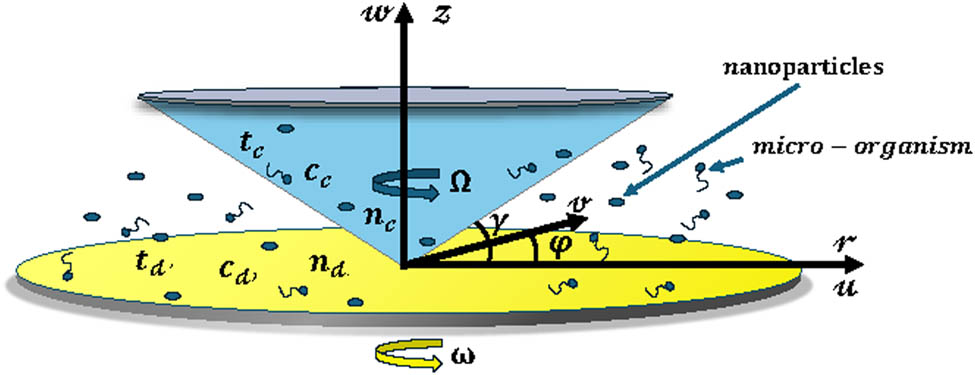
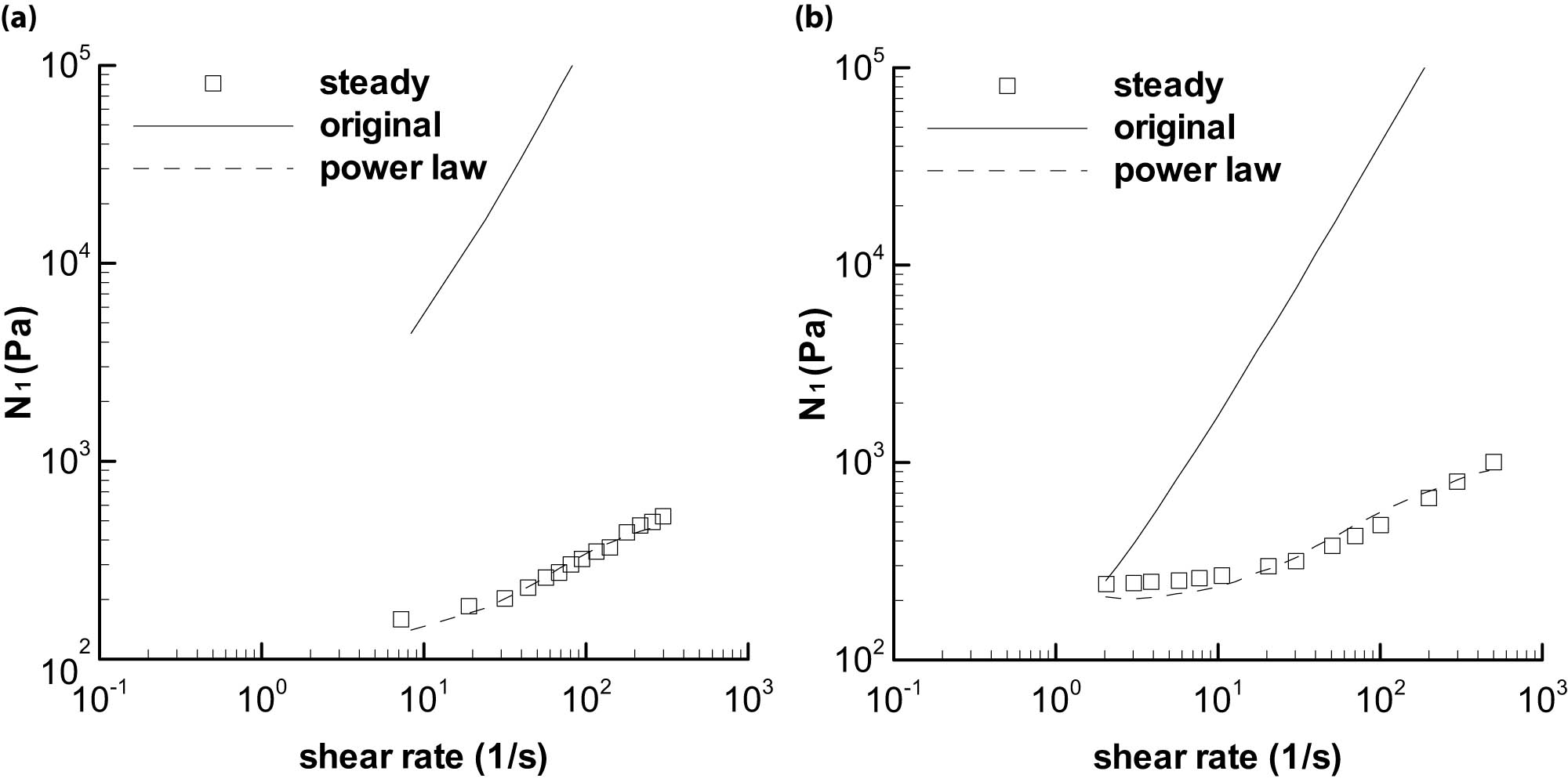
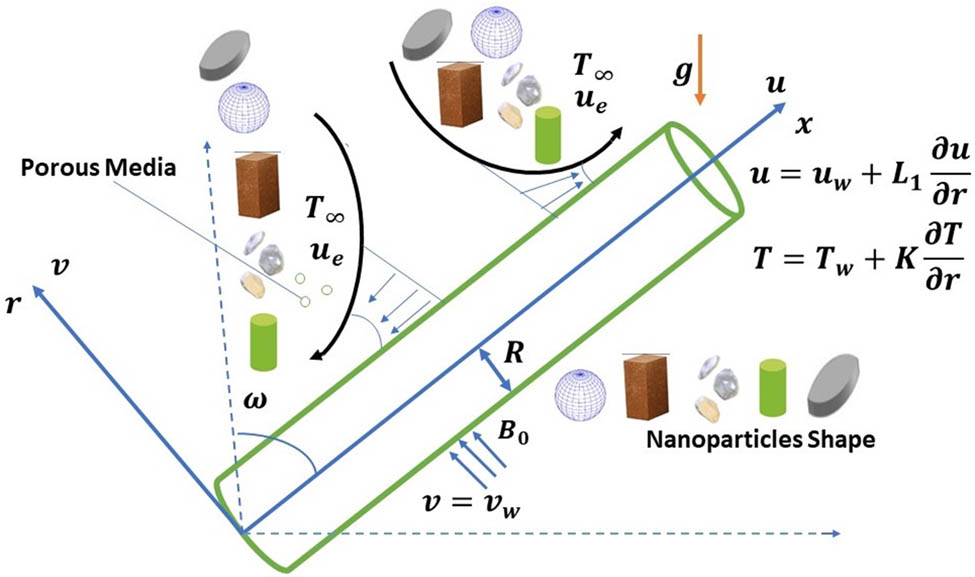
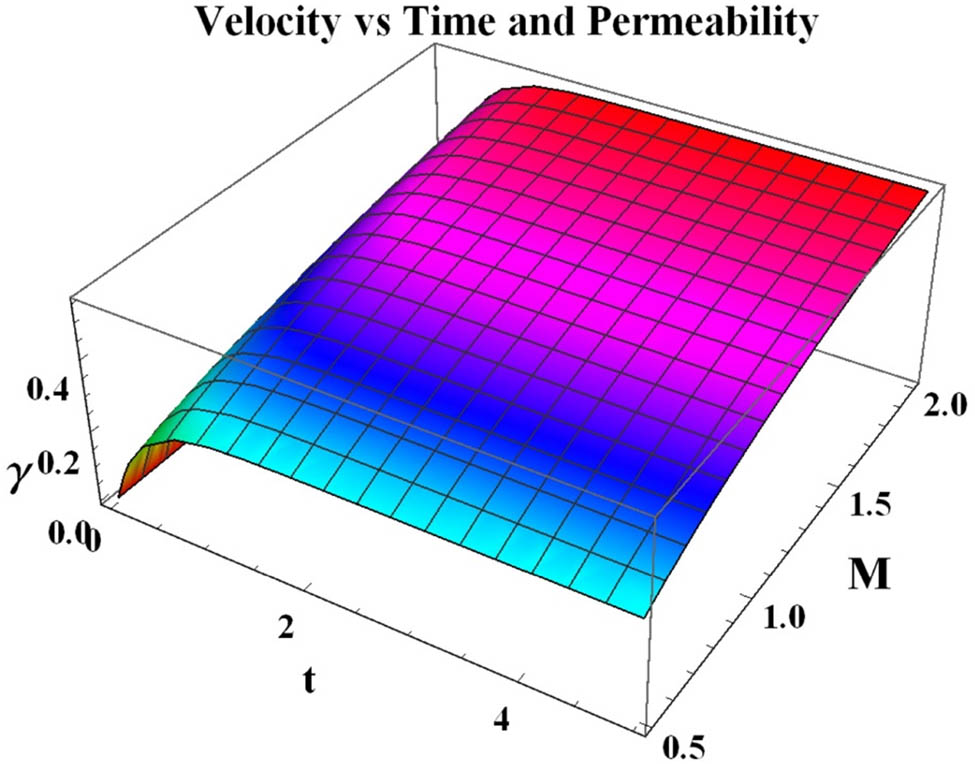
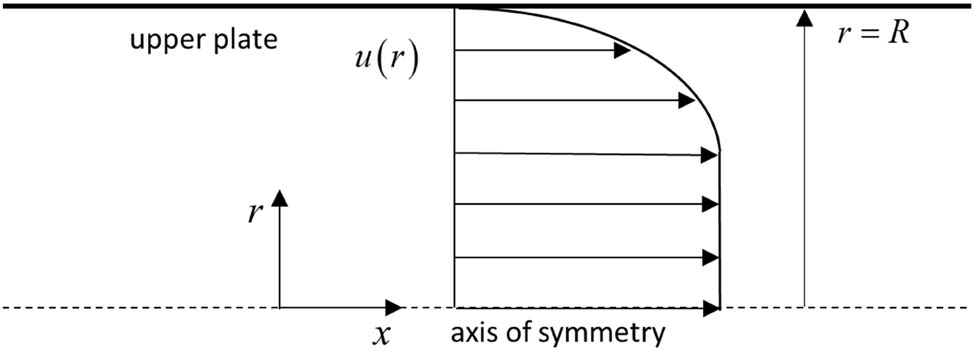
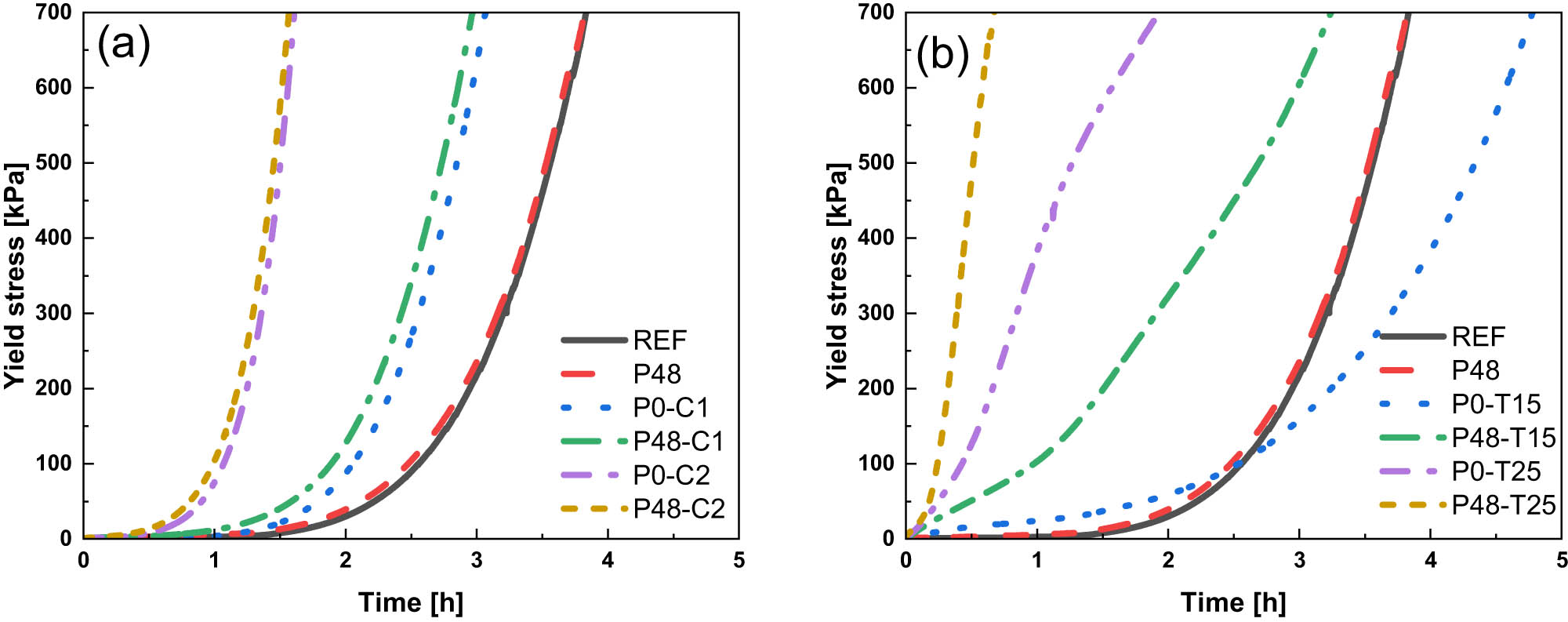
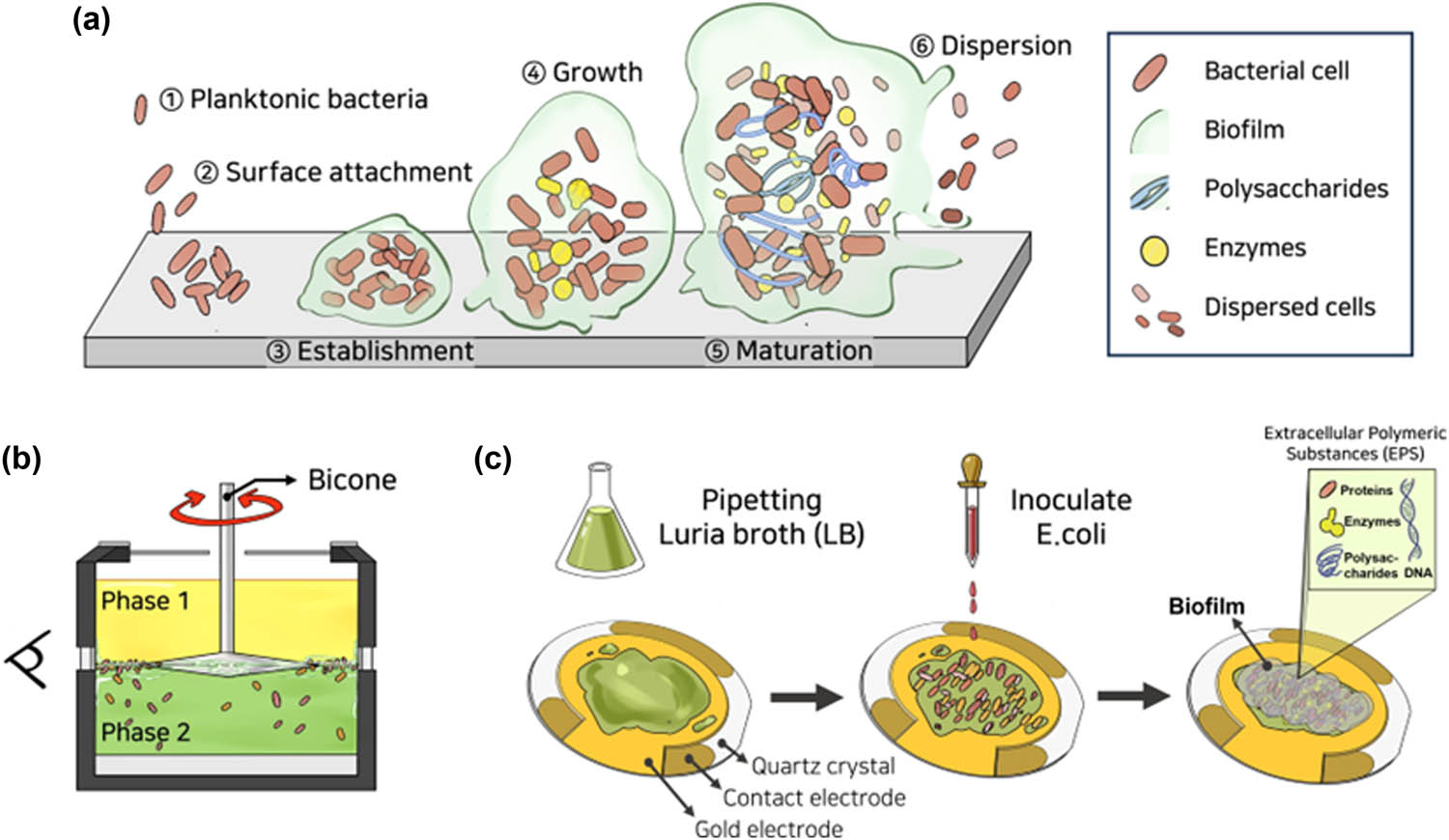
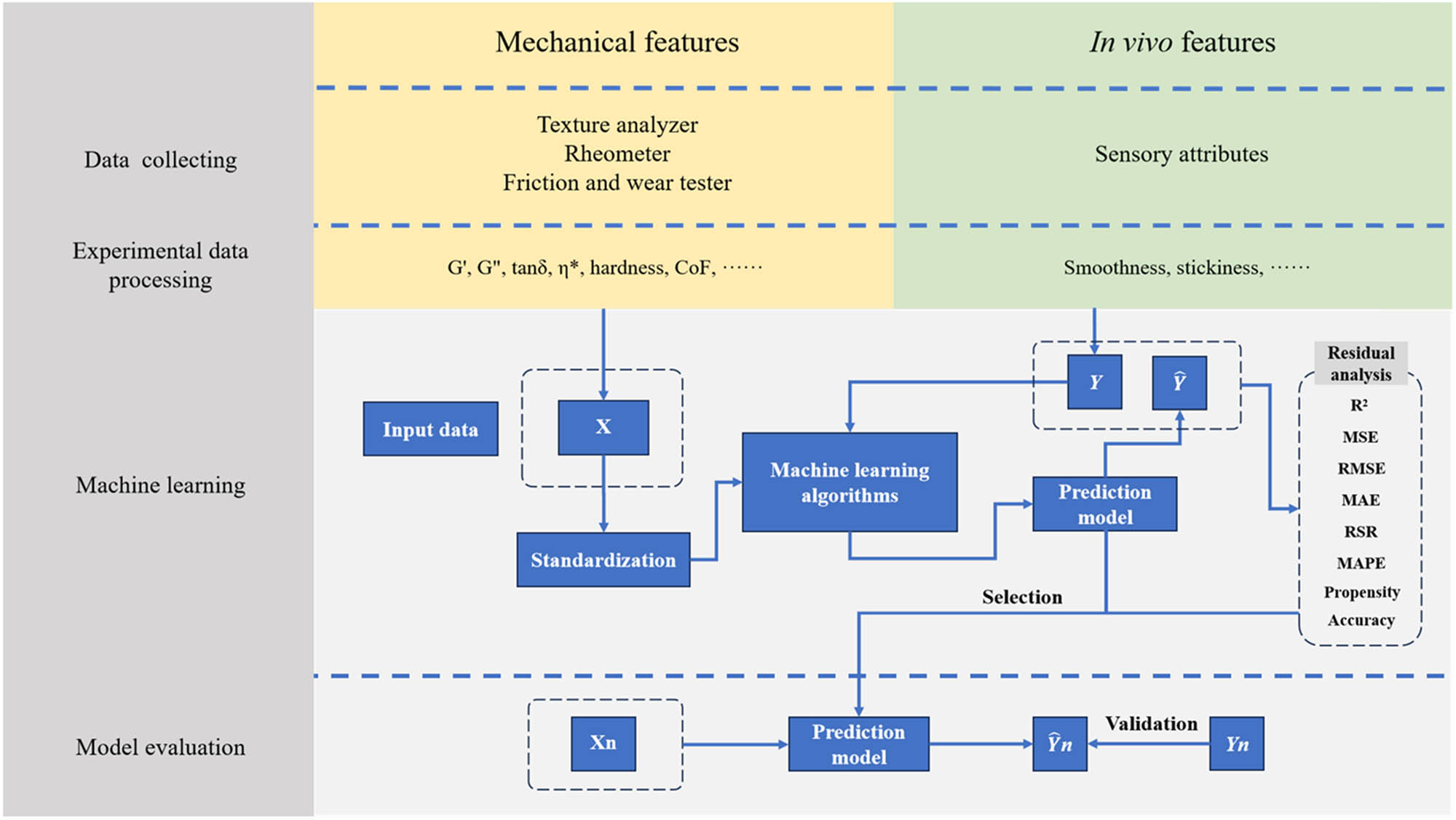
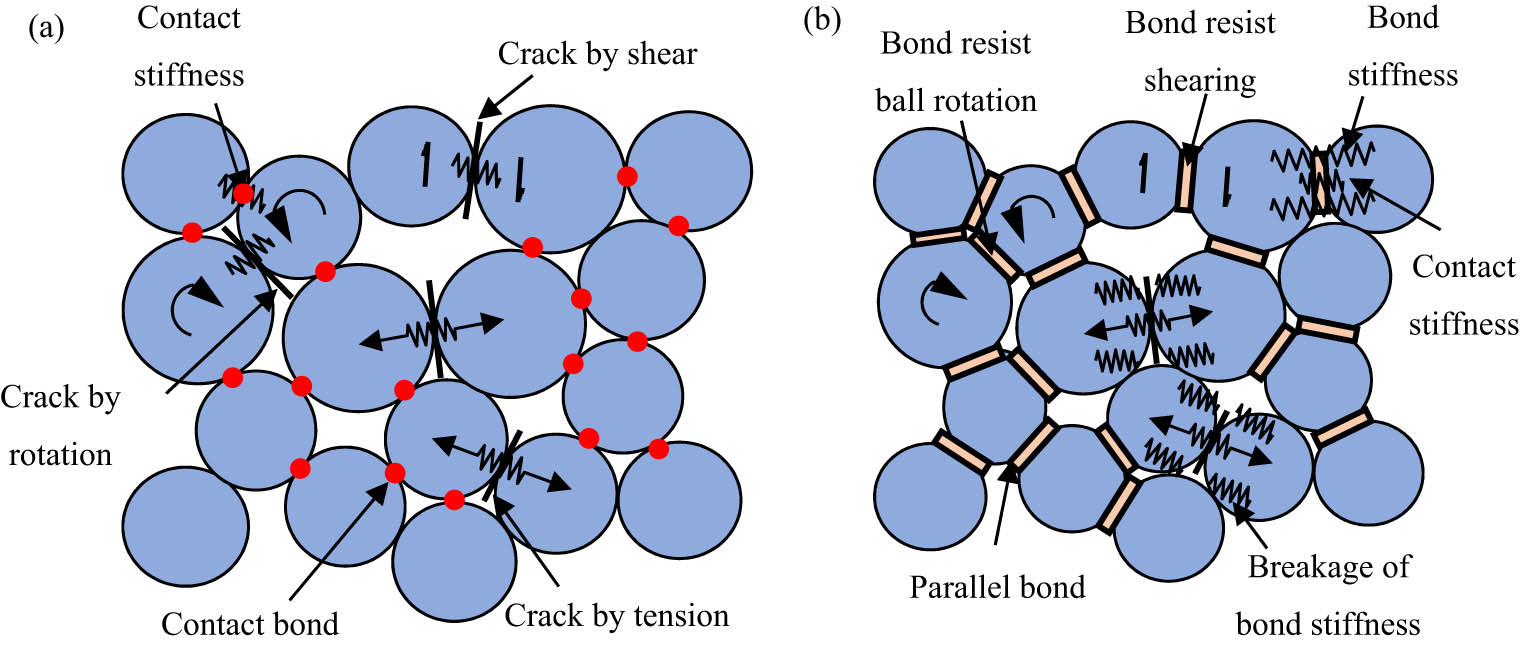
The cone–disk system (CDS) involves a cone, which contacts a disk at its tip. This type of flow problem is used in some devices in medical sciences, such as viscosimeters and conical diffusers. The 3-D flow of a bio-nanofluid within the gap of a CDS is examined for the four selected arrangements: (i) rotating cone with stationary disk, (ii) rotating disk with stationary cone, (iii) co-rotation of cone and disk, and (iv) counter-rotation of cone and disk. The well-known Buongiorno’s nanofluid model is applied to illustrate the flow behavior with Stefan blowing. The governing system constitutes the continuity, momentum, energy, conservation of nanoparticle volume fraction (NPVF) equation, and density of the motile microorganism (DMM) equations. The Lie group approach is used to obtain invariant transformations. Numerical simulations are done for various rotational Reynolds numbers and various gap angles to explore the flow, heat, NPVF, and DMM transport features. The radial and tangential skin friction factors, Nusselt, Sherwood, and density numbers are calculated and inspected using tabular and graphical results. The slip and blowing parameters are demonstrated to affect the fluid friction, heat, NPVF, and DMM transfer rates from the disk and cone for the selected models.
Inhalt
- Research Articles
-
Open AccessDeep learning-based image analysis for confirming segregation in fresh self-consolidating concrete17. April 2025
-
4. Juli 2025
-
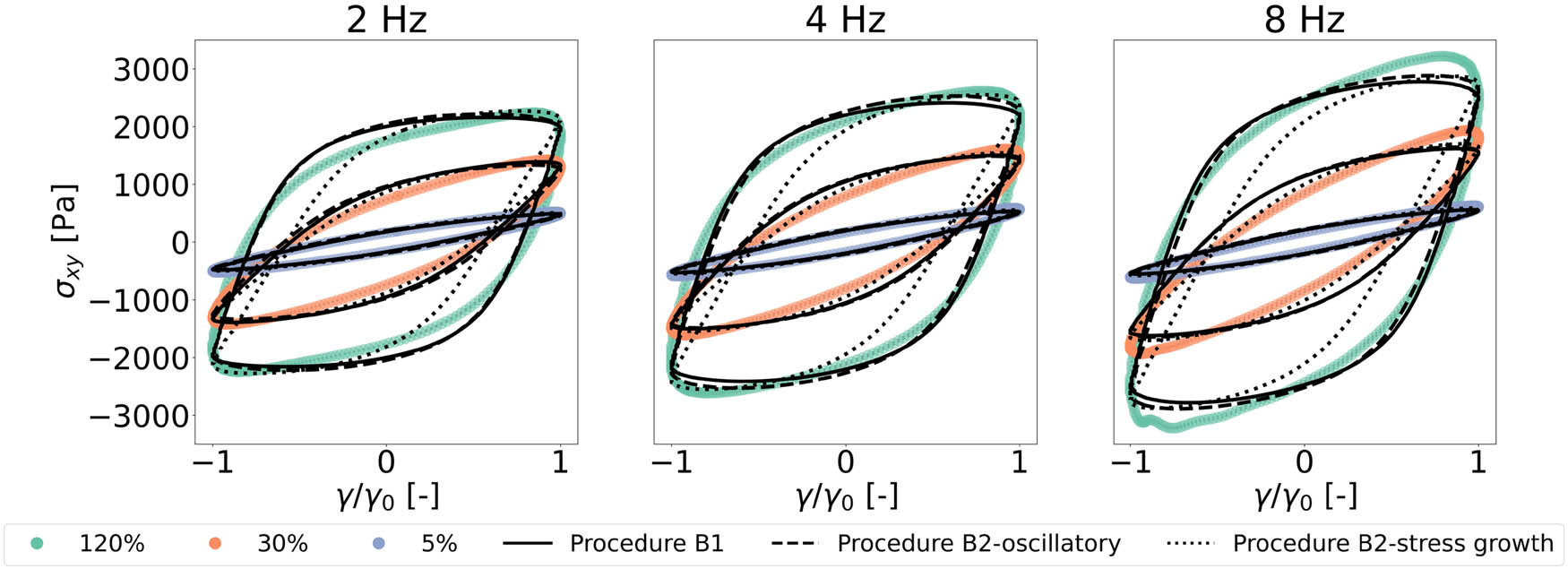
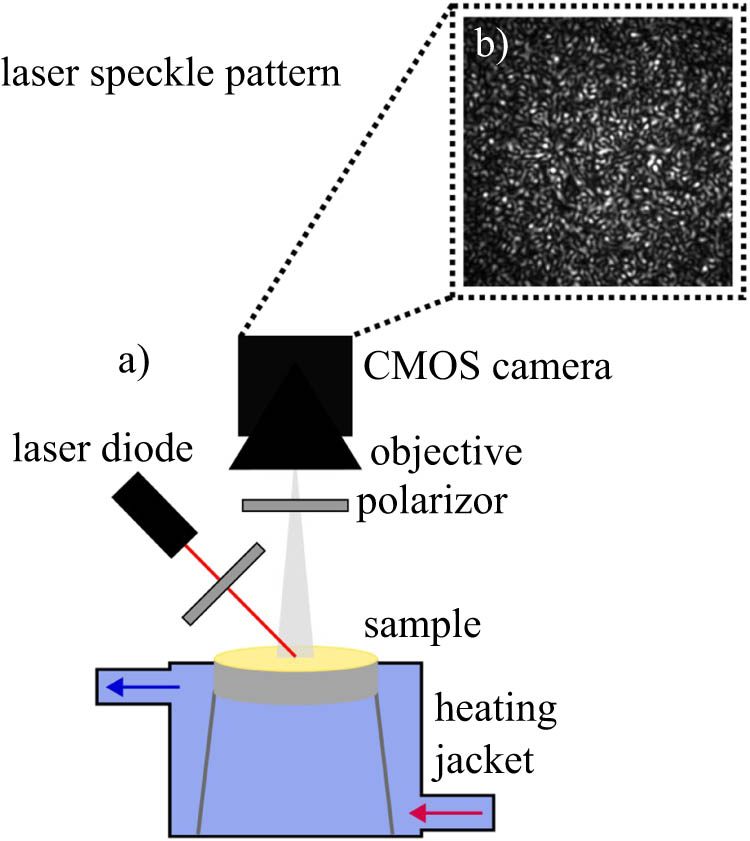
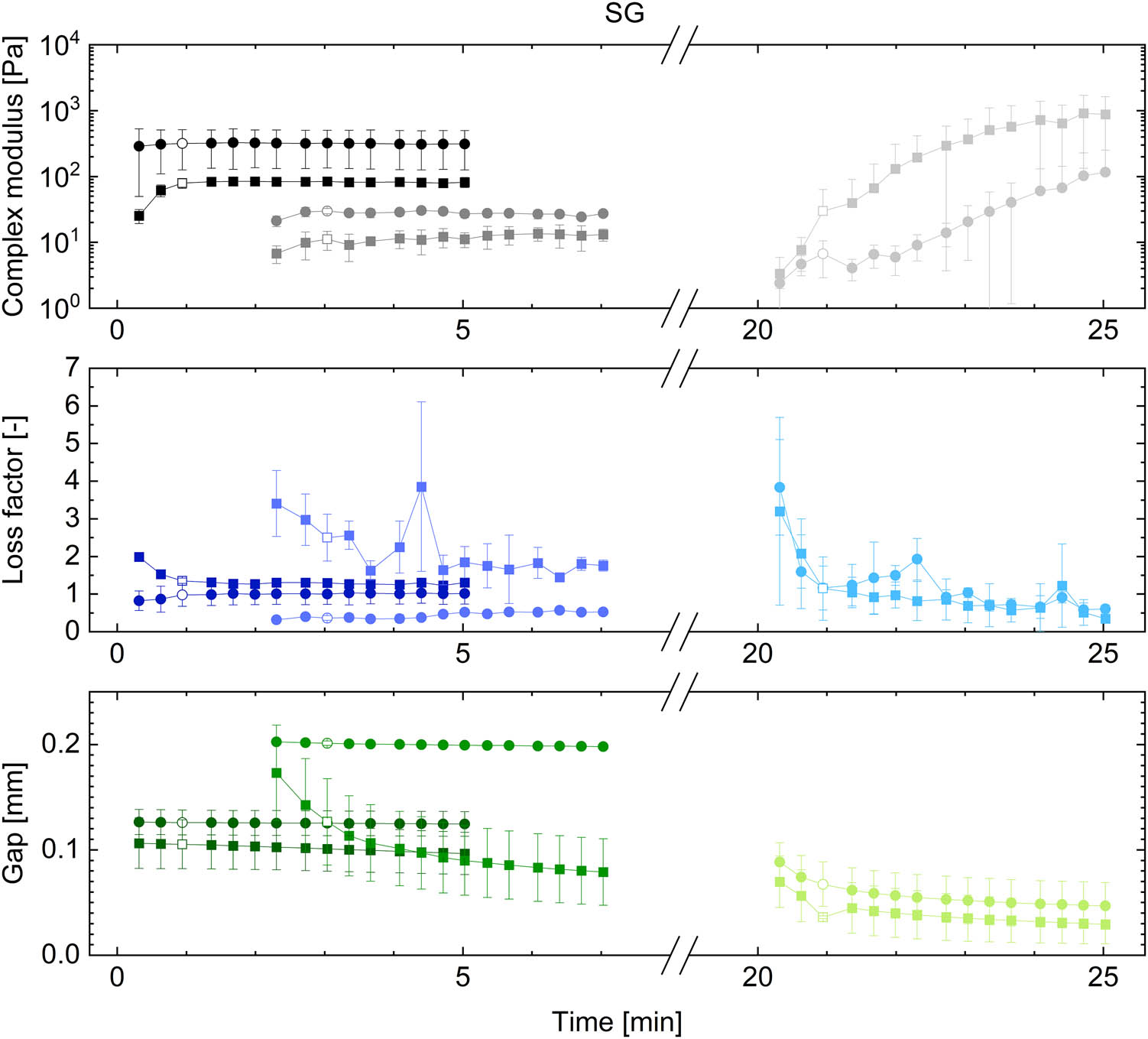
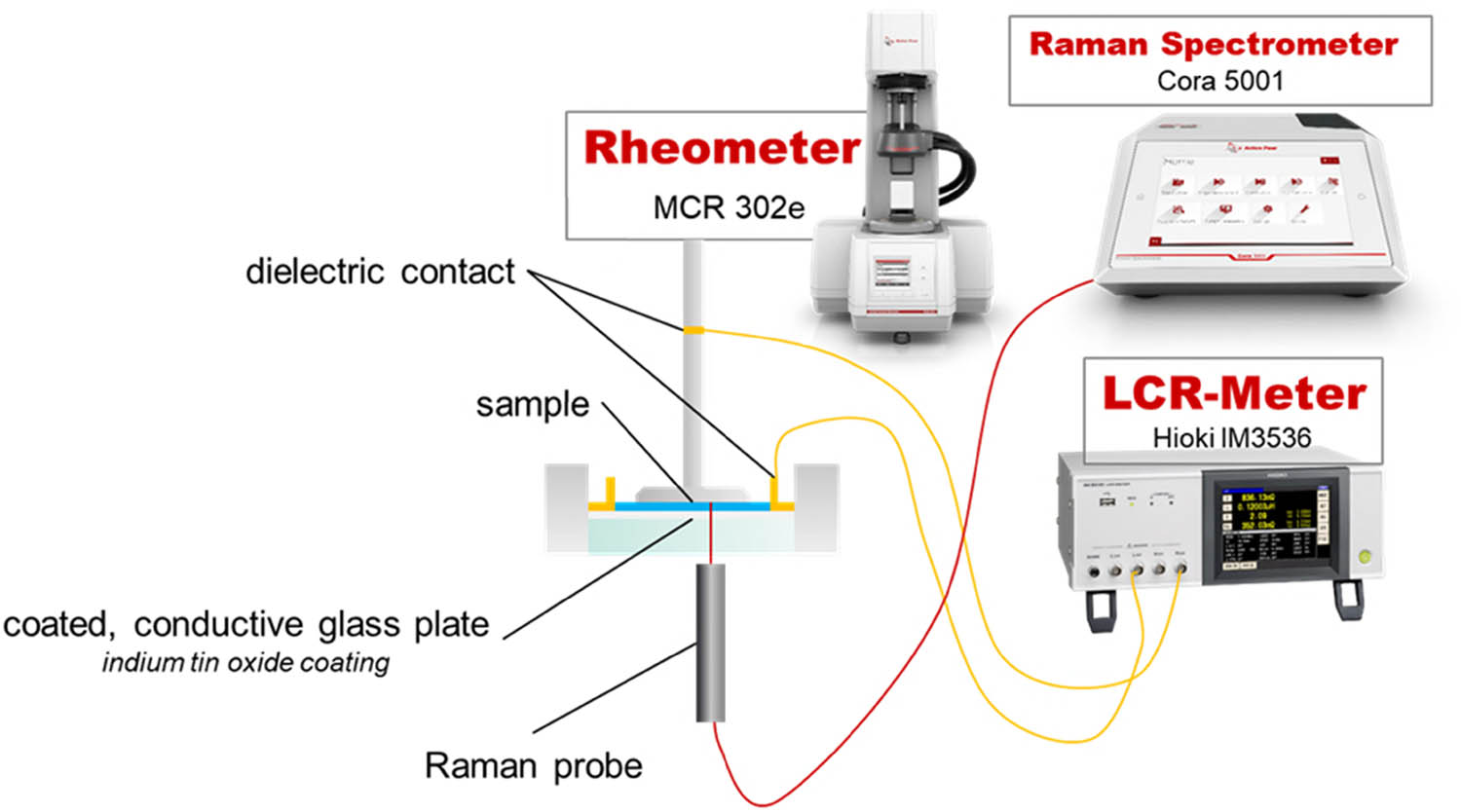
Open AccessRheological analysis of saliva samples in the context of phonation in ectodermal dysplasia13. Oktober 2025
- Brief Report
-
5. März 2025
- Special Issue on the Rheological Properties of Low-carbon Cementitious Materials for Conventional and 3D Printing Applications
- Special Issue on The rheological test, modeling and numerical simulation of rock material - Part II
- Special Issue on The rheology of emerging plant-based food systems
-
4. April 2025
-
27. Mai 2025
-
9. Juni 2025
-
3. Juli 2025
-
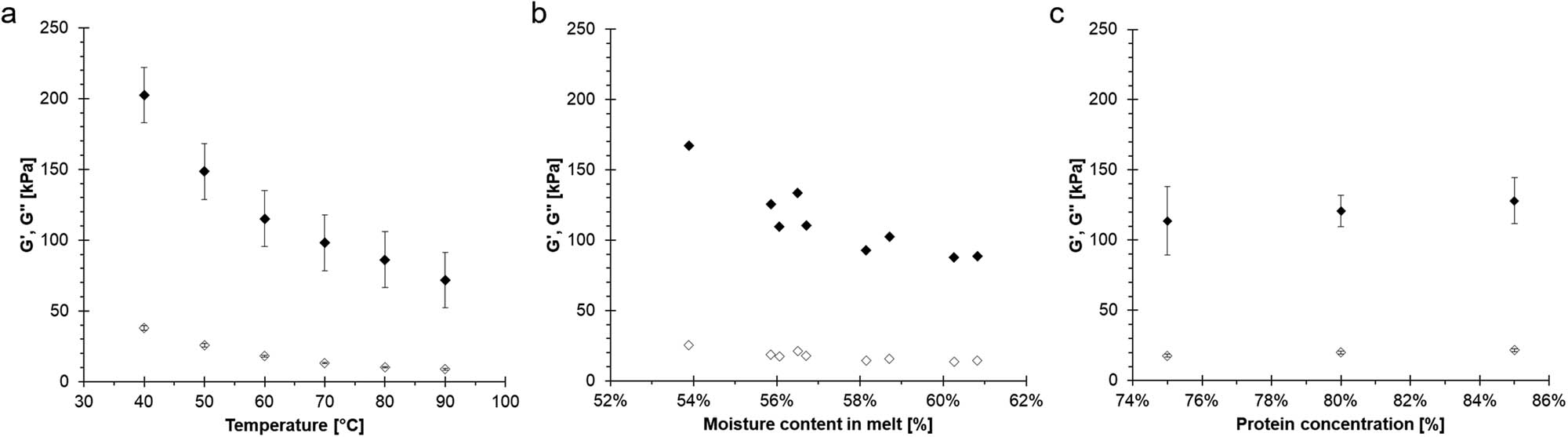
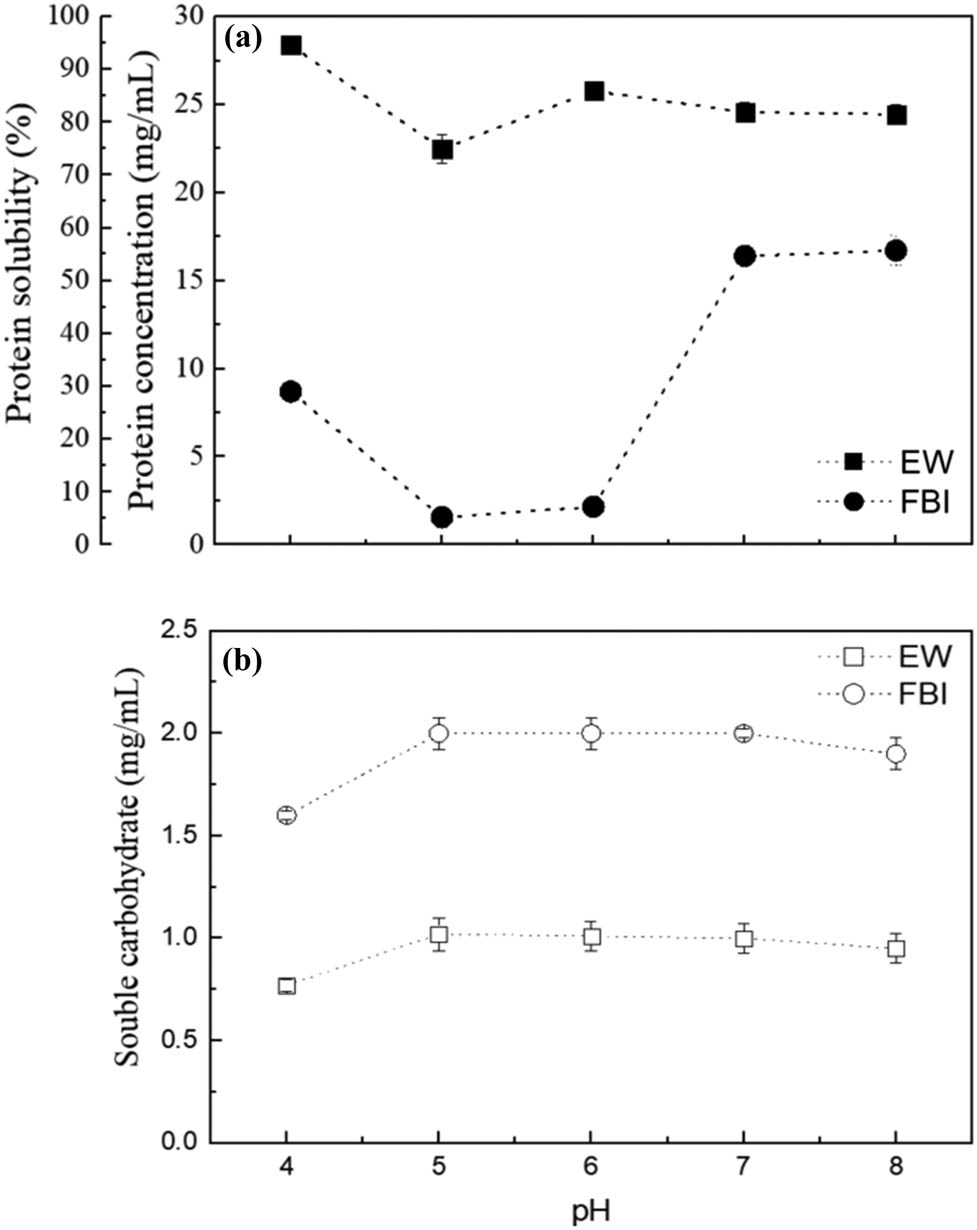
Open AccessRheological analysis of swelling food soils for optimized cleaning in plant-based food production30. September 2025
-
16. Oktober 2025
-
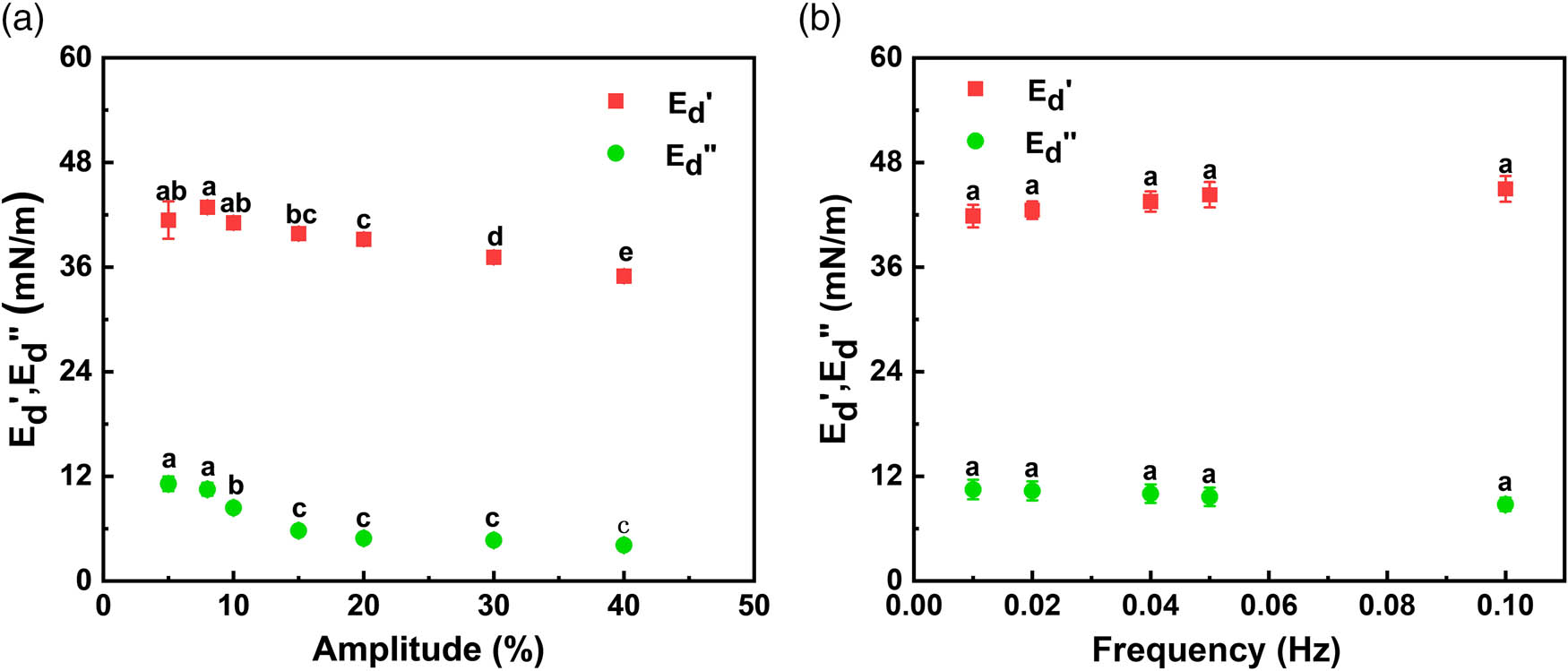
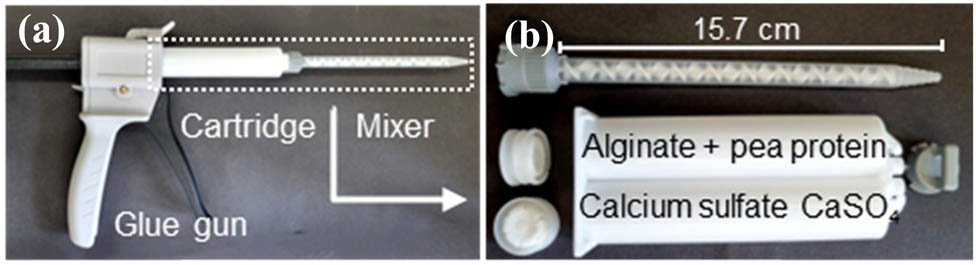
Open AccessInfluence of pea protein on alginate gelation behaviour: Implications for plant-based inks in 3D printing22. Oktober 2025
- Special Issue on Hydromechanical coupling and rheological mechanism of geomaterials
- Special Issue on Rheology of Petroleum, Bitumen, and Building Materials