Abstract
CuC20H24ClN5O12, monoclinic, P
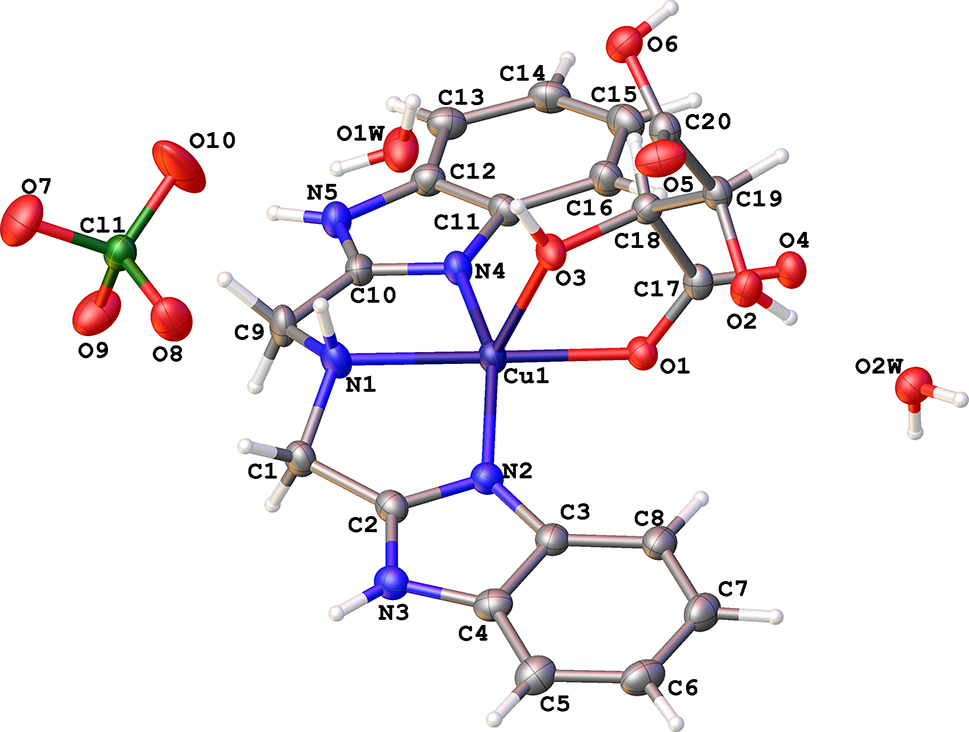
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue block |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Ga Kα radiation (1.34139 Å) |
| μ: | 5.94 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Photon III, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 54.9°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 25,044, 4607, 0.099 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3932 |
| N(param)refined: | 373 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3, 6], Diamond [4], Olex2 [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.6343 (13) | 0.3976 (5) | 0.8240 (9) | 0.0458 (19) |
| H1A | 0.536673 | 0.402955 | 0.877406 | 0.055* |
| H1B | 0.745638 | 0.375556 | 0.887761 | 0.055* |
| C2 | 0.6775 (11) | 0.4737 (5) | 0.7694 (9) | 0.0407 (18) |
| C3 | 0.7466 (11) | 0.5585 (5) | 0.6256 (9) | 0.0429 (19) |
| C4 | 0.7391 (11) | 0.5968 (5) | 0.7502 (10) | 0.045 (2) |
| C5 | 0.7714 (13) | 0.6748 (6) | 0.7690 (12) | 0.055 (2) |
| H5 | 0.765751 | 0.700269 | 0.854549 | 0.066* |
| C6 | 0.8128 (13) | 0.7138 (6) | 0.6549 (12) | 0.059 (3) |
| H6 | 0.834786 | 0.767640 | 0.661520 | 0.070* |
| C7 | 0.8227 (13) | 0.6746 (6) | 0.5299 (12) | 0.055 (2) |
| H7 | 0.853594 | 0.702884 | 0.454745 | 0.066* |
| C8 | 0.7896 (12) | 0.5978 (5) | 0.5125 (10) | 0.047 (2) |
| H8 | 0.795624 | 0.572243 | 0.427064 | 0.057* |
| C9 | 0.6120 (14) | 0.2649 (5) | 0.7188 (9) | 0.050 (2) |
| H9B | 0.507455 | 0.237811 | 0.744546 | 0.060* |
| H9A | 0.723289 | 0.257576 | 0.796307 | 0.060* |
| C10 | 0.6444 (12) | 0.2333 (5) | 0.5830 (9) | 0.0403 (18) |
| C11 | 0.6884 (11) | 0.2283 (5) | 0.3705 (8) | 0.0405 (18) |
| C12 | 0.6975 (12) | 0.1532 (5) | 0.4223 (9) | 0.0432 (18) |
| C13 | 0.7313 (13) | 0.0896 (5) | 0.3468 (10) | 0.049 (2) |
| H13 | 0.738172 | 0.038900 | 0.384037 | 0.059* |
| C14 | 0.7544 (13) | 0.1060 (6) | 0.2121 (10) | 0.052 (2) |
| H14 | 0.781257 | 0.064796 | 0.155650 | 0.062* |
| C15 | 0.7404 (14) | 0.1787 (6) | 0.1569 (10) | 0.054 (2) |
| H15 | 0.754667 | 0.185910 | 0.062876 | 0.065* |
| C16 | 0.7063 (13) | 0.2417 (6) | 0.2324 (9) | 0.048 (2) |
| H16 | 0.695453 | 0.291871 | 0.192646 | 0.058* |
| C17 | 0.6145 (12) | 0.4388 (5) | 0.2397 (8) | 0.0386 (17) |
| C18 | 0.4088 (10) | 0.4368 (5) | 0.2403 (8) | 0.0367 (16) |
| H18 | 0.352877 | 0.388333 | 0.193599 | 0.044* |
| C19 | 0.3103 (11) | 0.5060 (5) | 0.1594 (8) | 0.0388 (17) |
| H19 | 0.312744 | 0.500843 | 0.057115 | 0.047* |
| C20 | 0.1093 (12) | 0.5117 (5) | 0.1709 (9) | 0.0432 (19) |
| Cu1 | 0.65223 (15) | 0.38791 (7) | 0.52418 (11) | 0.0379 (3) |
| N1 | 0.5700 (12) | 0.3473 (4) | 0.6979 (7) | 0.0505 (18) |
| H1 | 0.432310 | 0.351136 | 0.673812 | 0.061* |
| N2 | 0.7072 (10) | 0.4811 (4) | 0.6400 (7) | 0.0411 (15) |
| N3 | 0.6977 (9) | 0.5407 (4) | 0.8394 (8) | 0.0434 (16) |
| H3 | 0.686548 | 0.547896 | 0.926919 | 0.052* |
| N4 | 0.6545 (9) | 0.2787 (4) | 0.4771 (7) | 0.0391 (14) |
| N5 | 0.6680 (10) | 0.1591 (4) | 0.5585 (8) | 0.0443 (16) |
| H5A | 0.665389 | 0.120872 | 0.617484 | 0.053* |
| O1 | 0.7324 (7) | 0.4245 (3) | 0.3569 (6) | 0.0396 (12) |
| O2 | 0.6586 (9) | 0.4545 (3) | 0.1274 (6) | 0.0439 (13) |
| O3 | 0.3936 (7) | 0.4373 (4) | 0.3837 (6) | 0.0453 (14) |
| H3A | 0.279 (5) | 0.429 (7) | 0.385 (12) | 0.068* |
| O4 | 0.3975 (9) | 0.5756 (3) | 0.2117 (6) | 0.0440 (13) |
| H4 | 0.497117 | 0.579858 | 0.185692 | 0.066* |
| O5 | 0.0426 (9) | 0.5700 (4) | 0.2072 (9) | 0.0608 (18) |
| O6 | 0.0183 (9) | 0.4470 (4) | 0.1397 (7) | 0.0491 (14) |
| H6A | 0.019407 | 0.433993 | 0.056518 | 0.074* |
| Cl1a | 0.1526 (5) | 0.3263 (2) | 0.8571 (4) | 0.0460 (8) |
| O7a | 0.0261 (13) | 0.3024 (6) | 0.9402 (11) | 0.079 (3) |
| O8a | 0.1815 (14) | 0.4066 (4) | 0.8631 (9) | 0.068 (3) |
| O9a | 0.3253 (11) | 0.2911 (5) | 0.9247 (13) | 0.076 (3) |
| O10a | 0.091 (3) | 0.3002 (8) | 0.7186 (10) | 0.138 (7) |
| Cl1Ab | 0.150 (4) | 0.3403 (14) | 0.819 (3) | 0.0460 (8) |
| O7Ab | 0.098 (8) | 0.356 (3) | 0.951 (4) | 0.079 (3) |
| O8Ab | 0.224 (7) | 0.4098 (18) | 0.770 (5) | 0.068 (3) |
| O9Ab | 0.288 (7) | 0.280 (2) | 0.833 (7) | 0.076 (3) |
| O10Ab | −0.013 (7) | 0.319 (4) | 0.712 (6) | 0.138 (7) |
| O1W | 0.0989 (9) | 0.3964 (5) | 0.4683 (8) | 0.0634 (18) |
| H1WA | 0.112523 | 0.375842 | 0.551277 | 0.095* |
| H1WB | −0.011267 | 0.407532 | 0.419137 | 0.095* |
| O2W | 0.6867 (9) | 0.6229 (4) | 0.1044 (7) | 0.0492 (14) |
| H2WA | 0.671867 | 0.669088 | 0.069096 | 0.074* |
| H2WB | 0.803817 | 0.614028 | 0.137396 | 0.074* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.867 (10), boccupancy: 0.133 (10).
1 Source of materials
Bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine (IDB) was prepared according to an earlier described method [7]. IDB (0.277 g, 1.0 mmol) and L-malic acid (0.134 g, 1.0 mmol) were firstly dissolved in hot methanol (30.0 mL) and then a solution of Cu(ClO4)2(H2O)6 (0.371 g, 1.0 mmol) in 20.0 mL methanol was added drop by drop. The mixed solution was stirred for 1 h at 60 °C. Then, the reaction mixture was filtered and the filtrate solution was evaporated at room temperature for two weeks. Some blue crystals were obtained at the bottom of the glass vessel (0.40 g, yield: 64 %).
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and restrained to ride on their parent atoms with C–H = 0.95 Å (aromatic), 0.99 Å (methylene), 1.00 Å (methine) and U iso(H) = 1.2U eq (aromatic, methylene and methine). Hydrogen atoms bonded to nitrogen and oxygen atoms were initially found from the difference maps and restrained to be at their indicative positions using command ’AFIX′. The thermal factors of these hydrogen atoms were set 1.2 times (for N) or 1.5 times (for O) of their parent atoms. During the refinement, the perchlorate anion was found to be disordered over two positions with the final occupancies being 0.87(1):0.13(1) for the major and minor components. Commands DFIX, DANG and EADP were used to constrain the Cl–O,O···O distances and thermal factors.
3 Comment
Cu(II)-containing complexes are of great interest in relation of the active site of natural superoxidase dismutase (SOD), hemerythrin and nuclease [8], [9], [10]. These model compounds can be used as mimics aiming to provide further insight into the mechanism of metal sites in complex biological systems. Some of the important considerations in the preparation of model compounds include donor atoms and the resulting geometry around the metal center. Although there is each one copper(II) and one zinc(II) ions in the active site of the natural SOD, research indicates the two back-to-back single-electron redox reactions occur only around the Cu(II) ion which plays a decisive role in the whole catalytic process, and the metal zinc ion only stabilize the skeleton of the enzymatic protein. Therefore, much synthesis of superoxide dismutase model compounds have mainly focused on the micking of copper metal complexes containing imidazole or benzimidazole ligands due to their structurally similarity.
The crystal of the title compund (I) crystallized in the chiral space group P21 because of the use of the chiral ligand L-malic acid. Its asymmetric unit was composed of each one [Cu(IDB)(L-mal)]+ cation, one counter perchlorate anion and two water molecules. In (I), IDB acts as a tridentate ligand coordinating through one tertiary N atom (N1) and two benzimidazole (bzim) N atoms (N2 and N4) to copper. And the L-malate anion coordinates to the central copper ion in a way of bidentated ligand via the O1 and O3 atoms. Thus, a distorted five-coordinated environment was formed around the copper center with a τ parameter of 0.35 showing a moderately distortion of the square-pyramidal polyhedron [11]. The donor sets of N1/N2/N4/O1 constitute the basic plane and O3 atom resides at the apical position. The Cu1–N1 (2.049(7) Å) bond distance is slightly longer that the other two Cu–N2 (1.957(7) Å) and Cu1–N4 (1.954(7) Å), which should be ascribed to the steric hindrance originating from the IDB ligand. The Cu1–O1 of 1.960(5) Å is apparently shorter than the Cu1–O3 (2.256(5) Å) which also meets the requirement of the copper center. The bond angles around Cu1 atom from 76.0(2) to 178.8(2)° are comparable to some analogs [12], [13], [14].
Analysis by Platon [15] indicates that in this component [Cu(IDB)(L-mal)]+, the
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: None declared.
References
1. Bruker. SMART and SAINT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg K. DIAMOND; Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn Germany, 2006.Search in Google Scholar
5. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
6. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Szczepura, L. F., Witham, L. M., Takeuchi, K. J. Tris(2-pyridyl) tripod ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1998, 174, 5–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010–8545(98)00122–2.10.1016/S0010-8545(98)00122-2Search in Google Scholar
8. Fu, H., Zhou, Y. H., Chen, W. L., Deqing, Z. G., Tong, M. L., Ji, L. N., Mao, Z. W. Complexation, structure, and superoxide dismutase activity of the imidazolate-bridged dinuclear copper moiety with β-cyclodextrin and its guanidinium-containing derivative. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4924–4925.10.1021/ja057717cSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Tsou, C. C., Yang, W. L., Liaw, W. F. Nitrite activation to nitric oxide via one-fold protonation of iron(II)-O,O-nitrito complex: relevance to the nitrite reductase activity of deoxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemerythrin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18758–18761.10.1021/ja4105864Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Desbouis, D., Troitsky, I. P., Belousoff, M. J., Spiccia, L., Graham, B. Copper(II), zinc(II) and nickel(II) complexes as nuclease mimetics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 897–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.12.005.Search in Google Scholar
11. Addison, A. W., Rao, T. N., Reedijk, J., van Rijn, J., Verschoor, G. C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands, the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane] copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1039/DT9840001349.Search in Google Scholar
12. Su, G. H., Liu, Y. P., Chen, X., Nie, F. M. Crystal structure of [bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″] phthalato-κ2O,O′copper(II)-methanol-water (1:1:2), C25H27CuN5O7. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2015, 230, 292–294. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2014–9089.10.1515/ncrs-2014-9089Search in Google Scholar
13. Wu, H., Wang, H., Wang, X., Pan, G., Shi, F., Zhang, Y., Bai, Y., Kong, J. V-shaped ligand bis(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine containing three copper(ii) ternary complexes: synthesis, structure, DNA-binding properties and antioxidant activity. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1052–1061. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NJ01145C.Search in Google Scholar
14. Nie, F. M., Lu, F., Chen, J., Yang, Y. L. Synthesis, crystal structures and magnetic properties of the copper(II) complexes containing isophthalate anion as coligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 4198–4204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2009.06.028.Search in Google Scholar
15. Spek, A. L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155.10.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3

