Abstract
C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.3261(4) Å, b = 39.755(2) Å, c = 6.2518(4) Å, β = 96.880(6)∘, V = 1314.21(15) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0487, wR ref (F2) = 0.1040, T = 153(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Pinkish block |
| Size: | 0.50 × 0.43 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.08 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART CCD 1K, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 29.4°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5576, 3001, 0.020 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2534 |
| N(param)refined: | 177 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co1 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.000000 | 0.02721 (15) |
| Cl1 | 1.0851 (2) | 0.25890 (3) | 0.2589 (2) | 0.0808 (4) |
| S1 | 0.45480 (14) | 0.37215 (2) | 0.63064 (13) | 0.0391 (2) |
| O1 | 0.4036 (5) | 0.36262 (7) | 0.8415 (4) | 0.0583 (7) |
| O2 | 0.2502 (4) | 0.37940 (6) | 0.4677 (4) | 0.0496 (6) |
| O3 | 0.3648 (4) | 0.45644 (5) | 0.4356 (3) | 0.0357 (5) |
| O4 | 0.6571 (4) | 0.46159 (5) | 0.2111 (3) | 0.0354 (5) |
| O5 | 0.7698 (3) | 0.49036 (5) | −0.2059 (3) | 0.0356 (5) |
| H5A | 0.925245 | 0.482193 | −0.204072 | 0.053* |
| H5B | 0.766446 | 0.506404 | −0.304622 | 0.053* |
| O6 | 0.7403 (3) | 0.53539 (5) | 0.1659 (3) | 0.0326 (4) |
| H6A | 0.756214 | 0.552908 | 0.082584 | 0.049* |
| H6B | 0.714259 | 0.544319 | 0.290084 | 0.049* |
| N1 | 0.6319 (5) | 0.40488 (6) | 0.6614 (4) | 0.0363 (6) |
| C1 | 0.9095 (7) | 0.29014 (9) | 0.3655 (6) | 0.0526 (9) |
| C2 | 0.9753 (7) | 0.30086 (9) | 0.5732 (6) | 0.0536 (9) |
| H2 | 1.115853 | 0.291169 | 0.659335 | 0.064* |
| C3 | 0.8359 (6) | 0.32576 (9) | 0.6553 (6) | 0.0471 (8) |
| H3 | 0.879005 | 0.333362 | 0.799019 | 0.057* |
| C4 | 0.6320 (6) | 0.33972 (8) | 0.5274 (5) | 0.0391 (7) |
| C5 | 0.5675 (7) | 0.32881 (10) | 0.3193 (6) | 0.0558 (9) |
| H5 | 0.427153 | 0.338408 | 0.232359 | 0.067* |
| C6 | 0.7081 (8) | 0.30386 (10) | 0.2381 (6) | 0.0631 (10) |
| H6 | 0.665742 | 0.296182 | 0.094445 | 0.076* |
| H1 | 0.723 (8) | 0.4037 (11) | 0.773 (7) | 0.076* |
| C7 | 0.7264 (5) | 0.41985 (7) | 0.4732 (5) | 0.0335 (6) |
| H7A | 0.737654 | 0.402018 | 0.364239 | 0.040* |
| H7B | 0.899830 | 0.428319 | 0.516677 | 0.040* |
| C8 | 0.5673 (5) | 0.44845 (7) | 0.3690 (4) | 0.0277 (6) |
| O7 | 0.9773 (6) | 0.58449 (8) | −0.0379 (4) | 0.0753 (9) |
| H7C | 0.880553 | 0.601409 | −0.016463 | 0.113* |
| H7D | 0.961894 | 0.579674 | −0.174688 | 0.113* |
1 Source of material
The mixture of glycine (7.51 g, 100 mmol), sodium hydroxide (8.00 g, 200 mmol) and 100 mL water were stirred in a 250 mL round-bottom flask. Then, 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl chloride (21.11 g, 0.5 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 h. After the reaction is completed, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 1 with 6 mol/L HCl solution. White precipitates were precipitated from the reaction mixture, filtered, washed with distilled water, and dried to obtain ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine.
A mixture of ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine (124.8 mg, 0.5 mmol) and Co(CH3COO)2·4H2O (124.5 mg, 0.5 mmol) was dissolved in 50 ml of 50 % methanolic solution at room temperature. Then the pH was adjusted to 7 with 2 mol/L NaOH solution. The reaction mixture was heated for 12 h at 80 °C in a Teflon-lined reaction vessel and then filtered. Pinkish block-shaped crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation at room temperature within two weeks.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were added using riding models. Their Uiso values were set to 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms. The structure was solved with the ShelXT [3] structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL [4].
3 Comment
Due to the difficulty in obtaining single crystals of peptide metal complexes, searching for ligands with similar structures to peptides can help understand the interactions between peptides and metals [5], [6], [7]. Sulfonamide is a group with various biological activities [8], [9], [10]. When amino acids are protected by sulfonamide groups, they can not only act as monodentate ligands through carboxyl O, but also act as bidentate ligands through carboxyl O and amino N. Sometimes –SO2− group can also participate in coordination [11], [12], [13]. The pH dependent coordination behavior of sulfonylated amino acids is similar to that of many short peptides. Therefore, sulfonylated amino acid complexes can serve as models for studying the interaction between metals and peptides [14], [15], [16]. Some ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine complexes have been successfully synthesized in our group [17, 18]. This contribution constitutes a component of our continuous research focus on complexes of sulfonylated amino acids.
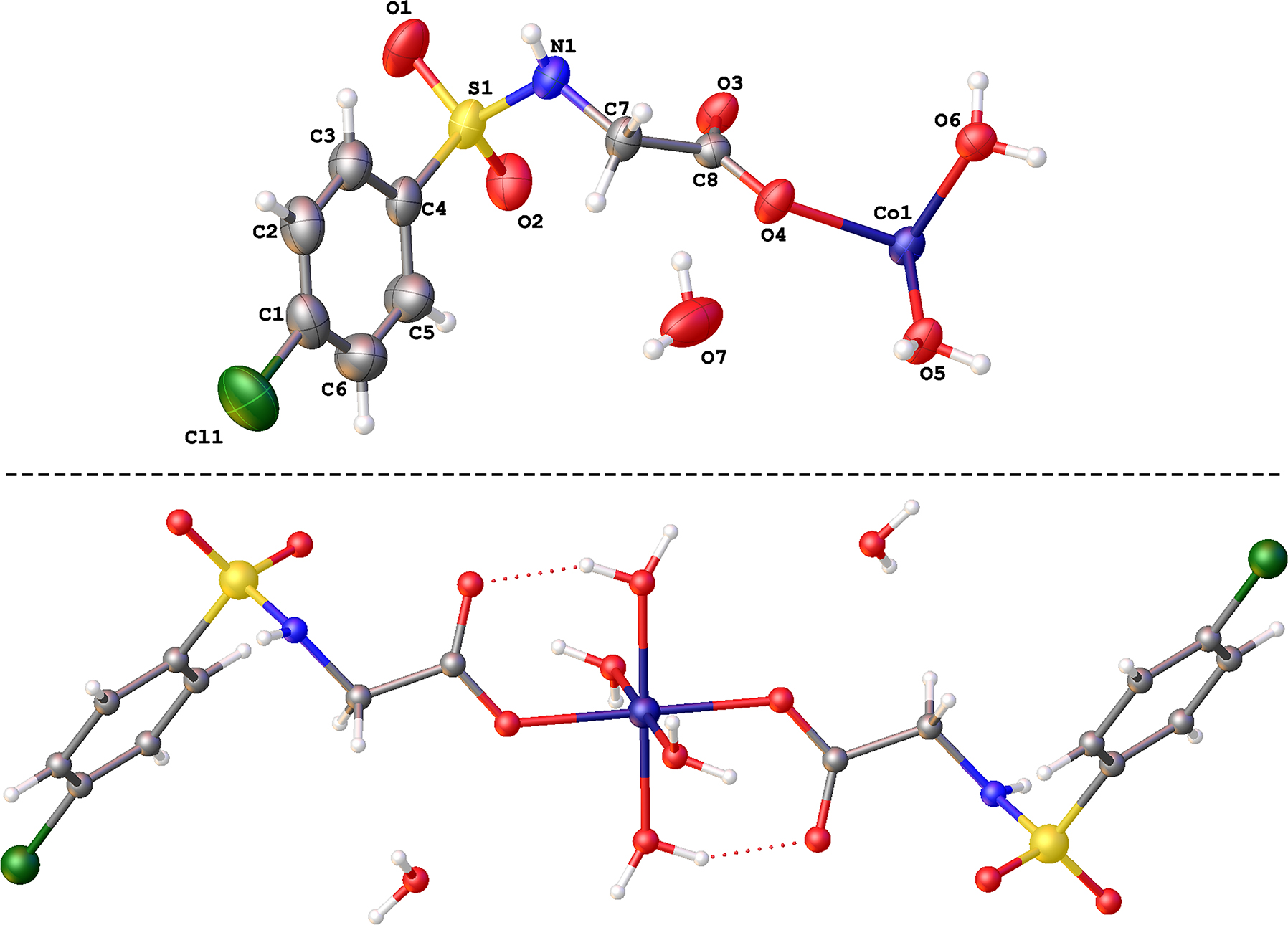
In this paper, the synthesis and crystal structure of a new cobalt(II) complex with ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine were reported. The asymmetric unit is composed of an independent Co(II) ion, one ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine ligand, two coordinated water molecules, and one lattice water molecule (upper part of the figure). The crystallographically unique Co(II) ion of the title complex is six-coordinated by two O atoms (O4, O4′ which are equivalent) from two ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine groups, four O atoms (O5, O5′, O6, O6′, in which O5 and O5′ are equivalent, O6 and O6′ are equivalent) from four coordinated water molecules, giving rise to an octahedron geometry (lower part of the figure). Co–O bond lengths fall in the range 2.0764(18)–2.1234(18) Å, which are within the normal values [19, 20]. The extended three-dimensional supramolecular network is formed through hydrogen bonds O–H⋯O (O5⋯O6 a : 2.786(3) Å, O5–H5A⋯O6 a angle 173.6°; O5–O3 b : 2.608(3) Å, O5–H5B⋯O3 angle 152.5°; a = 2 – X, 1 – Y, –Z; b = 1 – X, 1 – Y, –Z).
-
Research ethics: Not applicable.
-
Author contributions: The authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Research funding: This work was financially supported by the Youth Growth S&T Personnel Foundation of Guizhou Education Department (KY[2020]132), Key Laboratory of Agricultural Resources and Environment in High Education Institute of Guizhou Province (Qianjiaoji[2023]025), and Porous Materials and Green Catalysis Innovation Team in High Education Institute of Guizhou Province (Qianjiaoji[2023]086).
-
Data availability: The raw data can be obtained on request from the corresponding author.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA (2009).Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8, https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8, https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Lillo, V., Galán-Mascarós, J. R. Transition metal complexes with oligopeptides: single crystals and crystal structures. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 9821–9833; https://doi.org/10.1039/c4dt00650j.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Battistuzzi, G., Borsari, M., Menabue, L., Saladini, M., Sola, M. Amide group coordination to the Pb2+ ion. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 4239–4247; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic950599h.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Sigel, H., Martin, R. B. Coordinating properties of the amide bond. Stability and structure of metal ion complexes of peptides and related ligands. Chem. Rev. 1982, 82, 385–426; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00050a003.Search in Google Scholar
8. Si, Y., Basak, S., Li, Y., Merino, J., Iuliano, J. N., Walker, S. G., Tonge, P. J. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of a sulfonamide-based class of oxaborole leucyl-tRNA-synthetase inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1231–1238; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00071.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Naaz, F., Srivastava, R., Singh, A., Singh, N., Verma, R., Singh, V. K., Singh, R. K. Molecular modeling, synthesis, antibacterial and cytotoxicity evaluation of sulfonamide derivatives of benzimidazole, indazole, benzothiazole and thiazole. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3414–3428; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2018.05.015.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Ghorab, M. M., Ragab, F. A., Heiba, H. I., El-Gazzar, M. G., Zahran, S. S. Synthesis, anticancer and radiosensitizing evaluation of some novel sulfonamide derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 682–692; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.036.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Hou, H. W., Chen, S. H., Wang, L. Y., Ma, L. F. Syntheses, structures and luminescence of three new supramolecular complexes containing N–P-acetamidobenzenesulfonyl-glycine acid. J. Coord. Chem. 2008, 61, 2690–2702; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970801975539.Search in Google Scholar
12. Menabue, L., Saladini, M. N-(arylsulfonyl)glycines as cyclometalating ligands. Crystal and molecular structures of disodium bis(μ-chloro)bis[μ-N-(phenylsulfonyl)glycinato-O,N,C]bis[μ-N-(phenylsulfonyl)glycinato-O,O′]tetrapalladate(II) hexahydrate and disodium bis(μ-chloro)bis(μ-N-tosylglycinato-O,N,C) bis(μ-N-tosylglycinato-O,O′)tetrapalladate(II)-4.5-water-2-N-tosylglycine. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 1651–1655, https://doi.org/10.1021/ic00007a042.Search in Google Scholar
13. Chen, X. M., Liu, Z. J., Zhao, R. F. , Cheng, J. S., Qin, L., Long, Z. D. Crystal structure of aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)(((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl) glycine-κ2N,O)copper(II) dihydrate, C18H20CuN4O9S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 1141–1143, https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0206.Search in Google Scholar
14. Krämer, R. Bioinorganic models for the catalytic cooperation of metal ions and functional groups in nuclease and peptidase enzymes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1991, 182, 243–261; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-8545(98)00235-5.Search in Google Scholar
15. Bonamartni Corradi, A. Structures and stabilities of metal(II) (Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), Pd(II), Cd(II)) compounds of N-protected amino acids. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1992, 117, 45–98; https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-8545(92)80020-r.Search in Google Scholar
16. Corradi, A. B., Menabue, L., Saladini, M., Sola, M., Battaglia, L. P. Deprotonated amide nitrogen co-ordination to the cadmium(II) ion in ternary 2,2′-bipyridine complexes with N-sulfonyl amino acids. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1992, 17, 2623–2628, https://doi.org/10.1039/dt9920002623.Search in Google Scholar
17. Liu, Z. J., Chen, X. M., Hao, S. Y., Cheng, M. Q. Syntheses, crystal structures, and thermal properties of two transition metal complexes with 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl-glycine acid ligand. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.–Org. Nano–Met. Chem. 2016, 46, 529–533; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2014.988810.Search in Google Scholar
18. Cheng, M. Q., Chen, X. M., Liu, Z. J., Feng, C. Q. Syntheses, structures, and thermal properties of two new Mn(II) and Ni(II) complexes of 3-nitrobenzenesulfonyl-glycine acid and 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl-glycine acid ligands. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano–Met. Chem. 2013, 44, 27–32; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2013.763278.Search in Google Scholar
19. Yuan, S., Li, X.-D. Crystal structure of tetraaqua-cis-bis(4- (sulfonylglycinato)benzoato)-copper(II), Cu(H2O)4(C9H8NO6S)2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2008, 223, 267–268; https://doi.org/10.1524/ncrs.2008.0113.Search in Google Scholar
20. Battaglia, L. P., Corradi, A. B., Menabue, L., Saladini, M., Sola, M., Gavioli, G. B. Solution and solid state behavior of Co2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ tosylaminoacidate systems: crystal and molecular structure of bis(N-tosylglycinato)tetraaquocobalt(II) and bis(N-tosyl-β-alaninato) tetraaquozinc(II) complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1985, 107, 73–79; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-1693(00)80693-3.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3

