Abstract
C12H8Br2O2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 4.1957(13) Å, b = 13.402(4) Å, c = 11.160(3) Å, β = 99.645(10)°, V = 618.7(3) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0287, wRref(F2) = 0.0701, T = 273(2) K.
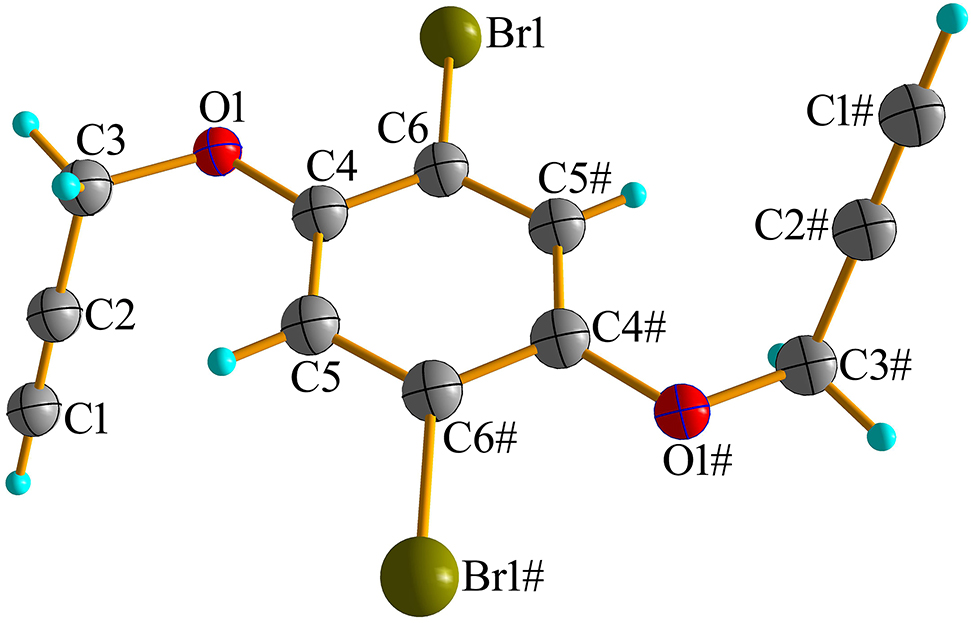
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.18 × 0.17 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 6.53 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.2°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6207, 1503, 0.043 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 1120 |
| N(param)refined: | 73 |
| Programs: | Olex2 [1], Bruker [2], SHELX [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.98931 (7) | 0.46954 (2) | 0.75639 (2) | 0.04303 (13) |
| O1 | 0.6210 (5) | 0.65299 (14) | 0.66838 (17) | 0.0406 (5) |
| C1 | 0.6053 (10) | 0.8509 (3) | 0.4731 (3) | 0.0702 (11) |
| H1 | 0.6648 | 0.8885 | 0.4103 | 0.084* |
| C2 | 0.5314 (8) | 0.8043 (2) | 0.5510 (3) | 0.0468 (7) |
| C3 | 0.4427 (8) | 0.7443 (2) | 0.6493 (3) | 0.0432 (7) |
| H3A | 0.4798 | 0.7830 | 0.7238 | 0.052* |
| H3B | 0.2137 | 0.7290 | 0.6309 | 0.052* |
| C4 | 0.5531 (6) | 0.5795 (2) | 0.5825 (2) | 0.0311 (6) |
| C5 | 0.3405 (6) | 0.5896 (2) | 0.4736 (2) | 0.0325 (6) |
| H5 | 0.2317 | 0.6495 | 0.4550 | 0.039* |
| C6 | 0.7098 (6) | 0.4891 (2) | 0.6074 (2) | 0.0309 (6) |
1 Source of materials
In a round bottomed flask, add 2,5–dibromobenzene-1,4-diol (0.267 g, 1 mmol), 2–bromoethyl metal ether (0.590 g, 5 mmol), K2CO3(0.267 g, 2 mmol), and 30 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide. React at 105 °C for 68 h, cool, filter to remove K2CO3, reduce pressure distillation to remove solvent, separate by column chromatography, and use dichloromethane and petroleum ether as eluents to obtain a white solid. Dissolve a small amount of solid in ethanol and let it evaporate for 9 days before growing crystals.
2 Experimental details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. Using Olex2 [1], the structure was solved using Charge Flipping and refined with the ShelXL [3] refinement. All hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically, with the d(C–H) = 0.97–0.99 Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq(C) and Uiso(H) = 1.5 times Ueq(O).
3 Comment
The bromine atom of dibromobenzene is easily reacted with vinyl pyridine to form compounds with large conjugated structures, which have excellent luminescent properties and are therefore favored by researchers [5]. Click chemistry has been well applied in many fields such as drug development and biomedical materials [6], and the reaction of copper catalyzed azides forming 5-membered heteroatomic rings with alkynes is one of the classic click reactions [7]. The modification of alkynyl groups on the benzene ring provides a basis for the click reaction. We synthesized compound 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy) benzene using the reaction of 2,5-dibromobenzene-1,4-diol and propylene bromide. The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C12H8Br2O2, contains one half molecule located around an inversion center. The orientation of the two alkyne groups is opposite, located above and below the benzene ring, with C3–O1–C4–C5 torsion angles of 5.02(0.36)°. Bond lengths and angles are in the expected ranges [8, 9].
Funding source: Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: ZK[2022]395, 19NSP042, 26222030209
Funding source: rovincial General Project of University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Fund, China
Award Identifier / Grant number: No. 202210660045
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (grant number ZK[2022]395, 19NSP042, 26222030209), the Provincial General Project of University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Fund, China (No. 202210660045).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8, https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.0; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Gong, X., Zhang, Q., Zhang, S., Xia, Y., Bai, Q. H., Chen, S. Y., Ni, X. L. A cationic fluorescent probe for BF4− and PF6− anions by aggregation self-assembly: an efficient approach to recognition of anions in aqueous solution. Dyes Pigments 2019, 163, 502–508; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.12.038.Search in Google Scholar
6. Hu, F., Qi, G. B., Kenry, M. D., Zhou, S. W., Wu, M., Wu, W. B., Liu, B. Visualization and in situ ablation of intracellular bacterial pathogens through metabolic labeling. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9288–9292; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201910187.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Mao, D., Hu, F., Kenry, Q. G. B., Ji, S. H., Wu, W. B., Kong, D. L., Liu, B. One-step in vivo metabolic labeling as a theranostic approach for overcoming drug-resistant bacterial infections. Mater. Horizons 2020, 7, 1138–1143; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mh01675a.Search in Google Scholar
8. Bolton, O., Lee, K., Kim, H.-J., Lin, K. Y., Kim, J. Activating efficient phosphorescence from purely organic materials by crystal design. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 205–210; https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.984.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Shi, H., An, Z., Li, P.-Z., Yin, J., Xing, G., He, T., Chen, H., Wang, J., Sun, H., Huang, W., Zhao, Y. Enhancing organic phosphorescence by manipulating heavy-atom interaction. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 808–813; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01400.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3

