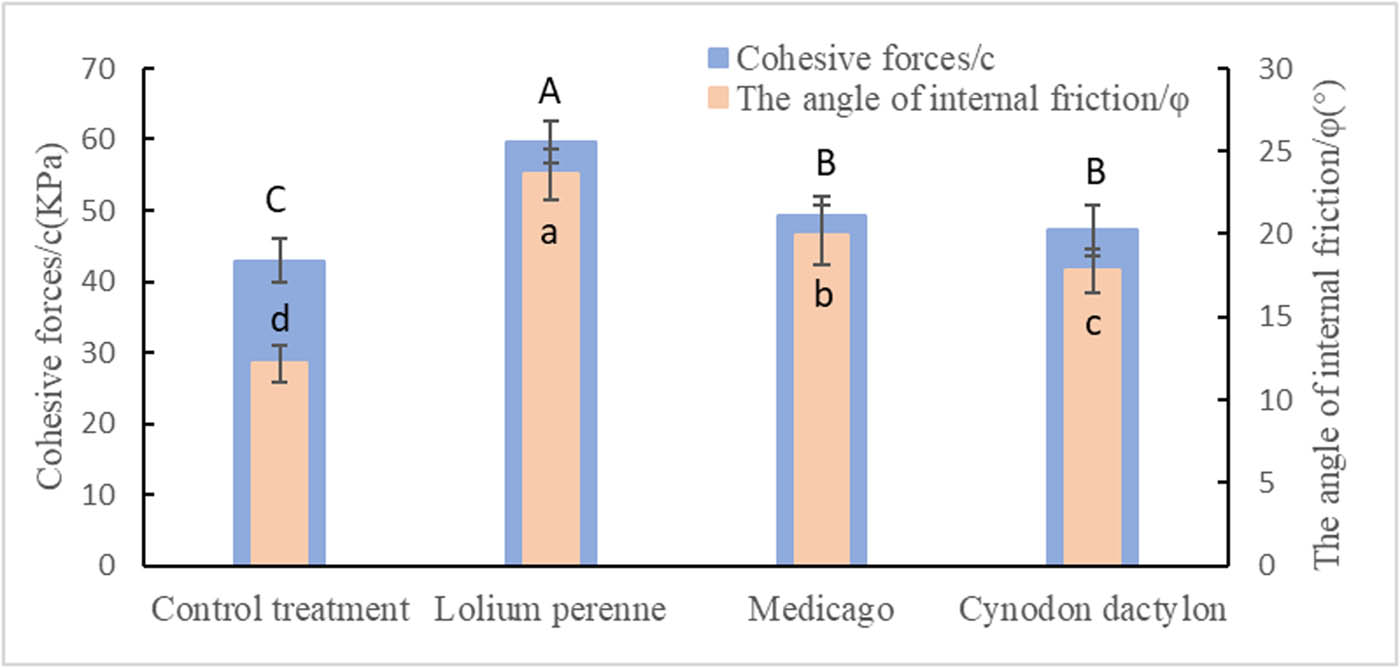
Soil cohesion forces and the angle of internal friction under the influence of different herbaceous plants.
The consolidation effect of the root system on soil is mainly attributed to two factors: the mechanical effect of the root system and the effect of root secretion. Lolium perenne and Cynodon dactylon, which are shallow-rooted plants, develop a dense network of roots that grow horizontally on the soil surface, effectively consolidating the top soil. Medicago, a deep-rooted herb, primarily grows its root system downward. The deep root system of Medicago enhances the soil’s ability to adsorb negative ions, thereby improving the binding of fine particulate matter. Additionally, Medicago’s root system secretes substances such as growth hormones that promote the adsorption and gelation between soil particles. This secretion also facilitates the aggregation of organic matter, resulting in the formation of larger particles with excellent cementation properties [29]. Due to the variations in the root systems of these three herbaceous plants, Lolium perenne exhibits the highest increase in soil cohesion and angle of internal friction due to its extensive root mass and numerous root systems. Cynodon dactylon, with its rhizomes and stolons, has a lower root mass per unit area compared to Lolium perenne. Similarly, Medicago, being a taproot plant, has fewer fibrous root systems. Consequently, both Cynodon dactylon and Medicago have a relatively lower soil consolidation capacity compared to Lolium perenne, but the presence of roots significantly enhances the soil’s consolidation capacity.
3.6 Study on the effect of different herbaceous root systems on soil microstructure
As shown in Figure 10, the soil micromorphological characteristics of different herbaceous plant treatments were observed at 500 μm. It was observed that after planting herbaceous crops, the large agglomerates in the soil, which originally had a strong adhesive force, were dispersed due to the interspersed effect of the root system. As a result, the originally smooth surface of the particles exhibited varying degrees of basal knot. Cynodon dactylon, which has a shallow root system and is a stoloniferous plant, showed a weaker ability to decompose soil agglomerates compared to Lolium perenne. Similarly, Medicago, which is a main-rooted crop with fewer fibrous roots, also exhibited a weaker ability to decompose soil agglomerates compared to Lolium perenne. Overall, the decomposition of soil agglomerates was weaker in Cynodon dactylon and Medicago compared to Lolium perenne.
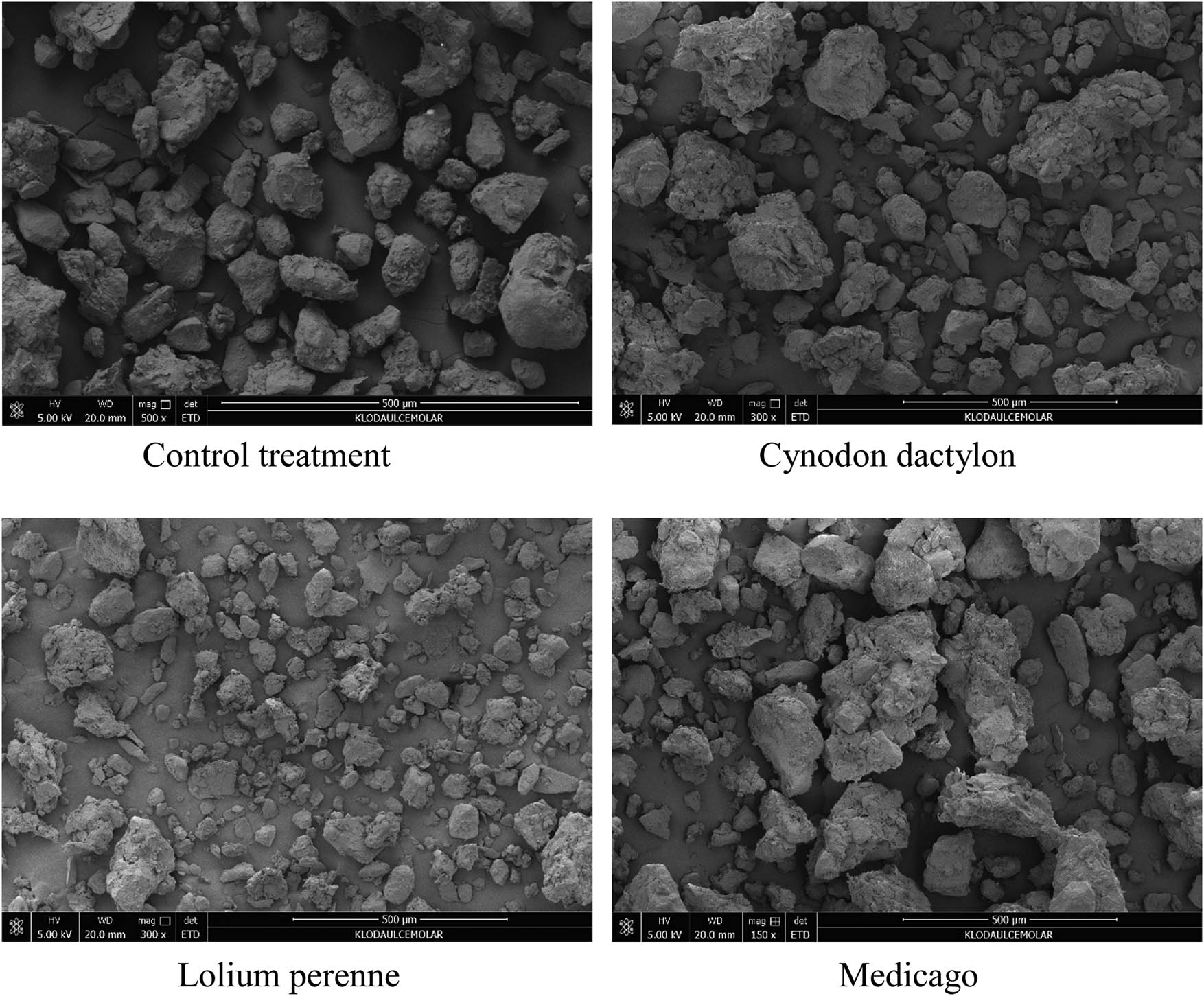

Soil microstructure under the influence of different herbaceous plants.
By analyzing the soil fabrics of different herbaceous treatments, it was observed that the Control treatment showed a smooth surface of soil particles and a natural state of soil fabrics due to natural mineral weathering. However, the presence of plant roots significantly influenced the soil fabrics in the three herbaceous treatments. The soil under Lolium perenne and Cynodon dactylon treatments exhibited complex soil fabrics, with obvious concave–convex stacking of soil particles and distinct crescent-shaped, filamentous, and bow-shaped soil fabrics. Similar soil fabrics were also observed in the Medicago treatment, although they were less abundant. These findings indicate that the entanglement and interpenetration effects of plant root systems play a significant role in the dispersion of soil macroaggregates and the soil fabrics.
4 Conclusions
The morphological characteristics of the root systems of the three herbaceous plants differ significantly. Lolium perenne is a tufted plant with a well-developed root system, numerous tillers, and long, slender roots that are closely intertwined. Cynodon dactylon has a rhizomatous root system with a wide branching angle. Medicago, meanwhile, exhibits a clear dominance of the main root and fewer lateral fibrous roots. It is important to note that the root morphology of these herbaceous plants plays a crucial role in influencing changes in soil properties. Because of their significant root structure characteristics, the root length of the three crops is significantly different, which mainly depends on the herbaceous plant morphology.
The proportion of soil tends to decrease following the planting of herbaceous plants. Lolium perenne, characterized by its extensive root system, contributes to the entanglement and interpenetration of roots, which in turn increases the soil porosity and results in the most significant reduction in soil specific gravity. The influence of plant roots on soil specific gravity primarily stems from the effects of herbaceous root morphology and root density on soil porosity. Furthermore, the growth of plants and the activities of their roots facilitate the accumulation and decomposition of soil organic matter. The decomposition process releases gases and alters the soil pore structure, ultimately leading to a reduction in soil specific gravity.
After planting herbaceous plants, the water-holding capacity of the soil is significantly improved. This improvement can be attributed to two main factors. First, the above-ground biomass of the plants provides shade, which helps to reduce surface evaporation. Second, the extension and interpenetration of plant roots enhance the soil porosity and consequently improve the water-holding capacity of the rhizosphere soil.
After planting herbaceous plants, the soil experienced compaction and deformation due to the applied load, resulting in a decrease in the pore ratio. Among the three herbaceous plants, Lolium perenne treatment exhibited the highest pore ratio under the same pressure. Furthermore, as the applied load increased, the decrease in the soil pore ratio under Lolium perenne treatment was slower compared to the other two plants. The variation in soil pore space, attributed to the difference in root volume per unit area, plays a crucial role in soil consolidation capacity. Additionally, the mechanical action of the root system and the cementing effect of root secretions are significant factors in enhancing the soil cohesion and internal friction angle. Notably, the well-developed root system of Lolium perenne demonstrated the highest consolidation capacity for the soil. When selecting herbs for slope protection in areas with expansive soils, it is advisable to choose plants with well-developed root systems whenever possible. The intricate and reinforcing nature of these robust root systems provide significant mechanical support, while the substantial quantity of root secretions contributes to soil consolidation, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of slope protection in expansive soil regions.
Root growth also significantly affects the micromorphological structure of the soil. In the case of Lolium perenne treatment, there was a noticeable dispersion of large aggregates, higher abundance, and a higher number of soil barriers compared to the Medicago and Cynodon dactylon treatments. These findings suggest that the effects of plant roots on the soil particle composition and nodule structure are closely related to the morphology of the plant roots.
The root structure of plants significantly influences the characteristics of expansive soils. Specifically, Lolium perenne and Medicago are particularly effective in enhancing soil slope stability due to their distinctive root traits. This research provides valuable insights into the mechanisms by which plant roots contribute to slope stability.
-
Funding information: This research was funded by Shaanxi Province Key Research Program Projects (2023-ZDLSF-28) and Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group internal projects (DJNY2024-21).
-
Author contributions: Cao Tingting: experimental design and writing – preparation; Zhang Haiou: experimental operation and analysis; Sun Xubo: formal analysis and investigation; Guo Zhen: project administration; Wang Jiaqi: data curation; Hu Yantao: supervision.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there is no possible conflicts of interest.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research was not related to either human or animal use.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Comino E, Marengo P, Rolli V. Root reinforcement effect of different grass species: A comparison between experimental and models results. Soil Till Res. 2010;110:60–8. 10.1016/j.still.2010.06.009.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Gu J. Analysis on strengthening of plant to slope soil under orthogonal states. Appl Mech Mater. 2014;580:34–7.10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.580-583.34Search in Google Scholar
[3] Zhang ZT, Gao WH, Wang X, Zhang JQ, Tang XY. Degradation-induced evolution of particle roundness and its effect on the shear behaviour of railway ballast. Transp Geotech. 2020;24:100388. 10.1016/j.trgeo.2020.100388.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Capilleri PP, Motta E, Raciti E. Experimental study on native plant root tensile strength for slope stabilization. Procedia Eng. 2016;158:116–21.10.1016/j.proeng.2016.08.415Search in Google Scholar
[5] Liu YL, Liu XL, Fu X, Wu YN, Li ZJ. Numerical simulation of plant roots protection effects on the silty clays slope with low liquid limit. Changsha, China: IEEE; 2015. p. 533–7.10.1109/ISDEA.2015.138Search in Google Scholar
[6] Luo YM, Zhou DP, Zhang JY. The study on stability mechanism of red bed slopes with eco-protection in the Southwest of China. Adv Biomed Eng. 2012;7:39–45.Search in Google Scholar
[7] McIvor I, Metral B, Douglas GB. Variation in root density of poplar trees at different plant densities. Proc Agron Soc NZ. 2005;35:66–73.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Olinic T, Stanciu AM, Butcaru AC, Luchian V. Bio-reinforcement of slopes. Sci Pap Ser E Land Reclam Earth Observ Surv Environ Eng. 2023;12:25–30.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Sanchez-Castillo L, Kosugi KL, Masaoka N, Kubota T. Eco-morphological characteristics of fern species for slope conservation. J Mt Sci. 2019;16:504–15. 10.1007/s11629-018-5106-z.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Osman N, Dorairaj D, Halim A, Zelan NIA. Dynamics of plant ecology and soil conservation: Implications for cut-slope protection. Acta Oecol. 2021;111:103744. 10.1016/j.actao.2021.103744.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Su LJ, Hu BL, Xie QJ. Experimental and theoretical study of mechanical properties of root-soil interface for slope protection. J Mt Sci. 2020;17:2784–95. 10.1007/s11629-020-6077-4.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Preti F. Forest protection and protection forest: Tree root degradation over hydrological shallow landslides triggering. Ecol Eng. 2013;61:633–45. 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.11.009.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Wang Y, Shu Z, Zheng Y, Xiao S. Plant root reinforcement effect for coastal slope stability. J Coast Res. 2015;73:216–9. 10.2112/SI73-038.1.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zhang ZT, Gao WH. Effect of different test methods on the disintegration behaviour of soft rock and the evolution model of disintegration breakage under cyclic wetting and drying. Eng Geol. 2020;279:105888. 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105888.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Ma Q, Huang C, Xiao H, Chen Q. Thermal properties of carbon fiber-reinforced lightweight substrate for ecological slope protection. Energies. 2019;12(15):2927. 10.3390/en12152927.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Xu R, Li X, Yang W, Jiang C, Rabiei M. Use of local plants for ecological restoration and slope stability: A possible application in Yanan, Loess Plateau, China. Geomatics Nat Hazards Risk. 2019;10(1):2106–28. 10.1080/19475705.2019.1679891.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Zhou X, Fu D, Wan J, Xiao H, He X, Li Z, et al. The shear strength of root-soil composites in different growth periods and their effects on slope stability. Appl Sci. 2023;13(19):11116. 10.3390/app131911116.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Jia X, Zhang W, Wang X, Jin Y, Cong P. Numerical analysis of an explicit smoothed particle finite element method on shallow vegetated slope stability with different root architectures. Sustainability. 2022;14(18):11272. 10.3390/su141811272.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Kumar A, Das SK, Nainegali L, Reddy KR. Effect of grass species root for enhanced slope protection in amended coalmine overburden dump soil. Plant Soil. 2023;498(1):1–18. 10.1007/s11104-023-06450-4.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Esmaiili M, Abdi E, Nieber JL, Jafary M, Majnounian B. How roots of Picea abies and Fraxinus excelsior plantations contribute to soil strength and slope stability: evidence from a study case in the Hyrcanian Forest, Iran. Soil Res. 2021;59(3):287–98. 10.1071/SR20083.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Zhou Y, Ma W. Plant roots in the active zone improving the performance of ecological reinforced soil retaining walls. Bull Eng Geol Environ. 2023;82(11):414. 10.1007/s10064-023-03420-z.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Fu H, Zha H, Zeng L, Jia C, Bian H. Research progress on ecological protection technology of highway slope: status and challenges. Transp Saf Environ. 2020;2(1):3–17. 10.1093/tse/tdaa006.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Masi EB, Segoni S, Tofani V. Root reinforcement in slope stability models: A review. Geosciences. 2021;11(5):212. 10.3390/geosciences11050212.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Himmelbauer ML, Vateva V, Lozanova L, Loiskandl W, Rousseva S. Site effects on root characteristics and soil protection capability of two cover crops grown in South Bulgaria. J Hydrol Hydromech. 2013;61(1):30–8. 10.2478/johh-2013-0005.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Ding H, Xue L, Liu H, Li L, Wang H, Zhai M. Influence of root volume, plant spacing, and planting pattern of tap-like tree root system on slope protection effect. Forests. 2022;13(11):1925. 10.3390/f13111925.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Zhou YY, Wang XM. Mesomechanics characteristics of soil reinforcement by plant roots. Bull Eng Geol Environ. 2019;78:3719–28. 10.1007/s10064-018-1370-y.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Wang Y, Xu W, Wang Z, Zhu Y. The impact of vegetation roots on shallow stability of expansive soil slope under rainfall conditions. Appl Sci. 2023;13(21):11619. 10.3390/app132111619.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Zhai K, Zhang J, Zhang L, Luo X, Wang K. Integrating root morphology based on whole-pullout test of model roots: A case study. Appl Sci. 2024;14(2):764. 10.3390/app14020764.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Gonzalez-Ollauri A, Mickovski SB. Plant-Best: A novel plant selection tool for slope protection. Ecol Eng. 2017;106:154–73. 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.04.066.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Zhang ZT, Zhou GM. Investigating the compaction and the mechanical behaviors of coal gangue as subgrade filler and constructing highway subgrade in practice. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):26272. 10.1038/s41598-024-77816-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Wang B, Wang S. Shear strength analysis and slope stability study of straight root herbaceous root soil composite. Appl Sci. 2023;13(23):12632. 10.3390/app132312632.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Chen Z, Qiao O, Liu Y, Ma K, Song H, Li C. Interplays between plants and environmental factors determine pullout resistance on different revegetated slopes in mining areas. J Environ Manag. 2024;351:119741. 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119741.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Saifuddin M, Normaniza O. Rooting characteristics of some tropical plants for slope protection. J Trop For Sci. 2016;28:469–78.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Seismic response and damage model analysis of rocky slopes with weak interlayers
- Multi-scenario simulation and eco-environmental effect analysis of “Production–Living–Ecological space” based on PLUS model: A case study of Anyang City
- Remote sensing estimation of chlorophyll content in rape leaves in Weibei dryland region of China
- GIS-based frequency ratio and Shannon entropy modeling for landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study in Kundah Taluk, Nilgiris District, India
- Natural gas origin and accumulation of the Changxing–Feixianguan Formation in the Puguang area, China
- Spatial variations of shear-wave velocity anomaly derived from Love wave ambient noise seismic tomography along Lembang Fault (West Java, Indonesia)
- Evaluation of cumulative rainfall and rainfall event–duration threshold based on triggering and non-triggering rainfalls: Northern Thailand case
- Pixel and region-oriented classification of Sentinel-2 imagery to assess LULC dynamics and their climate impact in Nowshera, Pakistan
- The use of radar-optical remote sensing data and geographic information system–analytical hierarchy process–multicriteria decision analysis techniques for revealing groundwater recharge prospective zones in arid-semi arid lands
- Effect of pore throats on the reservoir quality of tight sandstone: A case study of the Yanchang Formation in the Zhidan area, Ordos Basin
- Hydroelectric simulation of the phreatic water response of mining cracked soil based on microbial solidification
- Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality in tropical monsoon climate region based on “pattern–process–quality” – a case study of Cambodia
- Early Permian to Middle Triassic Formation petroleum potentials of Sydney Basin, Australia: A geochemical analysis
- Micro-mechanism analysis of Zhongchuan loess liquefaction disaster induced by Jishishan M6.2 earthquake in 2023
- Prediction method of S-wave velocities in tight sandstone reservoirs – a case study of CO2 geological storage area in Ordos Basin
- Ecological restoration in valley area of semiarid region damaged by shallow buried coal seam mining
- Hydrocarbon-generating characteristics of Xujiahe coal-bearing source rocks in the continuous sedimentary environment of the Southwest Sichuan
- Hazard analysis of future surface displacements on active faults based on the recurrence interval of strong earthquakes
- Structural characterization of the Zalm district, West Saudi Arabia, using aeromagnetic data: An approach for gold mineral exploration
- Research on the variation in the Shields curve of silt initiation
- Reuse of agricultural drainage water and wastewater for crop irrigation in southeastern Algeria
- Assessing the effectiveness of utilizing low-cost inertial measurement unit sensors for producing as-built plans
- Analysis of the formation process of a natural fertilizer in the loess area
- Machine learning methods for landslide mapping studies: A comparative study of SVM and RF algorithms in the Oued Aoulai watershed (Morocco)
- Chemical dissolution and the source of salt efflorescence in weathering of sandstone cultural relics
- Molecular simulation of methane adsorption capacity in transitional shale – a case study of Longtan Formation shale in Southern Sichuan Basin, SW China
- Evolution characteristics of extreme maximum temperature events in Central China and adaptation strategies under different future warming scenarios
- Estimating Bowen ratio in local environment based on satellite imagery
- 3D fusion modeling of multi-scale geological structures based on subdivision-NURBS surfaces and stratigraphic sequence formalization
- Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms in Google Earth Engine for urban land use dynamics in rapidly urbanizing South Asian cities
- Study on the mechanism of plant root influence on soil properties in expansive soil areas
- Simulation of seismic hazard parameters and earthquakes source mechanisms along the Red Sea rift, western Saudi Arabia
- Tectonics vs sedimentation in foredeep basins: A tale from the Oligo-Miocene Monte Falterona Formation (Northern Apennines, Italy)
- Investigation of landslide areas in Tokat-Almus road between Bakımlı-Almus by the PS-InSAR method (Türkiye)
- Predicting coastal variations in non-storm conditions with machine learning
- Cross-dimensional adaptivity research on a 3D earth observation data cube model
- Geochronology and geochemistry of late Paleozoic volcanic rocks in eastern Inner Mongolia and their geological significance
- Spatial and temporal evolution of land use and habitat quality in arid regions – a case of Northwest China
- Ground-penetrating radar imaging of subsurface karst features controlling water leakage across Wadi Namar dam, south Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Rayleigh wave dispersion inversion via modified sine cosine algorithm: Application to Hangzhou, China passive surface wave data
- Fractal insights into permeability control by pore structure in tight sandstone reservoirs, Heshui area, Ordos Basin
- Debris flow hazard characteristic and mitigation in Yusitong Gully, Hengduan Mountainous Region
- Research on community characteristics of vegetation restoration in hilly power engineering based on multi temporal remote sensing technology
- Identification of radial drainage networks based on topographic and geometric features
- Trace elements and melt inclusion in zircon within the Qunji porphyry Cu deposit: Application to the metallogenic potential of the reduced magma-hydrothermal system
- Pore, fracture characteristics and diagenetic evolution of medium-maturity marine shales from the Silurian Longmaxi Formation, NE Sichuan Basin, China
- Study of the earthquakes source parameters, site response, and path attenuation using P and S-waves spectral inversion, Aswan region, south Egypt
- Source of contamination and assessment of potential health risks of potentially toxic metal(loid)s in agricultural soil from Al Lith, Saudi Arabia
- Regional spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of rural construction areas in the Nanxi River Basin via GIS
- An efficient network for object detection in scale-imbalanced remote sensing images
- Effect of microscopic pore–throat structure heterogeneity on waterflooding seepage characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs
- Environmental health risk assessment of Zn, Cd, Pb, Fe, and Co in coastal sediments of the southeastern Gulf of Aqaba
- A modified Hoek–Brown model considering softening effects and its applications
- Evaluation of engineering properties of soil for sustainable urban development
- The spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of sustainable development in China’s provincial areas
- Application of a mixed additive and multiplicative random error model to generate DTM products from LiDAR data
- Gold vein mineralogy and oxygen isotopes of Wadi Abu Khusheiba, Jordan
- Prediction of surface deformation time series in closed mines based on LSTM and optimization algorithms
- 2D–3D Geological features collaborative identification of surrounding rock structural planes in hydraulic adit based on OC-AINet
- Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of Chl-a in Chinese lakes between 1986 and 2023
- Land use classification through fusion of remote sensing images and multi-source data
- Nexus between renewable energy, technological innovation, and carbon dioxide emissions in Saudi Arabia
- Analysis of the spillover effects of green organic transformation on sustainable development in ethnic regions’ agriculture and animal husbandry
- Factors impacting spatial distribution of black and odorous water bodies in Hebei
- Large-scale shaking table tests on the liquefaction and deformation responses of an ultra-deep overburden
- Impacts of climate change and sea-level rise on the coastal geological environment of Quang Nam province, Vietnam
- Reservoir characterization and exploration potential of shale reservoir near denudation area: A case study of Ordovician–Silurian marine shale, China
- Seismic prediction of Permian volcanic rock reservoirs in Southwest Sichuan Basin
- Application of CBERS-04 IRS data to land surface temperature inversion: A case study based on Minqin arid area
- Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of Sanjiaoding gold mine in Saishiteng area
- Research on the deformation prediction model of surrounding rock based on SSA-VMD-GRU
- Geochronology, geochemical characteristics, and tectonic significance of the granites, Menghewula, Southern Great Xing’an range
- Hazard classification of active faults in Yunnan base on probabilistic seismic hazard assessment
- Characteristics analysis of hydrate reservoirs with different geological structures developed by vertical well depressurization
- Estimating the travel distance of channelized rock avalanches using genetic programming method
- Landscape preferences of hikers in Three Parallel Rivers Region and its adjacent regions by content analysis of user-generated photography
- New age constraints of the LGM onset in the Bohemian Forest – Central Europe
- Characteristics of geological evolution based on the multifractal singularity theory: A case study of Heyu granite and Mesozoic tectonics
- Soil water content and longitudinal microbiota distribution in disturbed areas of tower foundations of power transmission and transformation projects
- Oil accumulation process of the Kongdian reservoir in the deep subsag zone of the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China
- Investigation of velocity profile in rock–ice avalanche by particle image velocimetry measurement
- Optimizing 3D seismic survey geometries using ray tracing and illumination modeling: A case study from Penobscot field
- Sedimentology of the Phra That and Pha Daeng Formations: A preliminary evaluation of geological CO2 storage potential in the Lampang Basin, Thailand
- Improved classification algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing images based on the hybrid spectral network model
- Map analysis of soil erodibility rates and gully erosion sites in Anambra State, South Eastern Nigeria
- Identification and driving mechanism of land use conflict in China’s South-North transition zone: A case study of Huaihe River Basin
- Evaluation of the impact of land-use change on earthquake risk distribution in different periods: An empirical analysis from Sichuan Province
- A test site case study on the long-term behavior of geotextile tubes
- An experimental investigation into carbon dioxide flooding and rock dissolution in low-permeability reservoirs of the South China Sea
- Detection and semi-quantitative analysis of naphthenic acids in coal and gangue from mining areas in China
- Comparative effects of olivine and sand on KOH-treated clayey soil
- YOLO-MC: An algorithm for early forest fire recognition based on drone image
- Earthquake building damage classification based on full suite of Sentinel-1 features
- Potential landslide detection and influencing factors analysis in the upper Yellow River based on SBAS-InSAR technology
- Assessing green area changes in Najran City, Saudi Arabia (2013–2022) using hybrid deep learning techniques
- An advanced approach integrating methods to estimate hydraulic conductivity of different soil types supported by a machine learning model
- Hybrid methods for land use and land cover classification using remote sensing and combined spectral feature extraction: A case study of Najran City, KSA
- Streamlining digital elevation model construction from historical aerial photographs: The impact of reference elevation data on spatial accuracy
- Analysis of urban expansion patterns in the Yangtze River Delta based on the fusion impervious surfaces dataset
- A metaverse-based visual analysis approach for 3D reservoir models
- Late Quaternary record of 100 ka depositional cycles on the Larache shelf (NW Morocco)
- Integrated well-seismic analysis of sedimentary facies distribution: A case study from the Mesoproterozoic, Ordos Basin, China
- Study on the spatial equilibrium of cultural and tourism resources in Macao, China
- Urban road surface condition detecting and integrating based on the mobile sensing framework with multi-modal sensors
- Application of improved sine cosine algorithm with chaotic mapping and novel updating methods for joint inversion of resistivity and surface wave data
- Review Articles
- Humic substances influence on the distribution of dissolved iron in seawater: A review of electrochemical methods and other techniques
- Applications of physics-informed neural networks in geosciences: From basic seismology to comprehensive environmental studies
- Ore-controlling structures of granite-related uranium deposits in South China: A review
- Shallow geological structure features in Balikpapan Bay East Kalimantan Province – Indonesia
- A review on the tectonic affinity of microcontinents and evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean in Northeastern Tibet
- Special Issue: Natural Resources and Environmental Risks: Towards a Sustainable Future - Part II
- Depopulation in the Visok micro-region: Toward demographic and economic revitalization
- Special Issue: Geospatial and Environmental Dynamics - Part II
- Advancing urban sustainability: Applying GIS technologies to assess SDG indicators – a case study of Podgorica (Montenegro)
- Spatiotemporal and trend analysis of common cancers in men in Central Serbia (1999–2021)
- Minerals for the green agenda, implications, stalemates, and alternatives
- Spatiotemporal water quality analysis of Vrana Lake, Croatia
- Functional transformation of settlements in coal exploitation zones: A case study of the municipality of Stanari in Republic of Srpska (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Hypertension in AP Vojvodina (Northern Serbia): A spatio-temporal analysis of patients at the Institute for Cardiovascular Diseases of Vojvodina
- Regional patterns in cause-specific mortality in Montenegro, 1991–2019
- Spatio-temporal analysis of flood events using GIS and remote sensing-based approach in the Ukrina River Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Flash flood susceptibility mapping using LiDAR-Derived DEM and machine learning algorithms: Ljuboviđa case study, Serbia
- Geocultural heritage as a basis for geotourism development: Banjska Monastery, Zvečan (Serbia)
- Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS and AHP techniques – A case study of the zone of influence of Kolubara Mining Basin
- Impact of the agri-geographical transformation of rural settlements on the geospatial dynamics of soil erosion intensity in municipalities of Central Serbia
- Where faith meets geomorphology: The cultural and religious significance of geodiversity explored through geospatial technologies
- Applications of local climate zone classification in European cities: A review of in situ and mobile monitoring methods in urban climate studies
- Complex multivariate water quality impact assessment on Krivaja River
- Ionization hotspots near waterfalls in Eastern Serbia’s Stara Planina Mountain
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Seismic response and damage model analysis of rocky slopes with weak interlayers
- Multi-scenario simulation and eco-environmental effect analysis of “Production–Living–Ecological space” based on PLUS model: A case study of Anyang City
- Remote sensing estimation of chlorophyll content in rape leaves in Weibei dryland region of China
- GIS-based frequency ratio and Shannon entropy modeling for landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study in Kundah Taluk, Nilgiris District, India
- Natural gas origin and accumulation of the Changxing–Feixianguan Formation in the Puguang area, China
- Spatial variations of shear-wave velocity anomaly derived from Love wave ambient noise seismic tomography along Lembang Fault (West Java, Indonesia)
- Evaluation of cumulative rainfall and rainfall event–duration threshold based on triggering and non-triggering rainfalls: Northern Thailand case
- Pixel and region-oriented classification of Sentinel-2 imagery to assess LULC dynamics and their climate impact in Nowshera, Pakistan
- The use of radar-optical remote sensing data and geographic information system–analytical hierarchy process–multicriteria decision analysis techniques for revealing groundwater recharge prospective zones in arid-semi arid lands
- Effect of pore throats on the reservoir quality of tight sandstone: A case study of the Yanchang Formation in the Zhidan area, Ordos Basin
- Hydroelectric simulation of the phreatic water response of mining cracked soil based on microbial solidification
- Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality in tropical monsoon climate region based on “pattern–process–quality” – a case study of Cambodia
- Early Permian to Middle Triassic Formation petroleum potentials of Sydney Basin, Australia: A geochemical analysis
- Micro-mechanism analysis of Zhongchuan loess liquefaction disaster induced by Jishishan M6.2 earthquake in 2023
- Prediction method of S-wave velocities in tight sandstone reservoirs – a case study of CO2 geological storage area in Ordos Basin
- Ecological restoration in valley area of semiarid region damaged by shallow buried coal seam mining
- Hydrocarbon-generating characteristics of Xujiahe coal-bearing source rocks in the continuous sedimentary environment of the Southwest Sichuan
- Hazard analysis of future surface displacements on active faults based on the recurrence interval of strong earthquakes
- Structural characterization of the Zalm district, West Saudi Arabia, using aeromagnetic data: An approach for gold mineral exploration
- Research on the variation in the Shields curve of silt initiation
- Reuse of agricultural drainage water and wastewater for crop irrigation in southeastern Algeria
- Assessing the effectiveness of utilizing low-cost inertial measurement unit sensors for producing as-built plans
- Analysis of the formation process of a natural fertilizer in the loess area
- Machine learning methods for landslide mapping studies: A comparative study of SVM and RF algorithms in the Oued Aoulai watershed (Morocco)
- Chemical dissolution and the source of salt efflorescence in weathering of sandstone cultural relics
- Molecular simulation of methane adsorption capacity in transitional shale – a case study of Longtan Formation shale in Southern Sichuan Basin, SW China
- Evolution characteristics of extreme maximum temperature events in Central China and adaptation strategies under different future warming scenarios
- Estimating Bowen ratio in local environment based on satellite imagery
- 3D fusion modeling of multi-scale geological structures based on subdivision-NURBS surfaces and stratigraphic sequence formalization
- Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms in Google Earth Engine for urban land use dynamics in rapidly urbanizing South Asian cities
- Study on the mechanism of plant root influence on soil properties in expansive soil areas
- Simulation of seismic hazard parameters and earthquakes source mechanisms along the Red Sea rift, western Saudi Arabia
- Tectonics vs sedimentation in foredeep basins: A tale from the Oligo-Miocene Monte Falterona Formation (Northern Apennines, Italy)
- Investigation of landslide areas in Tokat-Almus road between Bakımlı-Almus by the PS-InSAR method (Türkiye)
- Predicting coastal variations in non-storm conditions with machine learning
- Cross-dimensional adaptivity research on a 3D earth observation data cube model
- Geochronology and geochemistry of late Paleozoic volcanic rocks in eastern Inner Mongolia and their geological significance
- Spatial and temporal evolution of land use and habitat quality in arid regions – a case of Northwest China
- Ground-penetrating radar imaging of subsurface karst features controlling water leakage across Wadi Namar dam, south Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Rayleigh wave dispersion inversion via modified sine cosine algorithm: Application to Hangzhou, China passive surface wave data
- Fractal insights into permeability control by pore structure in tight sandstone reservoirs, Heshui area, Ordos Basin
- Debris flow hazard characteristic and mitigation in Yusitong Gully, Hengduan Mountainous Region
- Research on community characteristics of vegetation restoration in hilly power engineering based on multi temporal remote sensing technology
- Identification of radial drainage networks based on topographic and geometric features
- Trace elements and melt inclusion in zircon within the Qunji porphyry Cu deposit: Application to the metallogenic potential of the reduced magma-hydrothermal system
- Pore, fracture characteristics and diagenetic evolution of medium-maturity marine shales from the Silurian Longmaxi Formation, NE Sichuan Basin, China
- Study of the earthquakes source parameters, site response, and path attenuation using P and S-waves spectral inversion, Aswan region, south Egypt
- Source of contamination and assessment of potential health risks of potentially toxic metal(loid)s in agricultural soil from Al Lith, Saudi Arabia
- Regional spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of rural construction areas in the Nanxi River Basin via GIS
- An efficient network for object detection in scale-imbalanced remote sensing images
- Effect of microscopic pore–throat structure heterogeneity on waterflooding seepage characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs
- Environmental health risk assessment of Zn, Cd, Pb, Fe, and Co in coastal sediments of the southeastern Gulf of Aqaba
- A modified Hoek–Brown model considering softening effects and its applications
- Evaluation of engineering properties of soil for sustainable urban development
- The spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of sustainable development in China’s provincial areas
- Application of a mixed additive and multiplicative random error model to generate DTM products from LiDAR data
- Gold vein mineralogy and oxygen isotopes of Wadi Abu Khusheiba, Jordan
- Prediction of surface deformation time series in closed mines based on LSTM and optimization algorithms
- 2D–3D Geological features collaborative identification of surrounding rock structural planes in hydraulic adit based on OC-AINet
- Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of Chl-a in Chinese lakes between 1986 and 2023
- Land use classification through fusion of remote sensing images and multi-source data
- Nexus between renewable energy, technological innovation, and carbon dioxide emissions in Saudi Arabia
- Analysis of the spillover effects of green organic transformation on sustainable development in ethnic regions’ agriculture and animal husbandry
- Factors impacting spatial distribution of black and odorous water bodies in Hebei
- Large-scale shaking table tests on the liquefaction and deformation responses of an ultra-deep overburden
- Impacts of climate change and sea-level rise on the coastal geological environment of Quang Nam province, Vietnam
- Reservoir characterization and exploration potential of shale reservoir near denudation area: A case study of Ordovician–Silurian marine shale, China
- Seismic prediction of Permian volcanic rock reservoirs in Southwest Sichuan Basin
- Application of CBERS-04 IRS data to land surface temperature inversion: A case study based on Minqin arid area
- Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of Sanjiaoding gold mine in Saishiteng area
- Research on the deformation prediction model of surrounding rock based on SSA-VMD-GRU
- Geochronology, geochemical characteristics, and tectonic significance of the granites, Menghewula, Southern Great Xing’an range
- Hazard classification of active faults in Yunnan base on probabilistic seismic hazard assessment
- Characteristics analysis of hydrate reservoirs with different geological structures developed by vertical well depressurization
- Estimating the travel distance of channelized rock avalanches using genetic programming method
- Landscape preferences of hikers in Three Parallel Rivers Region and its adjacent regions by content analysis of user-generated photography
- New age constraints of the LGM onset in the Bohemian Forest – Central Europe
- Characteristics of geological evolution based on the multifractal singularity theory: A case study of Heyu granite and Mesozoic tectonics
- Soil water content and longitudinal microbiota distribution in disturbed areas of tower foundations of power transmission and transformation projects
- Oil accumulation process of the Kongdian reservoir in the deep subsag zone of the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China
- Investigation of velocity profile in rock–ice avalanche by particle image velocimetry measurement
- Optimizing 3D seismic survey geometries using ray tracing and illumination modeling: A case study from Penobscot field
- Sedimentology of the Phra That and Pha Daeng Formations: A preliminary evaluation of geological CO2 storage potential in the Lampang Basin, Thailand
- Improved classification algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing images based on the hybrid spectral network model
- Map analysis of soil erodibility rates and gully erosion sites in Anambra State, South Eastern Nigeria
- Identification and driving mechanism of land use conflict in China’s South-North transition zone: A case study of Huaihe River Basin
- Evaluation of the impact of land-use change on earthquake risk distribution in different periods: An empirical analysis from Sichuan Province
- A test site case study on the long-term behavior of geotextile tubes
- An experimental investigation into carbon dioxide flooding and rock dissolution in low-permeability reservoirs of the South China Sea
- Detection and semi-quantitative analysis of naphthenic acids in coal and gangue from mining areas in China
- Comparative effects of olivine and sand on KOH-treated clayey soil
- YOLO-MC: An algorithm for early forest fire recognition based on drone image
- Earthquake building damage classification based on full suite of Sentinel-1 features
- Potential landslide detection and influencing factors analysis in the upper Yellow River based on SBAS-InSAR technology
- Assessing green area changes in Najran City, Saudi Arabia (2013–2022) using hybrid deep learning techniques
- An advanced approach integrating methods to estimate hydraulic conductivity of different soil types supported by a machine learning model
- Hybrid methods for land use and land cover classification using remote sensing and combined spectral feature extraction: A case study of Najran City, KSA
- Streamlining digital elevation model construction from historical aerial photographs: The impact of reference elevation data on spatial accuracy
- Analysis of urban expansion patterns in the Yangtze River Delta based on the fusion impervious surfaces dataset
- A metaverse-based visual analysis approach for 3D reservoir models
- Late Quaternary record of 100 ka depositional cycles on the Larache shelf (NW Morocco)
- Integrated well-seismic analysis of sedimentary facies distribution: A case study from the Mesoproterozoic, Ordos Basin, China
- Study on the spatial equilibrium of cultural and tourism resources in Macao, China
- Urban road surface condition detecting and integrating based on the mobile sensing framework with multi-modal sensors
- Application of improved sine cosine algorithm with chaotic mapping and novel updating methods for joint inversion of resistivity and surface wave data
- Review Articles
- Humic substances influence on the distribution of dissolved iron in seawater: A review of electrochemical methods and other techniques
- Applications of physics-informed neural networks in geosciences: From basic seismology to comprehensive environmental studies
- Ore-controlling structures of granite-related uranium deposits in South China: A review
- Shallow geological structure features in Balikpapan Bay East Kalimantan Province – Indonesia
- A review on the tectonic affinity of microcontinents and evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean in Northeastern Tibet
- Special Issue: Natural Resources and Environmental Risks: Towards a Sustainable Future - Part II
- Depopulation in the Visok micro-region: Toward demographic and economic revitalization
- Special Issue: Geospatial and Environmental Dynamics - Part II
- Advancing urban sustainability: Applying GIS technologies to assess SDG indicators – a case study of Podgorica (Montenegro)
- Spatiotemporal and trend analysis of common cancers in men in Central Serbia (1999–2021)
- Minerals for the green agenda, implications, stalemates, and alternatives
- Spatiotemporal water quality analysis of Vrana Lake, Croatia
- Functional transformation of settlements in coal exploitation zones: A case study of the municipality of Stanari in Republic of Srpska (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Hypertension in AP Vojvodina (Northern Serbia): A spatio-temporal analysis of patients at the Institute for Cardiovascular Diseases of Vojvodina
- Regional patterns in cause-specific mortality in Montenegro, 1991–2019
- Spatio-temporal analysis of flood events using GIS and remote sensing-based approach in the Ukrina River Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Flash flood susceptibility mapping using LiDAR-Derived DEM and machine learning algorithms: Ljuboviđa case study, Serbia
- Geocultural heritage as a basis for geotourism development: Banjska Monastery, Zvečan (Serbia)
- Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS and AHP techniques – A case study of the zone of influence of Kolubara Mining Basin
- Impact of the agri-geographical transformation of rural settlements on the geospatial dynamics of soil erosion intensity in municipalities of Central Serbia
- Where faith meets geomorphology: The cultural and religious significance of geodiversity explored through geospatial technologies
- Applications of local climate zone classification in European cities: A review of in situ and mobile monitoring methods in urban climate studies
- Complex multivariate water quality impact assessment on Krivaja River
- Ionization hotspots near waterfalls in Eastern Serbia’s Stara Planina Mountain

