Abstract
C15H13NO7S, triclinic, P
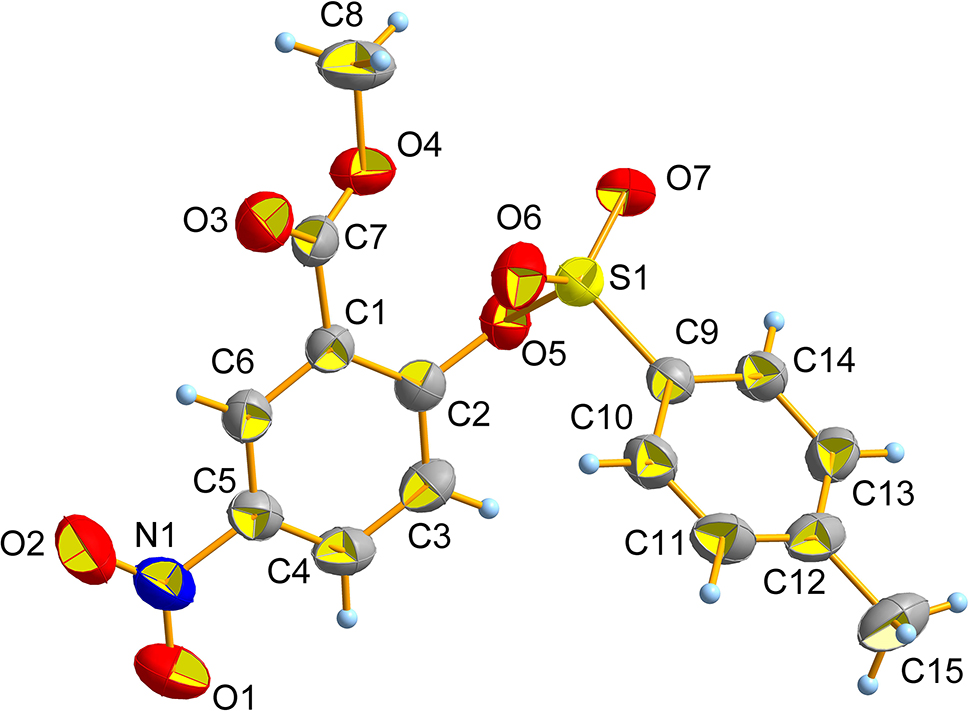
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block |
| Size: | 0.47 x 0.41 x 0.36 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.24 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7654, 2813, 0.013 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2548 |
| N(param)refined: | 220 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.1349 (2) | 0.1088 (2) | 0.12603 (10) | 0.0437 (4) |
| C2 | −0.0220 (2) | 0.1560 (2) | 0.19044 (10) | 0.0428 (4) |
| C3 | −0.2028 (3) | 0.2616 (2) | 0.17379 (12) | 0.0539 (4) |
| H3 | −0.3040 | 0.2927 | 0.2177 | 0.065* |
| C4 | −0.2333 (3) | 0.3210 (2) | 0.09195 (12) | 0.0579 (5) |
| H4 | −0.3559 | 0.3902 | 0.0799 | 0.069* |
| C5 | −0.0788 (3) | 0.2758 (2) | 0.02866 (11) | 0.0508 (4) |
| C6 | 0.1045 (3) | 0.1729 (2) | 0.04390 (10) | 0.0488 (4) |
| H6 | 0.2070 | 0.1466 | −0.0005 | 0.059* |
| C7 | 0.3338 (3) | −0.0076 (2) | 0.13878 (11) | 0.0508 (4) |
| C8 | 0.4928 (4) | −0.2518 (4) | 0.22346 (18) | 0.0916 (8) |
| H8A | 0.5468 | −0.3177 | 0.1785 | 0.137* |
| H8B | 0.4599 | −0.3328 | 0.2746 | 0.137* |
| H8C | 0.5950 | −0.1815 | 0.2299 | 0.137* |
| C9 | 0.0056 (2) | 0.3421 (2) | 0.36042 (9) | 0.0430 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0187 (3) | 0.5068 (2) | 0.31029 (11) | 0.0541 (4) |
| H10 | 0.1010 | 0.5175 | 0.2576 | 0.065* |
| C11 | −0.0920 (3) | 0.6540 (2) | 0.33980 (13) | 0.0610 (5) |
| H11 | −0.0838 | 0.7650 | 0.3064 | 0.073* |
| C12 | −0.2154 (3) | 0.6418 (2) | 0.41794 (13) | 0.0556 (4) |
| C13 | −0.2253 (3) | 0.4749 (2) | 0.46665 (12) | 0.0551 (4) |
| H13 | −0.3074 | 0.4643 | 0.5193 | 0.066* |
| C14 | −0.1165 (3) | 0.3241 (2) | 0.43890 (10) | 0.0489 (4) |
| H14 | −0.1250 | 0.2129 | 0.4721 | 0.059* |
| C15 | −0.3336 (3) | 0.8056 (3) | 0.44917 (17) | 0.0802 (7) |
| H15A | −0.4455 | 0.8505 | 0.4180 | 0.120* |
| H15B | −0.2419 | 0.8945 | 0.4418 | 0.120* |
| H15C | −0.3887 | 0.7762 | 0.5076 | 0.120* |
| N1 | −0.1097 (3) | 0.3362 (2) | −0.05944 (11) | 0.0654 (4) |
| O1 | −0.2682 (3) | 0.4299 (3) | −0.07302 (12) | 0.1049 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0242 (3) | 0.2892 (3) | −0.11453 (10) | 0.0956 (6) |
| O3 | 0.4951 (2) | 0.0139 (2) | 0.09306 (9) | 0.0733 (4) |
| O4 | 0.3075 (2) | −0.13692 (17) | 0.20448 (9) | 0.0631 (4) |
| O5 | −0.00912 (17) | 0.08901 (15) | 0.27484 (7) | 0.0488 (3) |
| O6 | 0.32249 (18) | 0.20630 (19) | 0.26435 (8) | 0.0625 (4) |
| O7 | 0.1708 (2) | 0.01357 (17) | 0.39140 (8) | 0.0658 (4) |
| S1 | 0.14808 (6) | 0.15465 (5) | 0.32361 (2) | 0.04730 (16) |
1 Source of material
4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (1.049 g, 5.5 mmol), dissolved in THF (10 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of methyl-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzoate (0.986 g, 5 mmol) and trimethylamine (0.505 g, 5 mmol) in THF (10 mL) with constant stirring at room temperature for 12 h. The solvent was removed and the residue was separated using flash column chromatography to obtain the target product (yield: 1.370 g, 78 %). Crystals were obtained by recrystallization from dichloromethane at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were identified in difference Fourier syntheses. The Uiso values of the methyl groups and phenolic hydroxyl were set to 1.5Ueq(C), and the Uiso values of all other hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2Ueq(C).
3 Comment
p-Toluene sulfonates can coordinate with metals as catalysts, which can be used as intermediates for the synthesis of drugs for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, and can also be used as self-assembled supramoleculars with potential applications in optoelectronics and pharmaceutical products [5], [6], [7]. Their crystal structures have always been in the focus of scientists [8], [9], [10].
Herein, a novel p-toluene sulfonate compound was synthesized and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction [1], [2], [3], [4]. In the crystal structure, a nitro group, a methyl formate group and a para-toluene sulfonate group are connected to the same benzene ring with C(5)–N(1), C(1)–C(7), C(2)–O(5) bonds, respectively. The bond lengths of N(1)–C(5), N(1)–O(1), C(7)–O(3), C(7)–O(4) and C(8)–O(4) are 1.476(2), 1.208(2), 1.200(2), 1.331(2) and 1.444(2) Å, respectively [11]. The bond lengths of S(1)–O(5), S(1)–O(6), S(1)–O(7) and S(1)–C(9) are 1.6104(12), 1.4202(13), 1.4157(13) and 1.7469(16) Å, respectively. The bond angles of O(5)–S(1)–O(6), O(5)–S(1)–C(9), O(6)–S(1)–C(9) and O(7)–S(1)–C(9) are 108.36(7), 103.44(7), 109.32(8) and 110.12(8)°, indicating the S(1) atom is in the sp3 unequal hybridization state. The dihedral angle between the plane through C(1)–C(6) and the plane through C(9)–C(14) is 49.513°.
Funding source: Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021JJ30291
Funding source: the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21A0518, 21C0691
Funding source: Yongzhou Guiding Science and Technology Plan Project
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support by Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (2021JJ30291), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (21A0518, 21C0691), Yongzhou Guiding Science and Technology Plan Project (2021).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (2021JJ30291), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (21A0518, 21C0691), Yongzhou Guiding Science and Technology Plan Project (2021).
References
1. Bruker. APEX3, SAINT-Plus, XPREP; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Selvi, G., Tercan, M., Özdemir, N., Dayan, O. The preparation of new palladium (II) complexes with Schiff base type ligands and its impregnated Al2O3 materials: as the catalysts for degradation/reduction of organic dyes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e6009; https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6009.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Navarrete-Gutiérrez, A., Aguirre, G., Cisterna, J. Isomeric effect in structural studies of substituted nitro hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzaldehyde and nitro 2,3-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134436; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134436.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Zhang, Y. F., Huang, L., Sun, Y. B., Han, B., Cheng, H. S. Comparative study of (Z)-4-oxo-4-ureido-but-2-enoic acid and p-toluenesulfonic acid 3-nitrophenyl ester by crystal engineering and DFT calculation. J. Cryst. Growth 2013, 374, 79–87; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2013.03.033.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Vembu, N., Nallu, M., Garrison, J., Youngs, W. J. 4-Chlorophenyl 4-toluenesulfonate: supramolecular aggregation through C–H–O, C–H–Cl and C–H–π interactions. Acta Crystallogr. 2003, E59, o936–o938; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536803012066.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Chennakali, K., Fun, H.-K., Sriraghavan, K., Ramakrishnan, V. T. 2-Acetyl-6-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl p-toluenesulfonate. Acta Crystallogr. 1999, C55, 944–946.10.1107/S0108270199001791Suche in Google Scholar
10. Cooley, T. A., Riley, S., Biros, S. M., Staples, R. J., Ngassa, F. N. Crystal structure of 2,4-dinitrophenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate: a new polymorph. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, E71, 1085–1088; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989015015650.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Manivannan, V., Vembu, N., Nallu, M., Sivakumar, K., Fronczek, F. R. 4-Nitrophenyl 4-toluenesulfonate: supramolecular aggregation through weak C–H–O, C–H–π and van der Waals interactions. Acta Crystallogr. 2005, E61, o75–o78; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536804032015.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3

