Abstract
C7H6N2O4, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 8.1416(3) Å, b = 10.2220(3) Å, c = 9.2212(3) Å, β = 91.7600(10)°, V = 767.06(4) Å3, Z = 15, R gt (F) = 0.1022, wRref(F2) = 0.1077, T = 296.15 K.
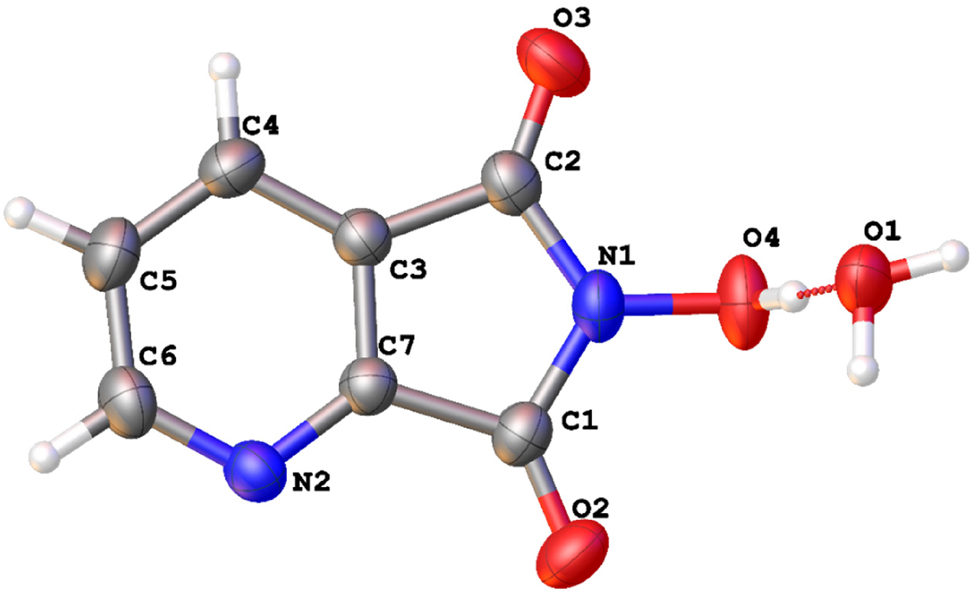
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data and the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex2, φ and ω scan |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.6°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 12460, 1,776, 0.020 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1573 |
| N(param)refined: | 130 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 Bruker 4 |
1 Source of materials
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received without further purification, and 2,3-pyridinedicarboxylic anhydride was synthesized by our laboratory. Under N2, anhydrous sodium acetate (3.956 g, 48.2 mmol) and hydroxylamine hydrochloride (3.956 g, 57.1 mmol) were dissolved in acetic acid (25 mL). Then, the above mixture solution was refluxed for 5 min. The mixture was filtered to remove precipitated NaCl. And then, 2,3-pyridinedicarboxylic anhydride (3.956 g, 26.6 mmol) was added to the filtrate, and the mixture was refluxed for 25 min. After completion, the mixture was filtered and concentrated to a saturated solution under vacuum, a yellow precipitate is formed. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with diethyl ether. The crystals were obtained by recrystallization in the cooled acetonitrile solution. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO‑d6) δ: 11.04 (s, 1H) 8.94 (m, 1H), 8.24 (m, 1H), 7.77 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO‑d6) δ: 162.66, 154.58, 149.01, 130.96, 128.03, 125.32.
2 Experimental details
Olex2 1 software and the SHELXL 2 refinement were used to solve and refine the crystal structure. Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
Organic nitrogen hydroxy compounds (N–OH), as a novel class of organic catalysts, with N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) being the most representative, have recently been employed as an effective system for C–H bonds activation via hydrogen extraction. 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 The molecule features the unique properties of the N–OH function which is different from the previously proposed systems. 10 , 11 Thus, organic nitrogen hydroxy compounds have attracted increasing interest from both the academic and industrial communities over the past decade. 12 These compounds primarily achieve classical C–H bond oxidation reactions through the homolytic cleavage of the hydroxyl bond in N–OH to form N-oxyl radical. 13 , 14 , 15 As a result, this kind of compound has a wide range of applications in carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-silicon bond formation reactions. 12 With the continuous in-depth research on the synthesis and application of organic nitrogen hydroxy compounds, exploring the structural characteristics of these compounds is of great significance for understanding their structure-activity relationships.
However, reports on the crystal structures of organic nitrogen hydroxy compounds remain limited. To date, only two classes of symmetrical organic nitrogen hydroxyl compounds have been reported, i.e., HPPDO 16 and DNHPI. 17
The molecular structure comprises at least two distinct planes: the pyridine ring plane, the pyrrole ring plane. In the crystal, the torsion angles of the nitrogen hydroxyl group (angle N(1)–O(4)H) is 106.8°. The O–H bond length in the nitrogen hydroxyl group is 0.95 Å, which is longer than the O–H bond length in water molecules (0.85 Å). Additionally, the hydrogen in the nitrogen hydroxyl group can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, which are present. All geometric parameters fall within expected ranges. 16 , 17
Funding source: Guiyang University Multidisciplinary Team Construction Projects in 2025
Award Identifier / Grant number: Gyxk202505
Funding source: Research Fund of Guizhou Provincial Department of Education
Award Identifier / Grant number: Qianjiaoji[2024]284
-
Research funding: We gratefully acknowledge support by the Guiyang University Multidisciplinary Team Construction Projects in 2025 [Gyxk202505] and Research Fund of Guizhou Provincial Department of Education (No. Qianjiaoji[2024]284).
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. BRUKER. Saint, Apex2 and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2019.Search in Google Scholar
5. Ishii, Y.; Sakaguchi, S. A New Strategy for Alkane Oxidation with O2 Using N-Hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) as a Radical Catalyst Catal. Surv. Jpn. 1999, 3, 27–35.Search in Google Scholar
6. Ishii, Y.; Sakaguchi, S.; Iwahama, T. PInnovation of Hydrocarbon Oxidation with Molecular Oxygen and Related Reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2001, 343, 393–427; https://doi.org/10.1002/1615-4169(200107)343:5<393::aid-adsc393>3.0.co;2-k.10.1002/1615-4169(200107)343:5<393::AID-ADSC393>3.3.CO;2-BSearch in Google Scholar
7. Minisci, F.; Recupero, F.; Pedulli, G. F.; Lucarini, M. Transition Metal Salts Catalysis in the Aerobic Oxidation of Organic Compounds: Thermochemical and Kinetic Aspects and New Synthetic Developments in the Presence of N-Hydroxy-Derivative Catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 2003, 63, 63–90.10.1016/S1381-1169(03)00286-3Search in Google Scholar
8. Zhao, J.; Deng, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Rong, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z. Q. NHPI-Catalyzed Electro-Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes and Ketones. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 15864–15876; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.4c02007.Search in Google Scholar
9. Sheldon, R. A.; Arends, I. W. C. E. Organocatalytic Oxidations Mediated by Nitroxyl Radicals. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1051–1071; https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.200404110.Search in Google Scholar
10. Karakurt, A.; Dalkara, S.; Ozalp, M.; Ozbey, S.; Kendi, E.; Stables, J. P. Synthesis of Some 1-(2-Naphthyl)-2-(imidazole-1-yl) ethanone oxime and Oxime Ether Derivatives and Their Anticonvulsant and Antimicrobial Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 36, 421–433; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0223-5234(01)01223-5.Search in Google Scholar
11. Grochowski, E.; Boleslawska, T.; Jurczak, J. Reaction of Diethyl Azodicarboxylate with Ethers in the Presence of N-Hydroxyimides as Catalysts. Synthesis 1997, 1997, 718–720.10.1055/s-1977-24550Search in Google Scholar
12. Francesco, R.; Carlo, P. Free Radical Functionalization of Organic Compounds Catalyzed by N–Hydroxyphthalimide. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3800–3842; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040170k.Search in Google Scholar
13. Rani, R.; Granchi, C. Bioactive Heterocycles Containing Endocyclic N-Hydroxy Groups. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 505–524; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.11.031.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Masui, M.; Hara, S.; Ueshima, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ozaki, S. Anodic Oxidation of Compounds Having Benzylic or Allylic Carbon and α-Carbon to Hetero Atom Using N-Hydroxyphthalimide as a Mediator. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 4209–4211; https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.31.4209.Search in Google Scholar
15. Cai, Y.; Koshino, N.; Saha, B.; Espenson, J. H. Kinetics of Self-Decomposition and Hydrogen Atom Transfer Reactions of Substituted Phthalimide N-Oxyl Radicals in Acetic Acid. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 238–243; https://doi.org/10.1021/jo048418t.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
16. Hui, Y.; Feng, X. Crystal Structure of 6-Hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b] pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3. Z. Kristallogr. - N. Cryst. Struct. 2025, 240, 647–648; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2025-0159.Search in Google Scholar
17. Centore, R.; Carella, A. N. N′-Dihydroxybenzene-1,2: 4,5-Tetracarboximide Dihydrate. Structure Reports 2013, 69, 1152–1153; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536813016991.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N


