Abstract
We applied an optimal control algorithm to an ultra-cold atomic system for constructing an atomic Sagnac interferometer in a ring trap. We constructed a ring potential on an atom chip by using an RF-dressed potential. A field gradient along the radial direction in a ring trap known as the dimple-ring trap is generated by using an additional RF field. The position of the dimple is moved by changing the phase of the RF field [1]. For Sagnac interferometers, we suggest transferring Bose–Einstein condensates to a dimple-ring trap and shaking the dimple potential to excite atoms to the vibrational-excited state of the dimple-ring potential. The optimal control theory is used to find a way to shake the dimple-ring trap for an excitation. After excitation, atoms are released from the dimple-ring trap to a ring trap by adiabatically turning off the additional RF field, and this constructs a Sagnac interferometer when opposite momentum components are overlapped. We also describe the simulation to construct the interferometer.
1 Introduction
Atom interferometers are dynamic tools applied for precision measurements and for studying the wave nature of interacting matter over the past few decades. Measurements of inertial effects such as acceleration and rotation [2,3,4,5], physical constants [6,7], gravitational constant [8,9], and dark energy [10,11] in free space have been demonstrated. Interferometers in a confined trap using the wave nature of matter have also been constructed in various potentials such as multi-well [12,13], ring [14,15,16,17,18], optical lattice [19,20,21,22], and certain wave-guide traps [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Atom interferometers require splitting, reflecting, and recombining coherent sources just as an optical interferometer. Various ways have been adopted to realize interferometric components by using Raman pulse [2,3,4,5,7], Bragg diffraction [25,26,27], and adiabatically changing trapping potentials [11,12].
An optimal control algorithm is a process to find a way from the initial state to the desired state by perturbing systems. It was adopted to optimize atomic systems and manipulate the desired atomic states such as
In this article, we describe a process to demonstrate an atomic Sagnac interferometer using ultra-cold atoms by using a vibrational-excited state in a ring trap potential. The RF-dressed trapping potentials that we experimentally demonstrated for a ring and a dimple-ring trap in ref. [1] are reviewed in Section 2. In Section 3, we introduce a way to construct a Sagnac interferometer. First, we adiabatically load ultra-cold atoms from the initial trapping potential to the ground state of the dimple-ring potential. And then, we shake the dimple-ring potential to excite atoms. The way to shake the potential is obtained from an optimal control algorithm. We describe the details of the optimal control algorithm we used in Section 3. The excited atoms are released to a ring potential, and they start to expand. We also simulated the Sagnac interferometry when opposite momentum components are overlapped.
2 RF-dressed dimple-ring potential
We demonstrated dimple-ring potential near an atom chip by using an RF-dressed potential [1,33]. Figure 1 shows the pattern of wires on our atom chip. We used the center wire to create an Ioffe magnetic trap with a bias magnetic field and the dimple wire for enhancing the longitudinal confinement of the trap. Each side wire, RF A and B, is used to create an RF-dressed potential, and the RF field on the center wire creates asymmetry in the potential such as the tilted double-well and dimple-ring potential [1]. The magnetic field is given by static,
where G is the gradient of the static trap and
![Figure 1
(a) Wire pattern for the dimple-ring potential; (b) dimple-ring potential as
δ
z
{\delta }_{z}
, where G = 50 T/m,
B
I
{B}_{\text{I}}
=
B
RF
{B}_{\text{RF}}
= 1 G,
B
RF
Z
{B}_{\text{RF}}^{Z}
= 100 mG,
ω
RF
{\omega }_{\text{RF}}
= 2π × 650 kHz, and δ = π/2 [1].](/document/doi/10.1515/phys-2020-0171/asset/graphic/j_phys-2020-0171_fig_001.jpg)
(a) Wire pattern for the dimple-ring potential; (b) dimple-ring potential as
RF-induced potential can be written as the following equation:
In equation (3),
The effective field in equation (5) is calculated as follows:
with a rotating matrix,
Since the detuning term is rotationally symmetric in the cylindrical coordinate, the coupling term determines the geometry of the RF-dressed potential. For simplicity, we assumed
where
Figure 1 shows the wire pattern of our chip and the potential for the dimple-ring trap as δ z , described by equations (6) and (7).
When
3 Optimal control algorithms for exciting atoms in a dimple-ring trap
We suggest the following method for constructing a Sagnac-type atom interferometer using a ring potential. First, we generated condensed atoms in an Ioffe trap, and then we transferred the atoms to a dimple-ring trap, i.e., to one of the dimples shown in Figure 1(b). We were able to add momentum to atoms by shaking the dimple-ring potential along the tangential direction to excite atoms in the trap. In order to make the excitation, we applied an optimal control algorithm to find a way of shaking the dimple-ring potential by changing
For simplicity, we assume that the trap and the perturbation are in one dimension to apply an optimal algorithm. In Figure 2, blue shows the initial state as the ground state in a dimple-ring trap, and red shows the desired state, which is the first excited state. When the 1D trapping potential is in black (Figure 2), we solved the Gross–Pitaevskii equation (GPE) to find the ground state of condensed atoms, and the excited state is calculated by optimizing GPE orthogonality with the ground state.
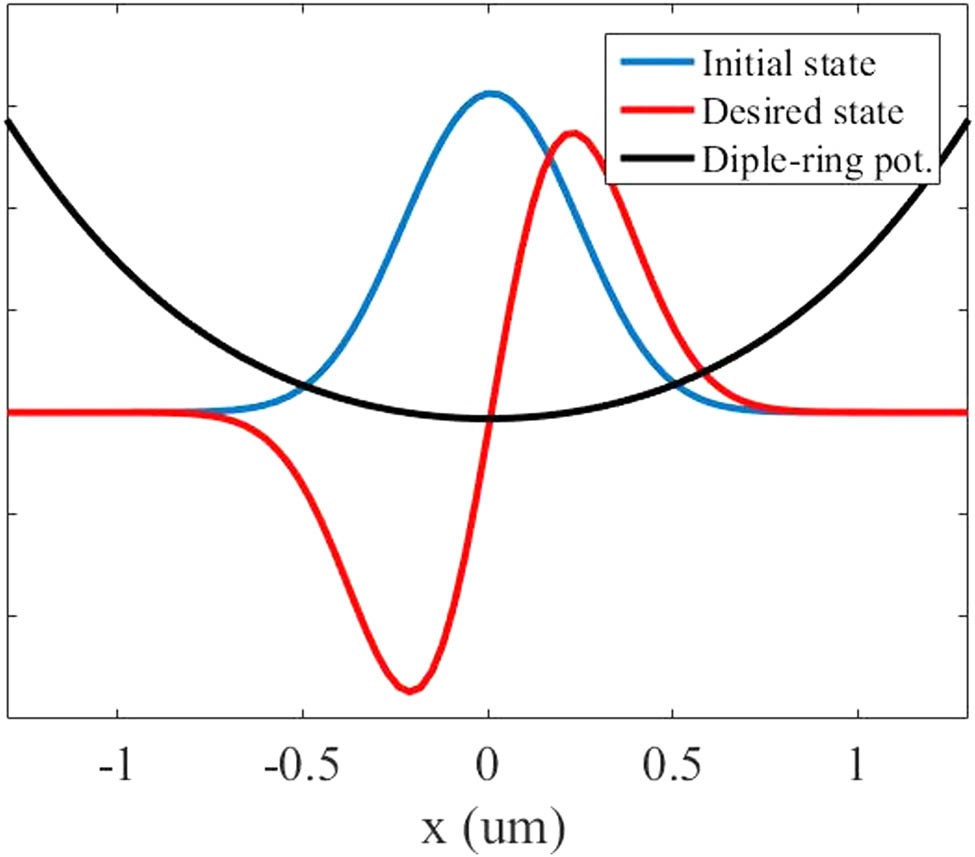
Dimple-ring potential given in black, where
The goal of the optimal algorithm is to find the appropriate shaking function of the dimple-ring trap to excite the atoms, and it runs by the following way [28,30].
First, the algorithm calculates the time evolution of the initial state with a given initial shaking, which can be any function. The initial function in our case is a sinusoidal function, which has the same initial and final conditions,
In the above equation,
where
From equations (8) and (9), we can write equation (10) as equation (11):
at initial conditions
It is difficult for the initial guess of λ to fulfill equation (11) simultaneously. However, equation (11c) can tell us how the control goes to minimize
Therefore, it calculates
Besides calculating the time-evolution of the wave function and the way to minimize the cost function we used as described in ref. [30], there are other mathematical ways about fractional derivatives to calculate differential equations [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45].
Figure 3(a) shows the atomic wave function as time when the dimple-ring potential is shaken, resulting in the optimized control to excite the ground state of the dimple-ring trap for 20 ms and hold the excited state in the dimple-ring trap for 20 ms. Figure 3(b) shows the optimized control in black and the initial guess in red. The cost function as a function of the iteration of the optimal algorithm is shown in the box. A smaller cost function means that the result is closer to the desired state and the control is smoother. We can see that the cost function is exponentially decreased as the iteration increased, and the decay time to the minimum depends on the initial guess of control. The time step of our optimal algorithm is set to 25 µs.

(a) Excitation of the ground state in the dimple-ring trap for 20 ms and holding it for 20 ms. (b) Initial guess of control in red and the optimized control in black, and cost function as a function of iteration is given in the box.
The range of phase for the optimized control is less than 3 deg, and the main frequency component is about 2.4 kHz in our case. Therefore, it requires a phase shifter that has 650 kHz in the main frequency, ±1.5 deg in the bandwidth, and 2.4 kHz in a dynamic range at least when we experimentally apply the result.
Figure 4 shows the next step of constructing the atomic Sagnac interferometer in a ring trap. After excitation, we suggest adiabatically transferring atoms from the dimple-ring trap to a ring trap by ramping down the RF field in the center wire. After that, we let atoms expand in a ring potential. Finally, we construct an atomic Sagnac interferometer in the ring trap when opposite momentum components are overlapped. The interferometric phase is obtained from the position of each atomic cloud and we expect that the system rotation changes the phase [35].

Expansion of the excited atoms in a ring trap. Time step is 800 µs.
4 Conclusion
We simulated a method to construct an atomic Sagnac interferometer in a ring trap. In order to add a bi-directional momentum, we suggest using the excited state. First, we load condensed atoms in a dimple-ring trap. After loading, we shake the trap to excite the atoms by changing the center wire RF field. The shaking function is obtained by the optimal control algorithm. The advantage of the optimal algorithm is that we are able to shake the atoms to find a way and just use it experimentally even though we do not know the physics of the result. After excitation, atoms are adiabatically transferred to a ring trap, and they expand in the ring trap similar to an optical Sagnac interferometer. Our main idea is to apply an optimal algorithm to our trapping system for constructing an atomic Sagnac interferometer. This does not require other experimental devices such as lasers for Bragg diffractions or Raman pulses and perturbing tapping potentials during interferometric integration time. We expect that this type of interferometer measures system rotation.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Rare Isotope Science Project of the Institute for Basic Science funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and NRF of Korea (2013M7A1A1075764) and the National Research Foundation of Korea under NRF-2017R1A2B4008175.
References
[1] Kim SJ, Yu H, Gang ST, Anderson DZ, Kim JB. Controllable asymmetric double well and ring potential on an atom chip. Phys Rev A. 2016;93:033612.10.1103/PhysRevA.93.033612Search in Google Scholar
[2] Geiger R, Ménoret V, Stern G, Zahzam N, Cheinet P, Battelier B, et al. Detecting inertial effects with airborne matter-wave interferometry. Nat Commun. 2011;2:474.10.1038/ncomms1479Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Wu X, Zi F, Dudley J, Bilotta RJ, Canoza P, Müller H. Multiaxis atom interferometry with a single-diode laser and a pyramidal magneto-optical trap. Optica. 2017;4:1545.10.1364/OPTICA.4.001545Search in Google Scholar
[4] Cheiney P, Fouché L, Templier S, Napolitano F, Battelier B, Bouyer P, et al. Navigation-compatible hybrid quantum accelerometer using a Kalman filter. Phys Rev Appl. 2018;10:034030.10.1103/PhysRevApplied.10.034030Search in Google Scholar
[5] Garrido Alzar CL. Compact chip-scale guided cold atom gyrometers for inertial navigation: Enableing technologies and design study. AVS Quantum Sci. 2019;1:014702.10.1116/1.5120348Search in Google Scholar
[6] Rosi G, Sorrentino F, Cacciapuoti L, Prevedelli M, Tino GM. Precision measurement of the Newtonian gravitational constant using cold atoms. Nature. 2014;510:518.10.1038/nature13433Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Parker RH, Yu C, Zhong W, Estey B, Müller H. Measurement of the fine-structure constant as a test of the Standard Model. Science. 2018;360:6385.10.1126/science.aap7706Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Aguilera DN, Ahlers H, Battelier B, Bawamia A, Bertoldi A, Bondarescu R, et al. STE-QUEST—test of the universality of free fall using cold atom interferometry. Classical Quantum Gravity. 2014;31:115010.10.1088/0264-9381/31/11/115010Search in Google Scholar
[9] Canuel B, Bertoldi A, Amand L, Borgo EP, Chantrait T, Danquigny C, et al. Exploring gravity with the MIGA large scale atom interferometer. Sci Rep. 2018;8:14064.10.1038/s41598-018-32165-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Hamilton P, Jaffe M, Haslinger P, Simmons Q, Müller H, Khoury J. Atom-interferometry constraints on dark energy. Science. 2015;349:849.10.1126/science.aaa8883Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Burrage C, Copeland EJ, Hinds EA. Probing dark energy with atom interferometry. J Cosmol Astropart Phys. 2015;3:042.10.1088/1475-7516/2015/03/042Search in Google Scholar
[12] Shin Y, Sanner C, Jo G-B, Pasquini TA, Saba M, Ketterle W, et al. Interference of Bose–Einstein condensates split with an atom chip. Phys Rev A. 2005;72:021604(R).10.1103/PhysRevA.72.021604Search in Google Scholar
[13] Sewell RJ, Dingjan J, Baumgartner F, Llorente-Garcia I, Eriksson S, Hinds EA, et al. Atom chip for BEC interferometry. J Phys B At Mol Opt Phys. 2010;43:051003.10.1088/0953-4075/43/5/051003Search in Google Scholar
[14] Gupta S, Murch KW, Moore KL, Purdy TP, Stamper-Kurn DM. Bose–Einstein condensation in a circular waveguide. Phys Rev Lett. 2005;95:143201.10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.143201Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Ryu C, Blinova AA, Blackburn PW, Boshier MG. Experimental realization of Josephson junctions for an atom SQUID. Phys Rev Lett. 2013;111:205301.10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.205301Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Bell TA, Glidden JAP, Humbert L, Bromley MWJ, Haine SA, Davis MJ, et al. Bose–Einstein condensation in large time-averaged optical ring potentials. New J Phys. 2016;18:035003.10.1088/1367-2630/18/3/035003Search in Google Scholar
[17] Turpin A, Polo J, Loiko YV, Küber J, Schmaltz F, Kalkandjiev TK, et al. Blue-detuned optical ring trap for Bose–Einstein condensates based on conical refraction. Opt Express. 2015;23:1638.10.1364/OE.23.001638Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Roy A, Angom D. Finite temperature expansion dynamics of Bose–Einstein condensates in ring traps. Phys Lett A. 2017;5:55.10.1016/j.physleta.2017.05.055Search in Google Scholar
[19] Weidner CA, Anderson DZ. Experimental demonstration of Shaken-lattice interferometry. Phys Rev Lett. 2018;120:263201.10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.263201Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Weidner CA, Yu H, Kosloff R, Anderson DZ. Atom interferometry using a shaken optical lattice. Phys Rev A. 2017;95:043624.10.1103/PhysRevA.95.043624Search in Google Scholar
[21] Choi DI, Niu Q. Bose–Einstein condensates in an optical lattice. Phys Rev Lett. 1999;82:2022.10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.2022Search in Google Scholar
[22] Morsch O, Oberthaler M. Dynamics of Bose–Einstein condensates in optical lattices. Rev Mod Phys. 2006;78:179.10.1103/RevModPhys.78.179Search in Google Scholar
[23] Böhi P, Riedel MF, Hoffrogge J, Reichel J, Hänsch T, Treutlein P. Coherent manipulation of Bose–Einstein condensates with state-dependent microwave potentials on an atom chip. Nat Phys. 2009;5:592.10.1038/nphys1329Search in Google Scholar
[24] Berrada T, van Frank S, Bücker R, Schumm T, Schaff J-F, Schmiedmayer J. Integrated Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2077.10.1038/ncomms3077Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] McDonald GD, Keal H, Altin PA, Debs JE, Bennetts S, Kuhn CCN, et al. Optically guided linear Mach–Zehnder atom interferometer. Phys Rev A. 2013;87:013632.10.1103/PhysRevA.87.013632Search in Google Scholar
[26] Burke JHT, Deissler B, Hughes KJ, Sackett CA. Confinement effects in a guided-wave atom interferometer with millimeter-scale arm separation. Phys Rev A. 2008;78:023619.10.1103/PhysRevA.78.023619Search in Google Scholar
[27] Wang YJ, Anderson DZ, Bright VM, Cornell EA, Diot Q, et al. Atom Michelson interferometer on a chip using a Bose–Einstein condensate. Phys Rev Lett. 2005;94:090405.10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.090405Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Bücker R, Berrada T, van Frank S, Schaff JF, Schumm T, Schmiedmayer J, et al. Vibrational state inversion of a Bose–Einstein condensate: optimal control and state tomography. J Phys B At Mol Opt Phys. 2013;46:104012.10.1088/0953-4075/46/10/104012Search in Google Scholar
[29] Bücker R, Grond J, Manz S, Berrada T, Betz T, Koller C, et al. Twin-atom beams. Nat Phys. 2011;7:608.10.1038/nphys1992Search in Google Scholar
[30] Hohenester U. OCTBEC—A Matlab toolbox for optimal quantum control of Bose–Einstein condensates. Comput Phys Commun. 2014;185:194.10.1016/j.cpc.2013.09.016Search in Google Scholar
[31] Rohringer W, Bücker R, Manz S, Betz T, Koller CH, Göbel M, et al. Stochastic optimization of a cold atom experiment using a genetic algorithm. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;93:264101.10.1063/1.3058756Search in Google Scholar
[32] Palao JP, Kosloff R. Optimal control theory for unitary transformations. Phys Rev A. 2003;68:062308.10.1103/PhysRevA.68.062308Search in Google Scholar
[33] Kim SJ, Yu H, Gang ST, Kim JB. Matter-wave beam splitter on an atom chip for a portable atom interferometer. Appl Phys B. 2017;123:154.10.1007/s00340-017-6719-6Search in Google Scholar
[34] Lesanovsky I, Schumm T, Hofferberth S, Andersson LM, Krüger P, Schmiedmayer J. Adiabatic radio-frequency potentials for the coherent manipulation of matter waves. Phys Rev A. 2006;73:033619.10.1103/PhysRevA.73.033619Search in Google Scholar
[35] Li-Juan C, Shu-Juan L, Bao-Long L. The interference effect of a Bose–Einstein condensate in a ring-shaped trap. Chin Phys Lett. 2012;29:050305.10.1088/0256-307X/29/5/050305Search in Google Scholar
[36] Akgül A. Reproducing kernel method for fractional derivative with non-local and non-singular kernel. 10.1007/978-3-030-11662-0_1.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Akgül EK. Solutions of the linear and nonlinear differential equations within the generalized fractional derivatives. Chaos. 2019;29:023108.10.1063/1.5084035Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[38] Akgül A. A novel method for a fractional derivative with non-local and non-singular kernel. Chaos Solit Fract. 2018;114:478.10.1016/j.chaos.2018.07.032Search in Google Scholar
[39] Baleanu D, Mousalou A, Rezapour S. A new method for investigating approximate solutions of some fractional integro-differential equations involving the Caputo–Fabrizio derivative. Adv Differ Equ. 2017;2017:51.10.1186/s13662-017-1088-3Search in Google Scholar
[40] Akgül A, Akgül EK. A novel method for solutions of fourth-order fractional boundary value problems. Fract Fraction. 2019;3:33.10.3390/fractalfract3020033Search in Google Scholar
[41] Boutarfa B, Akgül A, Inc M. New approach for the Fornberg–Whitham type equations. J Comput Appl Math. 2017;312:13.10.1016/j.cam.2015.09.016Search in Google Scholar
[42] Akgül A. On the solution of higher order difference equation. Math Meth Appl Sci. 2017;40:6165.10.1002/mma.3870Search in Google Scholar
[43] Akgül A. Reproducing kernel Hilbert space method based on reproducing kernel functions for investigating boundary layer flow of a Powell–Eyring non-Newtonian fluid. J Taibah Univ Sci. 2019;13:858.10.1080/16583655.2019.1651988Search in Google Scholar
[44] Akgül A, Bonyah E. Reproducing kernel Hilbert space method for the solutions of generalized Kuramoto–Sivashinsky equation. J Taibah Univ Sci. 2019;13:661.10.1080/16583655.2019.1618547Search in Google Scholar
[45] Akgül A. A novel method for the solution of Blasius equation in semi-infinite domains. Int J Optim Control Theor Appl. 2017;7:225.10.11121/ijocta.01.2017.00363Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 Hoon Yu et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Model of electric charge distribution in the trap of a close-contact TENG system
- Dynamics of Online Collective Attention as Hawkes Self-exciting Process
- Enhanced Entanglement in Hybrid Cavity Mediated by a Two-way Coupled Quantum Dot
- The nonlinear integro-differential Ito dynamical equation via three modified mathematical methods and its analytical solutions
- Diagnostic model of low visibility events based on C4.5 algorithm
- Electronic temperature characteristics of laser-induced Fe plasma in fruits
- Comparative study of heat transfer enhancement on liquid-vapor separation plate condenser
- Characterization of the effects of a plasma injector driven by AC dielectric barrier discharge on ethylene-air diffusion flame structure
- Impact of double-diffusive convection and motile gyrotactic microorganisms on magnetohydrodynamics bioconvection tangent hyperbolic nanofluid
- Dependence of the crossover zone on the regularization method in the two-flavor Nambu–Jona-Lasinio model
- Novel numerical analysis for nonlinear advection–reaction–diffusion systems
- Heuristic decision of planned shop visit products based on similar reasoning method: From the perspective of organizational quality-specific immune
- Two-dimensional flow field distribution characteristics of flocking drainage pipes in tunnel
- Dynamic triaxial constitutive model for rock subjected to initial stress
- Automatic target recognition method for multitemporal remote sensing image
- Gaussons: optical solitons with log-law nonlinearity by Laplace–Adomian decomposition method
- Adaptive magnetic suspension anti-rolling device based on frequency modulation
- Dynamic response characteristics of 93W alloy with a spherical structure
- The heuristic model of energy propagation in free space, based on the detection of a current induced in a conductor inside a continuously covered conducting enclosure by an external radio frequency source
- Microchannel filter for air purification
- An explicit representation for the axisymmetric solutions of the free Maxwell equations
- Floquet analysis of linear dynamic RLC circuits
- Subpixel matching method for remote sensing image of ground features based on geographic information
- K-band luminosity–density relation at fixed parameters or for different galaxy families
- Effect of forward expansion angle on film cooling characteristics of shaped holes
- Analysis of the overvoltage cooperative control strategy for the small hydropower distribution network
- Stable walking of biped robot based on center of mass trajectory control
- Modeling and simulation of dynamic recrystallization behavior for Q890 steel plate based on plane strain compression tests
- Edge effect of multi-degree-of-freedom oscillatory actuator driven by vector control
- The effect of guide vane type on performance of multistage energy recovery hydraulic turbine (MERHT)
- Development of a generic framework for lumped parameter modeling
- Optimal control for generating excited state expansion in ring potential
- The phase inversion mechanism of the pH-sensitive reversible invert emulsion from w/o to o/w
- 3D bending simulation and mechanical properties of the OLED bending area
- Resonance overvoltage control algorithms in long cable frequency conversion drive based on discrete mathematics
- The measure of irregularities of nanosheets
- The predicted load balancing algorithm based on the dynamic exponential smoothing
- Influence of different seismic motion input modes on the performance of isolated structures with different seismic measures
- A comparative study of cohesive zone models for predicting delamination fracture behaviors of arterial wall
- Analysis on dynamic feature of cross arm light weighting for photovoltaic panel cleaning device in power station based on power correlation
- Some probability effects in the classical context
- Thermosoluted Marangoni convective flow towards a permeable Riga surface
- Simultaneous measurement of ionizing radiation and heart rate using a smartphone camera
- On the relations between some well-known methods and the projective Riccati equations
- Application of energy dissipation and damping structure in the reinforcement of shear wall in concrete engineering
- On-line detection algorithm of ore grade change in grinding grading system
- Testing algorithm for heat transfer performance of nanofluid-filled heat pipe based on neural network
- New optical solitons of conformable resonant nonlinear Schrödinger’s equation
- Numerical investigations of a new singular second-order nonlinear coupled functional Lane–Emden model
- Circularly symmetric algorithm for UWB RF signal receiving channel based on noise cancellation
- CH4 dissociation on the Pd/Cu(111) surface alloy: A DFT study
- On some novel exact solutions to the time fractional (2 + 1) dimensional Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky system arising in physical science
- An optimal system of group-invariant solutions and conserved quantities of a nonlinear fifth-order integrable equation
- Mining reasonable distance of horizontal concave slope based on variable scale chaotic algorithms
- Mathematical models for information classification and recognition of multi-target optical remote sensing images
- Hopkinson rod test results and constitutive description of TRIP780 steel resistance spot welding material
- Computational exploration for radiative flow of Sutterby nanofluid with variable temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and diffusion coefficient
- Analytical solution of one-dimensional Pennes’ bioheat equation
- MHD squeezed Darcy–Forchheimer nanofluid flow between two h–distance apart horizontal plates
- Analysis of irregularity measures of zigzag, rhombic, and honeycomb benzenoid systems
- A clustering algorithm based on nonuniform partition for WSNs
- An extension of Gronwall inequality in the theory of bodies with voids
- Rheological properties of oil–water Pickering emulsion stabilized by Fe3O4 solid nanoparticles
- Review Article
- Sine Topp-Leone-G family of distributions: Theory and applications
- Review of research, development and application of photovoltaic/thermal water systems
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics of Thermal Transports and Energy Conversions
- Numerical analysis of sulfur dioxide absorption in water droplets
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part I
- Random pore structure and REV scale flow analysis of engine particulate filter based on LBM
- Prediction of capillary suction in porous media based on micro-CT technology and B–C model
- Energy equilibrium analysis in the effervescent atomization
- Experimental investigation on steam/nitrogen condensation characteristics inside horizontal enhanced condensation channels
- Experimental analysis and ANN prediction on performances of finned oval-tube heat exchanger under different air inlet angles with limited experimental data
- Investigation on thermal-hydraulic performance prediction of a new parallel-flow shell and tube heat exchanger with different surrogate models
- Comparative study of the thermal performance of four different parallel flow shell and tube heat exchangers with different performance indicators
- Optimization of SCR inflow uniformity based on CFD simulation
- Kinetics and thermodynamics of SO2 adsorption on metal-loaded multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Effect of the inner-surface baffles on the tangential acoustic mode in the cylindrical combustor
- Special Issue on Future challenges of advanced computational modeling on nonlinear physical phenomena - Part I
- Conserved vectors with conformable derivative for certain systems of partial differential equations with physical applications
- Some new extensions for fractional integral operator having exponential in the kernel and their applications in physical systems
- Exact optical solitons of the perturbed nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with Kerr law nonlinearity in nonlinear fiber optics
- Analytical mathematical schemes: Circular rod grounded via transverse Poisson’s effect and extensive wave propagation on the surface of water
- Closed-form wave structures of the space-time fractional Hirota–Satsuma coupled KdV equation with nonlinear physical phenomena
- Some misinterpretations and lack of understanding in differential operators with no singular kernels
- Stable solutions to the nonlinear RLC transmission line equation and the Sinh–Poisson equation arising in mathematical physics
- Calculation of focal values for first-order non-autonomous equation with algebraic and trigonometric coefficients
- Influence of interfacial electrokinetic on MHD radiative nanofluid flow in a permeable microchannel with Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects
- Standard routine techniques of modeling of tick-borne encephalitis
- Fractional residual power series method for the analytical and approximate studies of fractional physical phenomena
- Exact solutions of space–time fractional KdV–MKdV equation and Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky equation
- Approximate analytical fractional view of convection–diffusion equations
- Heat and mass transport investigation in radiative and chemically reacting fluid over a differentially heated surface and internal heating
- On solitary wave solutions of a peptide group system with higher order saturable nonlinearity
- Extension of optimal homotopy asymptotic method with use of Daftardar–Jeffery polynomials to Hirota–Satsuma coupled system of Korteweg–de Vries equations
- Unsteady nano-bioconvective channel flow with effect of nth order chemical reaction
- On the flow of MHD generalized maxwell fluid via porous rectangular duct
- Study on the applications of two analytical methods for the construction of traveling wave solutions of the modified equal width equation
- Numerical solution of two-term time-fractional PDE models arising in mathematical physics using local meshless method
- A powerful numerical technique for treating twelfth-order boundary value problems
- Fundamental solutions for the long–short-wave interaction system
- Role of fractal-fractional operators in modeling of rubella epidemic with optimized orders
- Exact solutions of the Laplace fractional boundary value problems via natural decomposition method
- Special Issue on 19th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering
- Joint use of eddy current imaging and fuzzy similarities to assess the integrity of steel plates
- Uncertainty quantification in the design of wireless power transfer systems
- Influence of unequal stator tooth width on the performance of outer-rotor permanent magnet machines
- New elements within finite element modeling of magnetostriction phenomenon in BLDC motor
- Evaluation of localized heat transfer coefficient for induction heating apparatus by thermal fluid analysis based on the HSMAC method
- Experimental set up for magnetomechanical measurements with a closed flux path sample
- Influence of the earth connections of the PWM drive on the voltage constraints endured by the motor insulation
- High temperature machine: Characterization of materials for the electrical insulation
- Architecture choices for high-temperature synchronous machines
- Analytical study of air-gap surface force – application to electrical machines
- High-power density induction machines with increased windings temperature
- Influence of modern magnetic and insulation materials on dimensions and losses of large induction machines
- New emotional model environment for navigation in a virtual reality
- Performance comparison of axial-flux switched reluctance machines with non-oriented and grain-oriented electrical steel rotors
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Conserved vectors with conformable derivative for certain systems of partial differential equations with physical applications”
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Model of electric charge distribution in the trap of a close-contact TENG system
- Dynamics of Online Collective Attention as Hawkes Self-exciting Process
- Enhanced Entanglement in Hybrid Cavity Mediated by a Two-way Coupled Quantum Dot
- The nonlinear integro-differential Ito dynamical equation via three modified mathematical methods and its analytical solutions
- Diagnostic model of low visibility events based on C4.5 algorithm
- Electronic temperature characteristics of laser-induced Fe plasma in fruits
- Comparative study of heat transfer enhancement on liquid-vapor separation plate condenser
- Characterization of the effects of a plasma injector driven by AC dielectric barrier discharge on ethylene-air diffusion flame structure
- Impact of double-diffusive convection and motile gyrotactic microorganisms on magnetohydrodynamics bioconvection tangent hyperbolic nanofluid
- Dependence of the crossover zone on the regularization method in the two-flavor Nambu–Jona-Lasinio model
- Novel numerical analysis for nonlinear advection–reaction–diffusion systems
- Heuristic decision of planned shop visit products based on similar reasoning method: From the perspective of organizational quality-specific immune
- Two-dimensional flow field distribution characteristics of flocking drainage pipes in tunnel
- Dynamic triaxial constitutive model for rock subjected to initial stress
- Automatic target recognition method for multitemporal remote sensing image
- Gaussons: optical solitons with log-law nonlinearity by Laplace–Adomian decomposition method
- Adaptive magnetic suspension anti-rolling device based on frequency modulation
- Dynamic response characteristics of 93W alloy with a spherical structure
- The heuristic model of energy propagation in free space, based on the detection of a current induced in a conductor inside a continuously covered conducting enclosure by an external radio frequency source
- Microchannel filter for air purification
- An explicit representation for the axisymmetric solutions of the free Maxwell equations
- Floquet analysis of linear dynamic RLC circuits
- Subpixel matching method for remote sensing image of ground features based on geographic information
- K-band luminosity–density relation at fixed parameters or for different galaxy families
- Effect of forward expansion angle on film cooling characteristics of shaped holes
- Analysis of the overvoltage cooperative control strategy for the small hydropower distribution network
- Stable walking of biped robot based on center of mass trajectory control
- Modeling and simulation of dynamic recrystallization behavior for Q890 steel plate based on plane strain compression tests
- Edge effect of multi-degree-of-freedom oscillatory actuator driven by vector control
- The effect of guide vane type on performance of multistage energy recovery hydraulic turbine (MERHT)
- Development of a generic framework for lumped parameter modeling
- Optimal control for generating excited state expansion in ring potential
- The phase inversion mechanism of the pH-sensitive reversible invert emulsion from w/o to o/w
- 3D bending simulation and mechanical properties of the OLED bending area
- Resonance overvoltage control algorithms in long cable frequency conversion drive based on discrete mathematics
- The measure of irregularities of nanosheets
- The predicted load balancing algorithm based on the dynamic exponential smoothing
- Influence of different seismic motion input modes on the performance of isolated structures with different seismic measures
- A comparative study of cohesive zone models for predicting delamination fracture behaviors of arterial wall
- Analysis on dynamic feature of cross arm light weighting for photovoltaic panel cleaning device in power station based on power correlation
- Some probability effects in the classical context
- Thermosoluted Marangoni convective flow towards a permeable Riga surface
- Simultaneous measurement of ionizing radiation and heart rate using a smartphone camera
- On the relations between some well-known methods and the projective Riccati equations
- Application of energy dissipation and damping structure in the reinforcement of shear wall in concrete engineering
- On-line detection algorithm of ore grade change in grinding grading system
- Testing algorithm for heat transfer performance of nanofluid-filled heat pipe based on neural network
- New optical solitons of conformable resonant nonlinear Schrödinger’s equation
- Numerical investigations of a new singular second-order nonlinear coupled functional Lane–Emden model
- Circularly symmetric algorithm for UWB RF signal receiving channel based on noise cancellation
- CH4 dissociation on the Pd/Cu(111) surface alloy: A DFT study
- On some novel exact solutions to the time fractional (2 + 1) dimensional Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky system arising in physical science
- An optimal system of group-invariant solutions and conserved quantities of a nonlinear fifth-order integrable equation
- Mining reasonable distance of horizontal concave slope based on variable scale chaotic algorithms
- Mathematical models for information classification and recognition of multi-target optical remote sensing images
- Hopkinson rod test results and constitutive description of TRIP780 steel resistance spot welding material
- Computational exploration for radiative flow of Sutterby nanofluid with variable temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and diffusion coefficient
- Analytical solution of one-dimensional Pennes’ bioheat equation
- MHD squeezed Darcy–Forchheimer nanofluid flow between two h–distance apart horizontal plates
- Analysis of irregularity measures of zigzag, rhombic, and honeycomb benzenoid systems
- A clustering algorithm based on nonuniform partition for WSNs
- An extension of Gronwall inequality in the theory of bodies with voids
- Rheological properties of oil–water Pickering emulsion stabilized by Fe3O4 solid nanoparticles
- Review Article
- Sine Topp-Leone-G family of distributions: Theory and applications
- Review of research, development and application of photovoltaic/thermal water systems
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics of Thermal Transports and Energy Conversions
- Numerical analysis of sulfur dioxide absorption in water droplets
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part I
- Random pore structure and REV scale flow analysis of engine particulate filter based on LBM
- Prediction of capillary suction in porous media based on micro-CT technology and B–C model
- Energy equilibrium analysis in the effervescent atomization
- Experimental investigation on steam/nitrogen condensation characteristics inside horizontal enhanced condensation channels
- Experimental analysis and ANN prediction on performances of finned oval-tube heat exchanger under different air inlet angles with limited experimental data
- Investigation on thermal-hydraulic performance prediction of a new parallel-flow shell and tube heat exchanger with different surrogate models
- Comparative study of the thermal performance of four different parallel flow shell and tube heat exchangers with different performance indicators
- Optimization of SCR inflow uniformity based on CFD simulation
- Kinetics and thermodynamics of SO2 adsorption on metal-loaded multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Effect of the inner-surface baffles on the tangential acoustic mode in the cylindrical combustor
- Special Issue on Future challenges of advanced computational modeling on nonlinear physical phenomena - Part I
- Conserved vectors with conformable derivative for certain systems of partial differential equations with physical applications
- Some new extensions for fractional integral operator having exponential in the kernel and their applications in physical systems
- Exact optical solitons of the perturbed nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with Kerr law nonlinearity in nonlinear fiber optics
- Analytical mathematical schemes: Circular rod grounded via transverse Poisson’s effect and extensive wave propagation on the surface of water
- Closed-form wave structures of the space-time fractional Hirota–Satsuma coupled KdV equation with nonlinear physical phenomena
- Some misinterpretations and lack of understanding in differential operators with no singular kernels
- Stable solutions to the nonlinear RLC transmission line equation and the Sinh–Poisson equation arising in mathematical physics
- Calculation of focal values for first-order non-autonomous equation with algebraic and trigonometric coefficients
- Influence of interfacial electrokinetic on MHD radiative nanofluid flow in a permeable microchannel with Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects
- Standard routine techniques of modeling of tick-borne encephalitis
- Fractional residual power series method for the analytical and approximate studies of fractional physical phenomena
- Exact solutions of space–time fractional KdV–MKdV equation and Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky equation
- Approximate analytical fractional view of convection–diffusion equations
- Heat and mass transport investigation in radiative and chemically reacting fluid over a differentially heated surface and internal heating
- On solitary wave solutions of a peptide group system with higher order saturable nonlinearity
- Extension of optimal homotopy asymptotic method with use of Daftardar–Jeffery polynomials to Hirota–Satsuma coupled system of Korteweg–de Vries equations
- Unsteady nano-bioconvective channel flow with effect of nth order chemical reaction
- On the flow of MHD generalized maxwell fluid via porous rectangular duct
- Study on the applications of two analytical methods for the construction of traveling wave solutions of the modified equal width equation
- Numerical solution of two-term time-fractional PDE models arising in mathematical physics using local meshless method
- A powerful numerical technique for treating twelfth-order boundary value problems
- Fundamental solutions for the long–short-wave interaction system
- Role of fractal-fractional operators in modeling of rubella epidemic with optimized orders
- Exact solutions of the Laplace fractional boundary value problems via natural decomposition method
- Special Issue on 19th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering
- Joint use of eddy current imaging and fuzzy similarities to assess the integrity of steel plates
- Uncertainty quantification in the design of wireless power transfer systems
- Influence of unequal stator tooth width on the performance of outer-rotor permanent magnet machines
- New elements within finite element modeling of magnetostriction phenomenon in BLDC motor
- Evaluation of localized heat transfer coefficient for induction heating apparatus by thermal fluid analysis based on the HSMAC method
- Experimental set up for magnetomechanical measurements with a closed flux path sample
- Influence of the earth connections of the PWM drive on the voltage constraints endured by the motor insulation
- High temperature machine: Characterization of materials for the electrical insulation
- Architecture choices for high-temperature synchronous machines
- Analytical study of air-gap surface force – application to electrical machines
- High-power density induction machines with increased windings temperature
- Influence of modern magnetic and insulation materials on dimensions and losses of large induction machines
- New emotional model environment for navigation in a virtual reality
- Performance comparison of axial-flux switched reluctance machines with non-oriented and grain-oriented electrical steel rotors
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Conserved vectors with conformable derivative for certain systems of partial differential equations with physical applications”

