Abstract
Bismuth oxide has been considered as a promising electrode material due to the high theoretical capacity, low cost, and non-toxic nature. However, its application has been limited by the low electrical conductivity. In this work, bismuth oxide/commercial activated carbon composite were successfully synthesized through hydrothermal method. Bismuth nitrate pentahydrate with concentrations of 8, 24, and 32 mmol were mixed with Na2SO4, NaOH, and commercial activated carbon. The mixture was then put into a hydrothermal reactor and heated at 110°C for 5 h. These composite materials can have a 102–105 higher electrical conductivity, depending on the bismuth oxide ratio, compared to both bismuth oxide and commercial AC separately.
1 Introduction
The battery is an electrical energy storage technology that is able to convert chemical energy into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions of reduction and oxidation [1]. Battery performance involves the transfer of electrons from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode) so as to produce an electric current and a potential difference [2]. The use of materials with high charge storage quality can materialize more durable discharge process and shorter or more efficient charging process, thereby reducing the consumption of electrical energy [3].
The battery consists of an electrode, electrolyte, and separator. The electrode is a battery component that contains active ingredients. The battery electrodes are divided into cathode and anode. The anode is a negative electrode associated with a half-cell oxidation reaction that releases electrons into the external circuit [4]. Materials that can be used as anodes must have good ion/charge conductivity, large energy capacity [5], long cycle life, easy to process, non-toxic, and low in price. One of the kind of materials that can be used as a battery anode is metal oxides because of its high theoretical capacity and low cost, such as bismuth oxide (Bi2O3), which has good electrical and optical properties [6], has a volumetric capacity value of 3,765 mA h cm−1, in the form of Bi2O3 has a potential difference of 2.8 V, is non-toxic, and relatively cheap [7]. However, the use of bismuth oxide as an anode has a drawback, namely the low conductivity value at 1.56 × 10−7 S m−1 [8], responsible for the slow ion/charge conductivity of the anode, inferring the need for additional materials to produce higher conductivity value, such as activated carbon.
Xia et al. [9] in their research on the synthesis of mesoporous carbon composites with Bi2O3 as an electrode material using a microwave, obtained excellent performance capacitance and specific capacity reaching 386 F g−1. Wang et al. [10] reported on the synthesis of activated carbon composites with bismuth oxide using the vacuum impregnation method as a supercapacitor. The result was that the activated carbon composite with bismuth oxide had a specific capacitance value of 332.6 F g−1 at 1 A g−1. In addition, a recent study by Astuti et al. [8] regarding the synthesis of Bi/rice husk AC composite by hydrothermal method with variations in the weight ratio of activated carbon and bismuth nitrate of 2:1, 1:1, and 1:2, produced electrical conductivities of 0.51 × 10−5, 1.24 × 10−5, and 0.59 × 10−5 S m−1, respectively. The electrical conductivity value obtained, based on the said results, did not significantly increase on the account that the composition between activated carbon and bismuth oxide that had been formed might not be precise, emphasizing that the ratio/composition of a composite is very important. Meanwhile, the synthesis of bismuth oxide using the hydrothermal method showed higher electrical conductivity of the product formed in comparison with pure bismuth oxide [11] and composites produced in Astuti et al. [8]. Recently, Astuti et al. [12] reported the production of bismuth oxide/activated carbon composite synthesized using hydrothermal method. The activated carbon was from rice husk. The investigation recommends on paying attention to the factors affecting the formation of composite particularly the composition factor of precursor.
Pertaining to the above, a Bi/AC composite was synthesized with various concentrations of bismuth nitrate pentahydrate (BNP) using the hydrothermal method to ensure that Bi2O3, as the main constituent of the composite, can be formed optimally and has a high electrical conductivity value. Moreover, the variation in the mole concentration of BNP used was designed to determine the effect of concentration on the formation of bismuth oxide and the characteristics of the composite material produced and would later be used as a battery anode. The combining of activated carbon with bismuth oxide into a composite was carried out to improve the electrical properties of bismuth oxide using the hydrothermal method with varying concentrations of BNP.
2 Research methodology
2.1 Materials
The materials used in this study were BNP (Sigma Aldrich), distilled water, sodium sulfate (Merck), sodium hydroxide (Merck), commercial activated carbon (Brataco). All chemicals were of analytical grade without further purification.
2.2 Research methodology
2.2.1 Synthesis of Bi/AC composites
Synthesis of Bi/AC composites were carried out using hydrothermal method with varying concentrations of BNP (Bi(NO3)3·5H2O) of 8, 24, and 32 mmol. 8 mmol of Bi(NO3)3·5H2O was added with 12 mmol Na2SO4, dissolved in 40 mL distilled water, then stirred using IKA RH Basic KT/C at 1,500 rpm for 45 min. The solution mixture was then added with 40 mL of 72 mmol of NaOH [13]. Later, 0.5 g of commercial coconut shell AC was added to the solution mixture. The solution mixture was then put into a hydrothermal reactor and heated at 110°C for 5 h. The resulting mixture solution was cooled and then filtered. The filtered precipitate was dried using an oven (Fisher Scientific) at a temperature of 110°C for 60 min. It was then sieved with a size of 100 mesh. The same treatment was applied to the synthesis of composites Bi(NO3)3·5H2O at 24 and 32 mmol.
2.2.2 Characterization of Bi/AC composites
The Bi/AC composites were characterized by Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) spectrometer Shimadzu IRAffinity-1 to determine the functional groups of the composite material. FTIR analysis was performed at wavenumbers 4,000–400 cm−1 with a frequency rate of 0.25 cm−1 at room temperature. The X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Shimadzu 7000 analysis for the identification of crystalline structures was carried out by measuring at an angle of 2θ with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 0.15406 nm). Composite conductivity values were determined using Electrochemical Impedance Spectrometry (EIS) (LCR meter HIOKI 3532-50). The samples were analyzed in the form of pellets with a diameter of 1.5 cm and a thickness of 2–5 mm. Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-Ray mapping, Jeol JED 6510LA, was used to determine surface morphology and composition of the composite material, while thermal gravimetric analysis–differential thermal analysis (TGA–DTG), Mettler Toledo TGA/DSC 3+, was used to measure changes in mass, thermal decomposition, and thermal stability of the composite material with measurements in the temperature range of 40–800°C. To determine the surface area, the adsorption–desorption isotherms, the pore size, and pore volume of the composite materials, the TriStar II 3020 Gas Sorption Analyzer (GSA) was used.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Bi/AC composites
Bi/AC composites were produced by mixing Bi(NO3)3·5H2O, sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and commercial AC. The mixing of Bi(NO3)3·5H2O and Na2SO4 formed a complex compound, Bi2O(OH)2SO4, as per equation (1), characterized by the presence of a white suspension. When the NaOH solution was added, the OH– ions from the NaOH solution would gradually react with the Bi2O(OH)2SO4 complex to form Bi(OH)3 as presented in equation (2). The Bi(OH)3 solution along with commercial AC were put into a hydrothermal reactor (autoclave) and then heated. During the heating process, Bi(OH)3 would hydrate and turn into Bi2O3 [13] as illustrated in equation (3). The overall reaction mechanism that occurred is as follows:
The colors of the synthesized Bi/AC vary with the ratio of bismuth oxide in the composite as seen in Figure 1. The 8 mmol Bi/AC composite produced a darker color because the percentages of BNP and commercial AC were almost the same and the color of the activated carbon was still dominated. The 24 mmol Bi/AC composite has light gray in color because the percentage of added BNP was more than the commercial AC, and thus the color of the activated carbon was not too dominant. The 32 mmol Bi/AC composite demonstrated a gray composite with a lumpy texture (agglomerate), as shown in Figure 2, attributed to the percentage of added BNP, which was higher than the commercial AC at 32 mmol. The color generated by the composites originated from the joint color of bismuth oxide, which is pale yellow [14], and commercial AC, which is black. The yellow color of Bi2O3 caused saturation of the black color on the activated carbon so that the resulting composite had appeared blackish gray.
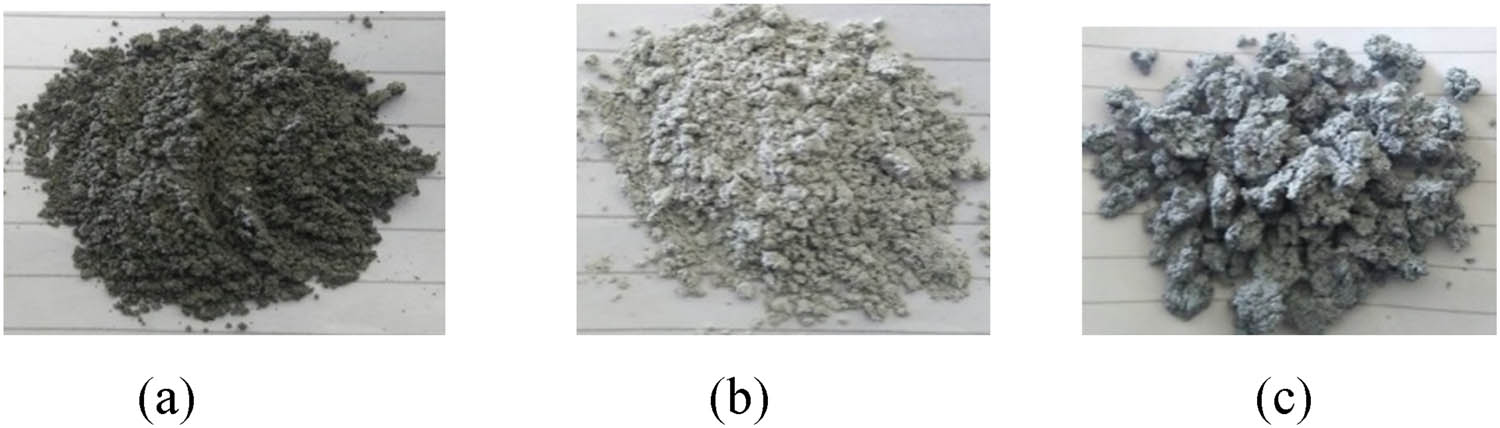
Bi/AC composites prepared with (a) 8 mmol, (b) 24 mmol, and (c) 32 mmol Bi(NO3)3·5H2O.
3.2 Material characteristics
3.2.1 Functional group structures
Figure 2 shows that the three composite samples had almost the same absorption peaks, namely the low absorption at wavenumber 826–833 cm−1, which identified the presence of the Bi–O–Bi group, and wavenumber 1,384–1,380 cm−1, which identified the stretching vibration of Bi–O [15]. The same peaks were also observed in the pure bismuth oxide sample, showcasing absorption at wavenumbers of about 840 cm−1, identifying the presence of the Bi–O–Bi group [16], and 1,384 cm−1, indicating the presence of the Bi–O group [17]. The results implied that Bi2O3 have been formed in the composite sample. Absorptions at around 1,600 cm−1 and 1,100 cm−1 were also observed in the three samples, indicating the presence of the C═C and C−O functional groups [18]. In the spectra of the commercial AC, these vibration modes were also observed at 1540.16 and 1040.90 cm−1. The spectra thus suggested that the composite had contained commercial AC. The absorption at wavenumber 3,440 cm−1 signified the vibrational stretching of the O–H group [19]. Complete FTIR test results on the functional groups of the 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites, pure Bi2O3, and commercial AC are shown in Table 1.
Functional groups in the FTIR spectra
| Functional group | Wavenumber in the observed sample (cm−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 mmol Bi/AC | 24 mmol Bi/AC | 32 mmol Bi/AC | Commercial AC | Bismuth oxide (Bi2O3) | |
| Bi–O | 1384.09 | 1383.77 | 1380.52 | — | 1384.67 |
| Bi–O–Bi | 826.25 | 833.75 | 826.25 | — | 839 |
| C═C | 1635.57 | 1640.70 | 1636.60 | 1540.16 | — |
| C–O | 1107.09 | 1116.28 | 1107.2 | 1040.90 | — |
| O–H | 3434.38 | 3448.04 | 343.72 | — | — |
3.2.2 XRD characterization
Figure 3 shows the diffractograms of composites, bismuth oxide database, commercial activated carbon and BNP. The XRD characterization result of the 8 mmol Bi/AC showed the presence of Bi2O3 with α-Bi2O3 (monoclinic) crystal structure denoted by peaks at 2θ = 27.453°, 33,316°, 26,992°, 46,372°, 26,992°, 37,667°; β-Bi2O3 (tetragonal) crystal structure demonstrated by peaks at 2θ = 30.184°, 46.372°; and γ-Bi2O3 (cubic) crystal structures at peaks of 2θ = 27.453° and 30.184°. The presence of commercial AC was indicated by the low intensity peaks at 2θ = 23.923°, 26.992°, 35.463°, while the pure BNP presence was denoted by the peak at 2θ = 30.184°. The 24 mmol Bi/AC composite showed the presence of α-Bi2O3 (monoclinic) crystal structure with low intensity peaks at 2θ = 46.86° and 56,692°; β-Bi2O3 (tetragonal) at 2θ = 30.094°, 32.672°, 46.860°; and γ-Bi2O3 (cubic) at 2θ = 30.094° and 32.672°. The presence of commercial AC was shown at 2θ = 23.879° and 35.201°, while the pure BNP were shown by peaks at 2θ = 30.094°, 32.672°, 42.099°, 53.239°. In the 32 mmol Bi/AC composite, the presence of Bi2O3 was indicated by the crystal structures of α-Bi2O3 (monoclinic) at 2θ = 27.485°, 33.305° and γ-Bi2O3 (cubic) at 2θ = 27.485°, 39.152° at low intensities. The presence of the commercial AC was denoted by peaks at 2θ = 22.463°, 35.594°, and the pure BNP was signified by peaks at 2θ = 21.822°, 28.97°, 31.373°, 35.594°, 40.712°, 53.274°. The complete data regarding the 2θ peaks of the composite samples compared with the 2θ peaks of Bi2O3 (JCPDS), commercial AC, and pure BNP data are shown in Table 2.
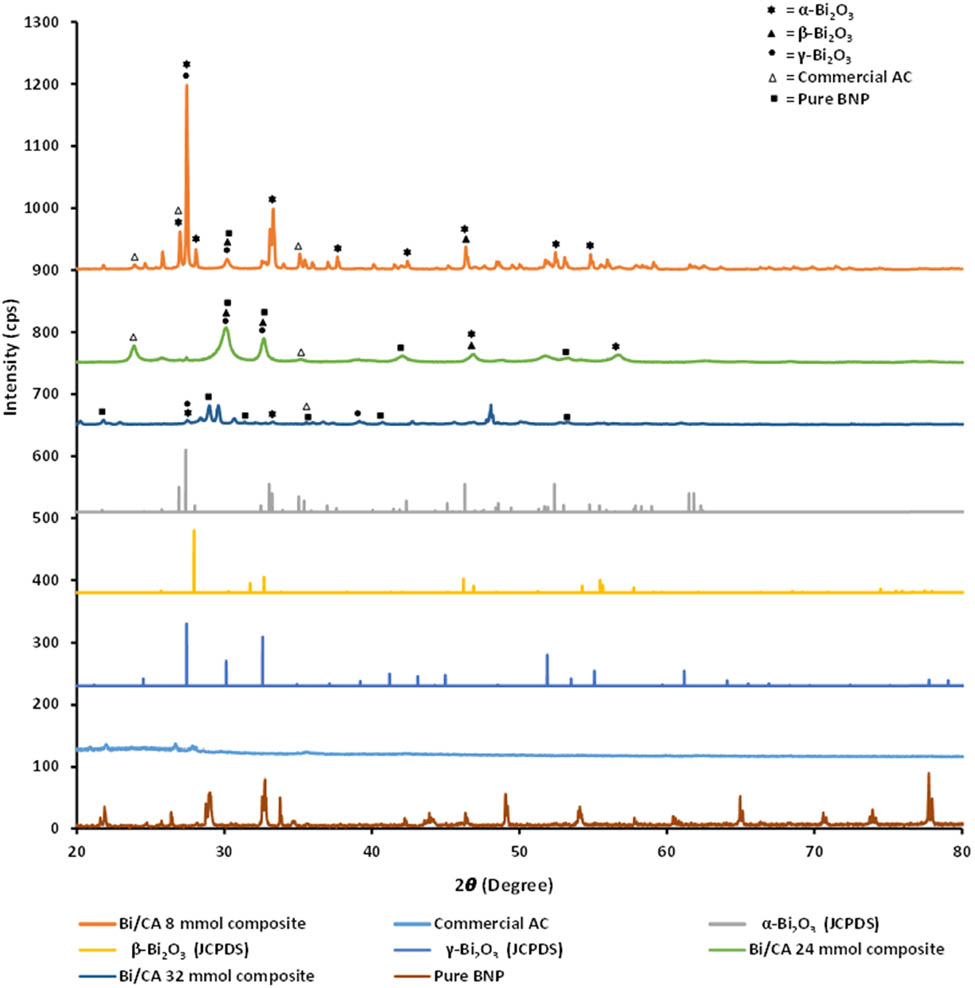
Diffractograms of 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites along with Bi2O3 (JCPDS database under the numbers 41-1449 for α-Bi2O3, 27-0050 for β-Bi2O3, and 45-1344 for γ-Bi2O3), commercial AC, and pure BNP.
XRD 2θ data comparison of the composite samples with Bi2O3 (JCPDS), commercial AC, and pure BNP
| Bi/Commercial AC Composite | 2θ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Bi2O3 | β-Bi2O3 | γ-Bi2O3 | Commercial AC | Pure BNP | |
| 8 mmol | 27.453° | 30.184° | 27.453° | 23.923° | 30.184° |
| 33.316° | |||||
| 26.992° | |||||
| 46.372° | 46.372° | 30.184° | 26.992° 35.463 | ||
| 26.992° | |||||
| 37.667° | |||||
| 24 mmol | 46.860° | 30.094° | 30.094° | 23.879° | 30.094° |
| 32.672° | |||||
| 56.692° | 32.672° | 32.672° | 35.201° | 42.099° | |
| 46.860° | 53.239° | ||||
| 32 mmol | 27.485° | — | 27.485° | 22.463° | 21.822° |
| 28.974° | |||||
| 31.373° | |||||
| 33.305° | 39.152° | 35.594° | 35.594° | ||
| 40,712° | |||||
| 53,274° | |||||
3.2.3 Electrical conductivity
Table 3 shows that the conductivity value of pure Bi2O3 was smaller than the conductivity value of activated carbon, connoting that the addition of activated carbon could increase the conductivity value of bismuth oxide. The addition of activated carbon functioned as a matrix in the composite prompted the distribution of bismuth oxide to be more even on the surface of the activated carbon [23]. The addition of activated carbon to bismuth oxide to create a composite also showed a higher conductivity value in the product made.
The conductivity values measured from the EIS test
| Sample | Conductivity (S m−1) |
|---|---|
| 8 mmol Bi/AC | 0.69 × 10−3 |
| 24 mmol Bi/AC | 0.15 × 10−2 |
| 32 mmol Bi/AC | 0.89 × 10−1 |
| Pure Bi2O3 | 0.15 × 10−6 [11] |
| BNP | 1.70 × 10−1 [12] |
| Commercial AC | 0.74 × 10−5 [22] |
The data shown in Table 3 demonstrate that the 32 mmol Bi/AC composite had the highest electrical conductivity value at 0.89 × 10−1 S m−1. This can be attributed to the fact that the 32 mmol composite had a higher percentage of BNP compared to the 8 mmol and 24 mmol composites. Measured through the EIS test, BNP was found to have a very high conductivity value, which was 1.70 × 10−1 S m−1. The 24 and 8 mmol Bi/AC composites had electrical conductivity values of 0.15 × 10−2 and 0.69 × 10−3 S m−1, respectively.
3.2.4 Distribution of elements containing in the composites
The SEM images of the 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites are shown in Figure 4, depicting long needle-like shape in the 8 mmol composite as the embodiment of the monoclinic Bi2O3 crystals [24]. Meanwhile, the 24 and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites were both irregular in shapes. The low content of Bi2O3 in the 24 and 32 mmol Bi/AC, as illustrated in the XRD data, brought the non-needle-like structure of the two composites.
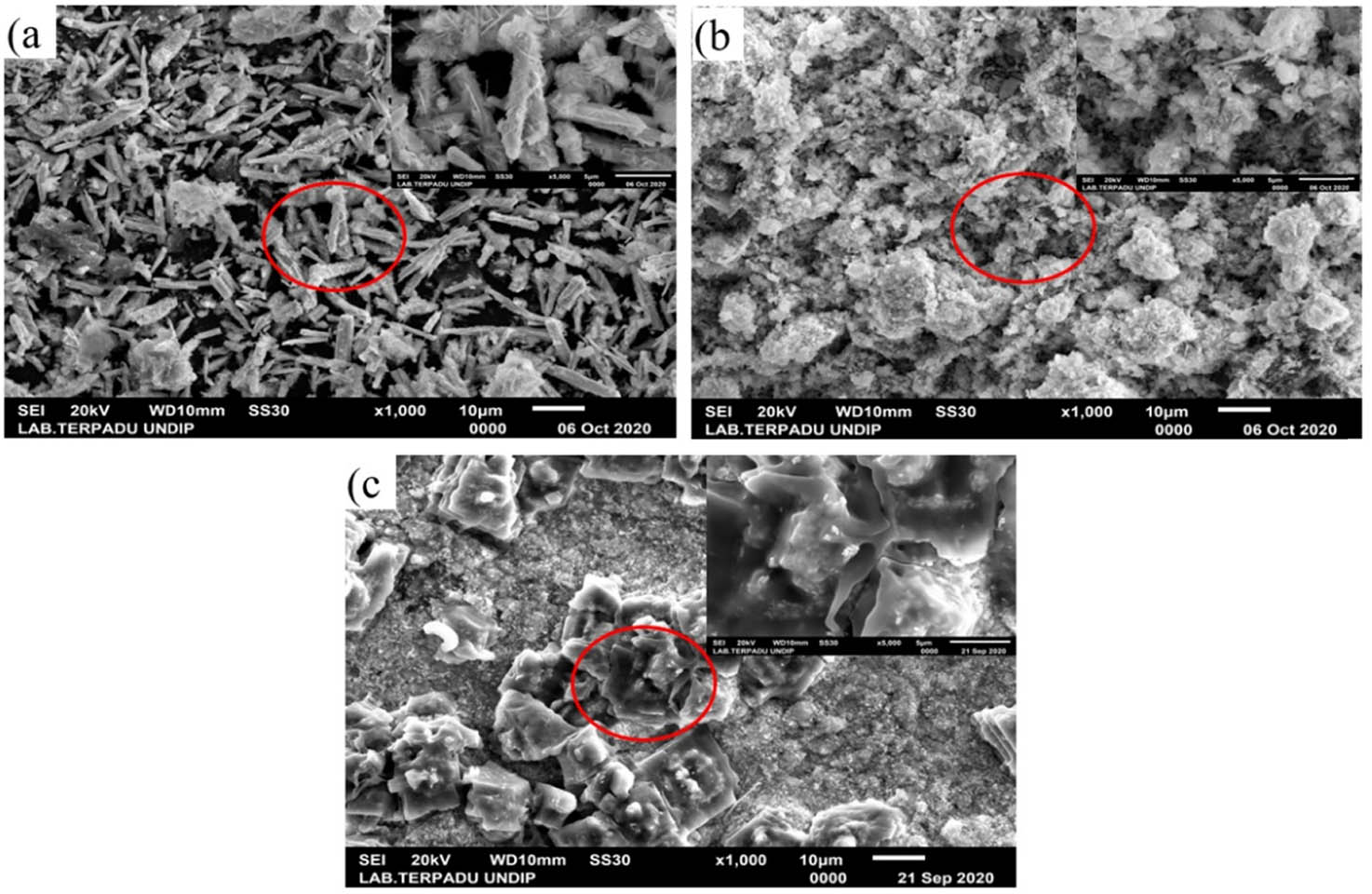
SEM images of Bi/AC composites prepared with (a) 8 mmol, (b) 24 mmol, and (c) 32 mmol BNP.
SEM mappings of 8, 24, and 32 mmol composites are shown in Figure 5. The 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites all had evenly distributed Bi element on the composite surface.
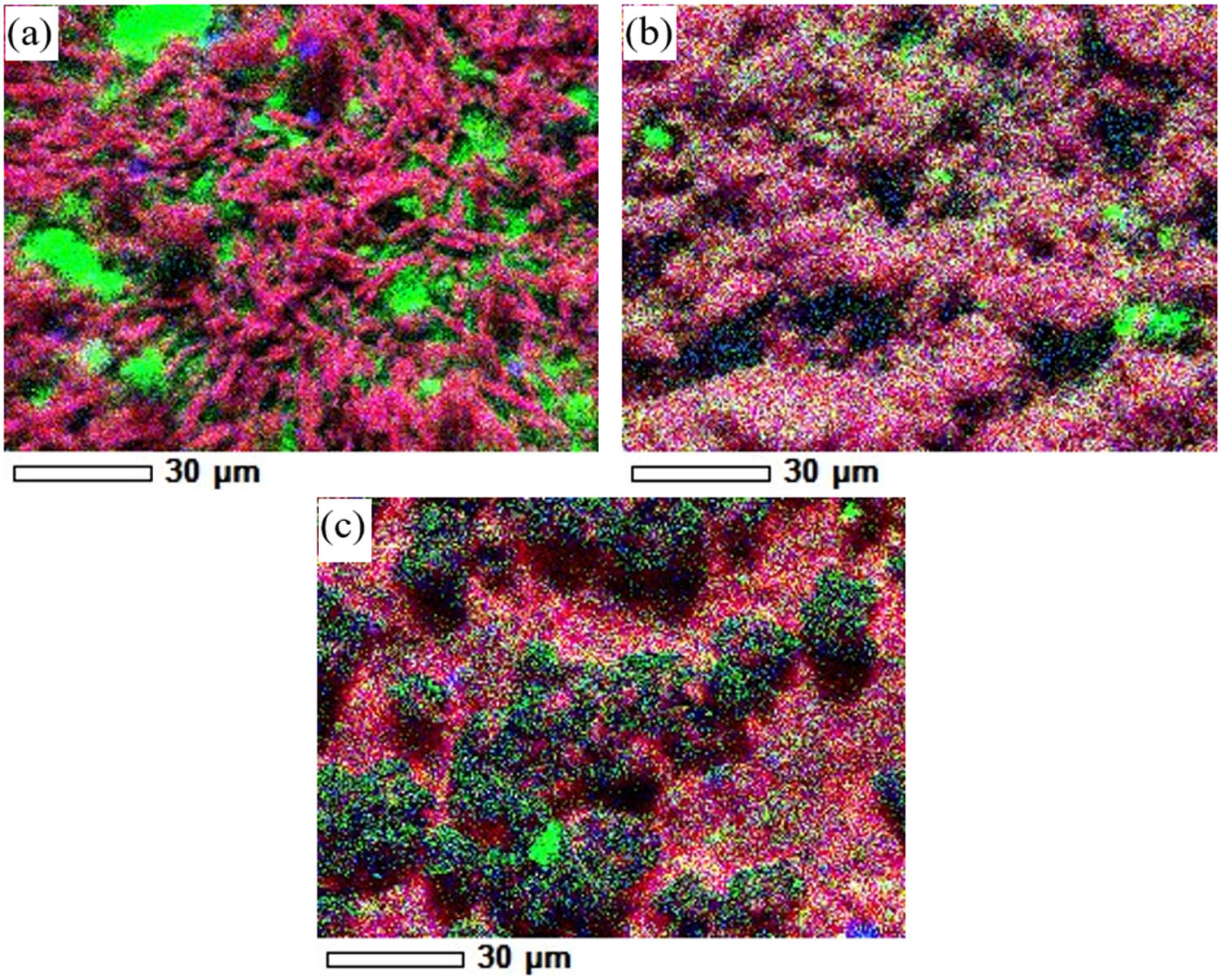
SEM mappings of Bi/AC composites prepared with (a) 8 mmol, (b) 24 mmol, and (c) 32 mmol BNP.
3.2.5 Transition phase
The TGA–DTG curves of the Bi/AC composites are shown in Figure 6, presenting the changes in mass of the 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites entailing the mass transformation phases from precursor to Bi2O3 and removal of the amorphous residue in the form of
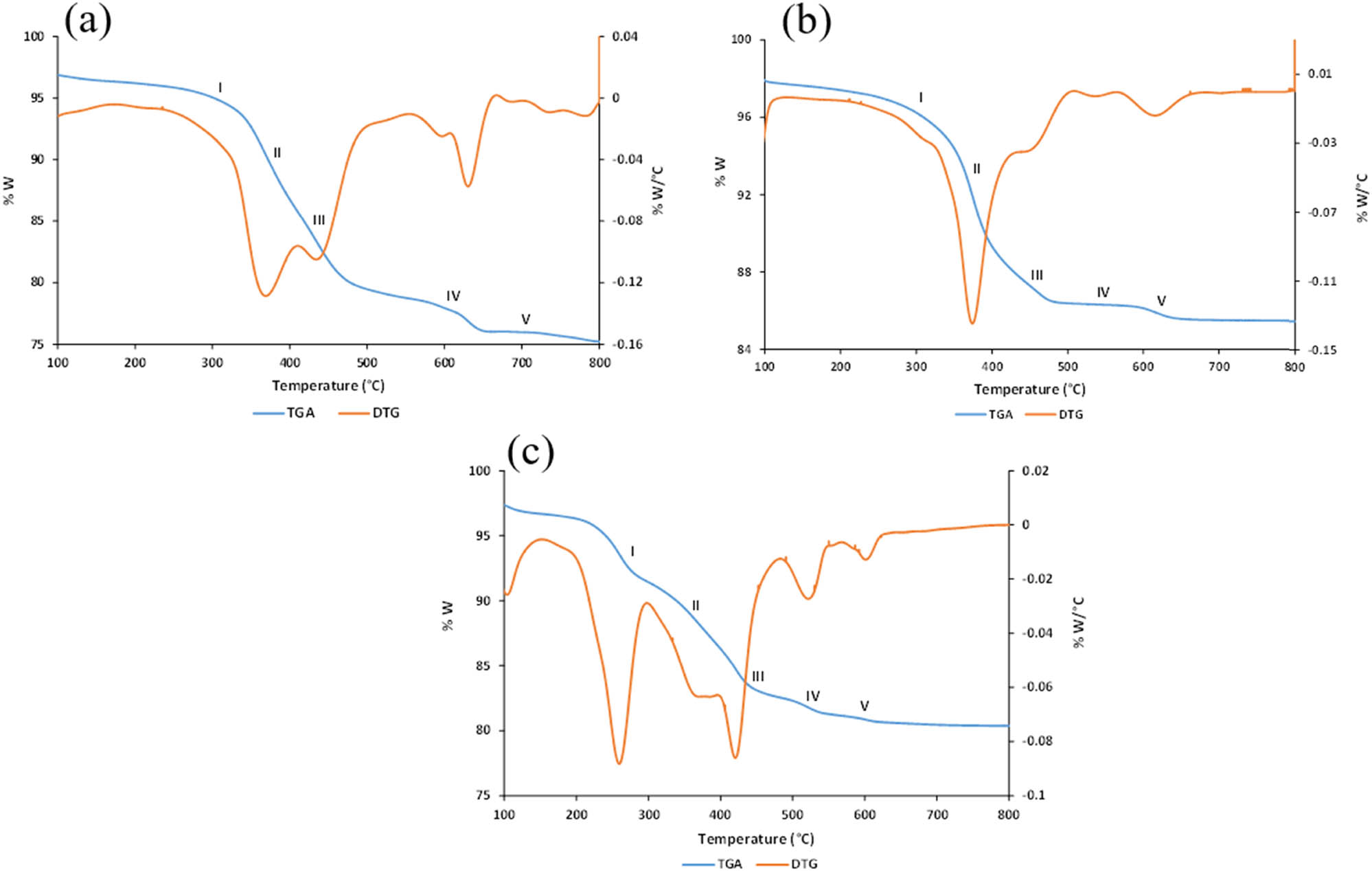
TGA–DTG curves of Bi/AC composites prepared with (a) 8 mmol, (b) 24 mmol, and (c) 32 mmol BNP.
3.2.6 Pore and surface properties
Figure 7 shows that the 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composite had similar patterns, whereby the adsorption process ensued from low pressure to the relative pressure of 1 (p/p°). At p/p° = 1, the adsorption process had reached its saturation point or maximum adsorption capacity, which would then be replaced by the desorption process. The 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites all had type IV adsorption isotherms characterized by the presence of loop hysteresis expressive of the porous nature of the materials as they were able to adsorb N2.
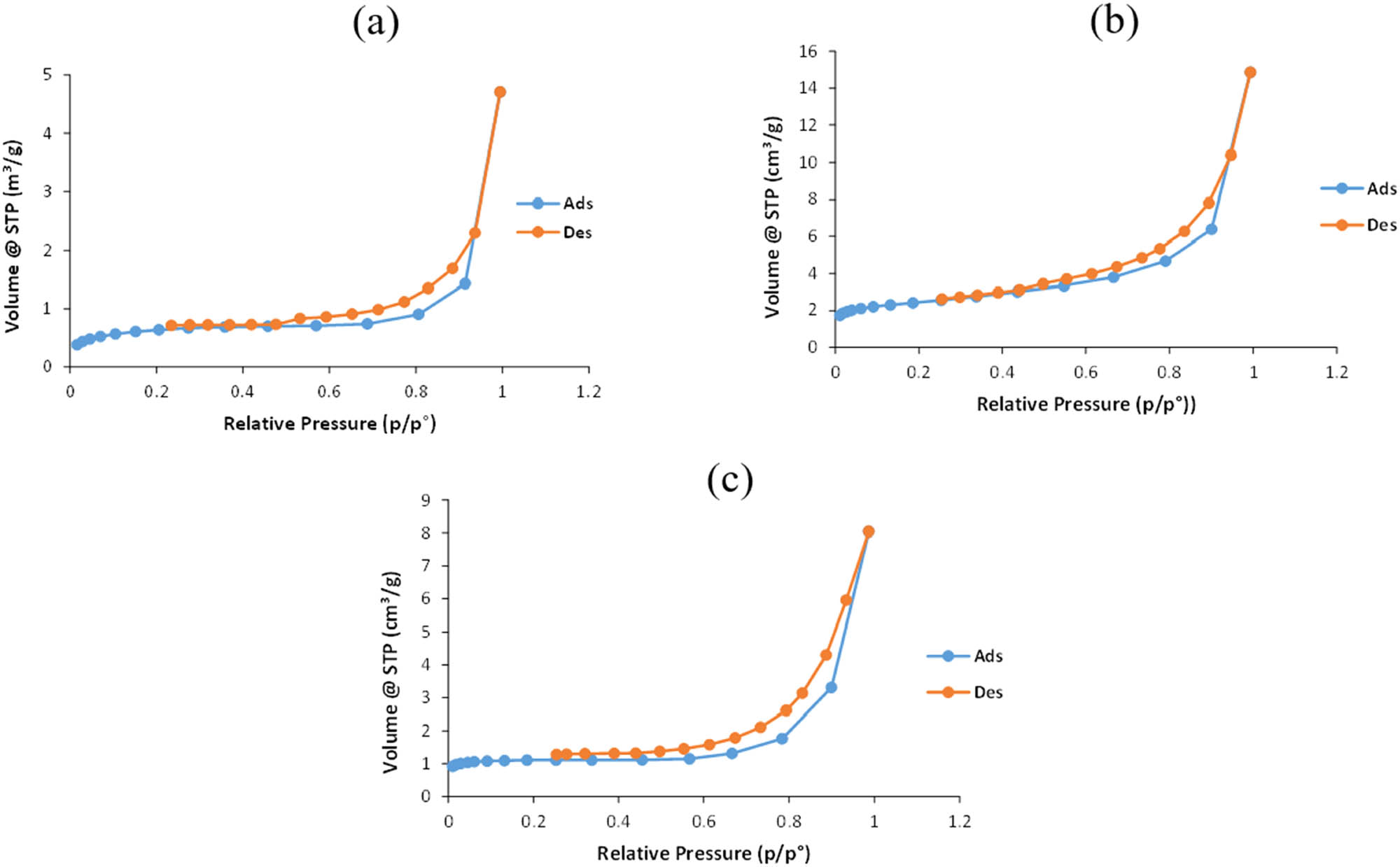
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of Bi/CA composites prepared with (a) 8 mmol, (b) 24 mmol, and (c) 32 mmol BNP.
Based on the data presented in Table 4, the 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/AC composites were all classified as mesoporous materials (2–50 nm pore size) [27]. Table 4 also marks that the 8 mmol Bi/AC composite had a small surface area and pore volume with a fairly large pore size, which can be assumed that the 8 mmol composite had smaller number of pores. The 24 mmol Bi/AC composite had a large surface area and pore volume, as well as small pore size implying a higher number of pores. Meanwhile, the 32 mmol composite had smaller surface area and pore volume than the 24 mmol composite but larger than the 8 mmol composite, with its pore size largest out of all three composites produced. Based on this, it can be concluded that the 32 mmol composite had fewer pores than the 24 mmol composite but had more pores than the 8 mmol composite.
GSA analysis results of 8, 24, and 32 mmol Bi/commercial AC composite
| Parameter | Composite sample | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 mmol Bi/CA | 24 mmol Bi/CA | 32 mmol Bi/CA | Commercial AC | |
| Surface area (m2 g−1) | 2.131 | 8.329 | 3.514 | 39.733 |
| Pore volume (cm3 g−1) | 0.007 | 0.022 | 0.0124 | 0.032 |
| Pore size (nm) | 13.655 | 11.044 | 14.167 | 3.267 |
Subhan [4] explained that a material with high porosity would give rise to a large resistance, thereby reducing the conductivity value of the material. However, it should be borne in mind that Bi/AC prepared with 32 mmol BNP contains high concentration of BNP as precursor which may results in the highest electrical conductivity compared to other composites [12].
4 Conclusion
Bi/AC composites were successfully synthesized with 8, 24, and 32 mmol variations in the amount of BNP, confirmed by FTIR and XRD analyses. The 8 mmol Bi/AC composite showed the presence of monoclinic Bi2O3 crystals and had an electrical conductivity value of 0.69 × 10−3 S m−1. The 24 and 32 mmol Bi/commercial AC composites showed a low Bi2O3 content based on the XRD characterization, and accordingly portrayed by Bi2O3 lack of appearance in the SEM characterization. The two composites had electrical conductivity values of 0.15 × 10−2 and 0.89 × 10−1 Sm−1, respectively. The three composites produced were all porous materials as they were able to adsorb N2 gas. The electrical conductivity of composites prepared with 24 and 32 mmol BNP could be due to the high content of impurities resulting from precursor BNP. This study is expected to provide a scientific contribution related to the utilization of activated carbon and bismuth oxide in the form of a composite as an alternative material for lithium-ion battery anode. Factors affecting composite properties such as the right composition during the synthesis process need special attention to gain composite with the desired properties.
-
Funding information: The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Research and Technology for the funding support in the 2021 fiscal year through the basic research scheme with grant No. 225-71/UN7.6.1/PP/2021.
-
Author contributions: Y.A. – conceptualization; Y.A. and S.T. – data curation and analysis and writing – original draft manuscript; Y.A., A.D., and H.W. – writing – review and validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Linden D, Reddy T. Handbook of batteries. USA: McGraw-Hill Companies Inc.; 2002.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Aflahannisa A, Astuti A. Sintesis nanokomposit karbon-TiO2 Sebagai Anoda baterai lithium. J Fisika Unand. 2016;5(4):357–63.10.25077/jfu.5.4.357-363.2016Search in Google Scholar
[3] Prihandoko B. Pemanfaatan soda lime silica dalam pembuatan komposit elektrolit baterai lithium = Application of soda lime silica for the composite synthesis of lithium battery electrolyte. PhD Thesis, Universitas Indonesia: Depok; 2008.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Subhan A. Fabrikasi dan karakterisasi Li4Ti5O12 untuk bahan anoda Baterai Lithium Keramik = Sinthesis and characterization of Li4Ti5O12 as anode material for lithium ceramic battery. PhD Thesis, Universitas Indonesia: Depok; 2011.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Goriparti S, Miele E, De Angelis F, Di Fabrizio E, Zaccaria RP, Capiglia C. Review on recent progress of nanostructured anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2014;257:421–43.10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.11.103Search in Google Scholar
[6] Bedoya Hincapie CM, Pinzon Cardenas MJ, Alfonso Orjuela JE, Restrepo Parra E, Olaya Florez JJ. Physical–chemical properties of bismuth and bismuth oxides: synthesis, characterization and applications. Dyna (Medellin). 2012;79(176):139–48.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Li Y, Trujillo MA, Fu E, Patterson B, Fei L, Xu Y, et al. Bismuth oxide: a new lithium-ion battery anode. J Mater Chem A Mater Energy Sustain. 2013 Oct;1(39):12123–7.10.1039/c3ta12655bSearch in Google Scholar
[8] Astuti Y, Aprialdi F, Haryanto I. Synthesis of activated carbon/bismuth oxide composite and its characterization for battery electrode. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing; 2019.10.1088/1757-899X/509/1/012153Search in Google Scholar
[9] Xia N, Yuan D, Zhou T, Chen J, Mo S, Liu Y. Microwave synthesis and electrochemical characterization of mesoporous carbon@ Bi2O3 composites. Mater Res Bull. 2011;46(5):687–91.10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.01.022Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wang S, Jin C, Qian W. Bi2O3 with activated carbon composite as a supercapacitor electrode. J Alloy Compd. 2014;615:12–7.10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.06.149Search in Google Scholar
[11] Astuti Y, Musthafa F, Arnelli A, Nurhasanah I. French fries-like bismuth oxide: physicochemical properties, electrical conductivity and photocatalytic activity. Bull Chem React Eng Catal. 2022;17(1):146–56.10.9767/bcrec.17.1.12554.146-156Search in Google Scholar
[12] Astuti Y, Mei R, Darmawan A, Arnelli A, Widiyandari H. Enhancement of electrical conductivity of bismuth oxide/activated carbon composite. Scientia Iranica In Press. 2022.10.24200/sci.2022.57674.5359Search in Google Scholar
[13] Wu C, Shen L, Huang Q, Zhang YC. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Bi2O3 nanowires. Mater Lett. 2011;65(7):1134–6.10.1016/j.matlet.2011.01.021Search in Google Scholar
[14] Astuti Y, Andianingrum R, Wulansari AD, Haris A. The influence of precipitating agents on the morphological and photocatalytic properties of bismuth oxide. Adv Sci Lett. 2017;23(7):6521–3.10.1166/asl.2017.9671Search in Google Scholar
[15] Bartonickova E, Cihlar J, Castkova K. Microwave-assisted synthesis of bismuth oxide. Process Appl Ceram. 2007;1(1–2):29–33.10.2298/PAC0702029BSearch in Google Scholar
[16] Das TR, Patra S, Madhuri R, Sharma PK. Bismuth oxide decorated graphene oxide nanocomposites synthesized via sonochemical assisted hydrothermal method for adsorption of cationic organic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018 Jan;509:82–93.10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.102Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Bandyopadhyay S, Dutta A. Thermal, optical and dielectric properties of phase stabilized δ–Dy-Bi2O3 ionic conductors. J Phys Chem Solids. 2017;102:12–20.10.1016/j.jpcs.2016.11.001Search in Google Scholar
[18] Sastrohamidjojo H. Dasar-dasar spektroskopi. UGM Press: Yogyakarta; 2018.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y, Shao Q, Chen C, Jiang H, Su F, Hu Q, et al. Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of beta-bismuth (III) oxide nanopowders and their enhanced photocatalytic properties. Powder Technol. 2020;370:226–36.10.1016/j.powtec.2020.05.068Search in Google Scholar
[20] Astuti Y, Elesta PP, Widodo D S, Widiyandari H, Balgis R. Hydrazine and urea fueled-solution combustion method for Bi2O3 synthesis: characterization of physicochemical properties and photocatalytic activity. Bull Chem React Eng Catal. 2020;15(1):104–11.10.9767/bcrec.15.1.5483.104-111Search in Google Scholar
[21] Astuti Y, Amri D, Widodo DS, Widiyandari H, Balgis R, Ogi T. Effect of fuels on the physicochemical properties and photocatalytic activity of bismuth oxide, synthesized using solution combustion method. Int J Technol. 2020;11(1):26–36.10.14716/ijtech.v11i1.3342Search in Google Scholar
[22] Astuti Y, Widiyandari H, Zaqia FA, Annisa L, Fajarwati RM, Hartinah S. Physicochemical characteristics and electrical conductivity of bismuth oxide/activated carbon composite. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Vol. 1053. Issue 1. IOP Publishing; 2021. p. 012014.10.1088/1757-899X/1053/1/012014Search in Google Scholar
[23] Arsita Y, Astuti A. Sintesis Komposit TiO2/Karbon Aktif Berbasis Bambu Betung (Dendrocalamus asper) dengan menggunakan metode solid state reaction. J Fisika Unand. 2016;5(3):268–72.10.25077/jfu.5.3.268-272.2016Search in Google Scholar
[24] Irmawati R, Nasriah MN, Taufiq-Yap Y, Hamid SA. Characterization of bismuth oxide catalysts prepared from bismuth trinitrate pentahydrate: influence of bismuth concentration. Catal Today. 2004;93701–709; Yang Q, Li Y, Yin Q, Wang P, Cheng Y.-B. Hydrothermal synthesis of bismuth oxide needles. Mater Lett. 2002;55(1–2):46–9.10.1016/j.cattod.2004.06.065Search in Google Scholar
[25] Levin EM, Roth RS. Polymorphism of bismuth sesquioxide. I. Pure Bi2O3. J Res Natl Bur Stand A Phys Chem. 1964 Mar–Apr;68A(2):189–95.10.6028/jres.068A.019Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Zhang L, Wang G, Xiong Z, Tang H, Jiang C. Fabrication of flower-like direct Z-scheme β-Bi2O3/g-C3N4 photocatalyst with enhanced visible light photoactivity for Rhodamine B degradation. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;436:162–71.10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.280Search in Google Scholar
[27] Rouquerol J, Avnir D, Fairbridge C, Everett D, Haynes J, Pernicone N, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem. 1994;66(8):1739–58.10.1351/pac199466081739Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous phase by bimetallic metal-organic framework M/Fe-MOF (M = Co, Cu, and Mg)
- Assessment of using electronic portal imaging device for analysing bolus material utilised in radiation therapy
- A detailed investigation on highly dense CuZr bulk metallic glasses for shielding purposes
- Simulation of gamma-ray shielding properties for materials of medical interest
- Environmental impact assesment regulation applications and their analysis in Turkey
- Sample age effect on parameters of dynamic nuclear polarization in certain difluorobenzen isomers/MC800 asphaltene suspensions
- Passenger demand forecasting for railway systems
- Design of a Robust sliding mode controller for bioreactor cultures in overflow metabolism via an interdisciplinary approach
- Gamma, neutron, and heavy charged ion shielding properties of Er3+-doped and Sm3+-doped zinc borate glasses
- Bridging chiral de-tert-butylcalix[4]arenes: Optical resolution based on column chromatography and structural characterization
- Petrology and geochemistry of multiphase post-granitic dikes: A case study from the Gabal Serbal area, Southwestern Sinai, Egypt
- Comparison of the yield and purity of plasma exosomes extracted by ultracentrifugation, precipitation, and membrane-based approaches
- Bioactive triterpenoids from Indonesian medicinal plant Syzygium aqueum
- Investigation of the effects of machining parameters on surface integrity in micromachining
- The mesoporous aluminosilicate application as support for bifunctional catalysts for n-hexadecane hydroconversion
- Gamma-ray shielding properties of Nd2O3-added iron–boron–phosphate-based composites
- Numerical investigation on perforated sheet metals under tension loading
- Statistical analysis on the radiological assessment and geochemical studies of granite rocks in the north of Um Taghir area, Eastern Desert, Egypt
- Two new polypodane-type bicyclic triterpenoids from mastic
- Structural, physical, and mechanical properties of the TiO2 added hydroxyapatite composites
- Tribological properties and characterization of borided Co–Mg alloys
- Studies on Anemone nemorosa L. extracts; polyphenols profile, antioxidant activity, and effects on Caco-2 cells by in vitro and in silico studies
- Mechanical properties, elastic moduli, transmission factors, and gamma-ray-shielding performances of Bi2O3–P2O5–B2O3–V2O5 quaternary glass system
- Cyclic connectivity index of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- The role of passage numbers of donor cells in the development of Arabian Oryx – Cow interspecific somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos
- Mechanical property evaluation of tellurite–germanate glasses and comparison of their radiation-shielding characteristics using EPICS2017 to other glass systems
- Molecular screening of ionic liquids for CO2 absorption and molecular dynamic simulation
- Microwave-assisted preparation of Ag/Fe magnetic biochar from clivia leaves for adsorbing daptomycin antibiotics
- Iminodisuccinic acid enhances antioxidant and mineral element accumulation in young leaves of Ziziphus jujuba
- Cytotoxic activity of guaiane-type sesquiterpene lactone (deoxycynaropicrin) isolated from the leaves of Centaurothamnus maximus
- Effects of welding parameters on the angular distortion of welded steel plates
- Simulation of a reactor considering the Stamicarbon, Snamprogetti, and Toyo patents for obtaining urea
- Effect of different ramie (Boehmeria nivea L. Gaud) cultivars on the adsorption of heavy metal ions cadmium and lead in the remediation of contaminated farmland soils
- Impact of a live bacterial-based direct-fed microbial (DFM) postpartum and weaning system on performance, mortality, and health of Najdi lambs
- Anti-tumor effect of liposomes containing extracted Murrayafoline A against liver cancer cells in 2D and 3D cultured models
- Physicochemical properties and some mineral concentration of milk samples from different animals and altitudes
- Copper(ii) complexes supported by modified azo-based ligands: Nucleic acid binding and molecular docking studies
- Diagnostic and therapeutic radioisotopes in nuclear medicine: Determination of gamma-ray transmission factors and safety competencies of high-dense and transparent glassy shields
- Calculation of NaI(Tl) detector efficiency using 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K radioisotopes: Three-phase Monte Carlo simulation study
- Isolation and identification of unstable components from Caesalpinia sappan by high-speed counter-current chromatography combined with preparative high-performance liquid chromatography
- Quantification of biomarkers and evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxicity properties of Dodonaea viscosa grown in Saudi Arabia using HPTLC technique
- Characterization of the elastic modulus of ceramic–metal composites with physical and mechanical properties by ultrasonic technique
- GC-MS analysis of Vespa velutina auraria Smith and its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities in vitro
- Texturing of nanocoatings for surface acoustic wave-based sensors for volatile organic compounds
- Insights into the molecular basis of some chalcone analogues as potential inhibitors of Leishmania donovani: An integrated in silico and in vitro study
- (1R,2S,5R)-5-Methyl-2-(propan-2-yl)cyclohexyl 4-amino-3-phenylbutanoate hydrochloride: Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity
- On the relative extraction rates of colour compounds and caffeine during brewing, an investigation of tea over time and temperature
- Characterization of egg shell powder-doped ceramic–metal composites
- Rapeseed oil-based hippurate amide nanocomposite coating material for anticorrosive and antibacterial applications
- Chemically modified Teucrium polium (Lamiaceae) plant act as an effective adsorbent tool for potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in wastewater remediation
- Efficiency analysis of photovoltaic systems installed in different geographical locations
- Risk prioritization model driven by success factor in the light of multicriteria decision making
- Theoretical investigations on the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer in the solvated 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde carbohydrazone
- Mechanical and gamma-ray shielding examinations of Bi2O3–PbO–CdO–B2O3 glass system
- Machine learning-based forecasting of potability of drinking water through adaptive boosting model
- The potential effect of the Rumex vesicarius water seeds extract treatment on mice before and during pregnancy on the serum enzymes and the histology of kidney and liver
- Impact of benzimidazole functional groups on the n-doping properties of benzimidazole derivatives
- Extraction of red pigment from Chinese jujube peel and the antioxidant activity of the pigment extracts
- Flexural strength and thermal properties of carbon black nanoparticle reinforced epoxy composites obtained from waste tires
- A focusing study on radioprotective and antioxidant effects of Annona muricata leaf extract in the circulation and liver tissue: Clinical and experimental studies
- Clinical comprehensive and experimental assessment of the radioprotective effect of Annona muricata leaf extract to prevent cellular damage in the ileum tissue
- Effect of WC content on ultrasonic properties, thermal and electrical conductivity of WC–Co–Ni–Cr composites
- Influence of various class cleaning agents for prosthesis on Co–Cr alloy surface
- The synthesis of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites for the effective removal of hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solution
- Study on the influence of physical interlayers on the remaining oil production under different development modes
- Optimized linear regression control of DC motor under various disturbances
- Influence of different sample preparation strategies on hypothesis-driven shotgun proteomic analysis of human saliva
- Determination of flow distance of the fluid metal due to fluidity in ductile iron casting by artificial neural networks approach
- Investigation of mechanical activation effect on high-volume natural pozzolanic cements
- In vitro: Anti-coccidia activity of Calotropis procera leaf extract on Eimeria papillata oocysts sporulation and sporozoite
- Determination of oil composition of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) seeds under influence of organic fertilizer forms
- Activated partial thromboplastin time maybe associated with the prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Treatment of rat brain ischemia model by NSCs-polymer scaffold transplantation
- Lead and cadmium removal with native yeast from coastal wetlands
- Characterization of electroless Ni-coated Fe–Co composite using powder metallurgy
- Ferrate synthesis using NaOCl and its application for dye removal
- Antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticholinesterase potential of Chenopodium murale L. extracts using in vitro and in vivo approaches
- Study on essential oil, antioxidant activity, anti-human prostate cancer effects, and induction of apoptosis by Equisetum arvense
- Experimental study on turning machine with permanent magnetic cutting tool
- Numerical simulation and mathematical modeling of the casting process for pearlitic spheroidal graphite cast iron
- Design, synthesis, and cytotoxicity evaluation of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyridazine, and pyridine: Griseofulvin heterocyclic extension derivatives
- Isolation and identification of promising antibiotic-producing bacteria
- Ultrasonic-induced reversible blood–brain barrier opening: Safety evaluation into the cellular level
- Evaluation of phytochemical and antioxidant potential of various extracts from traditionally used medicinal plants of Pakistan
- Effect of calcium lactate in standard diet on selected markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in ovariectomized rats
- Identification of crucial salivary proteins/genes and pathways involved in pathogenesis of temporomandibular disorders
- Zirconium-modified attapulgite was used for removing of Cr(vi) in aqueous solution
- The stress distribution of different types of restorative materials in primary molar
- Reducing surface heat loss in steam boilers
- Deformation behavior and formability of friction stir processed DP600 steel
- Synthesis and characterization of bismuth oxide/commercial activated carbon composite for battery anode
- Phytochemical analysis of Ziziphus jujube leaf at different foliar ages based on widely targeted metabolomics
- Effects of in ovo injection of black cumin (Nigella sativa) extract on hatching performance of broiler eggs
- Separation and evaluation of potential antioxidant, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory activities of limonene-rich essential oils from Citrus sinensis (L.)
- Bioactivity of a polyhydroxy gorgostane steroid from Xenia umbellata
- BiCAM-based automated scoring system for digital logic circuit diagrams
- Analysis of standard systems with solar monitoring systems
- Structural and spectroscopic properties of voriconazole and fluconazole – Experimental and theoretical studies
- New plant resistance inducers based on polyamines
- Experimental investigation of single-lap bolted and bolted/bonded (hybrid) joints of polymeric plates
- Investigation of inlet air pressure and evaporative cooling of four different cogeneration cycles
- Review Articles
- Comprehensive review on synthesis, physicochemical properties, and application of activated carbon from the Arecaceae plants for enhanced wastewater treatment
- Research progress on speciation analysis of arsenic in traditional Chinese medicine
- Recent modified air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction applications for medicines and organic compounds in various samples: A review
- An insight on Vietnamese bio-waste materials as activated carbon precursors for multiple applications in environmental protection
- Antimicrobial activities of the extracts and secondary metabolites from Clausena genus – A review
- Bioremediation of organic/heavy metal contaminants by mixed cultures of microorganisms: A review
- Sonodynamic therapy for breast cancer: A literature review
- Recent progress of amino acid transporters as a novel antitumor target
- Aconitum coreanum Rapaics: Botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Petrology and geochemistry of multiphase post-granitic dikes: A case study from the Gabal Serbal area, Southwestern Sinai, Egypt”
- Corrigendum to “Design of a Robust sliding mode controller for bioreactor cultures in overflow metabolism via an interdisciplinary approach”
- Corrigendum to “Statistical analysis on the radiological assessment and geochemical studies of granite rocks in the north of Um Taghir area, Eastern Desert, Egypt”
- Corrigendum to “Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry”
- Corrigendum to “Mechanical properties, elastic moduli, transmission factors, and gamma-ray-shielding performances of Bi2O3–P2O5–B2O3–V2O5 quaternary glass system”
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Copper(ii) complexes supported by modified azo-based ligands: Nucleic acid binding and molecular docking studies”
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- Study of solidification and stabilization of heavy metals by passivators in heavy metal-contaminated soil
- Human health risk assessment and distribution of VOCs in a chemical site, Weinan, China
- Preparation and characterization of Sparassis latifolia β-glucan microcapsules
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Improving the thermal performance of existing buildings in light of the requirements of the EU directive 2010/31/EU in Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Study of plant resources with ethnomedicinal relevance from district Bagh, Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan
- Studies on the chemical composition of plants used in traditional medicine in Congo
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Strip spraying technology for precise herbicide application in carrot fields
- Special Issue on Pharmacology and Metabolomics of Ethnobotanical and Herbal Medicine
- Phytochemical profiling, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus flower: A comparison between tepals and stigmas
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of polyphenolics from Withania adpressa (Coss.) Batt. against selected drug-resistant bacterial strains
- Integrating network pharmacology and molecular docking to explore the potential mechanism of Xinguan No. 3 in the treatment of COVID-19
- Chemical composition and in vitro and in vivo biological assortment of fixed oil extracted from Ficus benghalensis L.
- A review of the pharmacological activities and protective effects of Inonotus obliquus triterpenoids in kidney diseases
- Ethnopharmacological study of medicinal plants in Kastamonu province (Türkiye)
- Protective effects of asperuloside against cyclophosphamide-induced urotoxicity and hematotoxicity in rats
- Special Issue on Essential Oil, Extraction, Phytochemistry, Advances, and Application
- Identification of volatile compounds and antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal properties against drug-resistant microbes of essential oils from the leaves of Mentha rotundifolia var. apodysa Briq. (Lamiaceae)
- Phenolic contents, anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial capacities of MeOH extract from the aerial parts of Trema orientalis plant
- Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from Mentha pulegium and Rosmarinus officinalis against multidrug-resistant microbes and their acute toxicity study
- Special Issue on Marine Environmental Sciences and Significance of the Multidisciplinary Approaches
- An insightful overview of the distribution pattern of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the marine sediments of the Red Sea
- Antifungal–antiproliferative norcycloartane-type triterpenes from the Red Sea green alga Tydemania expeditionis
- Solvent effect, dipole moment, and DFT studies of multi donor–acceptor type pyridine derivative
- An extensive assessment on the distribution pattern of organic contaminants in the aerosols samples in the Middle East
- Special Issue on 4th IC3PE
- Energetics of carboxylic acid–pyridine heterosynthon revisited: A computational study of intermolecular hydrogen bond domination on phenylacetic acid–nicotinamide cocrystals
- A review: Silver–zinc oxide nanoparticles – organoclay-reinforced chitosan bionanocomposites for food packaging
- Green synthesis of magnetic activated carbon from peanut shells functionalized with TiO2 photocatalyst for Batik liquid waste treatment
- Coagulation activity of liquid extraction of Leucaena leucocephala and Sesbania grandiflora on the removal of turbidity
- Hydrocracking optimization of palm oil over NiMoO4/activated carbon catalyst to produce biogasoline and kerosine
- Special Issue on Pharmacology and metabolomics of ethnobotanical and herbal medicine
- Cynarin inhibits PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and activation in hepatic stellate cells through PPARγ
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Surfactant evaluation for enhanced oil recovery: Phase behavior and interfacial tension
- Topical Issue on phytochemicals, biological and toxicological analysis of aromatic medicinal plants
- Phytochemical analysis of leaves and stems of Physalis alkekengi L. (Solanaceae)
- Phytochemical and pharmacological profiling of Trewia nudiflora Linn. leaf extract deciphers therapeutic potentials against thrombosis, arthritis, helminths, and insects
- Pergularia tomentosa coupled with selenium nanoparticles salvaged lead acetate-induced redox imbalance, inflammation, apoptosis, and disruption of neurotransmission in rats’ brain
- Protective effect of Allium atroviolaceum-synthesized SeNPs on aluminum-induced brain damage in mice
- Mechanism study of Cordyceps sinensis alleviates renal ischemia–reperfusion injury
- Plant-derived bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid tetrandrine prevents human podocyte injury by regulating the miR-150-5p/NPHS1 axis
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking to explore the anti-osteoporosis mechanisms of β-ecdysone derived from medicinal plants
- Chinese medicinal plant Polygonum cuspidatum ameliorates silicosis via suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part I
- Investigation of improved optical and conductivity properties of poly(methyl methacrylate)–MXenes (PMMA–MXenes) nanocomposite thin films for optoelectronic applications
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2022)
- Model predictive control for precision irrigation of a Quinoa crop
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous phase by bimetallic metal-organic framework M/Fe-MOF (M = Co, Cu, and Mg)
- Assessment of using electronic portal imaging device for analysing bolus material utilised in radiation therapy
- A detailed investigation on highly dense CuZr bulk metallic glasses for shielding purposes
- Simulation of gamma-ray shielding properties for materials of medical interest
- Environmental impact assesment regulation applications and their analysis in Turkey
- Sample age effect on parameters of dynamic nuclear polarization in certain difluorobenzen isomers/MC800 asphaltene suspensions
- Passenger demand forecasting for railway systems
- Design of a Robust sliding mode controller for bioreactor cultures in overflow metabolism via an interdisciplinary approach
- Gamma, neutron, and heavy charged ion shielding properties of Er3+-doped and Sm3+-doped zinc borate glasses
- Bridging chiral de-tert-butylcalix[4]arenes: Optical resolution based on column chromatography and structural characterization
- Petrology and geochemistry of multiphase post-granitic dikes: A case study from the Gabal Serbal area, Southwestern Sinai, Egypt
- Comparison of the yield and purity of plasma exosomes extracted by ultracentrifugation, precipitation, and membrane-based approaches
- Bioactive triterpenoids from Indonesian medicinal plant Syzygium aqueum
- Investigation of the effects of machining parameters on surface integrity in micromachining
- The mesoporous aluminosilicate application as support for bifunctional catalysts for n-hexadecane hydroconversion
- Gamma-ray shielding properties of Nd2O3-added iron–boron–phosphate-based composites
- Numerical investigation on perforated sheet metals under tension loading
- Statistical analysis on the radiological assessment and geochemical studies of granite rocks in the north of Um Taghir area, Eastern Desert, Egypt
- Two new polypodane-type bicyclic triterpenoids from mastic
- Structural, physical, and mechanical properties of the TiO2 added hydroxyapatite composites
- Tribological properties and characterization of borided Co–Mg alloys
- Studies on Anemone nemorosa L. extracts; polyphenols profile, antioxidant activity, and effects on Caco-2 cells by in vitro and in silico studies
- Mechanical properties, elastic moduli, transmission factors, and gamma-ray-shielding performances of Bi2O3–P2O5–B2O3–V2O5 quaternary glass system
- Cyclic connectivity index of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- The role of passage numbers of donor cells in the development of Arabian Oryx – Cow interspecific somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos
- Mechanical property evaluation of tellurite–germanate glasses and comparison of their radiation-shielding characteristics using EPICS2017 to other glass systems
- Molecular screening of ionic liquids for CO2 absorption and molecular dynamic simulation
- Microwave-assisted preparation of Ag/Fe magnetic biochar from clivia leaves for adsorbing daptomycin antibiotics
- Iminodisuccinic acid enhances antioxidant and mineral element accumulation in young leaves of Ziziphus jujuba
- Cytotoxic activity of guaiane-type sesquiterpene lactone (deoxycynaropicrin) isolated from the leaves of Centaurothamnus maximus
- Effects of welding parameters on the angular distortion of welded steel plates
- Simulation of a reactor considering the Stamicarbon, Snamprogetti, and Toyo patents for obtaining urea
- Effect of different ramie (Boehmeria nivea L. Gaud) cultivars on the adsorption of heavy metal ions cadmium and lead in the remediation of contaminated farmland soils
- Impact of a live bacterial-based direct-fed microbial (DFM) postpartum and weaning system on performance, mortality, and health of Najdi lambs
- Anti-tumor effect of liposomes containing extracted Murrayafoline A against liver cancer cells in 2D and 3D cultured models
- Physicochemical properties and some mineral concentration of milk samples from different animals and altitudes
- Copper(ii) complexes supported by modified azo-based ligands: Nucleic acid binding and molecular docking studies
- Diagnostic and therapeutic radioisotopes in nuclear medicine: Determination of gamma-ray transmission factors and safety competencies of high-dense and transparent glassy shields
- Calculation of NaI(Tl) detector efficiency using 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K radioisotopes: Three-phase Monte Carlo simulation study
- Isolation and identification of unstable components from Caesalpinia sappan by high-speed counter-current chromatography combined with preparative high-performance liquid chromatography
- Quantification of biomarkers and evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxicity properties of Dodonaea viscosa grown in Saudi Arabia using HPTLC technique
- Characterization of the elastic modulus of ceramic–metal composites with physical and mechanical properties by ultrasonic technique
- GC-MS analysis of Vespa velutina auraria Smith and its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities in vitro
- Texturing of nanocoatings for surface acoustic wave-based sensors for volatile organic compounds
- Insights into the molecular basis of some chalcone analogues as potential inhibitors of Leishmania donovani: An integrated in silico and in vitro study
- (1R,2S,5R)-5-Methyl-2-(propan-2-yl)cyclohexyl 4-amino-3-phenylbutanoate hydrochloride: Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity
- On the relative extraction rates of colour compounds and caffeine during brewing, an investigation of tea over time and temperature
- Characterization of egg shell powder-doped ceramic–metal composites
- Rapeseed oil-based hippurate amide nanocomposite coating material for anticorrosive and antibacterial applications
- Chemically modified Teucrium polium (Lamiaceae) plant act as an effective adsorbent tool for potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in wastewater remediation
- Efficiency analysis of photovoltaic systems installed in different geographical locations
- Risk prioritization model driven by success factor in the light of multicriteria decision making
- Theoretical investigations on the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer in the solvated 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde carbohydrazone
- Mechanical and gamma-ray shielding examinations of Bi2O3–PbO–CdO–B2O3 glass system
- Machine learning-based forecasting of potability of drinking water through adaptive boosting model
- The potential effect of the Rumex vesicarius water seeds extract treatment on mice before and during pregnancy on the serum enzymes and the histology of kidney and liver
- Impact of benzimidazole functional groups on the n-doping properties of benzimidazole derivatives
- Extraction of red pigment from Chinese jujube peel and the antioxidant activity of the pigment extracts
- Flexural strength and thermal properties of carbon black nanoparticle reinforced epoxy composites obtained from waste tires
- A focusing study on radioprotective and antioxidant effects of Annona muricata leaf extract in the circulation and liver tissue: Clinical and experimental studies
- Clinical comprehensive and experimental assessment of the radioprotective effect of Annona muricata leaf extract to prevent cellular damage in the ileum tissue
- Effect of WC content on ultrasonic properties, thermal and electrical conductivity of WC–Co–Ni–Cr composites
- Influence of various class cleaning agents for prosthesis on Co–Cr alloy surface
- The synthesis of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites for the effective removal of hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solution
- Study on the influence of physical interlayers on the remaining oil production under different development modes
- Optimized linear regression control of DC motor under various disturbances
- Influence of different sample preparation strategies on hypothesis-driven shotgun proteomic analysis of human saliva
- Determination of flow distance of the fluid metal due to fluidity in ductile iron casting by artificial neural networks approach
- Investigation of mechanical activation effect on high-volume natural pozzolanic cements
- In vitro: Anti-coccidia activity of Calotropis procera leaf extract on Eimeria papillata oocysts sporulation and sporozoite
- Determination of oil composition of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) seeds under influence of organic fertilizer forms
- Activated partial thromboplastin time maybe associated with the prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Treatment of rat brain ischemia model by NSCs-polymer scaffold transplantation
- Lead and cadmium removal with native yeast from coastal wetlands
- Characterization of electroless Ni-coated Fe–Co composite using powder metallurgy
- Ferrate synthesis using NaOCl and its application for dye removal
- Antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticholinesterase potential of Chenopodium murale L. extracts using in vitro and in vivo approaches
- Study on essential oil, antioxidant activity, anti-human prostate cancer effects, and induction of apoptosis by Equisetum arvense
- Experimental study on turning machine with permanent magnetic cutting tool
- Numerical simulation and mathematical modeling of the casting process for pearlitic spheroidal graphite cast iron
- Design, synthesis, and cytotoxicity evaluation of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyridazine, and pyridine: Griseofulvin heterocyclic extension derivatives
- Isolation and identification of promising antibiotic-producing bacteria
- Ultrasonic-induced reversible blood–brain barrier opening: Safety evaluation into the cellular level
- Evaluation of phytochemical and antioxidant potential of various extracts from traditionally used medicinal plants of Pakistan
- Effect of calcium lactate in standard diet on selected markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in ovariectomized rats
- Identification of crucial salivary proteins/genes and pathways involved in pathogenesis of temporomandibular disorders
- Zirconium-modified attapulgite was used for removing of Cr(vi) in aqueous solution
- The stress distribution of different types of restorative materials in primary molar
- Reducing surface heat loss in steam boilers
- Deformation behavior and formability of friction stir processed DP600 steel
- Synthesis and characterization of bismuth oxide/commercial activated carbon composite for battery anode
- Phytochemical analysis of Ziziphus jujube leaf at different foliar ages based on widely targeted metabolomics
- Effects of in ovo injection of black cumin (Nigella sativa) extract on hatching performance of broiler eggs
- Separation and evaluation of potential antioxidant, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory activities of limonene-rich essential oils from Citrus sinensis (L.)
- Bioactivity of a polyhydroxy gorgostane steroid from Xenia umbellata
- BiCAM-based automated scoring system for digital logic circuit diagrams
- Analysis of standard systems with solar monitoring systems
- Structural and spectroscopic properties of voriconazole and fluconazole – Experimental and theoretical studies
- New plant resistance inducers based on polyamines
- Experimental investigation of single-lap bolted and bolted/bonded (hybrid) joints of polymeric plates
- Investigation of inlet air pressure and evaporative cooling of four different cogeneration cycles
- Review Articles
- Comprehensive review on synthesis, physicochemical properties, and application of activated carbon from the Arecaceae plants for enhanced wastewater treatment
- Research progress on speciation analysis of arsenic in traditional Chinese medicine
- Recent modified air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction applications for medicines and organic compounds in various samples: A review
- An insight on Vietnamese bio-waste materials as activated carbon precursors for multiple applications in environmental protection
- Antimicrobial activities of the extracts and secondary metabolites from Clausena genus – A review
- Bioremediation of organic/heavy metal contaminants by mixed cultures of microorganisms: A review
- Sonodynamic therapy for breast cancer: A literature review
- Recent progress of amino acid transporters as a novel antitumor target
- Aconitum coreanum Rapaics: Botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Petrology and geochemistry of multiphase post-granitic dikes: A case study from the Gabal Serbal area, Southwestern Sinai, Egypt”
- Corrigendum to “Design of a Robust sliding mode controller for bioreactor cultures in overflow metabolism via an interdisciplinary approach”
- Corrigendum to “Statistical analysis on the radiological assessment and geochemical studies of granite rocks in the north of Um Taghir area, Eastern Desert, Egypt”
- Corrigendum to “Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry”
- Corrigendum to “Mechanical properties, elastic moduli, transmission factors, and gamma-ray-shielding performances of Bi2O3–P2O5–B2O3–V2O5 quaternary glass system”
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Copper(ii) complexes supported by modified azo-based ligands: Nucleic acid binding and molecular docking studies”
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- Study of solidification and stabilization of heavy metals by passivators in heavy metal-contaminated soil
- Human health risk assessment and distribution of VOCs in a chemical site, Weinan, China
- Preparation and characterization of Sparassis latifolia β-glucan microcapsules
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Improving the thermal performance of existing buildings in light of the requirements of the EU directive 2010/31/EU in Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Study of plant resources with ethnomedicinal relevance from district Bagh, Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan
- Studies on the chemical composition of plants used in traditional medicine in Congo
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Strip spraying technology for precise herbicide application in carrot fields
- Special Issue on Pharmacology and Metabolomics of Ethnobotanical and Herbal Medicine
- Phytochemical profiling, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus flower: A comparison between tepals and stigmas
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of polyphenolics from Withania adpressa (Coss.) Batt. against selected drug-resistant bacterial strains
- Integrating network pharmacology and molecular docking to explore the potential mechanism of Xinguan No. 3 in the treatment of COVID-19
- Chemical composition and in vitro and in vivo biological assortment of fixed oil extracted from Ficus benghalensis L.
- A review of the pharmacological activities and protective effects of Inonotus obliquus triterpenoids in kidney diseases
- Ethnopharmacological study of medicinal plants in Kastamonu province (Türkiye)
- Protective effects of asperuloside against cyclophosphamide-induced urotoxicity and hematotoxicity in rats
- Special Issue on Essential Oil, Extraction, Phytochemistry, Advances, and Application
- Identification of volatile compounds and antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal properties against drug-resistant microbes of essential oils from the leaves of Mentha rotundifolia var. apodysa Briq. (Lamiaceae)
- Phenolic contents, anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial capacities of MeOH extract from the aerial parts of Trema orientalis plant
- Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from Mentha pulegium and Rosmarinus officinalis against multidrug-resistant microbes and their acute toxicity study
- Special Issue on Marine Environmental Sciences and Significance of the Multidisciplinary Approaches
- An insightful overview of the distribution pattern of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the marine sediments of the Red Sea
- Antifungal–antiproliferative norcycloartane-type triterpenes from the Red Sea green alga Tydemania expeditionis
- Solvent effect, dipole moment, and DFT studies of multi donor–acceptor type pyridine derivative
- An extensive assessment on the distribution pattern of organic contaminants in the aerosols samples in the Middle East
- Special Issue on 4th IC3PE
- Energetics of carboxylic acid–pyridine heterosynthon revisited: A computational study of intermolecular hydrogen bond domination on phenylacetic acid–nicotinamide cocrystals
- A review: Silver–zinc oxide nanoparticles – organoclay-reinforced chitosan bionanocomposites for food packaging
- Green synthesis of magnetic activated carbon from peanut shells functionalized with TiO2 photocatalyst for Batik liquid waste treatment
- Coagulation activity of liquid extraction of Leucaena leucocephala and Sesbania grandiflora on the removal of turbidity
- Hydrocracking optimization of palm oil over NiMoO4/activated carbon catalyst to produce biogasoline and kerosine
- Special Issue on Pharmacology and metabolomics of ethnobotanical and herbal medicine
- Cynarin inhibits PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and activation in hepatic stellate cells through PPARγ
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Surfactant evaluation for enhanced oil recovery: Phase behavior and interfacial tension
- Topical Issue on phytochemicals, biological and toxicological analysis of aromatic medicinal plants
- Phytochemical analysis of leaves and stems of Physalis alkekengi L. (Solanaceae)
- Phytochemical and pharmacological profiling of Trewia nudiflora Linn. leaf extract deciphers therapeutic potentials against thrombosis, arthritis, helminths, and insects
- Pergularia tomentosa coupled with selenium nanoparticles salvaged lead acetate-induced redox imbalance, inflammation, apoptosis, and disruption of neurotransmission in rats’ brain
- Protective effect of Allium atroviolaceum-synthesized SeNPs on aluminum-induced brain damage in mice
- Mechanism study of Cordyceps sinensis alleviates renal ischemia–reperfusion injury
- Plant-derived bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid tetrandrine prevents human podocyte injury by regulating the miR-150-5p/NPHS1 axis
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking to explore the anti-osteoporosis mechanisms of β-ecdysone derived from medicinal plants
- Chinese medicinal plant Polygonum cuspidatum ameliorates silicosis via suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part I
- Investigation of improved optical and conductivity properties of poly(methyl methacrylate)–MXenes (PMMA–MXenes) nanocomposite thin films for optoelectronic applications
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2022)
- Model predictive control for precision irrigation of a Quinoa crop

![Figure 2
FTIR spectra of pure Bi2O3 [20,21], commercial AC [22] and composites.](/document/doi/10.1515/chem-2022-0247/asset/graphic/j_chem-2022-0247_fig_002.jpg)
