Abstract
Utilizing the conventional approach, the positive temperature coefficient of resistivity (PTCR) performance of lead-free ceramics based on (1 − x%)(Ba1−y Y y )(Ti1.011−z Nb0.001Mn z )O3 − x%(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BBNTx) was examined. The BBNTx ceramics were prepared using the double donor dopant under firing at 1,350°C for 120 min in the air. The findings exhibited that when the Y3+ concentration elevates, the room-temperature resistivity of 99%(Ba1−y Y y )(Ti1.011−z Nb0.001Mn z )O3 – 1%(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BBNT1) samples initially falls and subsequently elevates. Moreover, the critical content of the samples is 0.15 mol%. Furthermore, the samples’ resistance jumping ratio can be effectively improved by adding Mn2+. The manganese dioxide level of 0.05 mol% yields the greatest resistance-jumping ratio. Besides, the impact of (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BNT) concentration on ceramics’ Curie temperature was examined in the work. Therefore, good free-lead PTCR thermistors were successfully prepared by doping 3% BNT, with a resistance jump of 4.1 magnitude.
1 Introduction
A ferroelectric substance known as barium titanate (BaTiO3) is doped with trace amounts of pentavalent or trivalent donors (Nb5+, Sm3+, Y3+, and so on). It is a semiconducting material that reveals an amazing rise in resistance when it gets close to the Curie temperature [1,2]. The effect of positive temperature coefficient of resistivity (PTCR) is the name given to this phenomenon, which has been satisfactorily described by both Heywang [3] and Jonker [4]. During the past several years, the market for PTCR thermistors of the high temperature [5] that can be used in self-controlled heaters has grown. The lead titanate is usually doped in the samples to improve the ceramics’ Curie temperature. However, the lead is toxic. Recently, the compounds of (Bi1/2Na1/2) TiO3 (BNT) [6,7] along with (Bi1/2K1/2)TiO3 (BKT) [6,7] were doped to create lead-free PTCR ceramics. The Nb5+, Y3+, Mn2+, and BNT content as well as their impact on the PTCR effect and electrical characteristics of the lead-free ceramics based on BBNTx however have received less attention. Thus, this research explores the impact of the double-donor dopant on the PTCR properties of BBNTx ceramics.
2 Materials and methods
The raw components were high-purity NaCO3 (>99.8%), Bi2O3 (>99.8%), BaCO3 (>99.8%), Nb2O5 (>99.99%), Y2O3 (>99.99%), Mn(NO3)2 (>99.5%), and TiO2 (>99.8%), which were weighed according to the formula: (1 − x%)(Ba1−y Y y )(Ti1.011−z Nb0.001Mn z )O3 − x%(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BBNTx). In our experiment, the concentration of x, y, z is in the range of 1–5 mol, 0.05–0.25 mol%, 0.03–0.09 mol%, respectively. First, the mixture of x%(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BNTx) was combined by wet ball milling in alcohol for 4 h with an agate ball in a ninon jar, and lather was dried in a 90°C drying oven, and the powders were calcined for 120 min at 900°C in air. Second, an agate ball in a ninon jar was applied to a wet ball mill with the combination of (1 − x%)(Ba1−y Y y )(Ti1.011−z Nb0.001Mn z )O3 for 4 h in alcohol. The powders were next dried at 90°C in a drying oven and calcined for 120 min at 1,100°C in air. These mixtures were all reground for 6 h using a ball mill. To create the green compacts, which have a size of 15 mm × 2 mm, the dried powders were combined with 5 wt% polyvinyl alcohol and compressed at 150 MPa. After that, the blocks were sintered in an air muffle furnace for 120 min at 1,350°C, with a 250°C·h−1 heating rate, and furnace cooling was utilized for cooling. After applying Ag–Zn alloy to the fired BBNTx ceramic surfaces, they were sintered at 540°C for 10 min to generate electrodes. A digital multimeter was subsequently utilized to measure the specimens’ resistance at room-temperature (RT), and a temperature-programmable furnace (ZW-1, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China) was employed to measure the resistance’s temperature dependence at 1.6 °C·min−1 heating rate between 25 and 250°C. Furthermore, scanning electron microscopy (SEM; Quanta FEG 250 FEI, American) was used to observe the surface microstructure of sintered ceramics. The line-intersection technique was applied to estimate the ceramics’ average grain size.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of the ceramics
The concentration of BNT has a major impact on the samples’ microstructure (Figure 1), and a discernible variation in grain size is seen. As concentrations of BNT rise, it slightly declines and becomes uniform, most likely as a result of decreased porosity as BNT content elevates. Consequently, variations in the rates of grain development might be the cause of the particle-size distribution. Cooling the liquid phase between 1,200 and 800°C allows it to solidify, and the higher the BNT concentration, the slower the mass-transfer and grain boundary movement processes become.
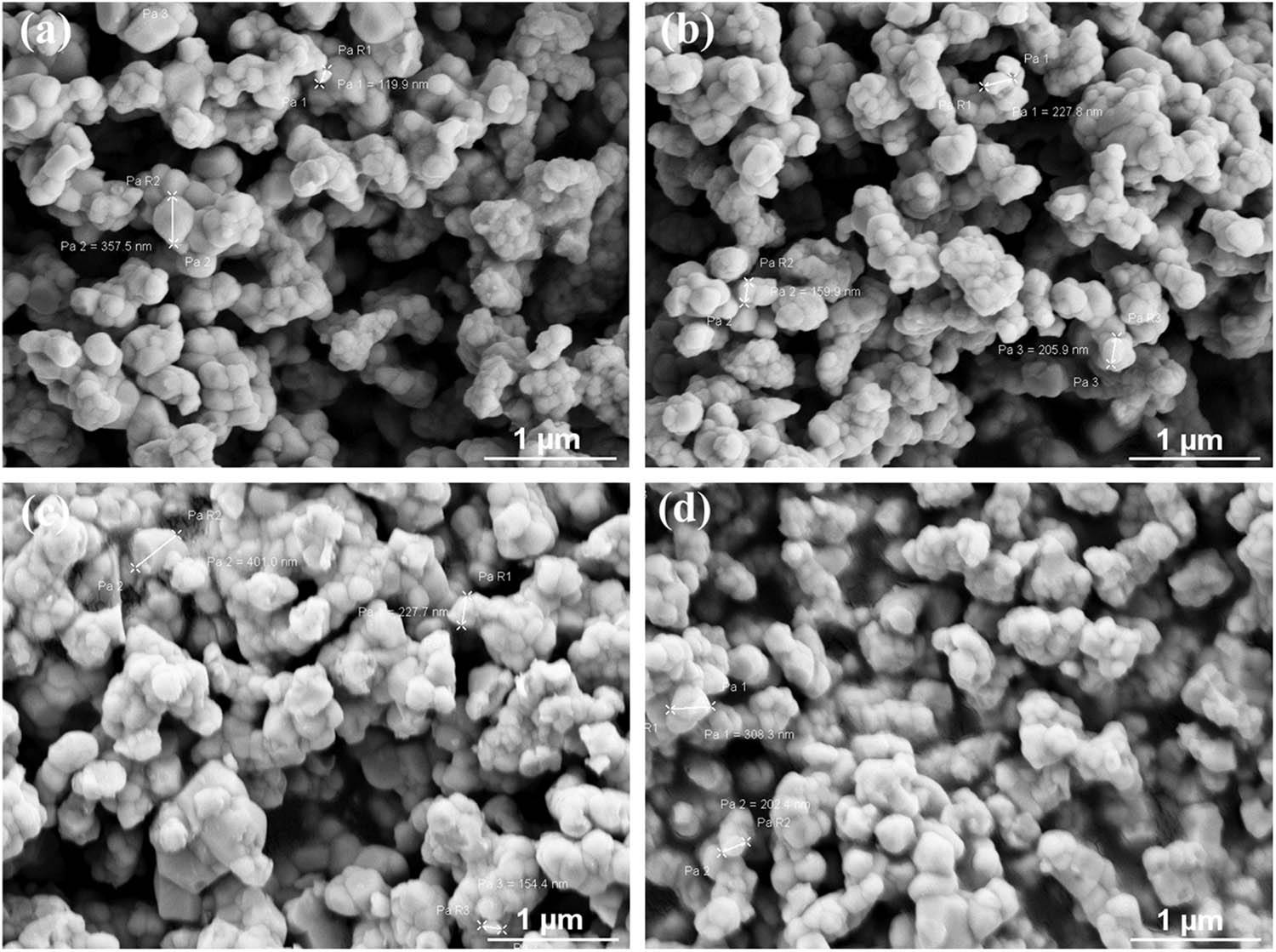
SEM micrograph on the surfaces of the BBNTx specimens sintered at 1350°C for 2 h with doping different BNT contents: (a) 1 mol%, (b) 2 mol%, (c) 3 mol%, and (d) 4 mol%.
3.2 Impact of the double-donor dopant concentration on PTCR influence
Based on the resistance jump (Log10[R max/R min]) and RT resistivity of the 99%(Ba1−y Y y )(Ti1.011−z Nb0.001Mn z )O3 − 1%(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BBNT1) (z = 0.05 mol%) ceramics, fired in the air at 1,350°C for 120 min, Figure 2 displays the impact of the dopant concentration on the PTCR influence, and the dopant content is presented in Figure 3, where R max and R min are the max and min resistance of the samples between RT and 250°C, respectively. Based on the figures, as the dopant concentration elevates, the ceramics’ RT resistivity initially lowers and subsequently increases. Conversely, a resistance jump displays a reverse tendency. This behavior indicates that 0.15 mol% Y3+ is the ideal donor-doped level. The resistivity leap raises with reducing RT resistivity. Moreover, the electrical compensation of the substituted Ti4+ and Ba2+ by the Nb5+ and Y3+, separately, is mostly responsible for the resistivity drop [8,9]:

Temperature dependence of resistivity of the BBNT1 ceramics sintered at 1,350°C for 2 h in air.

RT resistivity and the resistance jump of the BBNT1 ceramics as a function of the dopant concentration.
Conversely, the rise in resistivity is typically ascribed to the ionic compensation brought about by the co-generation of titanium and barium vacancies [10,11]
3.3 Impact of doping Mn concentration on electrical performance
The resistance jump and RT resistivity of the BBNT1 (y = 0.15 mol%) samples that are fired at a temperature of 1,350°C for 120 min are shown in Figure 4. These electrical properties are affected by the Mn(NO3)2 concentration in the range of 0.03–0.09 mol%, and the effect of the manganese nitrate concentration on the PTCR performance is shown in Figure 5. From Figure 4, as the concentration of Mn rises, the RT resistivity of the ceramics elevates rapidly. Furthermore, when the Mn concentration of the ceramics rises, it initially elevates and subsequently falls. The Mn2+ level of 0.05 mol%, which is revealed by 3.1 orders of magnitude and possesses an RT resistivity of 2.9 × 103 Ω·cm, yields the ideal resistance jump. The outcome suggests that the specimens’ PTCR properties can be enhanced by a modest dose of Mn(NO3)2.

RT resistivity and the resistance jump of the BBNT1 ceramics as a function of the Mn(NO3)2 concentration.

Temperature dependence of resistivity of the BBNT1 ceramics for different Mn(NO3)2 content sintered at 1,350°C for 2 h in air.
The impact of the electrical performances of the BBNTx (y = 0.15 mol%, z = 0.05 mol%) ceramics, which were sintered at a temperature of 1,350°C for 120 min, is shown in Figure 6. The impact of varying concentrations of BNT on the PTCR effect of ceramics in Figure 6 is illustrated in Figure 7 – the BBNTx samples with doping 1, 2, 3, and 4 mol% BNT. The figures demonstrate that when the BNT concentration rises, so does the specimens’ RT resistivity. Conversely, the jumping ratio of ceramics first increases very slightly and later decreases rapidly with increasing BNT concentrations. Therefore, with an RT resistivity of 7.2 ×103 Ω·cm in Table 1, the best PTCR effect under the BNT concentration is 3 mol%, which is revealed by 4.1 orders of magnitude. Usually, the ionic compensation brought about by the creation of cation vacancies is accounted for by the rise in resistivity.

RT resistivity and the jumping ratio of the BBNTx ceramics as a function of the BNT content.

Temperature dependence of resistivity of the BBNTx samples sintered at 1,350°C for 2 h in air.
Electrical properties and PTCR effect of the BBNTx samples fired at 1,350°C for 2 h in air
| Electrical properties | Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNT1 | BNT2 | BNT3 | BNT4 | BNT5 | |
| ρ (Ω·cm) | 3.0 × 103 | 4.3 × 103 | 7.2 × 103 | 1.4 × 105 | 1.6 × 106 |
| Lg(R max/R min) | 3.1 | 2.1 | 4.1 | 2.4 | 0.7 |
| T c (°C) | 137 | 143 | 147 | 150 | 154 |
4 Conclusion
Resistance jump and electrical characteristics of the BBNTx ceramics sintered in the air at 1,350°C for 120 min were examined in the article. The findings suggested that when the amount of Y dopant in BBNT1 ceramics rises, the RT resistivity initially reduces and subsequently elevates. However, a resistance jump shows a contrary tendency. Consequently, 0.15 mol% Y3+ is the critical donor-doped concentration. Furthermore, when the BNT and Mn level elevates, so does the samples’ RT resistivity. The manganese nitrate level of 0.05 mol% yields the best resistance jumping ratio. Moreover, the BNT concentration influences the PTCR properties of the ceramics. With an RT resistivity of 7.2 × 103 Ω·cm, the optimal PTCR effect is achieved at a doping BNT concentration of 3 mol%, as demonstrated by 4.1 orders of magnitude.
-
Funding information: This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51402258), the Key Research Platform and Program in Universities under the Department of Education of Guangdong Province (No. 2020GCZX003), the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Materials and Electronic Components (No. FHR-JS-202011007), the Research Laboratory of University Physics Course in Universities of Department of Education of Guangdong Province, the Fourth Batch of Innovative Research Teams at Zhaoqing University (TD202412), and the Quality Engineering Project in Zhaoqing University (No. zlgc202116).
-
Author contributions: Xiaoming Chen: writing – original draft, Yini Li: writing – review and editing, Sikang Zeng: writing – original draft; Xuxin Cheng: writing – review and methodology; Wei Zhang: writing – review and editing; Yuxin Wang: writing – review and methodology.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Illingsworth, J., H. M. Al-Allak, A. W. Brinkman, and J. Woods. The influence of Mn on the grain-boundary potential barrier characteristics of donor-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 67, No. 4, 1990, pp. 2088–2092.10.1063/1.345567Search in Google Scholar
[2] Heywang, W. The influence of Mn on the grain-boundary potential barrier characteristics of donor-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, Vol. 47, No. 10, 1964, id. 484.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Heywang, W. Bariumtitanat als sperrschichthalbleiter. Solid-State Electron, Vol. 3, No. 1, 1961, pp. 51–58.10.1016/0038-1101(61)90080-6Search in Google Scholar
[4] Jonker, G. H. Some aspects of semiconducting barium titanate. Solid-State Electron, Vol. 7, No. 12, 1964, pp. 895–903.10.1016/0038-1101(64)90068-1Search in Google Scholar
[5] Shirane, G. and S. Hoshino. On the phase transition in lead titanate. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol. 6, No. 4, 1951, pp. 265–270.10.1143/JPSJ.6.265Search in Google Scholar
[6] Smolensky, G. A., V. A. Isupov, A. I. Agranovskaya, and N. N. Krainik. New ferroelectrics of complex composition IV. Soviet Physics-Solid State, Vol. 2, 1961, id. 2651.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Takeda, H., T. Shimada, Y. Katsuyama, and T. Shiosaki. Fabrication and operation limit of lead-free PTCR ceramics using BaTiO3-(Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3 system. Journal of Electroceramics, Vol. 22, 2009, pp. 263–269.10.1007/s10832-007-9398-6Search in Google Scholar
[8] Chan, H. M., M. R. Harmer, and D. M. Smyth. Compensating defects in highly donor-doped BaTiO3. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, Vol. 69, No. 6, 1986, pp. 507–510.10.1111/j.1151-2916.1986.tb07453.xSearch in Google Scholar
[9] Pu, Y. P., H. D. Wu, J. F. Wei, and B. Wang. Influence of Nb5+ and Mn2+ on the PTCR effects of Ba0.92Ca0.05(Bi0.5Na0.5)0.03TiO3 ceramics. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, Vol. 22, 2011, pp. 1479–1482.10.1007/s10854-011-0333-xSearch in Google Scholar
[10] Brzozowski, E. and M. S. Castro. Influence of Nb5+ and Sb3+ dopants on the defect profile, PTCR effect, and GBBL characteristics of BaTiO3 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, Vol. 24, No. 8, 2004, pp. 2499–2507.10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2003.07.015Search in Google Scholar
[11] Nowotny, J. and M. Rekas. Defect structure, electrical properties, and transport in Barium Titanate. VII. Chemical diffusion in Nb-doped BaTiO3. Ceramics International, Vol. 20, No. 4, 1994, pp. 265–275.10.1016/0272-8842(94)90061-2Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- De-chlorination of poly(vinyl) chloride using Fe2O3 and the improvement of chlorine fixing ratio in FeCl2 by SiO2 addition
- Reductive behavior of nickel and iron metallization in magnesian siliceous nickel laterite ores under the action of sulfur-bearing natural gas
- Study on properties of CaF2–CaO–Al2O3–MgO–B2O3 electroslag remelting slag for rack plate steel
- The origin of {113}<361> grains and their impact on secondary recrystallization in producing ultra-thin grain-oriented electrical steel
- Channel parameter optimization of one-strand slab induction heating tundish with double channels
- Effect of rare-earth Ce on the texture of non-oriented silicon steels
- Performance optimization of PERC solar cells based on laser ablation forming local contact on the rear
- Effect of ladle-lining materials on inclusion evolution in Al-killed steel during LF refining
- Analysis of metallurgical defects in enamel steel castings
- Effect of cooling rate and Nb synergistic strengthening on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-strength rebar
- Effect of grain size on fatigue strength of 304 stainless steel
- Analysis and control of surface cracks in a B-bearing continuous casting blooms
- Application of laser surface detection technology in blast furnace gas flow control and optimization
- Preparation of MoO3 powder by hydrothermal method
- The comparative study of Ti-bearing oxides introduced by different methods
- Application of MgO/ZrO2 coating on 309 stainless steel to increase resistance to corrosion at high temperatures and oxidation by an electrochemical method
- Effect of applying a full oxygen blast furnace on carbon emissions based on a carbon metabolism calculation model
- Characterization of low-damage cutting of alfalfa stalks by self-sharpening cutters made of gradient materials
- Thermo-mechanical effects and microstructural evolution-coupled numerical simulation on the hot forming processes of superalloy turbine disk
- Endpoint prediction of BOF steelmaking based on state-of-the-art machine learning and deep learning algorithms
- Effect of calcium treatment on inclusions in 38CrMoAl high aluminum steel
- Effect of isothermal transformation temperature on the microstructure, precipitation behavior, and mechanical properties of anti-seismic rebar
- Evolution of residual stress and microstructure of 2205 duplex stainless steel welded joints during different post-weld heat treatment
- Effect of heating process on the corrosion resistance of zinc iron alloy coatings
- BOF steelmaking endpoint carbon content and temperature soft sensor model based on supervised weighted local structure preserving projection
- Innovative approaches to enhancing crack repair: Performance optimization of biopolymer-infused CXT
- Structural and electrochromic property control of WO3 films through fine-tuning of film-forming parameters
- Influence of non-linear thermal radiation on the dynamics of homogeneous and heterogeneous chemical reactions between the cone and the disk
- Thermodynamic modeling of stacking fault energy in Fe–Mn–C austenitic steels
- Research on the influence of cemented carbide micro-textured structure on tribological properties
- Performance evaluation of fly ash-lime-gypsum-quarry dust (FALGQ) bricks for sustainable construction
- First-principles study on the interfacial interactions between h-BN and Si3N4
- Analysis of carbon emission reduction capacity of hydrogen-rich oxygen blast furnace based on renewable energy hydrogen production
- Just-in-time updated DBN BOF steel-making soft sensor model based on dense connectivity of key features
- Effect of tempering temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Q125 shale gas casing steel
- Review Articles
- A review of emerging trends in Laves phase research: Bibliometric analysis and visualization
- Effect of bottom stirring on bath mixing and transfer behavior during scrap melting in BOF steelmaking: A review
- High-temperature antioxidant silicate coating of low-density Nb–Ti–Al alloy: A review
- Communications
- Experimental investigation on the deterioration of the physical and mechanical properties of autoclaved aerated concrete at elevated temperatures
- Damage evaluation of the austenitic heat-resistance steel subjected to creep by using Kikuchi pattern parameters
- Topical Issue on Focus of Hot Deformation of Metaland High Entropy Alloys - Part II
- Synthesis of aluminium (Al) and alumina (Al2O3)-based graded material by gravity casting
- Experimental investigation into machining performance of magnesium alloy AZ91D under dry, minimum quantity lubrication, and nano minimum quantity lubrication environments
- Numerical simulation of temperature distribution and residual stress in TIG welding of stainless-steel single-pass flange butt joint using finite element analysis
- Special Issue on A Deep Dive into Machining and Welding Advancements - Part I
- Electro-thermal performance evaluation of a prismatic battery pack for an electric vehicle
- Experimental analysis and optimization of machining parameters for Nitinol alloy: A Taguchi and multi-attribute decision-making approach
- Experimental and numerical analysis of temperature distributions in SA 387 pressure vessel steel during submerged arc welding
- Optimization of process parameters in plasma arc cutting of commercial-grade aluminium plate
- Multi-response optimization of friction stir welding using fuzzy-grey system
- Mechanical and micro-structural studies of pulsed and constant current TIG weldments of super duplex stainless steels and Austenitic stainless steels
- Stretch-forming characteristics of austenitic material stainless steel 304 at hot working temperatures
- Work hardening and X-ray diffraction studies on ASS 304 at high temperatures
- Study of phase equilibrium of refractory high-entropy alloys using the atomic size difference concept for turbine blade applications
- A novel intelligent tool wear monitoring system in ball end milling of Ti6Al4V alloy using artificial neural network
- A hybrid approach for the machinability analysis of Incoloy 825 using the entropy-MOORA method
- Special Issue on Recent Developments in 3D Printed Carbon Materials - Part II
- Innovations for sustainable chemical manufacturing and waste minimization through green production practices
- Topical Issue on Conference on Materials, Manufacturing Processes and Devices - Part I
- Characterization of Co–Ni–TiO2 coatings prepared by combined sol-enhanced and pulse current electrodeposition methods
- Hot deformation behaviors and microstructure characteristics of Cr–Mo–Ni–V steel with a banded structure
- Effects of normalizing and tempering temperature on the bainite microstructure and properties of low alloy fire-resistant steel bars
- Dynamic evolution of residual stress upon manufacturing Al-based diesel engine diaphragm
- Study on impact resistance of steel fiber reinforced concrete after exposure to fire
- Bonding behaviour between steel fibre and concrete matrix after experiencing elevated temperature at various loading rates
- Diffusion law of sulfate ions in coral aggregate seawater concrete in the marine environment
- Microstructure evolution and grain refinement mechanism of 316LN steel
- Investigation of the interface and physical properties of a Kovar alloy/Cu composite wire processed by multi-pass drawing
- The investigation of peritectic solidification of high nitrogen stainless steels by in-situ observation
- Microstructure and mechanical properties of submerged arc welded medium-thickness Q690qE high-strength steel plate joints
- Experimental study on the effect of the riveting process on the bending resistance of beams composed of galvanized Q235 steel
- Density functional theory study of Mg–Ho intermetallic phases
- Investigation of electrical properties and PTCR effect in double-donor doping BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics
- Special Issue on Thermal Management and Heat Transfer
- On the thermal performance of a three-dimensional cross-ternary hybrid nanofluid over a wedge using a Bayesian regularization neural network approach
- Time dependent model to analyze the magnetic refrigeration performance of gadolinium near the room temperature
- Heat transfer characteristics in a non-Newtonian (Williamson) hybrid nanofluid with Hall and convective boundary effects
- Computational role of homogeneous–heterogeneous chemical reactions and a mixed convective ternary hybrid nanofluid in a vertical porous microchannel
- Thermal conductivity evaluation of magnetized non-Newtonian nanofluid and dusty particles with thermal radiation
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- De-chlorination of poly(vinyl) chloride using Fe2O3 and the improvement of chlorine fixing ratio in FeCl2 by SiO2 addition
- Reductive behavior of nickel and iron metallization in magnesian siliceous nickel laterite ores under the action of sulfur-bearing natural gas
- Study on properties of CaF2–CaO–Al2O3–MgO–B2O3 electroslag remelting slag for rack plate steel
- The origin of {113}<361> grains and their impact on secondary recrystallization in producing ultra-thin grain-oriented electrical steel
- Channel parameter optimization of one-strand slab induction heating tundish with double channels
- Effect of rare-earth Ce on the texture of non-oriented silicon steels
- Performance optimization of PERC solar cells based on laser ablation forming local contact on the rear
- Effect of ladle-lining materials on inclusion evolution in Al-killed steel during LF refining
- Analysis of metallurgical defects in enamel steel castings
- Effect of cooling rate and Nb synergistic strengthening on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-strength rebar
- Effect of grain size on fatigue strength of 304 stainless steel
- Analysis and control of surface cracks in a B-bearing continuous casting blooms
- Application of laser surface detection technology in blast furnace gas flow control and optimization
- Preparation of MoO3 powder by hydrothermal method
- The comparative study of Ti-bearing oxides introduced by different methods
- Application of MgO/ZrO2 coating on 309 stainless steel to increase resistance to corrosion at high temperatures and oxidation by an electrochemical method
- Effect of applying a full oxygen blast furnace on carbon emissions based on a carbon metabolism calculation model
- Characterization of low-damage cutting of alfalfa stalks by self-sharpening cutters made of gradient materials
- Thermo-mechanical effects and microstructural evolution-coupled numerical simulation on the hot forming processes of superalloy turbine disk
- Endpoint prediction of BOF steelmaking based on state-of-the-art machine learning and deep learning algorithms
- Effect of calcium treatment on inclusions in 38CrMoAl high aluminum steel
- Effect of isothermal transformation temperature on the microstructure, precipitation behavior, and mechanical properties of anti-seismic rebar
- Evolution of residual stress and microstructure of 2205 duplex stainless steel welded joints during different post-weld heat treatment
- Effect of heating process on the corrosion resistance of zinc iron alloy coatings
- BOF steelmaking endpoint carbon content and temperature soft sensor model based on supervised weighted local structure preserving projection
- Innovative approaches to enhancing crack repair: Performance optimization of biopolymer-infused CXT
- Structural and electrochromic property control of WO3 films through fine-tuning of film-forming parameters
- Influence of non-linear thermal radiation on the dynamics of homogeneous and heterogeneous chemical reactions between the cone and the disk
- Thermodynamic modeling of stacking fault energy in Fe–Mn–C austenitic steels
- Research on the influence of cemented carbide micro-textured structure on tribological properties
- Performance evaluation of fly ash-lime-gypsum-quarry dust (FALGQ) bricks for sustainable construction
- First-principles study on the interfacial interactions between h-BN and Si3N4
- Analysis of carbon emission reduction capacity of hydrogen-rich oxygen blast furnace based on renewable energy hydrogen production
- Just-in-time updated DBN BOF steel-making soft sensor model based on dense connectivity of key features
- Effect of tempering temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Q125 shale gas casing steel
- Review Articles
- A review of emerging trends in Laves phase research: Bibliometric analysis and visualization
- Effect of bottom stirring on bath mixing and transfer behavior during scrap melting in BOF steelmaking: A review
- High-temperature antioxidant silicate coating of low-density Nb–Ti–Al alloy: A review
- Communications
- Experimental investigation on the deterioration of the physical and mechanical properties of autoclaved aerated concrete at elevated temperatures
- Damage evaluation of the austenitic heat-resistance steel subjected to creep by using Kikuchi pattern parameters
- Topical Issue on Focus of Hot Deformation of Metaland High Entropy Alloys - Part II
- Synthesis of aluminium (Al) and alumina (Al2O3)-based graded material by gravity casting
- Experimental investigation into machining performance of magnesium alloy AZ91D under dry, minimum quantity lubrication, and nano minimum quantity lubrication environments
- Numerical simulation of temperature distribution and residual stress in TIG welding of stainless-steel single-pass flange butt joint using finite element analysis
- Special Issue on A Deep Dive into Machining and Welding Advancements - Part I
- Electro-thermal performance evaluation of a prismatic battery pack for an electric vehicle
- Experimental analysis and optimization of machining parameters for Nitinol alloy: A Taguchi and multi-attribute decision-making approach
- Experimental and numerical analysis of temperature distributions in SA 387 pressure vessel steel during submerged arc welding
- Optimization of process parameters in plasma arc cutting of commercial-grade aluminium plate
- Multi-response optimization of friction stir welding using fuzzy-grey system
- Mechanical and micro-structural studies of pulsed and constant current TIG weldments of super duplex stainless steels and Austenitic stainless steels
- Stretch-forming characteristics of austenitic material stainless steel 304 at hot working temperatures
- Work hardening and X-ray diffraction studies on ASS 304 at high temperatures
- Study of phase equilibrium of refractory high-entropy alloys using the atomic size difference concept for turbine blade applications
- A novel intelligent tool wear monitoring system in ball end milling of Ti6Al4V alloy using artificial neural network
- A hybrid approach for the machinability analysis of Incoloy 825 using the entropy-MOORA method
- Special Issue on Recent Developments in 3D Printed Carbon Materials - Part II
- Innovations for sustainable chemical manufacturing and waste minimization through green production practices
- Topical Issue on Conference on Materials, Manufacturing Processes and Devices - Part I
- Characterization of Co–Ni–TiO2 coatings prepared by combined sol-enhanced and pulse current electrodeposition methods
- Hot deformation behaviors and microstructure characteristics of Cr–Mo–Ni–V steel with a banded structure
- Effects of normalizing and tempering temperature on the bainite microstructure and properties of low alloy fire-resistant steel bars
- Dynamic evolution of residual stress upon manufacturing Al-based diesel engine diaphragm
- Study on impact resistance of steel fiber reinforced concrete after exposure to fire
- Bonding behaviour between steel fibre and concrete matrix after experiencing elevated temperature at various loading rates
- Diffusion law of sulfate ions in coral aggregate seawater concrete in the marine environment
- Microstructure evolution and grain refinement mechanism of 316LN steel
- Investigation of the interface and physical properties of a Kovar alloy/Cu composite wire processed by multi-pass drawing
- The investigation of peritectic solidification of high nitrogen stainless steels by in-situ observation
- Microstructure and mechanical properties of submerged arc welded medium-thickness Q690qE high-strength steel plate joints
- Experimental study on the effect of the riveting process on the bending resistance of beams composed of galvanized Q235 steel
- Density functional theory study of Mg–Ho intermetallic phases
- Investigation of electrical properties and PTCR effect in double-donor doping BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics
- Special Issue on Thermal Management and Heat Transfer
- On the thermal performance of a three-dimensional cross-ternary hybrid nanofluid over a wedge using a Bayesian regularization neural network approach
- Time dependent model to analyze the magnetic refrigeration performance of gadolinium near the room temperature
- Heat transfer characteristics in a non-Newtonian (Williamson) hybrid nanofluid with Hall and convective boundary effects
- Computational role of homogeneous–heterogeneous chemical reactions and a mixed convective ternary hybrid nanofluid in a vertical porous microchannel
- Thermal conductivity evaluation of magnetized non-Newtonian nanofluid and dusty particles with thermal radiation

