Abstract
C15H14O2N4S, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 7.4484(6) Å, b = 17.3543(15) Å, c = 11.7814(9) Å, β = 106.377(3)°, V = 643.50(8) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0853, wRref(F2) = 0.0871, T = 100 K.
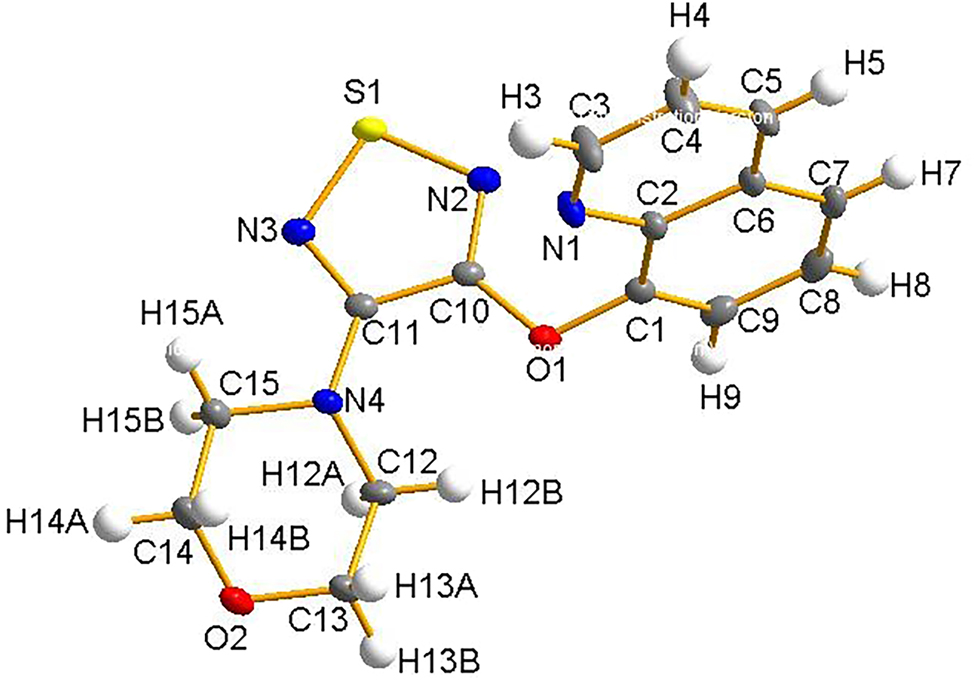
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.19 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.24 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex-II, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.4°, > 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 32252, 3621, 0.047 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 3399 |
| N(param)refined: | 199 |
| Programs: | Shelx, 1 Bruker programs, 2 Olex2, 3 Diamond 4 |
1 Source of materials
The title compound was synthesized by dissolving (200 mg, 1.38 mmol) of 8-hydroxyquinoline and (353 mg, 1.53 mmol, 1.10 equiv) of 4-(4-chloro-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine in 10 mL of anhydrous DMF under nitrogen. An amount of 910 mg (2.80 mmol, 2 equiv) of cesium carbonate was added to the reaction mixture, and the reaction was stirred at 120 °C for 18–24 h, monitored by TLC. Upon completion, the reaction was cooled, poured into 20 mL of water, and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography using ethyl acetate:hexane (3:7), and the product was recovered as a light-yellow solid. The product was dissolved in 5 mL of acetone and left to crystallize, resulting in the formation of light-yellow crystals.
2 Experimental details
All H-atoms were positioned on geometrically idealized positions and refined using the riding model with fixed C–H distances for aromatic C–H of 0.95 Å (C–H) [Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq]. The graphics were obtained using the DIAMOND 4 program with 50 % probability ellipsoids.
3 Comment
The molecular structure of 4-(4-((1,2-dihydroquinolin-8-yl)oxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl) morpholine was elucidated by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The thiadiazole ring exhibits nearly identical S–N bond lengths of S1–N2 1.6493(10) Å and S1–N3 1.6534(10) Å, consistent with delocalization across the heteroaromatic system. These values are in good agreement with reported bond lengths for neutral thiadiazole derivatives, which typically range from 1.64 to 1.68 A. 5 The short N2–C10 1.3024(13) Å and N3–C11 1.3211(14) Å bond distances indicate pronounced double-bond character. The S1–N2–C10 106.62(8)° and S1–N3–C11 107.82(8)° bond angles are notably smaller than the ideal 120° value, reflecting angular compression common in five-membered thiadiazole systems. 6 The quinoline fragment shows bond distances characteristic of aromatic heterocycles, with N1–C2 1.3657(13) Å and N1–C3 1.3140(15) Å bond distances both consistent with partial double-bond character. The C3–N1–C2 bond angle of 116.67(9)° is consistent with sp2 hybridization, and the C–C bond distances (1.36–1.42 A) also fall within the range expected for conjugated heteroaromatic rings. 7 The morpholine ring adopts a chair conformation, with N–C distances of N4–C11 1.3823(13) Å, N4–C12 1.4733(14) Å, and N4–C15 1.4657(14) Å. These values correspond closely to those reported for other morpholine-containing compounds. 8 , 9 Bond angles around N4, such as C11–N4–C12 116.63(9)° and C11–N4–C15 114.87(9)°, confirm slightly distorted tetrahedral geometry, which is frequently observed due to conformational strain in six-membered heterocycles. 8 The ether linkage connecting the quinoline and thiadiazole fragments is defined by O1–C10 1.3586(13) Å and O1–C1 1.3959(12) Å bond distances. These distances fall within the typical range for aryl–O-alkenyl bonds, while the C10–O1–C1 bond angle is 115.08(8)°. 10
Acknowledgements
University of Johannesburg is highly acknowledged for funding.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of Shelx. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
2. Bruker SAINT–Plus (Version 7.12) and SADABS (Version 2004/1), Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2004.Search in Google Scholar
3. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. Diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 3.0c; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2005.Search in Google Scholar
5. Aldoshin, S. M.; Rakitin, O. A.; Karasev, V. E.; Novikov, A. S. Structural Studies of Neutral1,2,5–Thiadazole Derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 4673.Search in Google Scholar
6. Akhter, M.; Sivakumar, R.; Aravindan, P. G.; Butcher, R. J. Bonding Features and Aromaticity in Thiadazoles. Acta Crystallogr. 2006, C62, o2067–o2071.Search in Google Scholar
7. Khuntia, S.; Mandal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Crystal Structres of Quinoline Derivatives, Bonding and Aromaticity. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1141, 25–32.Search in Google Scholar
8. Ragunathan, K. G.; Balakrishnan, T.; Nagarajan, S. Conformational Features of Morpholine Derivates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4215–4219.Search in Google Scholar
9. Willis, B. T. M.; Powell, A. K.; Blake, A. J. Structural Insights into Morpholine Substituted Heterocyles. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 3630–3641.Search in Google Scholar
10. Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X. Bonding Features in Aryl-O-Heteroaryl Ethers. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 5425–5432.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N


