Abstract
C50H32Cl6F4N4O4, triclinic,
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
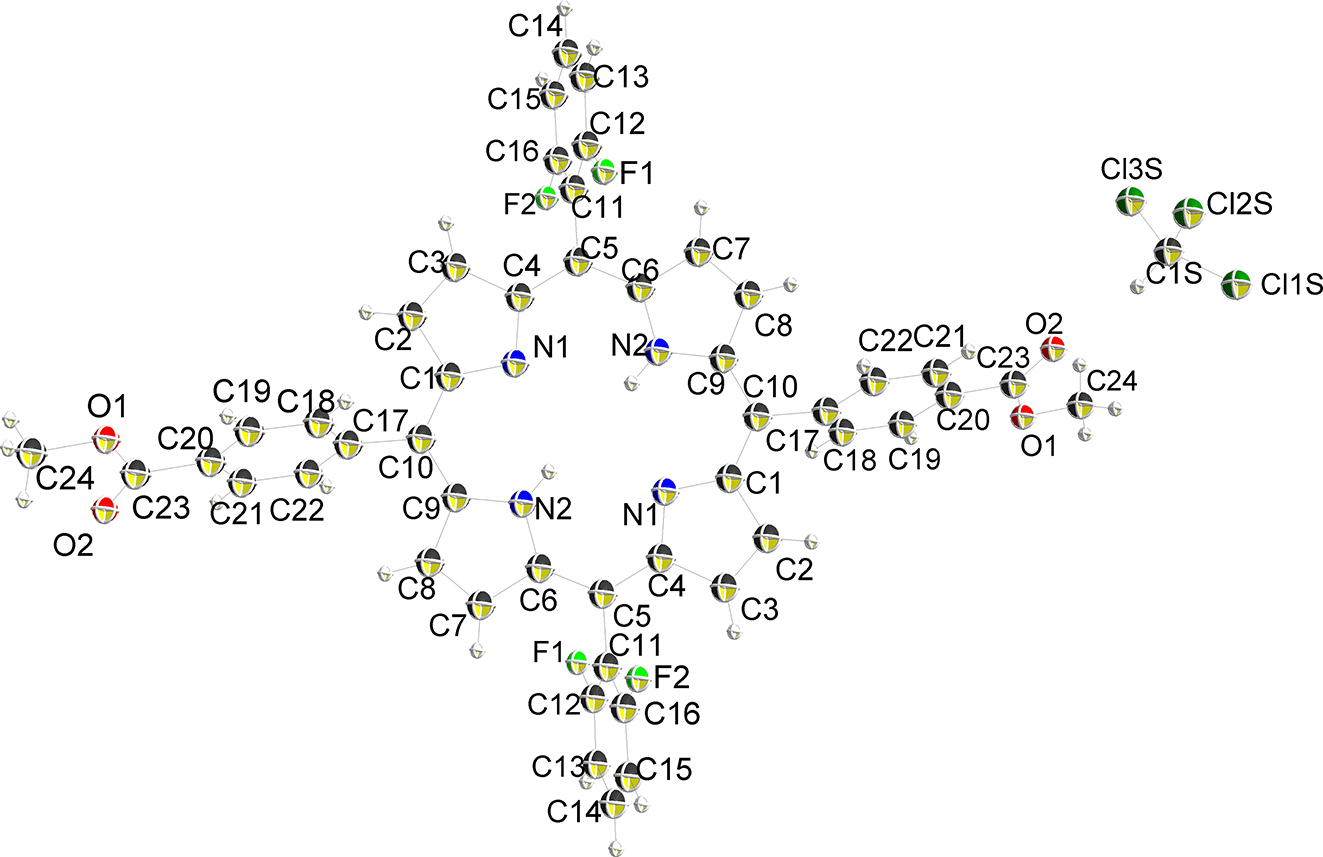
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.10 × 0.05 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | CuKα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 3.86 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 66.0°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 6205, 4076, 0.043 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3205 |
| N(param)refined: | 308 |
| Programs: | CrysAlis Pro [1], Olex2 [2], Shelx [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | −0.3442 (4) | 0.3524 (2) | 0.05240 (19) | 0.0254 (6) |
| C1S | 1.4212 (7) | 0.9357 (4) | 0.3317 (3) | 0.0616 (10) |
| H1S | 1.343549 | 0.927057 | 0.277662 | 0.074* |
| C2 | −0.4452 (4) | 0.2958 (2) | 0.1329 (2) | 0.0318 (6) |
| H2A | −0.555455 | 0.254554 | 0.132063 | 0.038* |
| C3 | −0.3487 (4) | 0.3144 (2) | 0.2085 (2) | 0.0321 (6) |
| H3 | −0.380183 | 0.289548 | 0.270166 | 0.039* |
| C4 | −0.1856 (4) | 0.3808 (2) | 0.17473 (19) | 0.0247 (5) |
| C5 | −0.0438 (4) | 0.4141 (2) | 0.23223 (18) | 0.0254 (6) |
| C6 | 0.1139 (4) | 0.4784 (2) | 0.20376 (18) | 0.0259 (6) |
| C7 | 0.2443 (4) | 0.5209 (2) | 0.2642 (2) | 0.0322 (6) |
| H7 | 0.244723 | 0.505999 | 0.328732 | 0.039* |
| C8 | 0.3678 (4) | 0.5869 (2) | 0.2116 (2) | 0.0315 (6) |
| H8 | 0.465833 | 0.625575 | 0.233778 | 0.038* |
| C9 | 0.3204 (4) | 0.5862 (2) | 0.11598 (19) | 0.0247 (5) |
| C10 | 0.4038 (4) | 0.6469 (2) | 0.0393 (2) | 0.0248 (6) |
| C11 | −0.0628 (4) | 0.3789 (2) | 0.33453 (19) | 0.0291 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0653 (5) | 0.2986 (3) | 0.3724 (2) | 0.0376 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0558 (6) | 0.2646 (3) | 0.4663 (2) | 0.0518 (9) |
| H13 | 0.146584 | 0.210811 | 0.489029 | 0.062* |
| C14 | −0.0919 (6) | 0.3125 (4) | 0.5256 (2) | 0.0575 (10) |
| H14 | −0.101712 | 0.290211 | 0.588984 | 0.069* |
| C15 | −0.2244 (6) | 0.3925 (4) | 0.4920 (2) | 0.0580 (11) |
| H15 | −0.324219 | 0.424608 | 0.531937 | 0.070* |
| C16 | −0.2063 (5) | 0.4242 (3) | 0.3976 (2) | 0.0439 (8) |
| C17 | 0.5556 (4) | 0.7224 (2) | 0.06003 (19) | 0.0262 (6) |
| C18 | 0.5063 (4) | 0.8320 (2) | 0.0507 (2) | 0.0302 (6) |
| H18 | 0.383290 | 0.857421 | 0.027781 | 0.036* |
| C19 | 0.6380 (4) | 0.9035 (2) | 0.0753 (2) | 0.0322 (6) |
| H19 | 0.603267 | 0.976493 | 0.069042 | 0.039* |
| C20 | 0.8220 (4) | 0.8663 (2) | 0.1091 (2) | 0.0300 (6) |
| C21 | 0.8721 (4) | 0.7572 (2) | 0.1191 (2) | 0.0340 (7) |
| H21 | 0.994457 | 0.732004 | 0.142749 | 0.041* |
| C22 | 0.7406 (4) | 0.6860 (2) | 0.0939 (2) | 0.0341 (7) |
| H22 | 0.776252 | 0.613033 | 0.099701 | 0.041* |
| C23 | 0.9665 (4) | 0.9407 (3) | 0.1392 (2) | 0.0373 (7) |
| C24 | 1.0484 (5) | 1.1182 (3) | 0.1414 (3) | 0.0504 (9) |
| H24A | 1.020229 | 1.186677 | 0.109154 | 0.076* |
| H24B | 1.188083 | 1.095033 | 0.128417 | 0.076* |
| H24C | 1.021009 | 1.123777 | 0.207632 | 0.076* |
| Cl1S | 1.5749 (2) | 1.04093 (11) | 0.30153 (11) | 0.0888 (5) |
| Cl2S | 1.5640 (2) | 0.81582 (11) | 0.35393 (10) | 0.0836 (4) |
| Cl3S | 1.2493 (3) | 0.96599 (15) | 0.42467 (16) | 0.1309 (8) |
| F1 | 0.2097 (3) | 0.25112 (18) | 0.31402 (15) | 0.0544 (6) |
| F2 | −0.3335 (4) | 0.5046 (2) | 0.36539 (15) | 0.0695 (8) |
| N1 | −0.1869 (3) | 0.40386 (18) | 0.07987 (16) | 0.0244 (5) |
| N2 | 0.1683 (3) | 0.51828 (18) | 0.11461 (15) | 0.0237 (5) |
| H2 | 0.114938 | 0.502963 | 0.064918 | 0.028* |
| O1 | 0.9218 (3) | 1.04173 (17) | 0.10955 (17) | 0.0403 (5) |
| O2 | 1.1075 (4) | 0.9118 (2) | 0.1845 (2) | 0.0600 (8) |
1 Source of materials
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received without further purification. Procedures for the preperation of trimethyl dimethyl4,4′-[10,20- bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate were adapted from the reported papers [5, 6]. Under N2 atmosphere, trifluoroacetic acid (0.3 ml) was added to a stirred solution of 20 g (122 mmol)methyl p-formylbenzoate and 100 ml pyrrole under nitrogen gas atmosphere. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 0.5 h. After that, TLC analysis (dichloromethane/hexane 3:1) showed the complete consumption of methy-lp-formylbenzoate. The excessive pyrrole was removed to afford the crude product. Then, the crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel eluted with (CH2Cl2/PE 3:1) to give the corresponding compound (15.62 g, 78 %) as a white solid. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DCCl3) δ 10.62 (s, 2H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 6.63 (s, 2H), 5.91 (s, 2H), 5.66 (s, 2H), 5.44 (s, 3H). Under N2 atmosphere, 4-(di(1H-pyrrole-2-yl)methyl)benzoate (1.12 g, 4 mmol) and 2,6-difluorobenzaldehyde (4 mmol) were dissolved in 500 ml dichloromethane, and then boron (tri) fluoride etherate (50 μL) was added. Subsequently, the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. After that, DDQ (2,3–dichloro-5,6- dicyano-p-benzoquinone) (4 mmol, 908 mg) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature 2 h. The reaction mixture was evaporated to dryness, and the crude product was purified by chromatography (silica gel) with dichloromethane, dichloromethane/PE (3:1, by vol.) and dichloromethane successively, finally with pure green product obtained (140 mg, 20.6 % yield). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DCCl3) δ 8.84 (8H, d, J = 5.6), 8.43 (4H, d, J = 8.0), 8.29 (4H, d, J = 8.0), 7.78 (2 H, s), 7.37 (4 H, m), 4.10 (6 H, s), −2.80 (2 H, s). MALDI–TOF–MS (m/z): [M]+ calcd. for C48H30F4N4O4, 803.2237; found, 803.2275. Single crystals were obtained from solution of the title compound in DCCl3 at room temperature for two days.
2 Experimental details
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data for the title structure was collected on SuperNova, Dual, Cu at home/near, AtlasS2 diffractometer by ‘CrysAlisPro 1.171.39.46’ [2]. A suitable crystal was selected and mounted on the diffractometer and the data was collected. The structure was solved with the Shelxt [3] structure solution program and refined with the xl [4] refinement package. The positions of the hydrogen atoms were generated geometrically. The cif-file of the title compound can be obtained free of charge from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif (2265016).
3 Comment
Fluorine, with the strong electrophilic properties and the unique properties of fluorine, can cause many interesting changes in the porphyrin ring when it is introduced. Fluoro-porphyrins are widely used in the fields of biology, biochemistry [7], catalysis [8], medicine [9] and materials [8] due to their unique structural characteristics. It is of great significance to design fluoro-porphyrin-containing compounds or porous materials. We have synthesized a fluoro-porphyrin-containing compound, which can be used for the synthesis of fluoro-porphyrin-containing metal-organic frameworks after hydrolysis. The crystal structure of the complex is shown in the figure. The symmetric unit contains the half porphyrin and one CHCl3 molecule. The substituent at the substitution positions of porphyrin 10,20 is 2,6-difluorophenyl and the substituent at position 5,10 is phenyl. The bond lengths and angles within molecule are in the expected ranges [10]. The distance of N1–C1, N1–C4, N2–C6, N2–C9 is 1.367(3), 1.370(4), 1.371(4), 1.374(3) Å, the distance of C1s–Clsl, C1s–Cls2, C1s–Cls3 is 1.743(4), 1.743(5), 1.732(5) Å, the distance of F1–C12, F2–C16 is 1.356(4), 1.347(4) Å. Void between porphyrin molecules in the structure are occupied by CHCl3 molecules.
Funding source: Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
Award Identifier / Grant number: Gui ke AD1924509
Funding source: Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine
Award Identifier / Grant number: XP018133
Funding source: College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program Training Program
Award Identifier / Grant number: S2021110600117
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was funded by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Gui ke AD19245096), Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine (2018BS018), and College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program Training Program (S2021110600117 and S202310600066).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Agilent Technologies. CrysAlisPro; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2017.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. Olex2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Lu, K. D., He, C. B., Lin, W. B. A chlorin-based nanoscale metal–organic framework for photodynamic therapy of colon cancers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7600–7603; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b04069.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Zeng, Z., Liao, Z. Y., Tang, T. S., Chen, C. S. Progress in the study of fluoroporphyrins. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 27, 24–33.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Bondon, A., Leroy, J. β–Fluorinated porphyrins and related compounds: an overview. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 3, 417–433; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.200700734.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Huang, N., Yuan, S., Drake, H., Yang, X. Y., Pang, J. D., Qin, J. S., Li, J. L., Zhang, Y. M., Wang, Q., Jiang, D. L., Zhou, H. C. Systematic engineering of single substitution in zirconium metal-organic frameworks toward high-performance catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18590–18597; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b09553.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Yang, L. X., Li, H. L., Liu, D., Su, H. F., Wang, K., Liu, G. Y., Luo, X. G., Wu, F. S. Organic small molecular nanoparticles based on self-assembly of amphiphilic fluoroporphyrins for photodynamic and photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. Colloids Surf., B 2019, 182, 110345; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110345.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Soman, R., Sujatha, S., Arunkumar, C. Quantitative crystal structure analysis of fluorinated porphyrin. J. Fluorine Chem. 2014, 163, 16–22; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2014.04.002.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2

