Abstract
The purpose of this study was to explore the regulatory mechanism of Annexin A1 (ANXA1) in glioma cells in the inflammatory microenvironment induced by tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and its effects on glioma cell proliferation. CCK-8 analysis demonstrated that TNF-α stimulation promotes rapid growth in glioma cells. Changes in tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and ANXA1 expression in glioma cells stimulated with TNF-α were revealed through western blot analysis and immunofluorescence staining. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis revealed that ANXA1 interacts with TNFR1. Moreover, we found that ANXA1 promotes glioma cell growth by activating the p65 and Akt signalling pathways. Finally, immunohistochemistry analysis showed an obvious correlation between ANXA1 expression and Ki-67 in glioma tissues. In summary, our results indicate that the TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 axis regulates the proliferation of glioma cells and that ANXA1 plays a regulatory role in the inflammatory microenvironment.
1 Introduction
Glioma, the most common brain tumour, is known for its aggressive biological features and poor prognosis [1]. The five-year survival rate for patients with glioma remains low despite the availability of a variety of treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy [2,3]. The prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is even worse: the average survival is less than 12 months after diagnosis. Unfortunately, the molecular mechanism has not been fully elucidated [4], and much progress in treating GBM is needed. The latest evidence indicates that different mechanisms, including epigenetic mechanisms, membrane proteins, and the inflammatory microenvironment, contribute to the occurrence and development of GBM [5].
The tumour microenvironment is the local environment within an organ where tumour cells arise and reside [6]. This microenvironment includes the tumour cells themselves, surrounding fibroblasts, inflammatory cells and other cells, and the cell matrix, microvessels, and infiltrating biological molecules in the vicinity [7]. Tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), an important cytokine that mediates many inflammatory reactions, is produced by activated macrophages and tumour cells. TNF-α has been shown to promote the formation and progression of the tumour inflammatory microenvironment [8]. Some evidence indicates that TNF-α is a double-edged sword that may exert dual effects on drug resistance, recurrence, and metastasis of glioma [9]. Tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1; 55 kDa) is one of the TNF-α receptors. TNFR1 is a transmembrane protein, the extracellular domain of which binds to TNF-α [10].
Annexins comprise a family of Ca2+-regulated membrane-binding proteins. Annexin A1 (ANXA1), a 37-kDa annexin protein, is involved in various cellular processes, such as transduction, apoptosis, differentiation, and proliferation [11]. ANXA1, expressed from a gene located on chromosome 9q12–q21.2, is also known as chromobindin-9, lipocortin 1, p35, calpactin II, and PLA2 inhibitory protein [12]. ANXA1 has a conserved C-terminal core domain consisting of four highly helical parallel repeats, each approximately 70 amino acids long [13]. Recent evidence shows that ANXA1 participates in the initiation and development of various cancers [14,15]. Excessive expression of ANXA1 in nonsmall-cell lung cancer promotes its carcinogenesis [16], but it is downregulated in breast cancer [17,18]. ANXA1 expression is low in normal brain tissues and largely distributed in ependymal cells and subependymal astrocytes [19]. However, ANXA1 expression is upregulated in malignant glioma tissues; it is secreted by necrotic glioma cells, and abnormal levels of ANXA1 in the tumour microenvironment can activate formyl peptide receptor 1 to enhance the proliferation and invasion of glioma [20]. FoxM1, a well-studied transcription factor, increases ANXA1 expression and promotes the proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis of glioma [21].
There have been many studies on the relationship between any TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 combination: absence of TNFR1 in intestinal inflammation enhances ANXA1 activity [22]; upregulation of ANXA1 inhibits maturation of human dendritic cells induced by TNF-α [23]; in preeclampsia, ANXA1 correlates positively with TNFR1 [24]. However, studies on the TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 axis with respect to tumours are rare.
In this study, we sought to assess changes in ANXA1 expression in the inflammatory microenvironment and the clinical significance of these changes.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Human specimens
In total, 90 specimens were collected from patients with newly diagnosed glioma at the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University from 2009 to 2015 with approval by the Human Research Council. The collection of specimens was based on the following inclusion criteria: (1) no radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or hormone treatment before surgery; (2) complete clinicopathological data available; and (3) postoperative pathological confirmation of a glioma diagnosis. All 90 patients agreed to participate in the study.
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies, and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the authors’ institutional review board or equivalent committee.
2.2 Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
We used the general two-step IHC method. Briefly, after specimens were dewaxed, rehydrated, and heated to retrieve antigens, the slices were treated with 3% H2O2 to block endogenous peroxidase activity. The slices were then incubated overnight with primary antibodies at 4°C, with nonimmune serum serving as a negative control. The next day, the slices were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and incubated with secondary antibodies before they were stained with 3,3-diaminobenzidine and haematoxylin, sealed with neutral gum, and dehydrated prior to analysis.
2.3 Evaluation of IHC staining
Two independent pathologists blinded to the patient data evaluated the immunostained specimens. The staining intensity was graded in comparison with the control as follows: 0 (no staining); 1 (low staining); 2 (moderate staining), and 3 (high staining). The tumour cell ratio score was as follows: 0 (<1%); 1 (1–10%); 2 (10–50%); 3 (50–75%); and 4 (>75%). The scores were summed and designated as follows: 0–3, low expression and 4–7, high expression.
2.4 Antibodies
The following primary antibodies were used in this study: anti-TNFR1 (1:2,000, rabbit, Abcam), anti-ANXA1 (1:1,000, goat, Santa Cruz), anti-Ki-67 (1:50, mouse, Abcam), anti-P65 (1:2,000, rabbit, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-p-P65 (1:1,000, rabbit, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-Akt (1:2,000, rabbit, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-p-Akt (S473) (1:1,000, rabbit, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-p-Akt (T308) (1:1,000, rabbit, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-GAPDH (1:5,000, mouse, Abcam), anti-α-tubulin = (1:5,000, mouse, Abcam), anti-Lamin B (1:2,000, mouse, Santa Cruz), anti-HA (1:5,000, mouse, Cell Signaling Technology), and anti-Flag (1:5,000, rabbit, Cell Signaling Technology).
2.5 Western blotting (WB)
We used a Bio–Rad protein assay to determine protein concentrations in extracts obtained from cells and tissues. Proteins were then mixed with 2× loading buffer before they were loaded onto gels, separated by sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. The membranes were incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C after blocking. The next morning, the membranes were washed with PBS and incubated with secondary antibodies at room temperature for 2 h. Finally, protein bands were developed with an electrochemiluminescence detection system after the membranes were washed a final time.
2.6 Cell culture
We mainly used U251 MG cells and HEK293T cells from the cell library of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. U251 MG cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS). HEK293T cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium 1640 (RPMI 1640) with 10% FBS. The cells were placed in a humidified, CO2 incubator maintained at 37°C, and the medium was changed every 1–3 days due to growth conditions or research needs.
2.7 Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Cells were collected with medium-strength lysis buffer and processed to produce lysates; the samples were then precleaned with Protein A/G PLUS-Agarose. The samples were then centrifuged at 800×g for 5 min to collect the supernatant, with 50 μL was used as input. The remaining cell lysate was then divided equally into two portions: one was mixed with IgG as a control; the other (IP group) was treated with appropriate primary antibodies (assume X). The samples were placed on a rotator at the proper speed and incubated at 4°C overnight. The next day, the samples were mixed with Protein A/G PLUS-Agarose, rotated for 4 h at 4°C, and centrifuged at 1,000×g for 8 min to collect the agarose. The samples were heated at 100°C for 10 min to elute the bound proteins, which were then mixed with 2× loading buffer. The samples were centrifuged at 1,000×g for 15 min, and the supernatants were loaded onto gels for electrophoresis.
2.8 Immunofluorescence staining (IFC)
Cells were plated on small discs in a 24-well plate. The next day, when the cells grew to an appropriate confluence, we discarded the medium, washed the coverslips with PBS, and fixed the cells with 4% paraformaldehyde. The cells were permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 before they were blocked in 1% bovine serum albumin for 20 min and incubated with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight. After washing with PBS, the coverslips were incubated with secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature and with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole for 1 h to stain nuclei. Finally, the coverslips were placed on slides face down and were viewed under an Olympus immunofluorescence microscope.
2.9 Separation of nuclear and cytoplasmic/cell membrane protein extracts
We used a commercial kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, China) to isolate cell proteins. Briefly, when cells reached confluence, we washed them with PBS before treating them with hypotonic lysate to disrupt the cell membrane. The lysates were centrifuged at 1.4 × 104×g for 2 min; the precipitate comprised nuclei, whereas the supernatant contained the cytoplasmic proteins and cell membrane. The precipitate was treated with hypertonic lysate and centrifuged, and the supernatant was used as the nuclear extract. An appropriate amount of 2* loading was added, mixed well, and stored at −80°C.
2.10 Transfection
Overexpression plasmids for ANXA1 and TNFR1 were purchased from the Public Protein/Plasmid Library and used to transfect HEK293T cells. ANXA1 shRNA sequences were synthesized by the Shanghai GeneChem Company as follows: 5′-AUUCUAUCAGAAGAUGUAU-3′(ShANXA1-1), 5′-CUUGUAUGAAGCAGGAGAA-3′(ShANXA1-2), 5′-AGCGCAAUUUGAUGCUGAU-3′(ShANXA1-3), and 5′-AACCAUCAUUGACAUUCUA-3′(ShANXA1-4). The control shRNA sequence was 5′-CCCCUUUUAAAAGGGGCCC-3′(Sh-NC). They were used to transfect U251 MG cells.
Cells were cultured in antibiotic-free medium, and plasmid was added at 80% confluence. The medium was changed after 6 h, and protein was extracted or the cells were stimulated after 48 h of culture.
2.11 Cell proliferation assays
U251 MG cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 1 × 104 per well in a volume of 100 μL. The orange formazan dye produced by the biological reduction of CCK-8 reagent (Cell Counting Kit-8, Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) by intracellular dehydrogenase can be dissolved in tissue culture medium, and the amount of formazan produced is proportional to the number of living cells. Two hours after the CCK-8 reagent was added to wells, we measured absorbance at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Immuno Mini NJ-2300).
2.12 Statistical analysis
We used the Spearman correlation coefficient to evaluate the relationship between ANXA1 and Ki-67 by IHC. The chi square (χ 2) test was used to detect the significance of ANXA1 expression with regard to different clinicopathological variables among the 90 clinical samples. Kaplan–Meier (K–M) curves and the log-rank test were used to analyse the influence of ANXA1 on survival. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was applied to calculate the risk of various clinical factors. The model defines survival outcome and survival time as dependent variables and can simultaneously analyse the impact of multiple factors on survival. The significance of the differences among the groups was analysed by one-way analysis of variance. All experiments were conducted independently at least three times. The SPSS 17.0 software package was used to process the data, and p values < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
2.13 Datasets
A dataset (mRNAseq_693) from the CGGA (Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas) database (http://www.cgga.org.cn/index.jsp) was used to analyse the correlation between ANXA1 and TNFR1, ANXA1 and Ki-67, and ANXA1 and survival.
3 Results
3.1 Proliferation changes in glioma cells stimulated with TNF-α and expression changes in TNFR1 and ANXA1 in glioma cells stimulated with TNF-α
To explore the effect of the inflammatory environment on cell proliferation, we treated U251 MG cells with TNF-α (1, 5, 10, 20, and 50 ng/mL) and detected absorbance by CCK-8 analysis at different time points. The fastest proliferation was detected in the 10 ng/mL group (Figure 1a). Next, to determine changes in TNFR1 and ANXA1 expression, we treated U251 MG cells with 10 ng/mL TNF-α and collected them at different time points (0, 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24 h). WB results showed that TNFR1 expression was upregulated at 2, 4, and 6 h. However, ANXA1 expression was downregulated at 0, 2, 4, and 6 h (Figure 1b). As the time of changes in expression of the two proteins coincided, we speculate a relationship between them.

CCK-8 and WB results of glioma cells treated with TNF-α. (a) CCK-8 analysis showed that different concentrations of TNF-α (1, 5, 10, 20, 50 ng/mL) stimulated U251MG cell proliferation within 24 h, and 10 ng/mL TNF-α stimulation achieved the best effect. Cells treated with an equal volume of culture medium served as the control. n = 3, *p < 0.05. (b) TNFR1 and ANXA1 expression at different time points in U251 MG cells stimulated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α. Bar charts show TNFR1 and ANXA1 expression compared to that of GAPDH. *, ^p < 0.05, compared to the CON group.
3.2 ANXA1 translocates to the nucleus in U251 MG cells stimulated with TNF-α
It has been reported that ANXA1 can localize to the cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell membrane [25]. As its location is not fixed, ANXA1 may have complex functions [26]. Based on this property, we explored whether ANXA1 translocates to the nucleus in glioma cells treated with TNF-α. Based on WB results, ANXA1 levels in the nuclear fraction was obviously increased at 2, 4, and 6 h after treatment, whereas it was dramatically reduced in the cytoplasm/cell membrane fraction at these time points (Figure 2a). We next validated the results by IFC. There was more ANXA1 present in the nucleus at 2, 4, and 6 h after treatment, and levels in the cytoplasm/cell membrane fraction returned to baseline at 24 h (Figure 2b and c).

Translocation of ANXA1 in U251 MG cells stimulated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α. (a) WB results of ANXA1 expression in nuclear and cytoplasmic/cell membrane fractions at different time points in U251 MG cells stimulated with TNF-α. White columns show ANXA1 in the cytoplasmic/cell membrane fraction compared to α-tubulin; black columns show ANXA1 in the nuclear fraction compared to Lamin B. *, ^p < 0.05, compared to the CON group. (b) IFC of ANXA1 at different time points (SP × 400). (c) Quantitative charts of ANXA1 in the nuclei of U251 MG cells stimulated with TNF-α. *p < 0.05, compared to the CON group.
3.3 Interaction between ANXA1 and TNFR1
As TNFR1 is a receptor of TNF-α, we explored whether translocation of ANXA1 is related to TNFR1. We used U251 MG cells to perform endogenous co-IP and discovered a direct interaction between TNFR1 and ANXA1 (Figure 3a). Next, eukaryotic expression plasmids for Flag-labelled ANXA1 and HA-labelled TNFR1 were constructed. HEK293T cells were transfected with the ANXA1-Flag plasmid and/or the TNFR1-HA plasmid. Cell proteins were collected and precipitated with an anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody, and expression of ANXA1-Flag or TNFR1-HA was detected by WB. The images shown in Figure 3b clearly reveal an interaction between TNFR1 and ANXA1. For verification, we used samples from the CGGA database to determine the relationship between ANXA1 and TNFR1 (Figure 3c), and a positive correlation between ANXA1 and TNFR1 gene expression was observed in both primary and recurrent glioma samples.

Relationship between ANXA1 and TNFR1. (a) Endogenous co-IP of TNFR1 and ANXA1 in U251 MG cells. The left picture shows the addition of ANXA1 antibody to the cell lysate, and the immunoblotting of the precipitated protein shows TNFR1 positivity. The right picture shows the addition of TNFR1 antibody to the cell lysate, and the immunoblotting of the precipitated protein shows ANXA1 positivity. (b) Exogenous co-IP of TNFR1 and ANXA1 by transfection of TNFR1-HA and/or ANXA1-Flag overexpression plasmids into HEK293T cells. The input group (left) is the WB of normal cell lysate after transfection of the plasmid. The middle figure shows that the Flag antibody can pull HA. The figure on the right shows that the HA antibody can pull Flag. (c) Correlation between ANXA1 and TNFR1 at the mRNA level was analysed using samples from the CGGA database.
3.4 Signalling pathways involved in the effects of TNF-α stimulation on glioma cell proliferation
We explored changes in P65 and Akt, key molecules in two classic carcinogenic pathways, expression and activation upon TNF-α stimulation by WB analysis. NF-κB is a dimeric protein formed by P65 and P50 that has an obvious function of inhibiting apoptosis, and phosphorylation of P65 is evidence of NF-κB activation. Akt, also known as protein kinase B, is an important downstream molecule of PI3K that plays a very important role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, survival, and glucose metabolism and has two important phosphorylation sites: Thr308 and Ser473. Levels of p-P65 were increased at 6 h; those of p-Akt (S473) were increased at 2 h, 4 h, and 6 h. However, no changes were observed in p-Akt (T308) at any time point (Figure 4a and b). This result indicates that TNF-α stimulation may activate P65 and Akt (S473 site).

Changes in expression and activation of proteins in the P65 and Akt signalling pathways in U251 MG cells treated with TNF-α. (a) WB results of the P65 and Akt signalling pathways at different time points. (b) Bar charts show p-P65 compared to total P65 and p-Akt (S473) and p-Akt (T308) compared to total Akt. *, ^p < 0.05, compared to the CON group.
3.5 Effects of silencing ANXA1 on signalling pathways and glioma cell proliferation
As the P65 and Akt signalling pathways contribute to the proliferation of glioma cells stimulated with TNF-α, we sought to determine whether these signalling pathways are regulated by ANXA1. The knockdown effects of ANXA1 shRNAs are shown in Figure 5a, with ShANXA1-4 resulting in the highest knockdown efficiency. Then, we processed U251 MG cells with the methods illustrated in Figure 5b. Cells were stimulated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 6 h, and by comparing the third column (TNF-α + Sh-NC) with the first column (Sh-NC), TNFR1 expression was upregulated after TNF-α treatment but not affected by ShANXA1-4 when comparing the second column (ShANXA1-4) with the first column (Sh-NC). We speculate that ANXA1 is located downstream of TNFR1. Moreover, expression levels of ANXA1, p-P65, and p-Akt (S473) were downregulated in cells transfected with ShANXA1-4 (the second column compared with the first column), and the increased levels of p-P65 and p-Akt (S473) after stimulation with TNF-α were reversed in cells transfected with ShANXA1-4 (the fourth column compared with the second column). Hence, the inhibitory effect of knocking down ANXA1 on the two molecules was rescued by stimulation of TNF-α, further verifying that the two signalling pathways might be regulated by ANXA1 and ANXA1 is downstream of TNFR1. CCK-8 analysis showed U251 MG cell proliferation was downregulated by ShANXA1-4 (cube) but rescued after stimulation with TNF-α (inverted triangle) (Figure 5c).

Effects of silencing ANXA1 on expression and activity of proteins in the P65 and Akt signalling pathways and on U251 MG cell proliferation. (a) Knockdown efficiency of the four shRNAs targeting ANXA1 in U251 MG cells. Bar chart shows ANXA1 expression compared to that of GAPDH. *p < 0.05, compared to the Sh-NC group. (b) Changes in TNFR1, ANXA1, P65, and p-Akt (S473) expression levels with different processes in U251 MG cells. Bar chart shows TNFR1 and ANXA1 compared to GAPDH, p-P65 compared to total P65, and p-Akt (S473) compared to total Akt. *p < 0.05. (c) Line chart showing CCK-8 analysis results. n = 3, *p < 0.05.
3.6 Upregulated expression of ANXA1 with increasing glioma grade and prognostic significance of ANXA1 in glioma patients
As the results above suggest that the effects of TNF-α on glioma cell proliferation are mediated by ANXA1, we explored expression of ANXA1 in 90 clinical specimens by IHC, the clinical features of which are shown in Table 1. From the results of the χ 2 test, ANXA1 expression differed in glioma specimens with different WHO grades. IHC results for ANXA1 and Ki-67 are depicted in Figure 6a. The scattering diagram in Figure 6b shows that expression of ANXA1 positively corresponds with that of Ki-67. We then evaluated the clinical significance of ANXA1. K–M curves and log-rank tests suggested that higher ANXA1 expression indicates poorer survival in glioma (Figure 6c). According to the Cox regression results shown in Table 2, among the many clinical factors that affect prognosis, only WHO grade and ANXA1 expression had a p value of less than 0.05. These findings indicate that in addition to WHO grade, ANXA1 expression can be used as an independent prognostic indicator of survival in glioma. Using the CGGA database, the correlation between ANXA1 and Ki-67 was analysed, and univariate survival analysis of ANXA1 at the mRNA level was performed (Figure 6d and e), with the same results as reported above.
Expression of ANXA1 and clinical pathology characteristics in 90 cases of glioma specimens
| Variables | Total | ANXA1 expression | χ 2 value | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Age (years) | |||||
| <40 | 19 | 10 | 9 | 0.032 | 0.858 |
| ≥40 | 71 | 39 | 32 | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 51 | 26 | 25 | 0.569 | 0.450 |
| Male | 39 | 23 | 16 | ||
| Tumour location | |||||
| Frontal | 20 | 11 | 9 | 0.146 | 0.986 |
| Parietal | 12 | 7 | 5 | ||
| Occipital | 18 | 10 | 8 | ||
| Temporal | 40 | 21 | 19 | ||
| Tumour size (cm) | |||||
| <4 | 26 | 15 | 11 | 0.156 | 0.693 |
| ≥4 | 64 | 34 | 30 | ||
| WHO grade | |||||
| II | 33 | 31 | 2 | 32.947 | 0.000* |
| III | 31 | 9 | 22 | ||
| IV | 26 | 9 | 17 | ||
| Extent of resection | |||||
| Biopsy | 34 | 20 | 14 | 1.459 | 0.482 |
| Total resection | 40 | 19 | 21 | ||
| Subtotal resection | 16 | 10 | 6 | ||
Pearson’s χ 2 test for statistical analysis.
*p < 0.05.
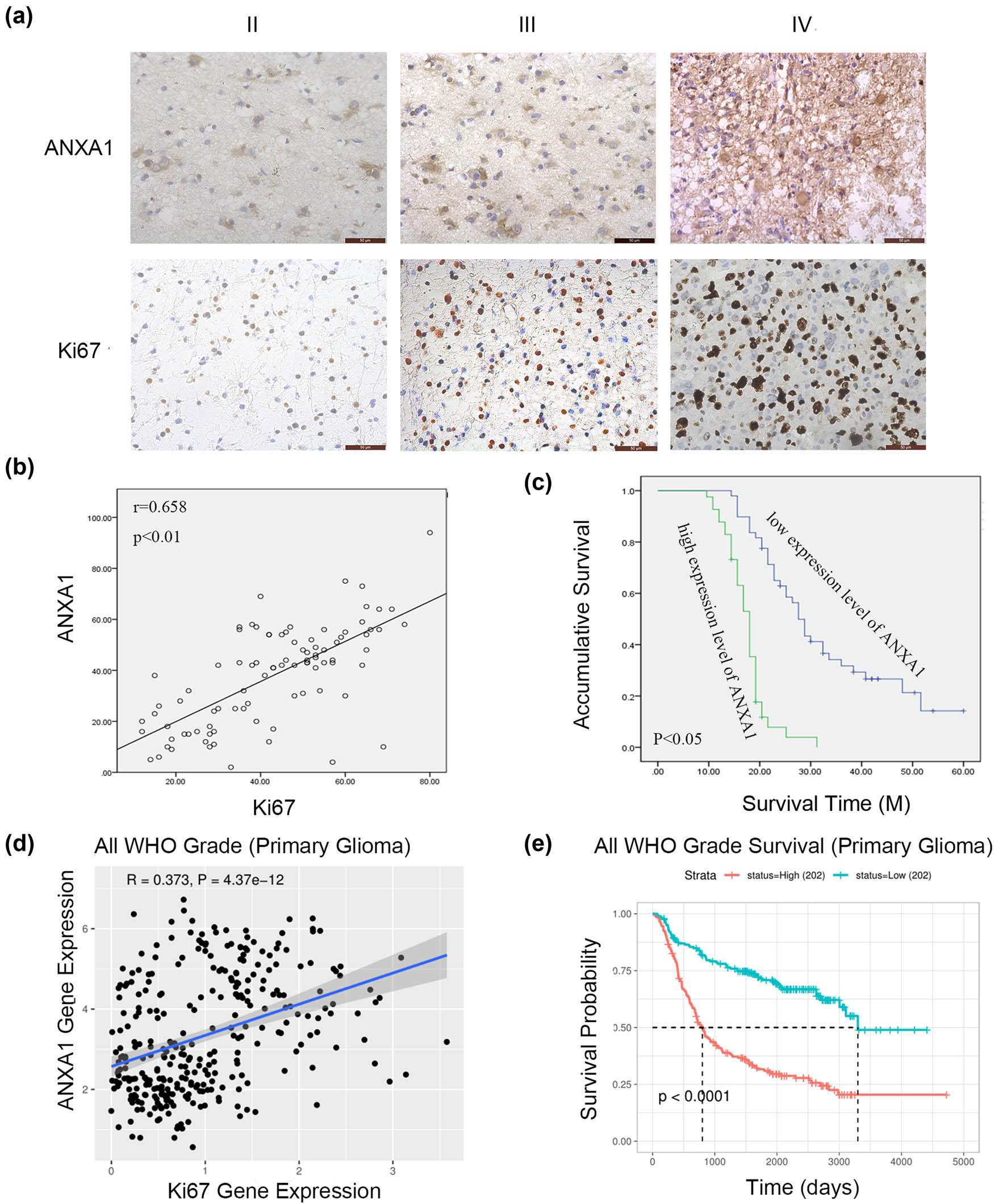
IHC results of ANXA1 expression and univariate analysis of ANXA1 in glioma. (a) Paraffin-embedded glioma tissue sections were stained with anti-ANXA1 antibodies and anti-Ki-67 antibodies followed by counterstaining with haematoxylin (SP × 400). (b) The relationship between ANXA1 and Ki-67 expression by IHC. (c) K–M analysis of ANXA1 in 90 glioma patients. (d) The relationship between ANXA1 and Ki-67 expression based on samples from the CGGA database. (e) K–M analysis of ANXA1 based on samples from the CGGA database.
Contribution of various potential prognostic factors to survival through Cox regression analysis of 90 glioma specimens
| Characteristics | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.157 | 0.588–2.279 | 0.673 |
| Gender | 1.379 | 0.794–2.397 | 0.254 |
| Tumour location | 0.883 | 0.670–1.165 | 0.380 |
| Tumour size | 1.496 | 0.771–2.903 | 0.233 |
| WHO grade | 5.377 | 3.325–8.694 | 0.000* |
| Extent of resection | 0.947 | 0.719–1.247 | 0.696 |
| ANXA1 expression | 2.670 | 1.503–4.743 | 0.001* |
CI: confidence interval.
*p < 0.05.
4 Discussion
Rapid and invasive tumour growth is associated with the low survival rate of glioma [27], and the tumour inflammatory microenvironment plays an indispensable role in this progression [5]. TNF-α is a vital proinflammatory mediator that plays a central role in the cytokine network [28,29]. To determine the optimal stimulation concentration and time of TNF-α, we evaluated the concentration and time gradient. As shown in Figure 1a, a low concentration of TNF-α promoted cell proliferation; in contrast, a high concentration of TNF-α made cells proliferate slowly and even may led to apoptosis. When the stimulating concentration of TNF-α was 10 ng/mL, cell growth was optimal and increased over time. Therefore, we chose 10 ng/mL TNF-α for experiments. TNFR1, a receptor of TNF-α, recruits a series of related proteins via the TNF receptor-associated death domain that interacts with its cytoplasmic domain to regulate signal transduction and cellular biological functions [30]. ANXA1 has been studied in many tumours in the past 20 years, with a variety of biological functions. ANXA1 is specifically expressed in tumours, which makes it an important biological indicator for early tumour diagnosis and prognosis.
Our experiments identified that expression of TNFR1 and ANXA1 is altered in glioma cells stimulated with TNF-α (Figure 1b). Coincidentally, the timing of the changes coincided. We hypothesize a connection between the two. We then explored the regulatory mechanism of ANXA1 and its role in glioma cell proliferation. It has been demonstrated that nuclear translocation of ANXA1 is involved in neuronal apoptosis after ischaemic stroke [31] and induces retinal ganglion cell apoptosis after ischaemia–reperfusion injury through the p65/IL-1beta pathway [32]. Our research showed that ANXA1 is translocated to the nucleus in glioma cells exposed to TNF-α (Figure 2). Nevertheless, the exact regulatory mechanism responsible remains unclear. Next, we performed co-IP in U251MG cells (Figure 3a, endogenous) and HEK293T cells (Figure 3b, exogenous). HEK293T cells rarely express the endogenous receptors required for extracellular ligands and are relatively easy to transfect; it is a very commonly used cell line for expressing and studying exogenous genes. Based on the results shown in Figure 3, we hypothesized that translocation of ANXA1 to the nucleus is related to its interaction with TNFR1.
TNF-α is involved in activation of the NF-kB and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways [33,34], and ANXA1 regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells via PI3K/AKT signalling [35]. We investigated P56 and Akt, the key molecules of the two pathways. The data in Figure 4 show that the two pathways are involved in the proliferation of glioma cells stimulated with TNF-α and that these two signalling pathways might be regulated by ANXA1 (Figure 5b). In addition, knockdown of ANXA1 slowed glioma cell proliferation (Figure 5c). All these results indicate that ANXA1 contributes to glioma cell proliferation upon TNF-α stimulation. In other words, TNF-α promotes cell proliferation via the TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 axis. Finally, we detected ANXA1 expression in primary clinical specimens and samples from the CGGA database and found that ANXA1 correlated positively with Ki-67 and was highly expressed in high-grade gliomas. According to data analysis, ANXA1 is a potential prognostic factor of gliomas, consistent with the literature. ANXA1 is useful as a prognostic biomarker in lower grade glioma patients with MGMT promoter methylation [36] and a prognostic indicator and an immunotherapy marker for the tumour microenvironment in glioma [37].
Although the main treatment for glioma is maximal safe resection with radiotherapy and chemotherapy [38,39], there have been remarkable advances in cancer immunotherapy since 2015, and multiple cancer types now benefit from these immunotherapies. However, as glioma immunotherapy still faces challenges [40], it is of great significance to discover new glioma biomarkers and study their internal mechanisms. Our research will help in the exploration of new immunotherapy mechanisms and lay the foundation for molecular targeted therapy of glioma. In general, the effect of ANXA1 on tumour cells seems to be diverse and sometimes even opposing due to mutations in the gene, hypermethylation of the promoter and subsequent loss of transcription, posttranslational modification of the protein, and defects in protein storage, among others [14]. When targeting ANXA1 for treatment or research, it is necessary to have a global view. Furthermore, it is necessary to consider its mechanism from multiple angles when conducting research on an organ, tissue, or cell.
5 Conclusion
In summary, our study elaborates on the possible mechanism of ANXA1 in the inflammatory microenvironment of glioma cells upon TNF-α stimulation and the role of ANXA1 in glioma cell proliferation. In addition, we analysed the clinical significance of ANXA1 and found its expression to be an independent risk factor for glioma.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81572491).
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analysed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Lah TT, Novak M, Breznik B. Brain malignancies: glioblastoma and brain metastases. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;60:262–73.10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.10.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Li Z, Ye L, Wang L, Quan R, Zhou Y, Li X. Identification of miRNA signatures in serum exosomes as a potential biomarker after radiotherapy treatment in glioma patients. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020;44:151436.10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2019.151436Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Zur I, Tzuk-Shina T, Guriel M, Eran A, Kaidar-Person O. Survival impact of the time gap between surgery and chemo-radiotherapy in Glioblastoma patients. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9595.10.1038/s41598-020-66608-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Han S, Liu Y, Cai SJ, Qian M, Ding J, Larion M, et al. IDH mutation in glioma: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(11):1580–89.10.1038/s41416-020-0814-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] De Boeck A, Ahn BY, D’Mello C, Lun X, Menon SV, Alshehri MM, et al. Glioma-derived IL-33 orchestrates an inflammatory brain tumor microenvironment that accelerates glioma progression. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4997.10.1038/s41467-020-18569-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Pitt JM, Marabelle A, Eggermont A, Soria JC, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(8):1482–92.10.1093/annonc/mdw168Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Lei X, Lei Y, Li JK, Du WX, Li RG, Yang J, et al. Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: biological functions and roles in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2020;470:126–33.10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Cruceriu D, Baldasici O, Balacescu O, Berindan-Neagoe I. The dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in breast cancer: molecular insights and therapeutic approaches. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020;43(1):1–18.10.1007/s13402-019-00489-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Ryu J, Ku BM, Lee YK, Jeong JY, Kang S, Choi J, et al. Resveratrol reduces TNF-alpha-induced U373MG human glioma cell invasion through regulating NF-kappaB activation and uPA/uPAR expression. Anticancer Res. 2011;31(12):4223–30.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Fu H, Wu H, Zhang X, Huang J, He X, Chen L, et al. Pre-clinical study of a TNFR1-targeted (18)F probe for PET imaging of breast cancer. Amino Acids. 2018;50(3-4):409–19.10.1007/s00726-017-2526-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Ganesan T, Sinniah A, Ibrahim ZA, Chik Z, Alshawsh MA. Annexin A1: a bane or a boon in cancer? a systematic review. Molecules. 2020;25(16):3700.10.3390/molecules25163700Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Hebeda CB, Machado ID, Reif-Silva I, Moreli JB, Oliani SM, Nadkarni S, et al. Endogenous annexin A1 (AnxA1) modulates early-phase gestation and offspring sex-ratio skewing. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6591–603.10.1002/jcp.26258Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Huang P, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Zhang P. Interaction between ANXA1 and GATA-3 in Immunosuppression of CD4( +) T Cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:1701059.10.1155/2016/1701059Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Fu Z, Zhang S, Wang B, Huang W, Zheng L, Cheng A. Annexin A1: a double-edged sword as novel cancer biomarker. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;504:36–42.10.1016/j.cca.2020.01.022Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Takaoka RTC, Sertorio ND, Magalini LPJ, Dos Santos LM, Souza HR, Iyomasa-Pilon MM, et al. Expression profiles of Annexin A1, formylated peptide receptors and cyclooxigenase-2 in gastroesophageal inflammations and neoplasias. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214(2):181–6.10.1016/j.prp.2017.12.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Fang Y, Guan X, Cai T, Long J, Wang H, Xie X, et al. Knockdown of ANXA1 suppresses the biological behavior of human NSCLC cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(5):3858–66.10.3892/mmr.2016.5022Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Gibbs LD, Vishwanatha JK. Prognostic impact of AnxA1 and AnxA2 gene expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2018;9(2):2697–704.10.18632/oncotarget.23627Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Guo C, Liu S, Sun MZ. Potential role of Anxa1 in cancer. Future Oncol. 2013;9(11):1773–93.10.2217/fon.13.114Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Schittenhelm J, Trautmann K, Tabatabai G, Hermann C, Meyermann R, Beschorner R. Comparative analysis of annexin-1 in neuroepithelial tumors shows altered expression with the grade of malignancy but is not associated with survival. Mod Pathol. 2009;22(12):1600–11.10.1038/modpathol.2009.132Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Yang Y, Liu Y, Yao X, Ping Y, Jiang T, Liu Q, et al. Annexin 1 released by necrotic human glioblastoma cells stimulates tumor cell growth through the formyl peptide receptor 1. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(3):1504–12.10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.05.059Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Cheng SX, Tu Y, Zhang S. FoxM1 promotes glioma cells progression by upregulating Anxa1 expression. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72376.10.1371/journal.pone.0072376Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Sena AA, Pedrotti LP, Barrios BE, Cejas H, Balderramo D, Diller A, et al. Lack of TNFRI signaling enhances annexin A1 biological activity in intestinal inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015;98(3):422–31.10.1016/j.bcp.2015.09.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Min Y, Han D, Fu Z, Wang H, Liu L, Tian Y. alpha-MSH inhibits TNF-alpha-induced maturation of human dendritic cells in vitro through the up-regulation of ANXA1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(1):61–8.10.1093/abbs/gmq109Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Perucci LO, Carneiro FS, Ferreira CN, Sugimoto MA, Soriani FM, Martins GG, et al. Annexin A1 Is Increased in the plasma of preeclamptic women. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138475.10.1371/journal.pone.0138475Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Gao Y, Chen Y, Xu D, Wang J, Yu G. Differential expression of ANXA1 in benign human gastrointestinal tissues and cancers. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:520.10.1186/1471-2407-14-520Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Solito E, Christian HC, Festa M, Mulla A, Tierney T, Flower RJ, et al. Post-translational modification plays an essential role in the translocation of annexin A1 from the cytoplasm to the cell surface. FASEB J. 2006;20(9):1498–500.10.1096/fj.05-5319fjeSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Goranci-Buzhala G, Mariappan A, Gabriel E, Ramani A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Buccarelli M, et al. Rapid and efficient invasion assay of glioblastoma in human brain organoids. Cell Rep. 2020;31(10):107738.10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107738Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Karki R, Sharma BR, Tuladhar S, Williams EP, Zalduondo L, Samir P, et al. Synergism of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma triggers inflammatory cell death, tissue damage, and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infection and cytokine shock syndromes. Cell. 2021;184(1):149–68 e17.10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Oshima H, Ishikawa T, Yoshida GJ, Naoi K, Maeda Y, Naka K, et al. TNF-alpha/TNFR1 signaling promotes gastric tumorigenesis through induction of Noxo1 and Gna14 in tumor cells. Oncogene. 2014;33(29):3820–9.10.1038/onc.2013.356Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Romagny S, Bouaouiche S, Lucchi G, Ducoroy P, Bertoldo JB, Terenzi H, et al. S-Nitrosylation of cIAP1 switches cancer cell fate from TNFalpha/TNFR1-mediated cell survival to cell death. Cancer Res. 2018;78(8):1948–57.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2078Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Xia Q, Li X, Zhou H, Zheng L, Shi J. S100A11 protects against neuronal cell apoptosis induced by cerebral ischemia via inhibiting the nuclear translocation of annexin A1. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(6):657.10.1038/s41419-018-0686-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Zhao Y, Li X, Gong J, Li L, Chen L, Zheng L, et al. Annexin A1 nuclear translocation induces retinal ganglion cell apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury through the p65/IL-1beta pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(6):1350–58.10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.04.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Liu S, Cao C, Zhang Y, Liu G, Ren W, Ye Y, et al. PI3K/Akt inhibitor partly decreases TNF-alpha-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):425.10.1186/s13018-019-1394-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Zusso M, Lunardi V, Franceschini D, Pagetta A, Lo R, Stifani S, et al. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):148.10.1186/s12974-019-1538-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Wei L, Li L, Liu L, Yu R, Li X, Luo Z. Knockdown of Annexin-A1 inhibits growth, migration and invasion of glioma cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. ASN Neuro. 2021;13:17590914211001218.10.1177/17590914211001218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Wang W, Li J, Lin F, Guo J, Zhao J. Expression and prognostic value of mRNAs in lower grade glioma with MGMT promoter methylated. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;75:45–51.10.1016/j.jocn.2020.03.037Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Lin Z, Wen M, Yu E, Lin X, Wang H, Chen J, et al. ANXA1 as a prognostic and immune microenvironmental marker for gliomas based on transcriptomic analysis and experimental validation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:659080.10.3389/fcell.2021.659080Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Weller M, van den Bent M, Preusser M, Le Rhun E, Tonn JC, Minniti G, et al. EANO guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diffuse gliomas of adulthood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(3):170–86.10.1038/s41571-020-00447-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Mair MJ, Geurts M, van den Bent MJ, Berghoff AS. A basic review on systemic treatment options in WHO grade II-III gliomas. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021;92:102124.10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102124Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Chuntova P, Chow F, Watchmaker PB, Galvez M, Heimberger AB, Newell EW, et al. Unique challenges for glioblastoma immunotherapy-discussions across neuro-oncology and non-neuro-oncology experts in cancer immunology. Meet Rep 2019 SNO Immuno-Oncol Think Tank Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(3):356–75.10.1093/neuonc/noaa277Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 Xiaotian Zhu et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Effects of direct oral anticoagulants dabigatran and rivaroxaban on the blood coagulation function in rabbits
- The mother of all battles: Viruses vs humans. Can humans avoid extinction in 50–100 years?
- Knockdown of G1P3 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the cytotoxicity of dexamethasone in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- LINC00665 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating mRNA via the m6A enzyme
- Association study of CLDN14 variations in patients with kidney stones
- Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook
- Regulation of miR-30b in cancer development, apoptosis, and drug resistance
- Informatic analysis of the pulmonary microecology in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis at three different stages
- Swimming attenuates tumor growth in CT-26 tumor-bearing mice and suppresses angiogenesis by mediating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway
- Characterization of intestinal microbiota and serum metabolites in patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy
- Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis
- Application of the FLP/LoxP-FRT recombination system to switch the eGFP expression in a model prokaryote
- Biomedical evaluation of antioxidant properties of lamb meat enriched with iodine and selenium
- Intravenous infusion of the exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury via suppressing the NF-κB pathway
- Effect of dietary pattern on pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its clinical significance
- Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation
- Effect of the genetic mutant G71R in uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 on the conjugation of bilirubin
- Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis
- Nutrition intervention in the management of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients
- circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis
- Bmi-1 directly upregulates glucose transporter 1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma
- Lacunar infarction aggravates the cognitive deficit in the elderly with white matter lesion
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A improved retinopathy via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats
- Comparison of axon extension: PTFE versus PLA formed by a 3D printer
- Elevated IL-35 level and iTr35 subset increase the bacterial burden and lung lesions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice
- A case report of CAT gene and HNF1β gene variations in a patient with early-onset diabetes
- Study on the mechanism of inhibiting patulin production by fengycin
- SOX4 promotes high-glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis of retinal endothelial cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Relationship between blood clots and COVID-19 vaccines: A literature review
- Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- Bioinformatics network analyses of growth differentiation factor 11
- NR4A1 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells: Involvement of TGF-β–Smad2/3/4–ZEB signaling
- Expression of Zeb1 in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell
- Study on the genetic damage caused by cadmium sulfide quantum dots in human lymphocytes
- Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NKX2.5 and congenital heart disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis
- Assessment of the anesthetic effect of modified pentothal sodium solution on Sprague-Dawley rats
- Genetic susceptibility to high myopia in Han Chinese population
- Potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in preeclampsia progression
- Silencing circular RNA-friend leukemia virus integration 1 restrained malignancy of CC cells and oxaliplatin resistance by disturbing dyskeratosis congenita 1
- Endostar plus pembrolizumab combined with a platinum-based dual chemotherapy regime for advanced pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as a first-line treatment: A case report
- The significance of PAK4 in signaling and clinicopathology: A review
- Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies
- Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Effect of cell receptors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Current insights
- MT-12 inhibits the proliferation of bladder cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagy through mitochondrial dysfunction
- Study of hsa_circRNA_000121 and hsa_circRNA_004183 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
- BuyangHuanwu Decoction attenuates cerebral vasospasm caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via PI3K/AKT/eNOS axis
- Effects of the interaction of Notch and TLR4 pathways on inflammation and heart function in septic heart
- Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis
- A rare presentation of type II Abernethy malformation and nephrotic syndrome: Case report and review
- Rapid death due to pulmonary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma in several weeks: A case report
- Hepatoprotective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in non-cancerous hepatic tissues following transcatheter arterial embolization
- Correlation between peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulations and primary systemic lupus erythematosus
- A novel SLC8A1-ALK fusion in lung adenocarcinoma confers sensitivity to alectinib: A case report
- β-Hydroxybutyrate upregulates FGF21 expression through inhibition of histone deacetylases in hepatocytes
- Identification of metabolic genes for the prediction of prognosis and tumor microenvironment infiltration in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- BTBD10 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by downregulating cyclin D1 and p-Akt
- Mucormycosis co-infection in COVID-19 patients: An update
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report
- Long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS1 is a prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells’ proliferation and invasion
- Preparation and evaluation of LA-PEG-SPION, a targeted MRI contrast agent for liver cancer
- Proteomic analysis of the liver regulating lipid metabolism in Chaohu ducks using two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Nasopharyngeal tuberculosis: A case report
- Characterization and evaluation of anti-Salmonella enteritidis activity of indigenous probiotic lactobacilli in mice
- Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection
- Bacteriospermia – A formidable player in male subfertility
- In silico and in vivo analysis of TIPE1 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Effects of KCa channels on biological behavior of trophoblasts
- Interleukin-17A influences the vulnerability rather than the size of established atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report
- Prognostic signature related to the immune environment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
- Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- Role of MMP-2 and CD147 in kidney fibrosis
- Geometric basis of action potential of skeletal muscle cells and neurons
- Babesia microti-induced fulminant sepsis in an immunocompromised host: A case report and the case-specific literature review
- Role of cerebellar cortex in associative learning and memory in guinea pigs
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technique for diagnosing a specific case of necrotizing meningoencephalitis caused by human herpesvirus 2
- Case report: Quadruple primary malignant neoplasms including esophageal, ureteral, and lung in an elderly male
- Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatoma carcinoma via the miR-125a-5p/VEGF pathway
- Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal membrane stem cells in inflammatory environments
- Knockdown of SHMT2 enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to radiotherapy through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with double filtration plasmapheresis in the treatment of severe lupus complicated by serious bacterial infections in children: A case report
- Simultaneous triple primary malignancies, including bladder cancer, lymphoma, and lung cancer, in an elderly male: A case report
- Preclinical immunogenicity assessment of a cell-based inactivated whole-virion H5N1 influenza vaccine
- One case of iodine-125 therapy – A new minimally invasive treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- S1P promotes corneal trigeminal neuron differentiation and corneal nerve repair via upregulating nerve growth factor expression in a mouse model
- Early cancer detection by a targeted methylation assay of circulating tumor DNA in plasma
- Calcifying nanoparticles initiate the calcification process of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the activation of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and promote the decay of echinococcosis
- Evaluation of prognostic markers in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2
- N6-Methyladenosine-related alternative splicing events play a role in bladder cancer
- Characterization of the structural, oxidative, and immunological features of testis tissue from Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Effects of glucose and osmotic pressure on the proliferation and cell cycle of human chorionic trophoblast cells
- Investigation of genotype diversity of 7,804 norovirus sequences in humans and animals of China
- Characteristics and karyotype analysis of a patient with turner syndrome complicated with multiple-site tumors: A case report
- Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Distribution characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in false-positive results detected by chemiluminescent immunoassay
- SRPX2 attenuated oxygen–glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced injury in cardiomyocytes via alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis
- Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
- Relationship between CRP gene polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism and sexual development in pubertal obese male rats
- Cloning and identification of the CTLA-4IgV gene and functional application of vaccine in Xinjiang sheep
- Antitumor activity of RUNX3: Upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PHF8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in old rat with osteoporosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis
- Bilateral dacryoadenitis in adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report
- A novel association between Bmi-1 protein expression and the SUVmax obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
- The role of erythrocytes and erythroid progenitor cells in tumors
- Relationship between platelet activation markers and spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis
- Abnormal methylation caused by folic acid deficiency in neural tube defects
- Silencing TLR4 using an ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-based shRNA system reduces ischemia-induced seizures in hyperglycemic rats
- Plant Sciences
- Seasonal succession of bacterial communities in cultured Caulerpa lentillifera detected by high-throughput sequencing
- Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia
- Novel Brassica hybrids with different resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans reveal unbalanced rDNA signal patterns
- Application of exogenous auxin and gibberellin regulates the bolting of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.)
- Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review
- Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.)
- Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings
- Selection and functional identification of Dof genes expressed in response to nitrogen in Populus simonii × Populus nigra
- Study on pecan seed germination influenced by seed endocarp
- Identification of active compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix from different geographical origins by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with GC-MS approaches
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species
- Genome-wide identification of MAPK family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis)
- Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of different organs at various development stages in Caragana intermedia
- Cloning and expression analysis of SERK1 gene in Diospyros lotus
- Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling revealed coping mechanisms of the edible and medicinal homologous plant Plantago asiatica L. cadmium resistance
- A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Assessment of drought tolerance indices in faba bean genotypes under different irrigation regimes
- The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus setaceus (Kunth) Jessop: Genome structure, gene composition, and phylogenetic analysis in Asparagaceae
- Food Science
- Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model
- Binge eating disorder during COVID-19
- Potential of honey against the onset of autoimmune diabetes and its associated nephropathy, pancreatitis, and retinopathy in type 1 diabetic animal model
- FTO gene expression in diet-induced obesity is downregulated by Solanum fruit supplementation
- Physical activity enhances fecal lactobacilli in rats chronically drinking sweetened cola beverage
- Supercritical CO2 extraction, chemical composition, and antioxidant effects of Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. oleoresin
- Functional constituents of plant-based foods boost immunity against acute and chronic disorders
- Effect of selenium and methods of protein extraction on the proteomic profile of Saccharomyces yeast
- Microbial diversity of milk ghee in southern Gansu and its effect on the formation of ghee flavor compounds
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Effects of heavy metals on bacterial community surrounding Bijiashan mining area located in northwest China
- Microorganism community composition analysis coupling with 15N tracer experiments reveals the nitrification rate and N2O emissions in low pH soils in Southern China
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Cinnamomum balansae Lecomte inferred by microsatellites
- Preliminary screening of microplastic contamination in different marine fish species of Taif market, Saudi Arabia
- Plant volatile organic compounds attractive to Lygus pratensis
- Effects of organic materials on soil bacterial community structure in long-term continuous cropping of tomato in greenhouse
- Effects of soil treated fungicide fluopimomide on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) disease control and plant growth
- Prevalence of Yersinia pestis among rodents captured in a semi-arid tropical ecosystem of south-western Zimbabwe
- Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on mitigating salt-induced Na+ toxicity and sustaining sea rice growth
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Poly-l-lysine-caused cell adhesion induces pyroptosis in THP-1 monocytes
- Development of alkaline phosphatase-scFv and its use for one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for His-tagged protein detection
- Development and validation of a predictive model for immune-related genes in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Agriculture
- Effects of chemical-based fertilizer replacement with biochar-based fertilizer on albic soil nutrient content and maize yield
- Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CPP-like gene family in Triticum aestivum L. under different hormone and stress conditions
- Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia
- Influence of furrow irrigation regime on the yield and water consumption indicators of winter wheat based on a multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
- Discovery of exercise-related genes and pathway analysis based on comparative genomes of Mongolian originated Abaga and Wushen horse
- Lessons from integrated seasonal forecast-crop modelling in Africa: A systematic review
- Evolution trend of soil fertility in tobacco-planting area of Chenzhou, Hunan Province, China
- Animal Sciences
- Morphological and molecular characterization of Tatera indica Hardwicke 1807 (Rodentia: Muridae) from Pothwar, Pakistan
- Research on meat quality of Qianhua Mutton Merino sheep and Small-tail Han sheep
- SI: A Scientific Memoir
- Suggestions on leading an academic research laboratory group
- My scientific genealogy and the Toronto ACDC Laboratory, 1988–2022
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study”
- Erratum to “A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis”

