Abstract
C22H23N3O9Cu, triclinic,
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.13 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 1.88 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 77.6°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 13,245, 4558, 0.039 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 4087 |
| N(param)refined: | 329 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | −0.0680 (3) | 0.6665 (2) | 0.75667 (16) | 0.0466 (5) |
| H1 | −0.017981 | 0.702609 | 0.708113 | 0.056* |
| C2 | −0.2242 (3) | 0.7539 (3) | 0.7845 (2) | 0.0573 (6) |
| H2 | −0.279368 | 0.846994 | 0.755059 | 0.069* |
| C3 | −0.2970 (3) | 0.7009 (3) | 0.8567 (2) | 0.0625 (7) |
| H3 | −0.402438 | 0.757956 | 0.876959 | 0.075* |
| C4 | −0.2126 (3) | 0.5621 (3) | 0.89921 (19) | 0.0560 (6) |
| H4 | −0.260180 | 0.525087 | 0.948538 | 0.067* |
| C5 | −0.0569 (3) | 0.4794 (2) | 0.86742 (15) | 0.0416 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0458 (3) | 0.3294 (2) | 0.90766 (14) | 0.0423 (5) |
| C7 | −0.0040 (3) | 0.2596 (3) | 0.98322 (17) | 0.0557 (6) |
| H7 | −0.106847 | 0.304420 | 1.010974 | 0.067* |
| C8 | 0.1037 (4) | 0.1211 (3) | 1.01626 (19) | 0.0633 (7) |
| H8 | 0.073508 | 0.071422 | 1.066710 | 0.076* |
| C9 | 0.2551 (4) | 0.0576 (3) | 0.97419 (19) | 0.0646 (7) |
| H9 | 0.328422 | −0.035164 | 0.995934 | 0.077* |
| C10 | 0.2969 (3) | 0.1327 (3) | 0.89971 (18) | 0.0572 (6) |
| H10 | 0.399427 | 0.089693 | 0.871280 | 0.069* |
| C11 | 0.3354 (3) | 0.6365 (3) | 0.81864 (16) | 0.0488 (5) |
| C12 | 0.3314 (2) | 0.6416 (2) | 0.71201 (15) | 0.0423 (5) |
| C13 | 0.3660 (3) | 0.7501 (3) | 0.65585 (18) | 0.0506 (5) |
| H13 | 0.396170 | 0.820311 | 0.682879 | 0.061* |
| C14 | 0.3549 (3) | 0.7512 (3) | 0.56175 (18) | 0.0525 (6) |
| H14 | 0.379141 | 0.821728 | 0.523842 | 0.063* |
| C15 | 0.3069 (3) | 0.6461 (3) | 0.52081 (16) | 0.0458 (5) |
| C16 | 0.2895 (3) | 0.6408 (3) | 0.42348 (17) | 0.0582 (6) |
| H16 | 0.310379 | 0.709627 | 0.382234 | 0.070* |
| C17 | 0.2427 (4) | 0.5359 (3) | 0.39017 (17) | 0.0628 (7) |
| H17 | 0.231864 | 0.533945 | 0.326044 | 0.075* |
| C18 | 0.2101 (3) | 0.4301 (3) | 0.45006 (17) | 0.0555 (6) |
| H18 | 0.177607 | 0.359486 | 0.425571 | 0.067* |
| C19 | 0.2262 (2) | 0.4309 (2) | 0.54490 (14) | 0.0414 (4) |
| C20 | 0.2756 (2) | 0.5389 (2) | 0.58185 (14) | 0.0390 (4) |
| C21 | 0.2931 (3) | 0.1775 (3) | 0.60016 (18) | 0.0537 (6) |
| H21A | 0.322089 | 0.154278 | 0.534669 | 0.064* |
| H21B | 0.235956 | 0.115767 | 0.624921 | 0.064* |
| C22 | 0.4453 (3) | 0.1377 (3) | 0.65315 (16) | 0.0499 (5) |
| Cu1 | 0.24617 (3) | 0.39114 (3) | 0.76500 (2) | 0.03891 (13) |
| N1 | 0.0152 (2) | 0.5306 (2) | 0.79716 (12) | 0.0396 (4) |
| N2 | 0.1935 (2) | 0.2667 (2) | 0.86674 (12) | 0.0438 (4) |
| N3 | 0.2891 (2) | 0.53944 (19) | 0.67594 (12) | 0.0378 (4) |
| O1 | 0.3328 (3) | 0.7512 (2) | 0.85545 (14) | 0.0748 (6) |
| O2 | 0.3376 (2) | 0.5178 (2) | 0.86003 (11) | 0.0530 (4) |
| O3 | 0.18771 (18) | 0.33480 (17) | 0.60691 (11) | 0.0451 (3) |
| O4 | 0.44274 (19) | 0.22149 (18) | 0.72007 (11) | 0.0474 (4) |
| O5 | 0.5635 (3) | 0.0249 (2) | 0.62955 (15) | 0.0767 (6) |
| O6 | 0.5905 (3) | 0.3070 (3) | 0.95692 (16) | 0.0831 (6) |
| H6A | 0.508609 | 0.382446 | 0.939031 | 0.125* |
| H6B | 0.596455 | 0.322175 | 1.014362 | 0.125* |
| O7 | 0.7470 (3) | 0.1554 (5) | 0.8035 (2) | 0.1204 (12) |
| H7A | 0.710738 | 0.217715 | 0.847541 | 0.181* |
| H7B | 0.664147 | 0.164423 | 0.774618 | 0.181* |
| O8 | 0.0612 (5) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.7446 (3) | 0.1287 (11) |
| H8A | 0.115716 | −0.014590 | 0.792587 | 0.193* |
| H8B | −0.030172 | 0.089099 | 0.761473 | 0.193* |
| O9 | −0.0714 (5) | 0.9267 (4) | 0.5844 (3) | 0.1298 (12) |
| H9A | −0.052639 | 0.986184 | 0.619243 | 0.195* |
| H9B | −0.094777 | 0.968119 | 0.530334 | 0.195* |
1 Source of materials
The synthesis of Cu(II) complex proceeds as following method: 0.2471 g 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid (1.0 mmol), 0.1997 g cupric acetate monohydrate (0.50 mmol), 0.1562 g 2,2′-bipyridine (1.0 mmol), and 0.080 g NaOH (2.0 mmol) were added to 25 mL of ethanol-water solution (v:v = 3:2) with stirring. The mixture immediately became cloudy, and continued to react at 75 °C for 5 h. After cooling to room temperature, it is filtered, and the filtrate remains still placed. The blue block crystals of the title Cu(II) complex were obtained in 18 days.
2 Experimental details
The hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically (C–H = 0.93–0.97 Å, O–H = 0.85 Å). Their Uiso values were set to 1.2Ueq or 1.5Ueq of the parent atoms.
3 Comment
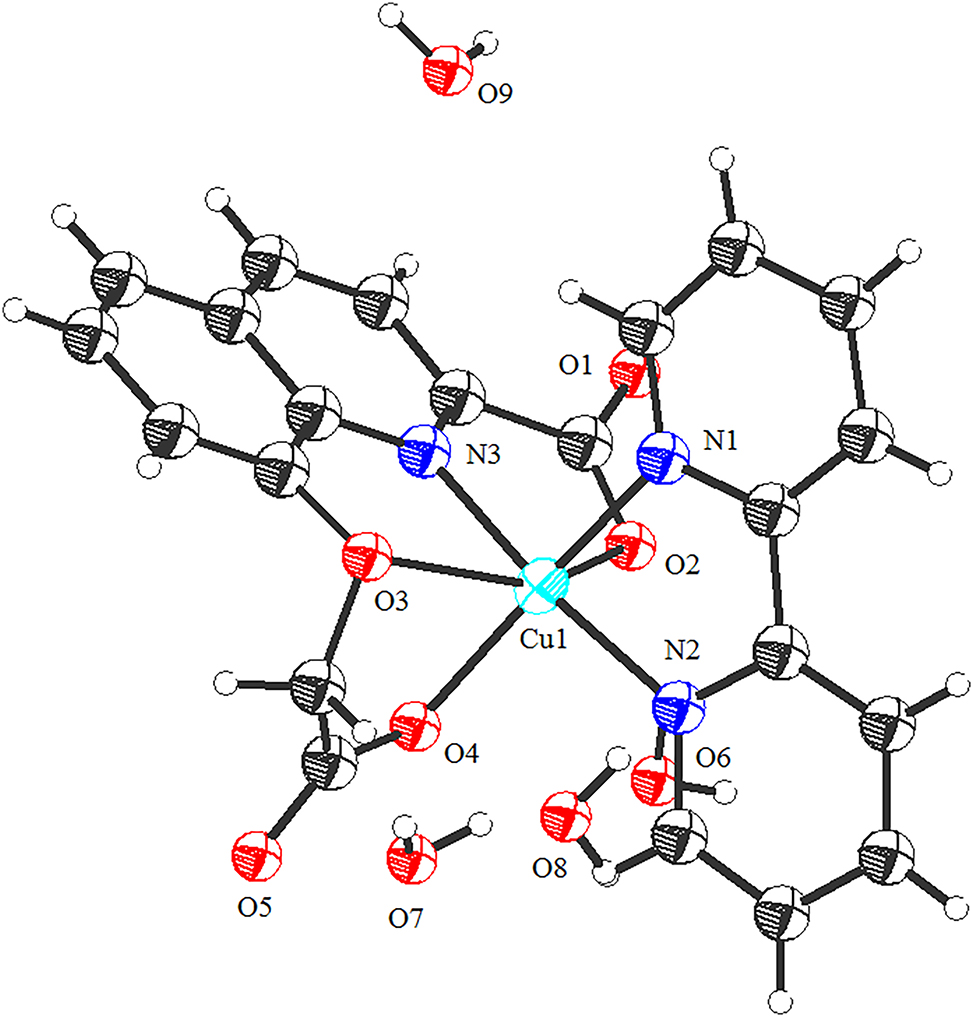
Recently, the studies on the structure and property of copper(II) complexes has been of one interest to chemists. Because they show novel structures [5] and excellent properties in anticancer properties [6], DNA binding and cleavage properties [7], magnetic property [8], etc. 8–carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid is an excellent polydentate ligand with four carboxylate-oxygen, one ether-oxygen and one pyridine-nitrogen atom. And it is known that it forms Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes as tetradentate O,O,N,O-chelates [9, 10]. Our research group has also been studying the synthesis, structural characterization and properties of copper complexes [11], [12], [13]. To continue the structure of the copper complexes, we have synthesized a copper complex using 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid, cupric acetate monohydrate, 2,2′-bipyridine, and NaOH as materials. The coordination environment of the title Cu(II) complex is shown in Figure. As shown in Figure, the title Cu(II) complex is composed of one copper(II) ion, one 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand, one 2,2′-bipyridine ligand, and four uncoordinated water molecules. The copper(II) ion is six-coordinated with three carboxylate oxygen atoms (O2 and O4), one ether oxygen atom (O3) and one nitrogen atom (N3) from the same deprotonated 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand, and two nitrogen atoms (N1 and N2) of 2,2′-bipyridine ligand, forming a distorted octahedron geometry with N2 and N3 atoms at axial position. The 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand is tetradentate coordination mode, however its two deprotonated carboxylate groups adopt monodentate coordination mode. The bond lengths of Cu–O are 1.9816(16)–2.2619(17) Å, and the Cu–N bond lengths are 1.9883(17)–2.0286(17) Å, and the coordination angles around Cu(II) ion are in the range of 77.67(7)–171.87(7)°. The 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand coordinates with the copper(II) ion through the N and O atoms, forming three stable five-membered rings (ring 1: Cu1–O2–C11–C12–N3–Cu1, ring 2: Cu1–O3–C19–C20–N3–Cu1, ring 3: Cu1–O3–C21–C22–O4–Cu1). And the dihedral angles of ring 1 and ring 2, ring 2 and ring 3 are 3.92° and 73.79°, respectively, indicating that the copper(II) complex molecule is non-planar. The copper(II) complex molecules form 1D chain by the O–H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Funding source: Talent Training Support of Henan Academy of Sciences
Award Identifier / Grant number: 220608086, 230608020, and 220208005
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21171132
Funding source: Science Foundation of Weifang
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2020ZJ1054
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This project was supported by the Talent Training Support of Henan Academy of Sciences (No. 220608086, 230608020, and 220208005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21171132, http://dx.doi.org/10.13039/501100001809), and Science Foundation of Weifang (2020ZJ1054).
References
1. Bruker. SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 3.2; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
5. Kan, S. J., Ma, Y. W., Chen, C. J., Qian, J. Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2N:N′) copper(II)] diperchlorate dihydrate, C22H22Cl2CuN10O10. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 693–695; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0155.Search in Google Scholar
6. Hou, L. X., Jia, X. Y., Wu, Y. R., Li, J. L., Yao, D., Gou, Y., Huang, G. J. Aroylhydrazone Cu(II) complexes: syntheses, crystal structures, and anticancer properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1239, 130469; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130469.Search in Google Scholar
7. Kumar, M. P., Tejaswi, S., Rambabu, A., Kalalbandi, V. K. A., Shivaraj. Synthesis, crystal structure, DNA binding and cleavage studies of copper(II) complexes with isoxazole Schiff bases. Polyhedron 2016, 102, 111–120.10.1016/j.poly.2015.07.052Search in Google Scholar
8. Glaser, T., Liratzis, I., Frohlich, R., Weyhermuller, T. A trinucleating ligand based on 1,8-naphthalenediol: synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of a linear Cu–II Cu–II Cu–II complex. Chem. Commun. 2007, 4, 356–358; https://doi.org/10.1039/b612555g.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Zhang, Y. P., Yang, J. J., Lu, J. Y., Gao, C. Y., Zhao, J. Z. Syntheses, structures, DNA/BSA binding and DNA cleavage of mononuclear manganese(II) and cobalt(II) complexes with N,O-chelating quinoline derivative ligand. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 32, 2172–2182.Search in Google Scholar
10. Lou, H. D., Yin, L., Zhang, B. Q., Ouyang, Z. W., Li, B., Wang, Z. X. Series of single-ion and 1D chain complexes based on quinolinic derivative: synthesis, crystal structures, HF–EPR, and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 7757–7762; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00812.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Wang, L. H., Liang, L., Li, X. T., Cao, S. H., Tai, X. S. The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 1251–1253; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0293.Search in Google Scholar
12. Cao, S. H., Li, X. Z., Gao, Y., Li, F. H., Li, K. X., Cao, X. X., Dai, Y. W., Mao, L. R., Wang, S. S., Tai, X. S. A simultaneously GSH-depleted bimetallic Cu(II) complex for enhanced chemodynamic cancer therapy. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11851–11858; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt01742f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Tai, X. S., Li, P. F., Liu, L. L. Preparation, characterization, and catalytic property of a Cu(II) complex with 2-carboxybenzaldehyde-p-toluenesulfonyl hydrazone ligand. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2018, 13, 7–13; https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.13.1.1012.7-13.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3

