Abstract
C12H16O4S, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 10.7916(4) Å, b = 14.2171(5) Å, c = 8.7371(3) Å, β = 107.0210(10)°, V = 1281.77(8) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0333, wRref(F2) = 0.0926, T = 170.00 K.
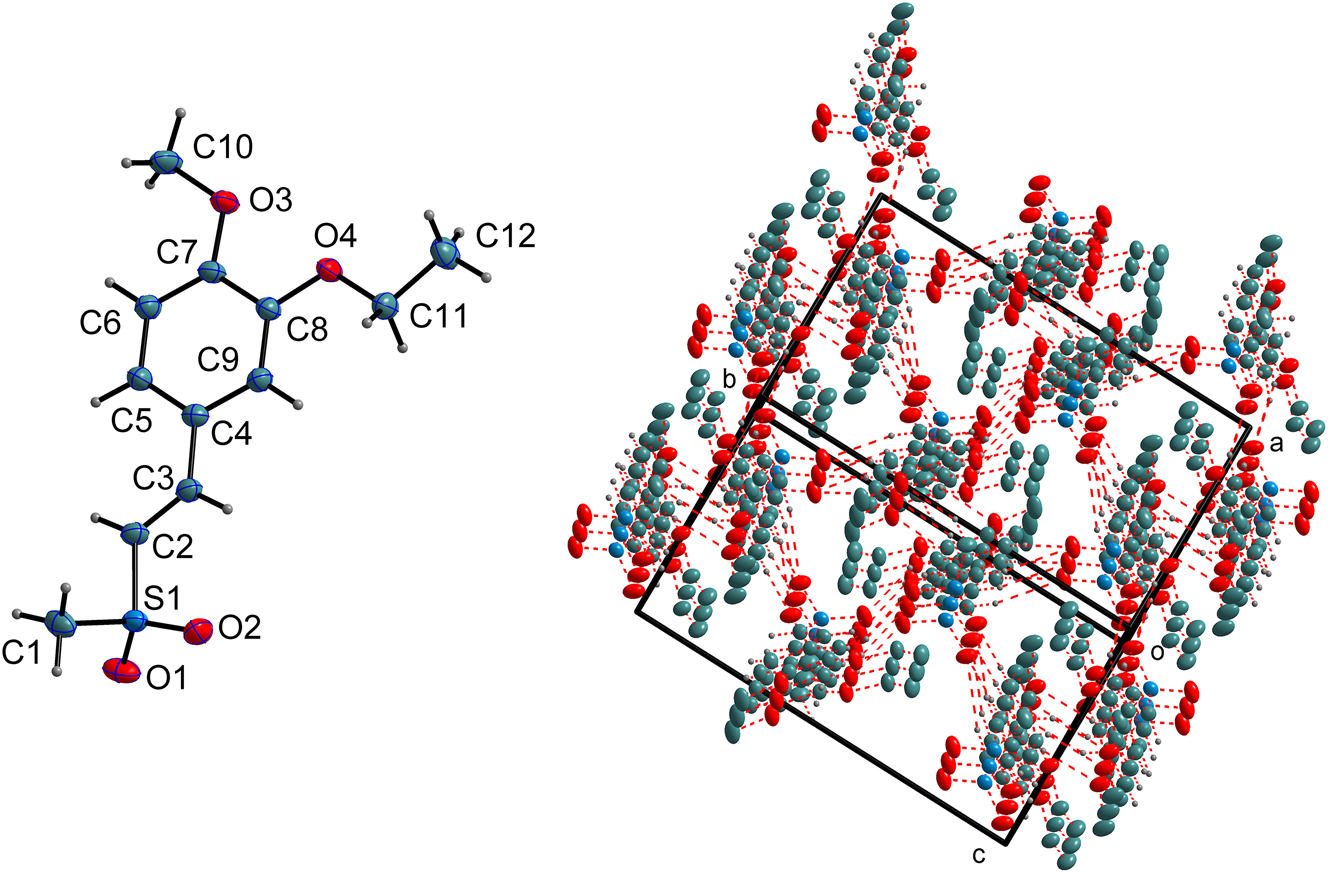
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Plate, colourless |
| Size: | 0.13 × 0.1 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Ga Kα radiation (1.34139 Å) |
| μ: | 1.49 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 60.6°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 15918, 2936, 0.031 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2613 |
| N(param)refined: | 157 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs, 1 OLEX2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 , PLATON 5 , 6 |
1 Source of materials
Purification of the crude title compound, (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene (6 g), was achieved by washing with petroleum ether. The material was suspended in petroleum ether (200 mL), and the solid was isolated by vacuum filtration. After washing the filter cake with additional petroleum ether (10 mL), the product was dried in vacuo at 40 °C, yielding (E)-1-ethoxy-2-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene as a white, crystalline powder. Single crystals of X-ray diffraction quality were obtained from the purified material: a solution of the compound (256 mg, 1.0 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) was prepared at room temperature and filtered into a small vial. The vial was covered with a perforated film, and slow evaporation of the solvent at ambient temperature afforded colorless plates over a period of several days.
2 Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and refined using a riding model. Methyl groups were treated as idealized rotating groups. The isotropic displacement parameters (Uiso) of the hydrogen atoms were constrained to 1.2 times the Ueq of their parent atom for the aromatic and methylene groups, and 1.5 times the Ueq for the methyl groups.
3 Comment
Apremilast, marketed under the trade name Otezla, is a first-in-class, orally administered small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4). Its development represents a significant advancement in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Apremilast is primarily indicated for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, active psoriatic arthritis, and oral ulcers associated disease. 7 , 8 As the management of these conditions has historically been dominated by injectable biologic agents, the oral route of administration for apremilast provides a critical therapeutic alternative, offering patients greater convenience and a distinct mechanism of action. 9
The title compound, (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, is a key intermediate in the convergent synthetic route to apremilast. The core framework of apremilast is assembled via a conjugate addition reaction, wherein the vinyl sulfone moiety of the title compound reacts with a nucleophilic phthalimide precursor. The (E)-geometry of this vinyl group is crucial for achieving high reactivity and diastereoselectivity in this transformation.
As part of our ongoing research interest on the structure-activity relationship about the antimicrobial agent, and understanding of hydrogen bonding schemes of related compounds, 10 , 11 , 12 this study presents the crystal structure of the title compound and provides a determination of its structure.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, contains one discrete molecule (cf. left part of the figure). The molecular structure of the title compound features a vinyl bridge (C2=C3) that connects the methylsulfonyl group to the substituted phenyl ring. The crystal diffraction data unambiguously establishes the configuration of this moiety. The geometry about the C2=C3 double bond is unequivocally assigned as E. This assignment is principally based on the C2–C3 bond distance of 1.328(2) Å, which is characteristic of a double bond, and the observed torsion angle of S1–C2–C3–C4, which is 178.44(11)°. A value proximal to ±180° indicates an anti-periplanar conformation of the connected S1 and C4 atoms across the vinyl group. This arrangement is likely the thermodynamically more stable isomer, as it minimizes the steric hindrance between the bulky sulfonyl and aryl groups.
A distinctive feature in the molecular conformation of the title compound is the high degree of planarity exhibited by its core structure. This extensive planar region comprises the phenyl ring, methoxy and ethoxy groups, vinyl bridge (C2=C3), and the S atom of the sulfonyl group (C4–C5–C6–C7–C8–C9–O3–C10–C11–O4–C12–C3–C2–S1). The RMS deviation of the plane is 0.0396 Å. Among these atoms, the greatest deviation from the calculated plane is observed for the C10 atom of the methoxy group, with a perpendicular distance of 0.1018 Å from the plane. To our best search, this conjugated planar structure moiety has not been previously reported in crystallographic literature. This spatial arrangement appears to achieve a favorable balance between maximizing electronic conjugation effects and minimizing steric hindrance between substituents.
In detail, the phenyl ring itself is planar. The vinyl group is observed to be nearly coplanar with the aromatic ring. This is quantitatively supported by the torsion angle C2–C3–C4–C9 (174.05(14)°). Additionally, the orientations of the methoxy and ethoxy substituents position their oxygen atoms and the first carbon atoms of their alkyl chains almost in the plane of the phenyl ring (e.g., C10–O3–C7–C6 = 5.3(2)°; C11–O4–C8–C9 = 3.8(2)°).
Smaller planar molecular fragments consisting of the phenyl ring, methoxy and ethoxy groups, and vinyl bridge, (C4–C5–C6–C7–C8–C9–O3–C10–C11–O4–C12–C3–C2), have been previously reported in the literature. 13 , 14 , 15
The crystal structure is stabilized by a network of weak C–H⋯O hydrogen bonding interactions (cf. right part of the figure. Some hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity). These include: C1–H1C⋯O3I with D⋯A = 3.373(2) Å, where I = 1−x, 1−y, 1−z; C2–H2⋯O1II with D⋯A = 3.3093(18) Å, where II = x, 3/2−y, 1/2+z; C5–H5⋯O1III with D⋯A = 3.3997(18) Å, where III = x, 3/2−y, 1/2+z; and C9–H9⋯O2IV with D⋯A = 3.1999(17) Å, where IV = 1−x, 1−y, −z. Additionally, there is an intramolecular hydrogen bond (medium strong): C3–H3⋯O2, with D⋯A distance of 2.8974(17) Å. These interactions connect the molecules into a two-dimensional network structure along the bc direction.
In addition to hydrogen bonds, the crystal packing is further stabilized by π–π stacking interactions. The phenyl rings of adjacent molecules are related through an inversion center and arranged in a parallel-displaced manner. The distance between ring centroids is 3.905 Å, with a perpendicular distance of 3.499 Å and a slippage distance of 1.733 Å.
The structure also exhibits a weak C–H⋯π interaction between a methyl hydrogen atom (H10A) and the phenyl ring of an adjacent molecule, with an H⋯Cg (centroid) distance of 2.95 Å. This intermolecular interaction occurs along the crystallographic direction (x, 3/2 −y, 1/2+z).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support by Ningbo Polytechnic University Zhejiang Collaborative Innovation Center, and Ningbo Polytechnic Academician Workstation.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted: responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Smart and Saint; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2019.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42 (2), 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxt – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. A 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Spek, A. L. Single-Crystal Structure Validation with the Program Platon. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36 (1), 7–13; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889802022112.Search in Google Scholar
6. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
7. Papp, K.; Reich, K.; Leonardi, C. L.; Kircik, L.; Chimenti, S.; Langley, R. G. B.; Hu, C.; Stevens, R. M.; Day, R. M.; Gordon, K. B.; Korman, N. J.; Griffiths, C. E. M. Apremilast, an Oral Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) Inhibitor, in Patients with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Results of a Phase III, Randomized, Controlled Trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73 (1), 37–49; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.049.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Schafer, P. Apremilast Mechanism of Action and Application to Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83 (12), 1583–1590; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.001.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Venkateswaralu, J.; Rajendiran, C.; Reddy, N. R.; Connolly, T. J.; Ruchelman, A. L.; Eckert, J.; Frank, A. J. Processes for the Preparation of (S)-1-(3-Ethoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methanesulfonylethylamine. United States Patent 20130217918A1 2013.Search in Google Scholar
10. Li, Y.; Wang, J. The Crystal Structure of Ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]Thiazole-3-Carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2025, 240 (3), 479–481; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2025-0069.Search in Google Scholar
11. Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. The Crystal Structure of 3-((4-Chloro-N-(2-methoxyethyl)benzamido)methyl)phenyl Methanesulfonate, C18H20ClNO5S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237 (6), 1033–1036; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0376.Search in Google Scholar
12. Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. The Crystal Structure of Ethyl 2,3,5-trifluoro-4-(4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyridin-1(2H)-yl)benzoate, C14H12F3NO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct 2022, 237 (6), 1087–1089; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0412.Search in Google Scholar
13. Huck, D. M.; Nguyen, H. L.; Horton, P. N.; Hursthouse, M. B.; Guillon, D.; Donnio, B.; Bruce, D. W. Mesomorphic Silver(I) Complexes of Polycatenar 2′- and 3′-Stilbazoles. Crystal and Molecular Structure of 3,4-Dimethoxy-3′-Stilbazole and of Two Silver Triflate Complexes. Polyhedron 2006, 25 (2), 307–324; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2005.07.023.Search in Google Scholar
14. Kolev, T.; Yancheva, D.; Kleb, D.-C.; Schürmann, M.; Glavcheva, Z.; Preut, H.; Bleckmann, P. Crystal Structure of 2-{3-[2-(3-Ethoxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-viny 1]-5,5-dimethyl-cyclohex-2-enylidene}-malononitrile, C22H24N2O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2001, 216 (1–4), 67–68; https://doi.org/10.1524/ncrs.2001.216.14.67.Search in Google Scholar
15. Jasinski, J. P.; Miller, W. M.; Samshuddin, S.; Narayana, B.; Yathirajan, H. S. (2E)-3-{4-[(1H-1,3-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methoxy]-3-ethoxyphenyl}-1-(4-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one Monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. E 2011, 67 (4), o834–o835; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536811008154.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N


