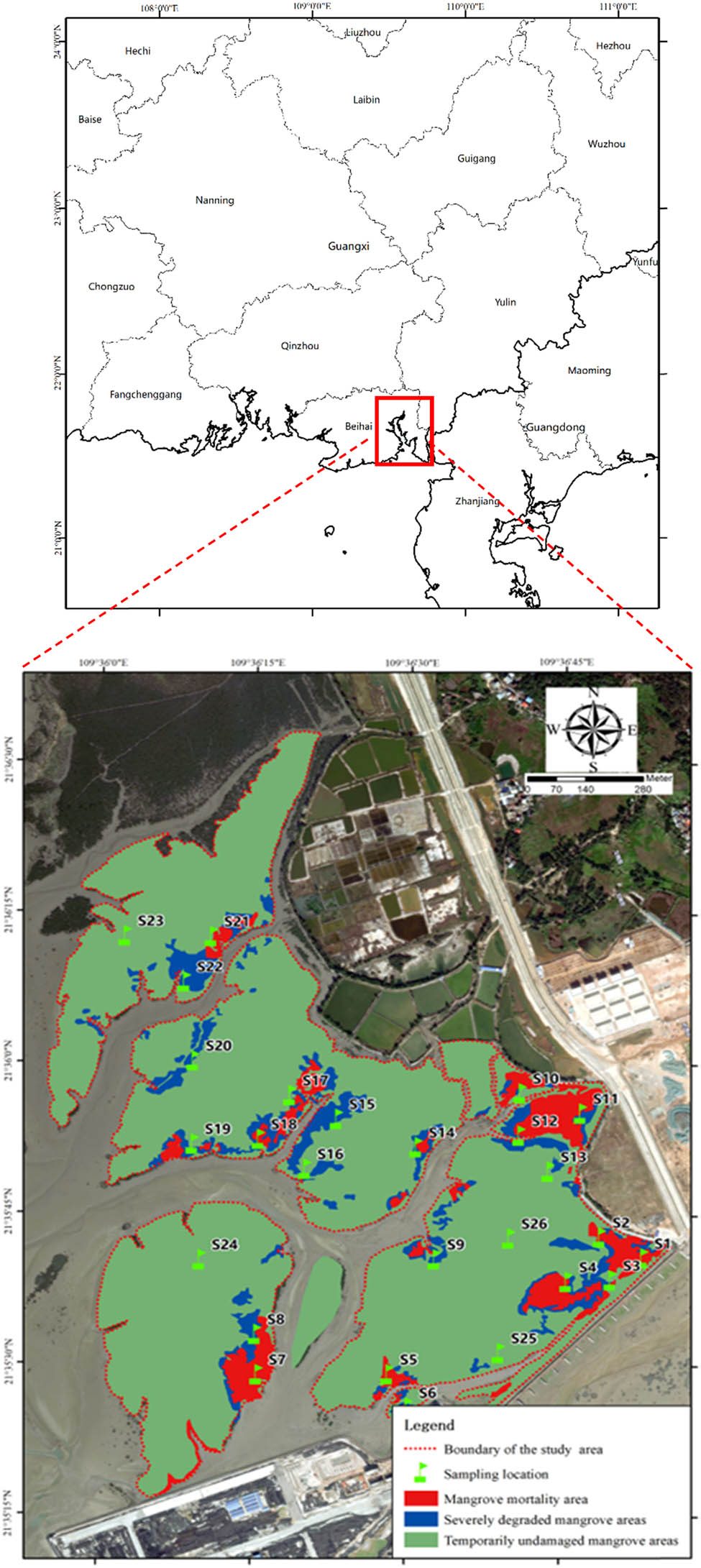
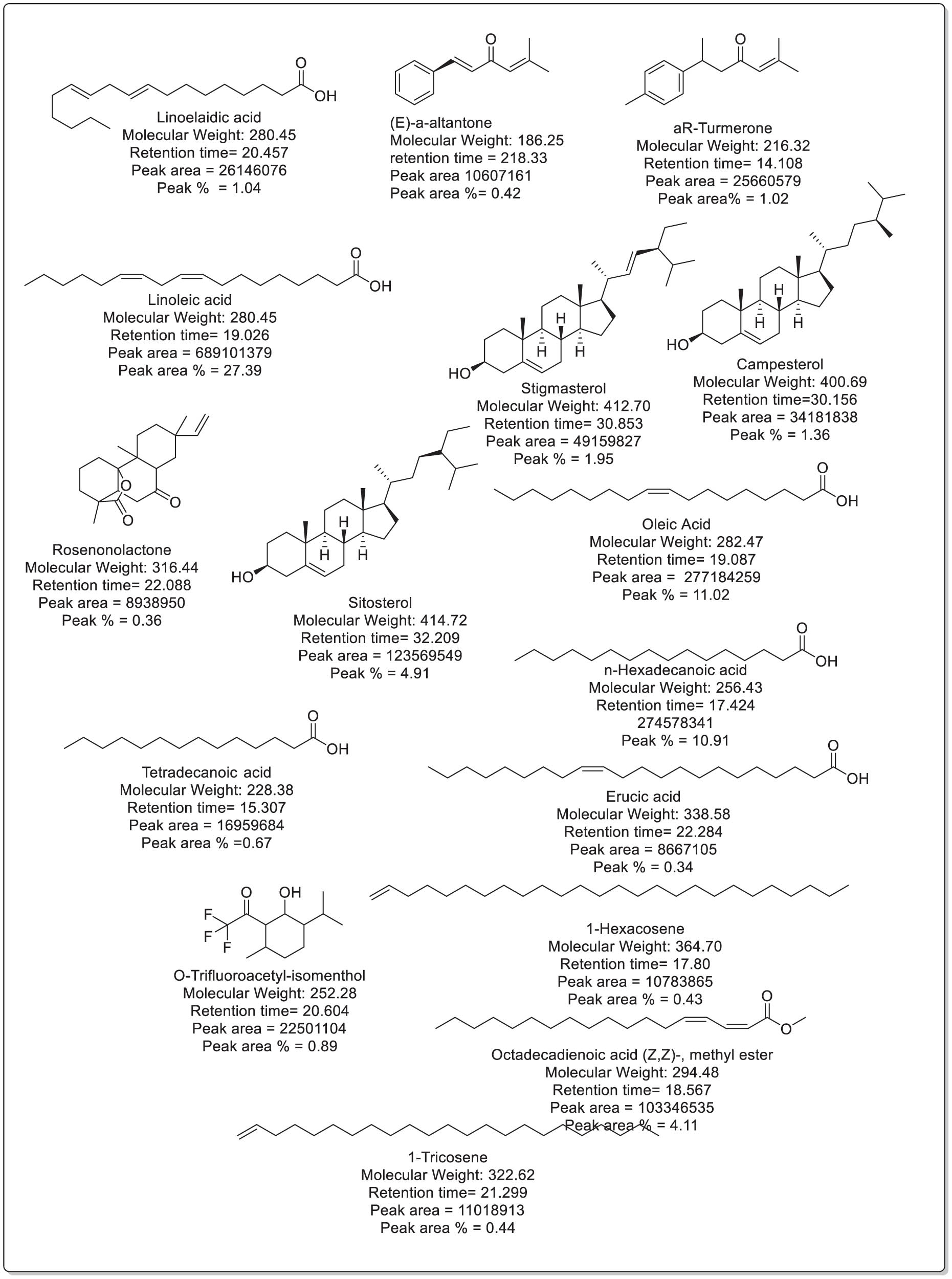
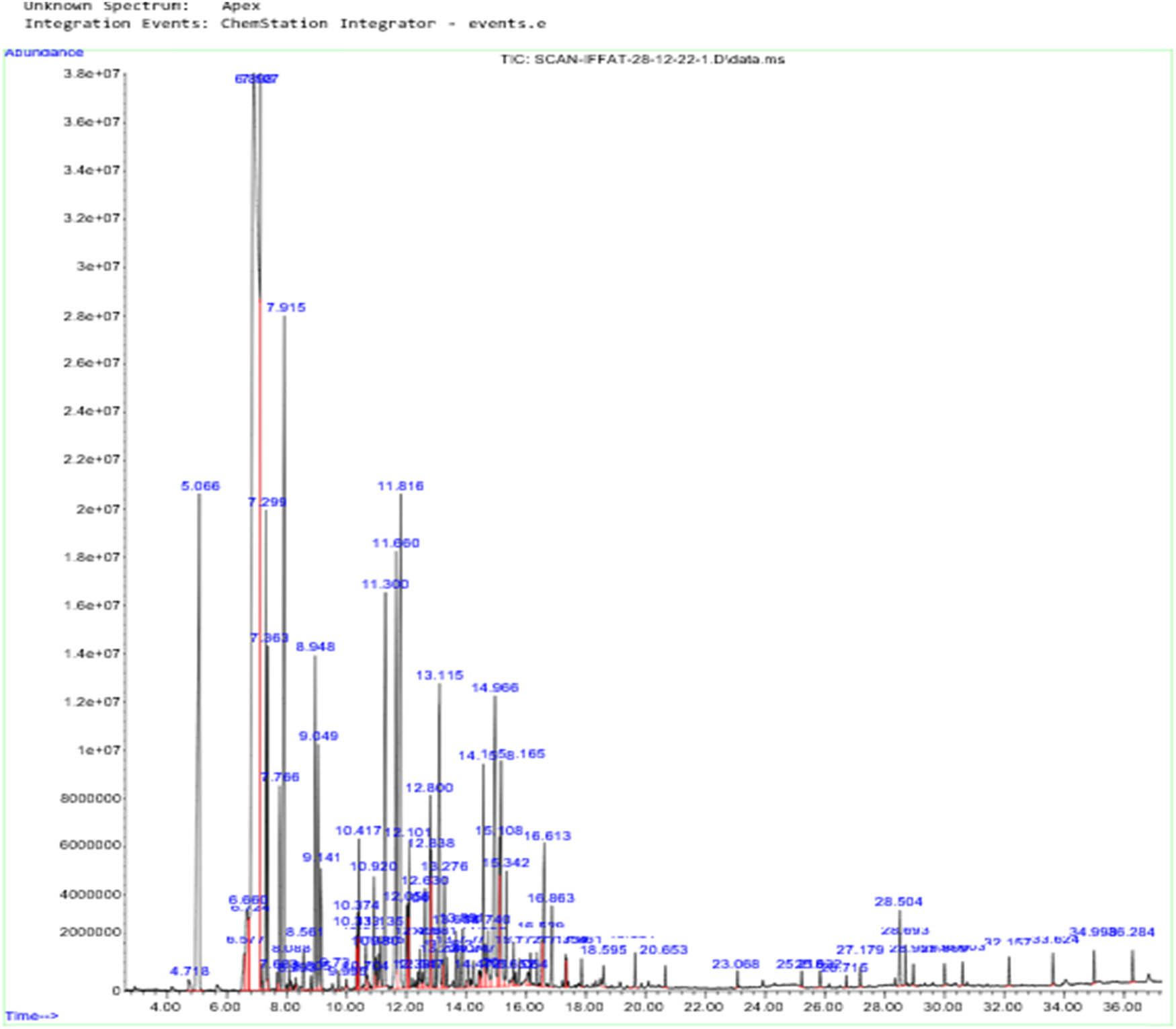
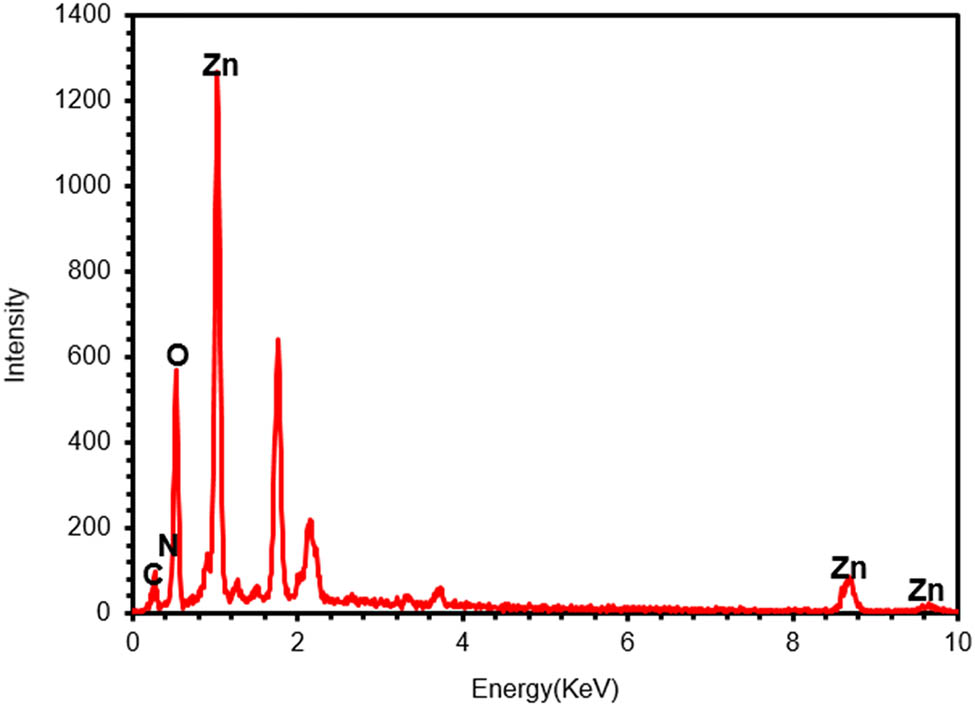
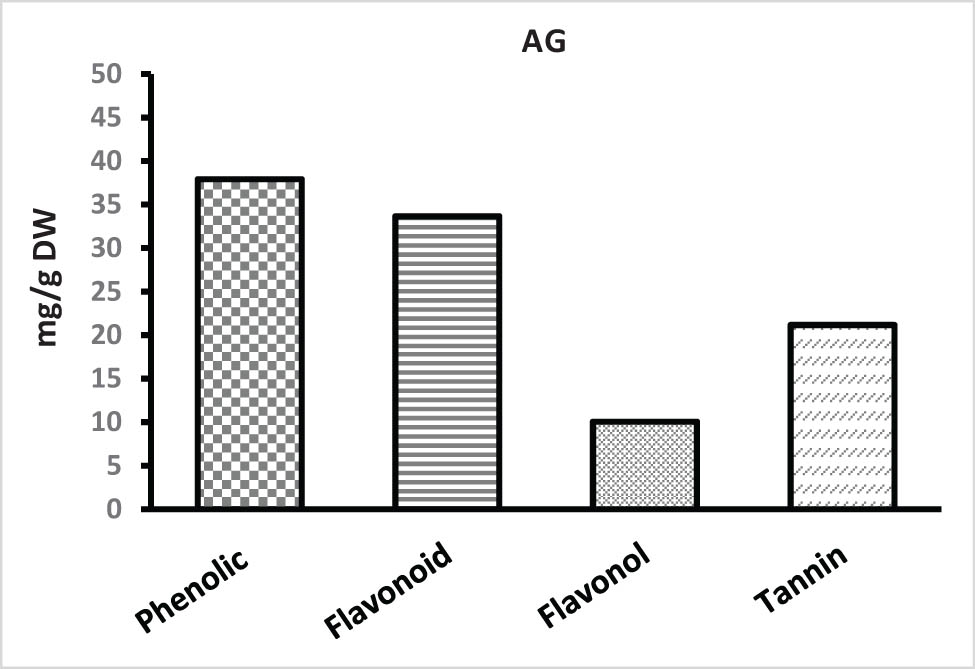
Diabetes mellitus is a global health problem requiring innovative approaches for effective management. Natural compounds derived from medicinal plants offer promising avenues due to their diverse biological activities. The aim of this study was to assess the inhibitory effects of Cedrus atlantica extracts on the enzymes α-amylase and α-glucosidase, which play a crucial role in the regulation of postprandial glucose levels, as well as to investigate their phytochemical composition and antioxidant capabilities. Aqueous extract of bark (EA), aqueous extract of cones (CA), and aqueous extract of leaves (FA) of C. atlántica were prepared and evaluated for enzyme inhibition using acarbose as a standard. The CA extract showed potent α-amylase inhibition (IC 50 307 ± 0.02 μg/mL) and remarkable α-glucosidase inhibition (IC 50 70 ± 0.04 μg/mL), outperforming the FA and EA extracts. Quantitative analysis revealed that EA and CA extracts had higher total phenolic content, flavonoid content, and tannin content than FA extract. Antioxidant assessments highlighted the outstanding performance of CA extract, with a low IC 50 ABTS (30.65 ± 0.1 μg/mL) and an impressive EC 50 FRAP (59.43 ± 1.19 μg/mL), outperforming FA extract. The results demonstrate the remarkable antidiabetic potential of C. atlantica extracts, particularly the CA extract, by inhibiting key enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion. These extracts possess various phytochemical compounds with significant antioxidant capacities, suggesting that they are suitable for pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic applications. Further research to isolate and identify the bioactive compounds in CA extract could lead to new therapeutic strategies for managing diabetes and oxidative stress-related conditions.
Contents
- Research Articles
-
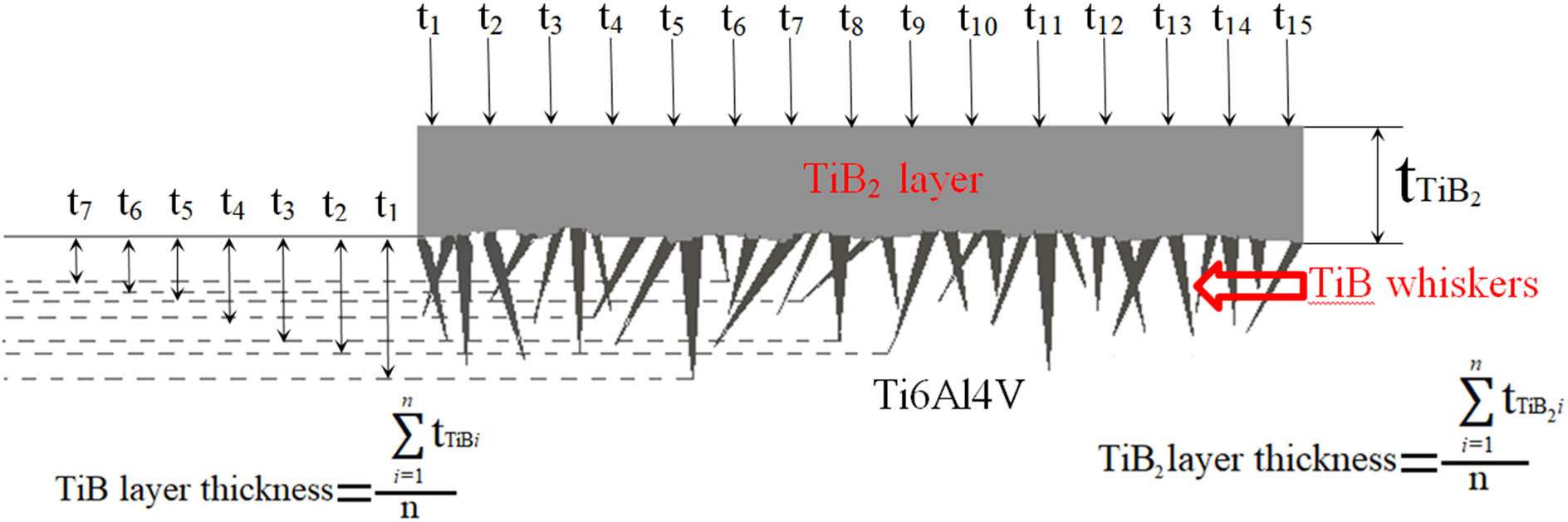
Open AccessInfluence of B4C addition on the tribological properties of bronze matrix brake pad materialsJanuary 22, 2025
-
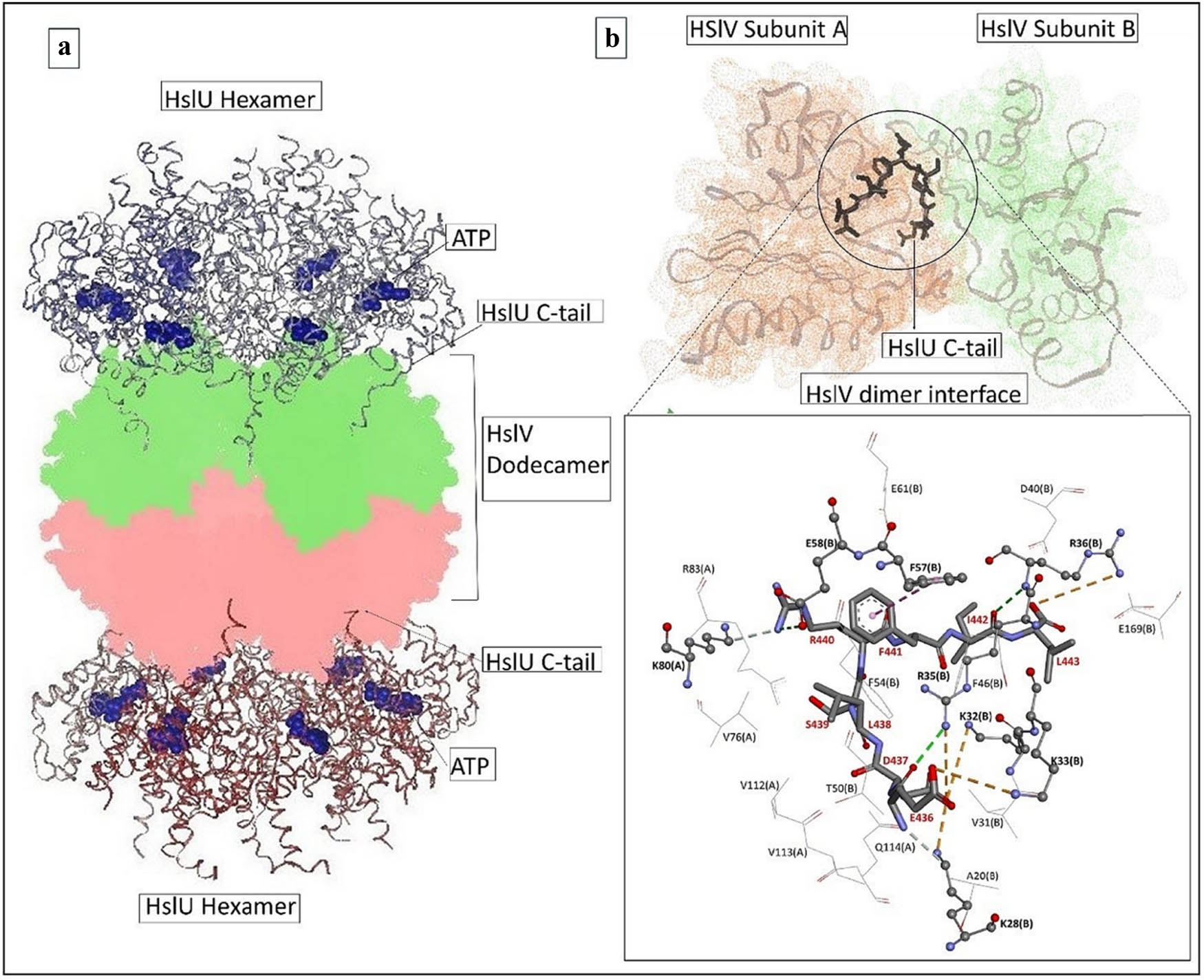
Open AccessDiscovery of the bacterial HslV protease activators as lead molecules with novel mode of actionFebruary 3, 2025
-
February 26, 2025
-
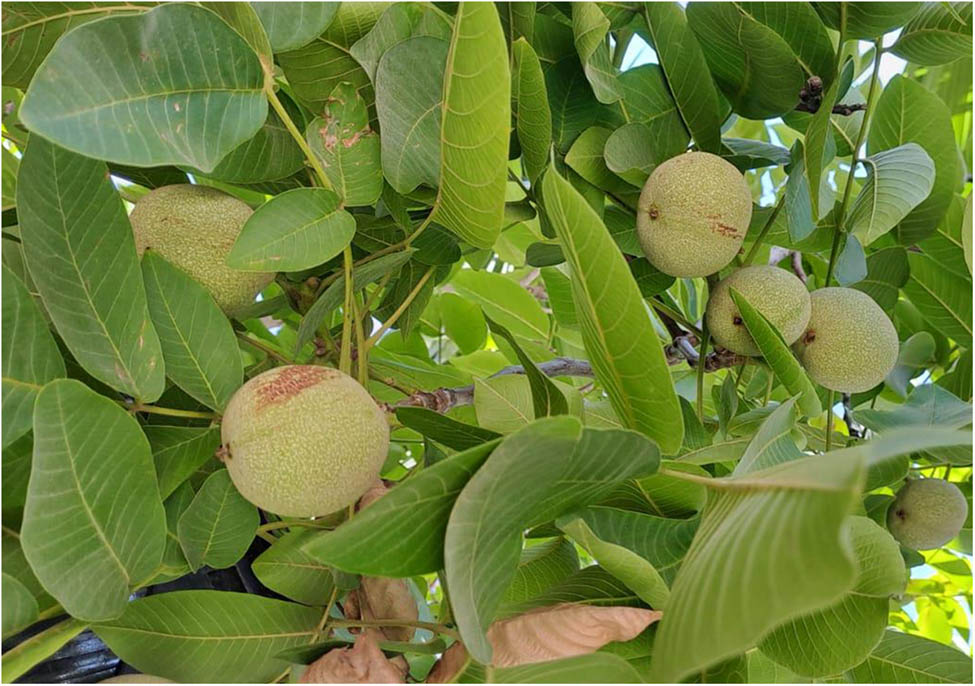
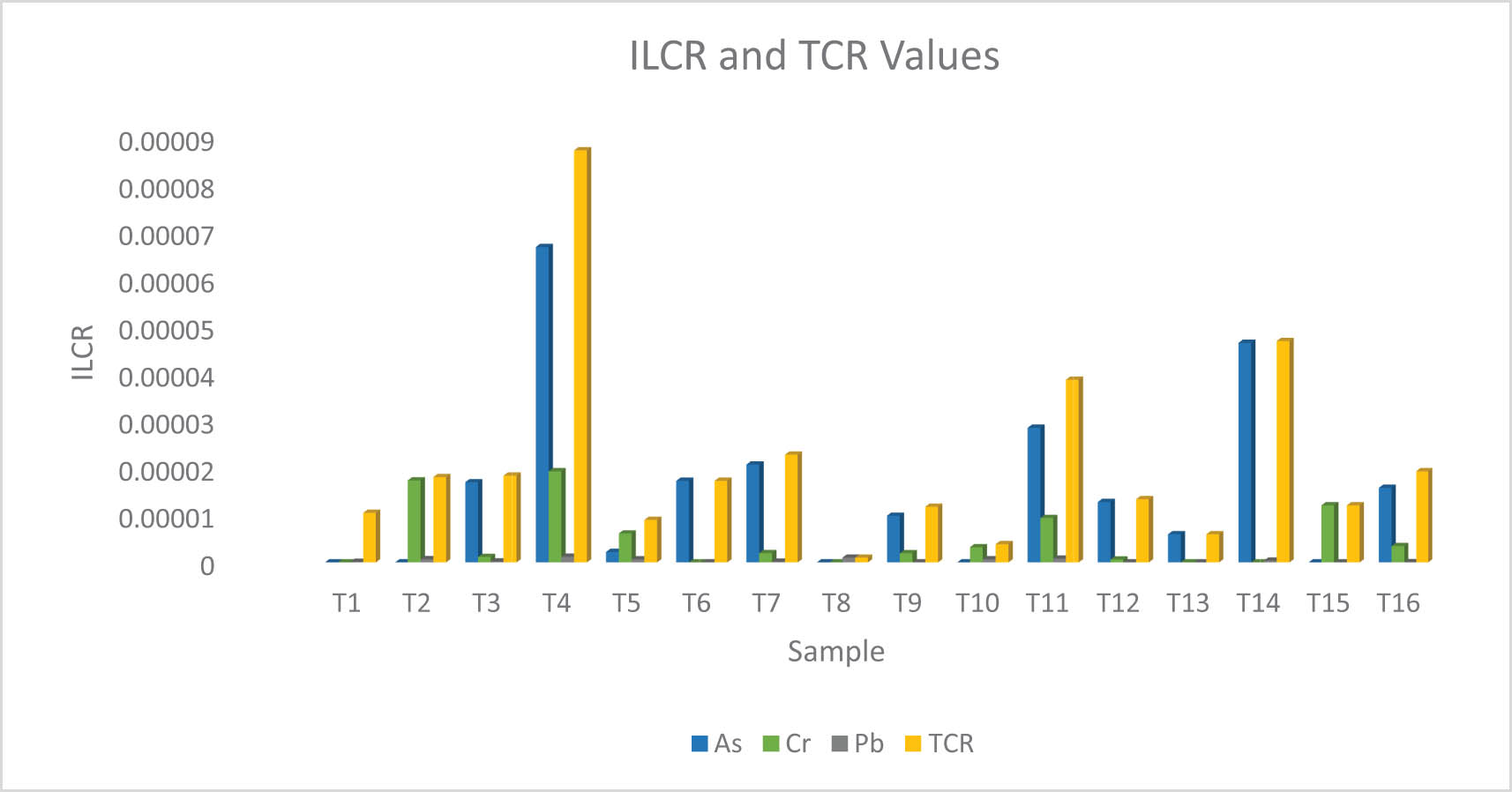
Open AccessAnalysis and health risk assessment of toxic elements in traditional herbal tea infusionsFebruary 28, 2025
-
Open AccessCadmium exposure in marine crabs from Jiaxing City, China: Insights into health risk assessmentMarch 3, 2025
-
Open AccessGreen-synthesized silver nanoparticles of Cinnamomum zeylanicum and their biological activitiesMarch 3, 2025
-
March 18, 2025
-
March 29, 2025
-
April 4, 2025
-
Open AccessRemoval of antiviral favipiravir from wastewater using biochar produced from hazelnut shellsApril 15, 2025
-
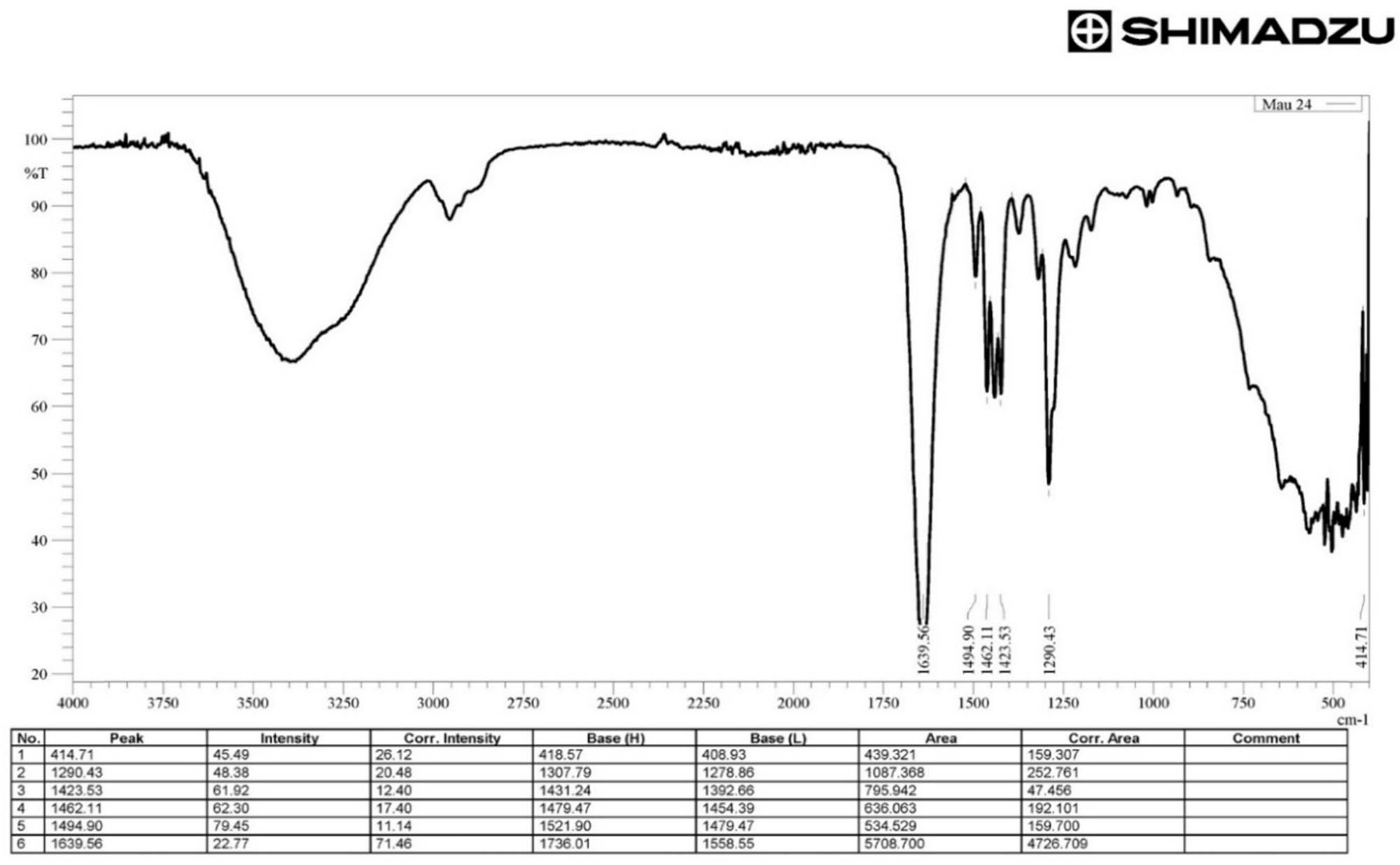
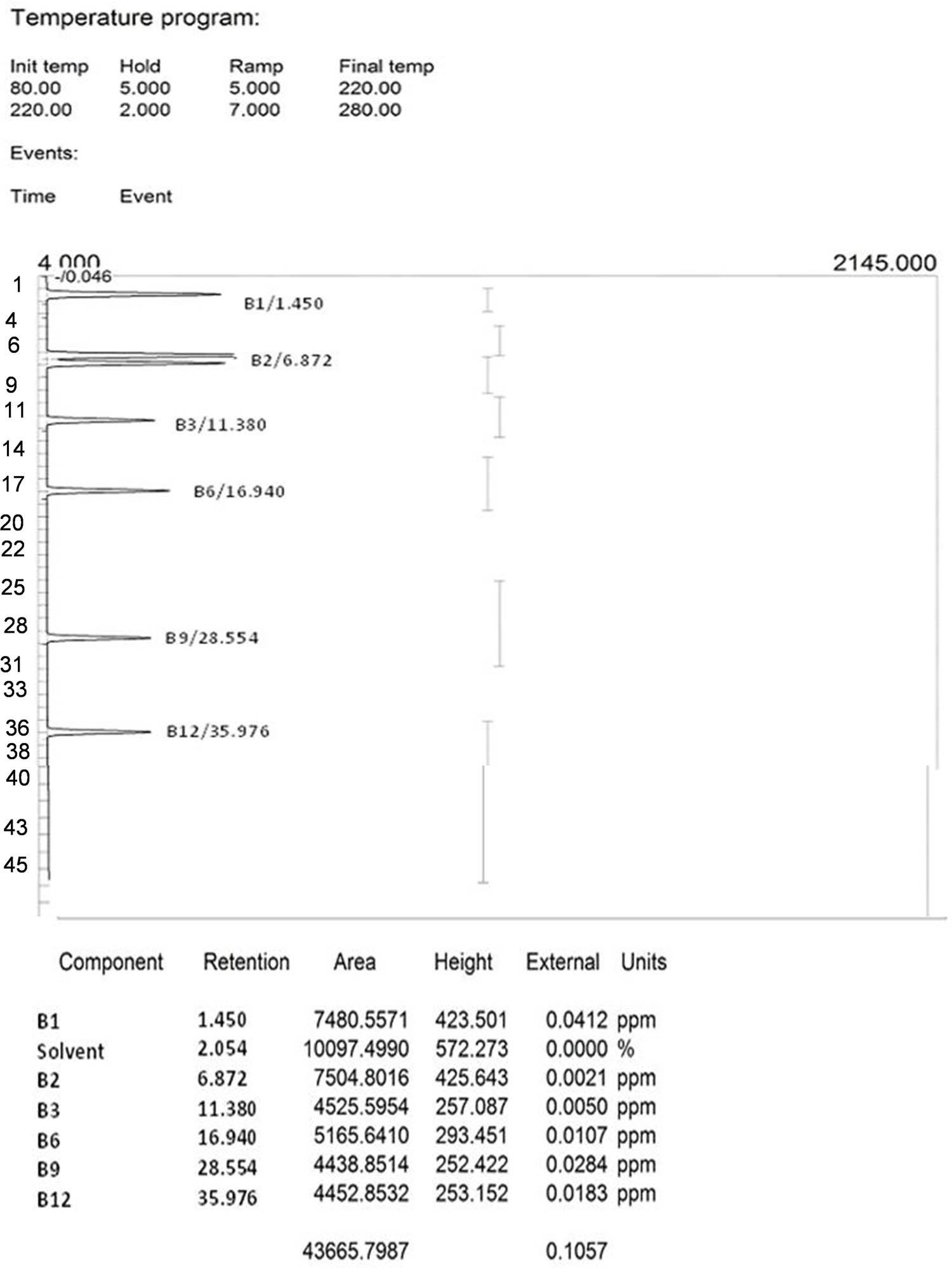
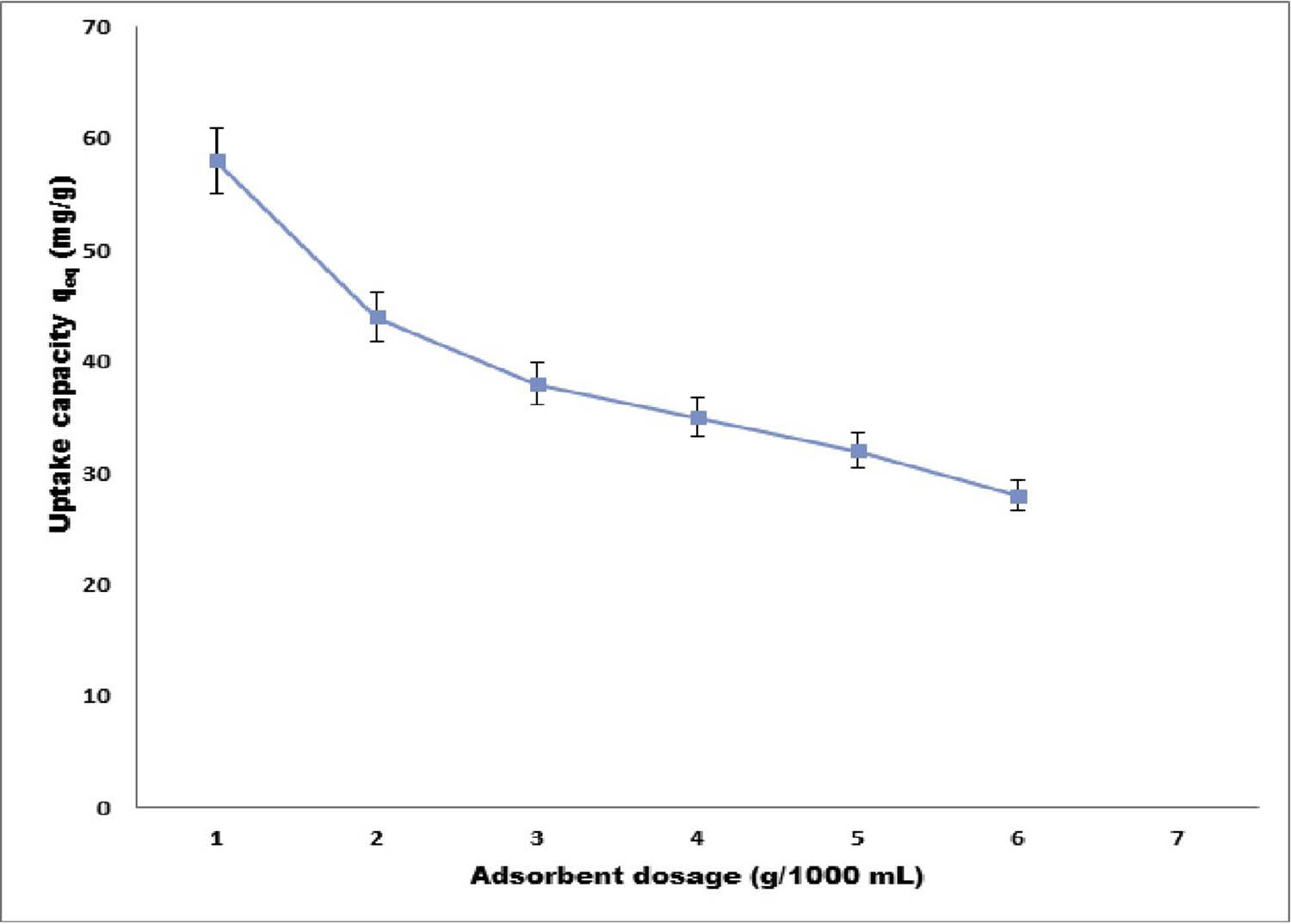
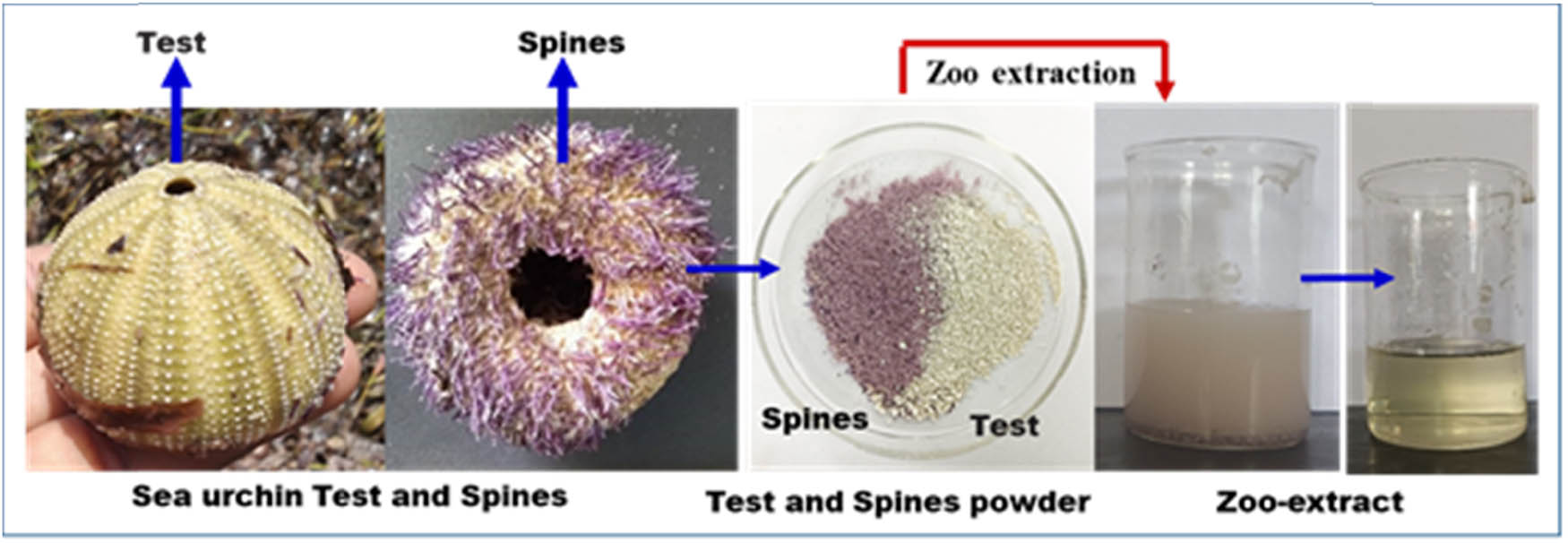
Open AccessNovel insecticidal properties of bioactive zoochemicals extracted from sea urchin Salmacis virgulataApril 23, 2025
-
Open AccessPreparation and wastewater treatment performance of zeolite-modified ecological concreteMay 3, 2025
-
May 12, 2025
-
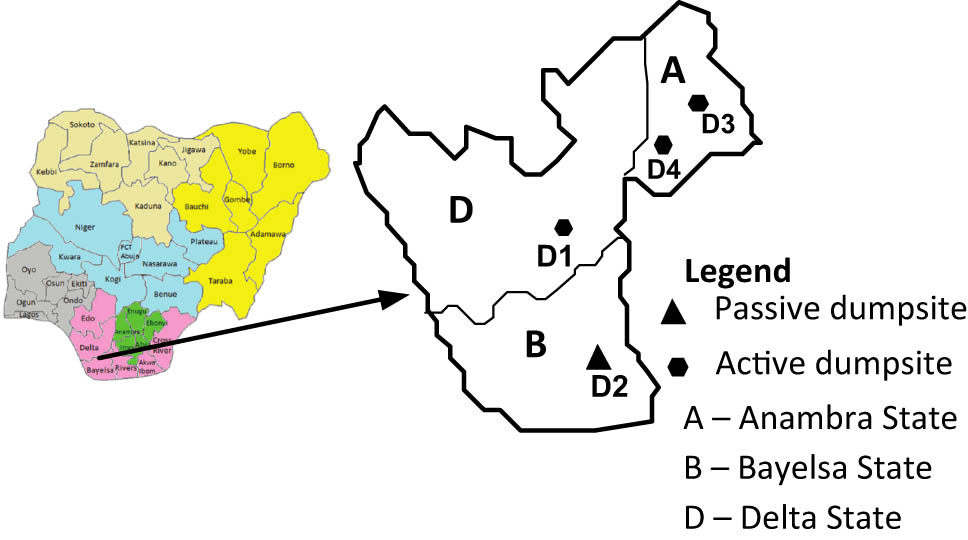
Open AccessElectrochemical and microbiological effects of dumpsite leachates on soil and air qualityMay 26, 2025
-
May 30, 2025
-
June 24, 2025
-
Open AccessStability studies of titanium–carboxylate complexes: A multi-method computational approachJuly 9, 2025
-
Open AccessEfficient adsorption performance of an alginate-based dental material for uranium(vi) removalJuly 10, 2025
-
August 26, 2025
-
Open AccessCorrelation study between GC–MS analysis of cigarette aroma compounds and sensory evaluationSeptember 11, 2025
-
Open AccessThe influence of feed space velocity and pressure on the cold flow properties of diesel fuelSeptember 18, 2025
-
Open AccessAcid etching behavior and mechanism in acid solution of iron components in basalt fibersSeptember 18, 2025
-
September 24, 2025
- Special Issue on Advancing Sustainable Chemistry for a Greener Future
- Special Issue on Phytochemicals, Biological and Toxicological Analysis of Plants
-
May 28, 2025
-
Open AccessChemical profile of Senna italica and Senna velutina seed and their pharmacological propertiesJune 20, 2025