Abstract
C23H21NO4, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 18.4694(3) Å, b = 6.9105(1) Å, c = 14.9464(3) Å, β = 93.749(2)°, V = 1903.57(6) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0426(3375), wR ref (F2) = 0.1183(3743), T = 293 K.
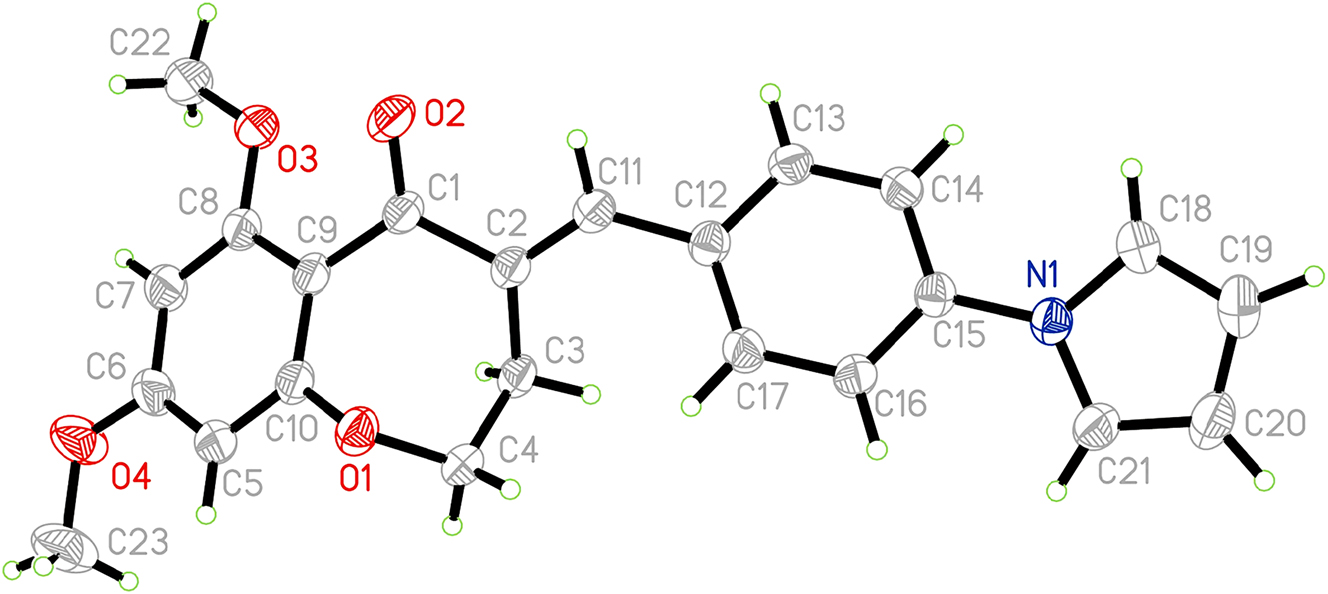
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data and the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Clear light colourless block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.13 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.73 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku Synergy, ω scan |
| θmax, completeness: | 74.9°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11441, 3743, 0.015 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3375 |
| N(param)refined: | 255 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 |
1 Source of material
Based on the literature synthesis, 4 , 5 1H-pyrrole (10.73 g, 0.16 mol), potassium carbonate (27.80 g, 0.20 mol) and N,N-dimethylformamide (6 mL) were added into a 250 mL round flask. The mixture was stirred and reacted under an oil bath at 353 K for 4 h. After that, the temperature was raised to 383 K, and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (2.5 g, 0.02 mol) was added. The reaction was continued for another 5 h. After filtration and spin evaporation, the residue was purified on a silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane:methanol = 30:1, v:v) to afford the intermediate. Next, the intermediate (0.86 g, 5.0 mmol) and 6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one (1.11 g, 5.0 mmol) were dissolved in 3 mL methanol. A 25 % sodium hydroxide solution (3 mL) was used as a catalyst. The system was reacted on ice for 10 min and then stirred at room temperature for 30 min. The reaction was stopped when it was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) that the intermediate had been completely consumed. The precipitate obtained by suction filtration was rinsed with 50 % methanol. The precipitate was collected and recrystallized from a dichloromethane and methanol solution (10 mL, 1:1, v:v) at room temperature to gain clear light yellow block crystals after three days.
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C–H) = 0.96 Å (methyl), Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.97 Å (methylene), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
3 Comment
Previous studies revealed that 3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one compounds have excellent anti-inflammatory properties. 6 , 7 It has been demonstrated that biological activity can be increased with the aid of introducing another pharmacophore, α,β-unsaturated ketone. 8 In addition, some research indicates that the introduction of a nitrogen-containing heterocycle at the end of the compound may reduce the toxicity and increase the biological activity of the compound. 9 , 10 Therefore, a 1H-pyrrole substituent at the C(15) position was introduced to obtain the title compound.
The single-crystal structure analysis reveals that the title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group, with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (cf. the figure). The bond lengths and bond angles are within the normal range. In this seven-membered oxazepine ring, dihedral angles are C(9)–C(1)–C(2)–C(3), C(1)–C(2)–C(3)–C(4), C(2)–C(3)–C(4)–O(1), and C(3)–C(4)–O(1)–C(10) are 4.09(17)°, −72.44(14)°, 43.21(16)° and 49.42(16)°, respectively. At the C(2) position, the α,β-unsaturated ketone was obtained through the Claisen–Schmidt condensation reaction. 11 , 12 The bond lengths of O(2)=C(1) is 1.2172(16) Å, while the bond length of C(2)=C(11) is 1.3381(18) Å. The torsion angle of O(2)=C(1)–C(2)=C(11) is about 2.97(19)°, while the torsion angle of C(1)–C(2)=C(11)–C(12) is about 177.57(12)°. There is a 1H-pyrrole substitution at the C(15) position. The bond length of C(15)–N(1) is 1.4192(15) Å. The torsion angle of C(18)–N(1)–C(15) is about 125.92(12)°, the torsion angle of C(21)–N(1)–C(18) is about 108.15(12)° and the torsion angle of C(21)–N(1)–C(15) is about 125.80(11)°. Because of the structural characteristics and the substituent effect, there is a large dihedral angle between the central parent nucleus and the substituted 1H-pyrrole, with the dihedral angle of about 34.01(3)°. Overall, the title compound has a linear structure. 13 This twisting and linear structure may increase the possibility of interaction with bioactive molecules. 14 , 15
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2023MH190) and College Students’ innovation and entrepreneurship training program (Discovery of benzoxazepines and the mechanism of action of targeted intervention in the cGAS–STING pathway for the treatment of neuroinflammation, by Mu-Chen Jiang, No. X202510440639).
References
1. Rigaku OD. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of Shelx. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Luan, M. Z.; Zhang, X. F.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, G. G. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Fluorine-Substituted Benzo[h]quinazoline-2-Amine Derivatives as NF-κB Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 132, 106360; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106360.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Zhang, X. F.; Luan, M. Z.; Yan, W. B.; Zhao, F. L.; Hou, Y.; Hou, G. G.; Meng, Q. G. Anti-neuroinflammatory Effects of Novel 5,6-Dihydrobenzo[h]Quinazolin-2-Amine Derivatives in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114322; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114322.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Gao, C. L.; Hou, G. G.; Liu, J.; Ru, T.; Xu, Y. Z.; Zhao, S. Y.; Ye, H.; Zhang, L. Y.; Chen, K. X.; Guo, Y. W.; Pang, T.; Li, X. W. Synthesis and Target Identification of Benzoxepane Derivatives as Potential Anti-neuroinflammatory Agents for Ischemic Stroke. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2429–2439; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201912489.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Li, N.; Yao, B. R.; Wang, C. H.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, G. G. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Activity Evaluation of Novel 3,4-Dihydro-1-Benzoxepin-5(2H)-One Derivatives as Protein-Tyrosine Kinase (PTK) Inhibitors. Acta Crystallogr. 2017, C73, 1003–1009; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229617015145.Search in Google Scholar
8. Yang, Y.; Gao, Z. F.; Hou, G. G.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, Y. Discovery of Anti-neuroinflammatory Agents from 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydrobenzo[2,3]oxepino[4,5-D]pyrimidin-2-Amine Derivatives by Regulating Microglia Polarization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 259, 115688; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115688.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Zhou, G.; Zorn, N.; Ting, P.; Aslanian, R.; Lin, M.; Cook, J.; Lachowicz, J.; Lin, A.; Smith, M.; Hwa, J.; van Heek, M.; Walker, S. Development of Novel Benzomorpholine Class of Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase I Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5 (5), 544–549; https://doi.org/10.1021/ml400527n.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
10. Girase, P. S.; Dhawan, S.; Kumar, V.; Shinde, S. R.; Palkar, M. B.; Karpoormath, R. An Appraisal of Anti-mycobacterial Activity with Structure-Activity Relationship of Piperazine and Its Analogues: A Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112967; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112967.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Chen, Y.; Wang, J. P.; Wang, M. D.; Yu, W. X.; Cui, Y. T.; Gao, H. X.; Hou, G. G.; Ren, Y. Crystal Structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)Benzylidene)-7-Fluoro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2h)-One, C20H15FN2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS. 2025, 240 (1), 19–21; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0294.Search in Google Scholar
12. Xia, D.-L.; Wang, J. P.; Yu, W. X.; Wang, M. D.; Gao, H. X.; Cui, Y. T.; Hou, G. G. Crystal Structure of (E)-6,8-Dimethoxy-4-(4-Morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-Dihydro-1-Benzoxepin-5(2h)-One, C23H25NO5. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2024, 239, 1133–1136; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0329.Search in Google Scholar
13. Yu, L.; Wang, J. P.; Wang, M. D.; Yu, W. X.; Cui, Y. T.; Gao, H. X.; Liu, Y. J.; Hou, G. G. Crystal Structure of (E)-6-(4-Ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-Fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One, C23H25FN2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2024, 239 (3), 515–517; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0066.Search in Google Scholar
14. Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y. Q.; Liu, Y. K.; Zhang, H. Q.; Hou, G. G.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, Y. Potential Anti-neuroinflammatory NF-κB Inhibitors Based on 3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One Derivatives. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1631–1640; https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1804899.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Yu, L.; Xia, D. L.; Chen, Y.; Miao, Y. H.; Xu, R.; Pan, Y. X.; Li, Y. L.; Li, W. X.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y. J.; Hou, G. G.; Zhao, J. B.; Zhang, L. Novel 3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One Derivatives Promote Apoptosis and Inhibit Migration of Hepatocellularcarcinoma Cells via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 296, 117898; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117898.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N


