Abstract
C15H12BrFN2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 9.9691(3) Å, b = 23.3493(6) Å, c = 12.1273(4) Å, β = 102.534(3)°, V = 2755.61(15) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0387, wRref(F2) = 0.1145, T = 293(2) K.
1 Source of materials
Dissolve 4-bromo-2-fluorophenylhydrazine hydrochloride (1.449 g, 6 mmol) in 30 mL of ethanol and stir at room temperature until it is dissolved. Subsequently, cinnamaldehyde (0.661 g, 5 mmol) was added dropwise to the above solution and the reaction was continued under the same conditions. After monitoring the reaction by TLC, add 30 mL of water to the reaction solution and extract the target compound with ethyl acetate (50 mL × 3). Then dry the combined organic phases overnight with Na2SO4 and remove the solvent by vacuum distillation. The residue was recrystallized from ethanol to obtain (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone yellow flocculent crystals 1 (Table 1).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Clear light colourless block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | CuKα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 4.07 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, Rigaku, ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 66.6°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 25193, 4837, 0.066 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 3,533 |
| N(param)refined: | 344 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 Olex2, 2 Shelx 3 |
2 Experimental details
All H atoms attached to carbon were included using a riding-model using Olex2, 1 with C–H = 0.93 Å, and their Uiso values were set to 1.2 Ueq
3 Comment
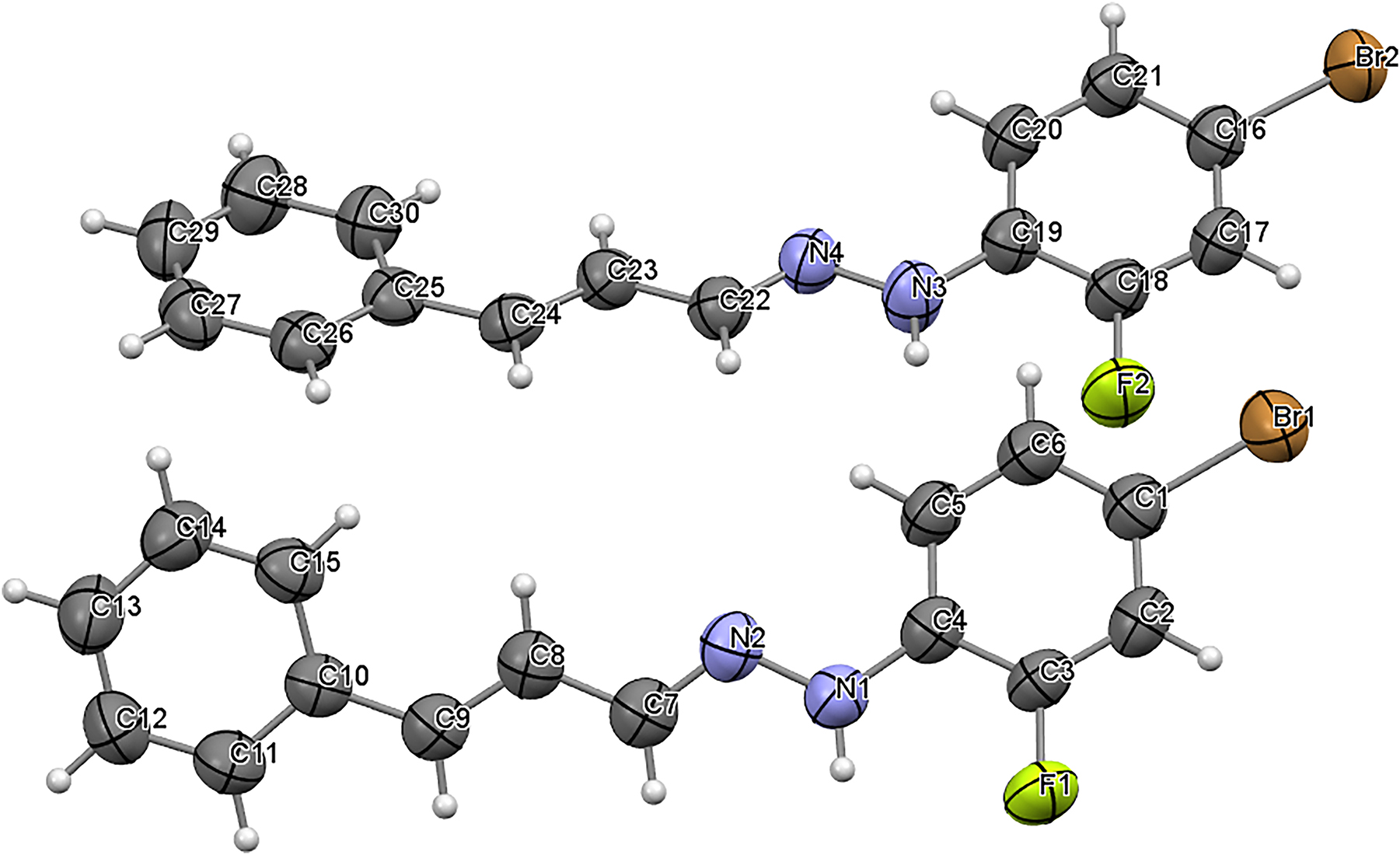
The title compound, (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl) hydrazone, was designed and synthesized by using the principle of active group splicing. To the best of the asymmetric unit of the title structure contains two (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl) hydrazone molecule. The bond lengths and angles within the structure of 1(1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone are unexceptional and lie within the expected ranges. 4 , 5 In details, the N2–C7 distance is 1.283(5) Å and the N4–C22 distance is 1.279(4) Å, which suggests a N=C double bond. It shows that the condensation reaction between the raw materials has produced a hydrazone. Cinnamaldehyde, a well-known natural product, is the main component of the volatile oil with unique flavor. Hydrazone compounds not only have diverse structures, but also have rich biological activities. At the same time, hydrazone compounds also have the advantages of simple preparation and low toxicity. 6 So far, researchers have successfully developed some fungicides, such as Benquinox and Ferimzone. These compounds play corresponding roles mainly by inhibiting different enzymes in cell activities. 7 The title compound is obtained by combining two active structural units, cinnamaldehyde and phenylhydrazone, by using the principle of active group splicing. 8
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: The work was supported by General Project for Natural Science Research in Jiangsu Province Universities (24KJD210004), Science and Technology Support Program Project of Taizhou (Agriculture, Social Development) (TS202323).
References
1. Mishra, N. K.; Bansal, D.; Supriya, S. Polyoxometalate-Supported Copper(I)-Pyrazole Complex: Unusual Stability, Geometrical Isomers, Organic Transformation, and Computation. ACS Omega 2022, 7 (35), 31403–31412; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c03795.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Puschmann, H.; Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K. Olex2 – A Complete Package for Molecular Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. A 2011, 67, C593; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767311084996.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Zoller, T.; Breuilles, P.; Uguen, D.; De Cian, A.; Fischer, J. An Unexpected Sequel of an Alcohol Oxidation Study: Stereoselective Cyclisation of an Unsaturated Keto-Sulfide. Tetrahedron Letters 1999, 40, 6253; https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(99)01298-8.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Yin, Z.-G.; Qian, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Feng, Y.-L.; 1-(2,4-Dinitrophenyl)-2-(3-phenylallylidene)hydrazine pyridine hemisolvate. Acta Crystallographica Section E: Structure Reports Online 2007, 63, o4625. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536807055444.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Goff, G. L.; Ouazzani, J. Natural Hydrazine-Containing Compounds: Biosynthesis, Isolation, Biological Activities and Synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22 (23), 6529–6544; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2014.10.011.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Verma, S.; Lal, S.; Narang, P.; Sudhakar, K. Quinoline Hydrazide/Hydrazone Derivatives: Recent Insights on Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202200571; https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202200571.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Denng, Y.; Chen, M. H.; Yi, J. M.; Zheng, Y. G. Design, Synthesis, and Anti-Tobacco Mosaic Virus Activity Evaluation of Quinazolinone Derivatives Containing Purine Moieties. Phytochem. Lett. 2024, 59, 10–14; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2023.11.003.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N


