Abstract
C13H10ClNO, monoclinic, P21 (no. 4), a = 4.3011(7) Å, b = 11.2236(19) Å, c = 11.776(2) Å, β = 94.281(5)°, V = 566.90(16) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0420, wR ref (F2) = 0.0827, T = 170 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.31 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 VENTURE, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.4°, 98 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5406, 2210, 0.046 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1683 |
| N(param)refined: | 145 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.9103 (9) | 0.7277 (3) | 0.1815 (4) | 0.0374 (10) |
| C2 | 0.7480 (9) | 0.6985 (3) | 0.2735 (4) | 0.0378 (10) |
| H2 | 0.679136 | 0.758834 | 0.322339 | 0.045* |
| C3 | 0.6860 (8) | 0.5793 (3) | 0.2939 (3) | 0.0337 (10) |
| H3 | 0.574375 | 0.558298 | 0.357605 | 0.040* |
| C4 | 0.7848 (9) | 0.4898 (3) | 0.2225 (3) | 0.0316 (9) |
| C5 | 0.9492 (9) | 0.5234 (4) | 0.1304 (3) | 0.0387 (10) |
| H5 | 1.018426 | 0.463738 | 0.080941 | 0.046* |
| C6 | 1.0148 (10) | 0.6419 (4) | 0.1091 (4) | 0.0401 (10) |
| H6 | 1.128772 | 0.663709 | 0.046240 | 0.048* |
| C7 | 0.7072 (8) | 0.3623 (3) | 0.2410 (3) | 0.0313 (9) |
| C8 | 0.5639 (9) | 0.2960 (4) | 0.1517 (4) | 0.0402 (10) |
| H8 | 0.524871 | 0.332306 | 0.079197 | 0.048* |
| C9 | 0.4768 (10) | 0.1782 (3) | 0.1662 (4) | 0.0438 (11) |
| H9 | 0.378542 | 0.134733 | 0.104255 | 0.053* |
| C10 | 0.5339 (9) | 0.1246 (4) | 0.2713 (4) | 0.0418 (11) |
| H10 | 0.471985 | 0.044363 | 0.282144 | 0.050* |
| C11 | 0.6812 (9) | 0.1877 (3) | 0.3606 (4) | 0.0377 (10) |
| H11 | 0.721479 | 0.150631 | 0.432734 | 0.045* |
| C12 | 0.7700 (8) | 0.3046 (3) | 0.3453 (3) | 0.0311 (9) |
| C13 | 0.8085 (8) | 0.4077 (3) | 0.5280 (3) | 0.0349 (10) |
| H13 | 0.941877 | 0.440281 | 0.588045 | 0.042* |
| Cl1 | 0.9912 (3) | 0.87769 (10) | 0.15545 (10) | 0.0573 (4) |
| N1 | 0.9411 (6) | 0.3644 (3) | 0.4379 (2) | 0.0319 (7) |
| H1 | 1.143752 | 0.372943 | 0.434966 | 0.038* |
| O1 | 0.5273 (6) | 0.4086 (3) | 0.5392 (2) | 0.0466 (8) |
1 Source of materials
To a stirred mixture of HCO2H (0.76 g, 14 mmol, 85 %) and N-butyl-imidazolium trifluoroacetate based ionic liquids (126 mg, 0.5 mmol) was added 4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-amine (2.03 g, 10 mmol) and then the reaction mixture was heated at 70 °C for 1 h. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion, the mixture was diluted with water (10 mL) and extracted with ether (30 mL). The combined organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporated to give residue under reduced pressure. The crude product was passed through a short pad silica-gel column (in order to remove any trace amount of ionic liquid left in the product) by elution with diethyl ether. The evaporation of the solvent under high vacuum afforded a light yellow solid. Yield: 88.4 %.
2 Experimental details
The collected diffraction data were then processed using the Bruker SAINT program [1], which applies standard corrections for absorption and decay of the X-ray source. The corrected data were then further analyzed using the SHELXT software suite to obtain the crystal structure [2]. The final refinement was performed using the Bruker Shelxl program [3], with the aid of the OLEX2 program for visualizing and refining the structure [4].
3 Comment
Formamides are a significant class of intermediates in organic syntheses, and their structures are present in a range of biologically vital compounds. The formyl group, which is essential as an amino-protecting group in peptide synthesis, has extensive applications in pharmaceutical research [5]. The structural studies of formamides derivatives have significant importance in designing and developing new materials with desired properties and applications in organic synthesis [6], [7], [8], [9].
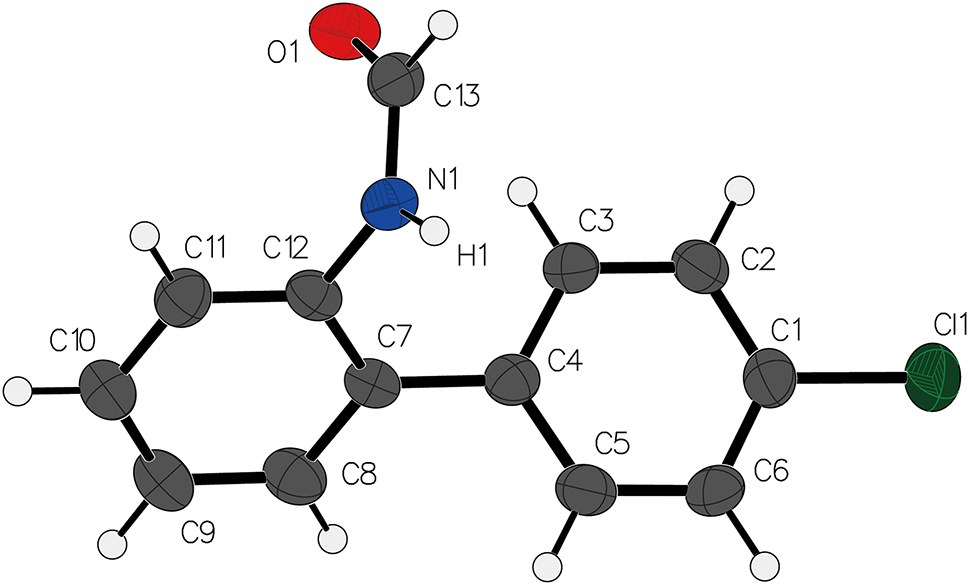
N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, hereafter referred to as the target compound, was synthesized and characterized through a combination of analytical methods. The two phenyl groups are non-coplanar, with a dihedral angle of 52.9°.
The crystal structure is comprised of the target molecule and layers of packing, which are primarily formed from hydrogen bonding N1–H1⋯O1. The bond length is 2.021(3) Å, and the bond angle is 139.8°. The packing is further stabilized by secondary interactions like π⃛π interactions. The result indicates that the polar C=O group is stabilized through a number of intermolecular interactions including one strong hydrogen bond between the carbonyl oxygen atom and the N-atom of an adjacent molecule. This bond forms a one-dimensional chain along a-axis direction.
Overall, the crystal structure of the target compound presented in this study provides detailed insights into the molecular organization and packing behavior. All parameters are in the typical ranges [10–14].
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Natural Science Foundation of Shannxi Province (2021JM-561), Scientific research plan project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (22JK0277), Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Drug Synthesis of Xianyang city (2021QXNL–PT-0008), Doctoral research fund project of Xianyang Vocational and Technical College (2021BK01) and the scientific research fund project of Xianyang Vocational and Technical College (2020KJB02).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Lei, M., Ma, L., Hu, L. A convenient one-pot synthesis of formamide derivatives using thiamine hydrochloride as a novel catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 4186–4188; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.06.005.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Orji, C. C., Michalczyk, R., Silks, L. A. P. Synthesis of 2′β-deoxy-[8-13C; amino,9-15N2]adenosine: unusual annulation conditions to assemble the purine core. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 4685–4689; https://doi.org/10.1021/jo9824753.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Schumacher, C., Molitor, C., Smid, S., Truong, K.-N., Rissanen, K., Bolm, C. Mechanochemical syntheses of N-containing heterocycles with TosMIC. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 14213–14222; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c01529.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Otevrel, J., Svestka, D., Bobal, P. Bianthryl-based organocatalysts for the asymmetric Henry reaction of fluoroketones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 5244–5248; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ob00884e.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Belova, L. O., Pletneva, M. V., Golub, N. A., Korlyukov, A. A., Kirilin, A. D., Petrogradskii, A. V. (4–Methoxyphenyl)amine and its derivatives in the synthesis of O-silylurethanes, ureas, and formamides. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 1531–1535; https://doi.org/10.1134/s1070363217070143.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Rofouei, M. K., Attar Gharamaleki, J., Younesian, F., Bruno, G., Rudbari, H. A. N-(2–Ethoxyphenyl)formamide. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o505; https://doi.org/10.1107/s160053681200205x.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Neue, B., Reiermann, R., Fröhlich, R., Wibbeling, B., Bergander, K., Würthwein, E.-U. Isocyanide cyclization reactions: 4–Methylene-4H-benzo[d] [1,3]oxazine, 3-benzyl-4-methylene-3,4-dihydroquinazolines and 3-(4-benzyl)-3H-quinazolin-4-ones – experiment and theory. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 4944–4952; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201300293.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Chiang, K.-H., Lu, S.-H., Yen, W.-P., Uramaru, N., Tseng, W. S., Chang, T.-W., Wong, F. F. Effective synthesis of N-arylformamide from α-halo-N-arylacetamides. Heteroat. Chem. 2016, 27, 235–242; https://doi.org/10.1002/hc.21321.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Boeyens, J. C. A., Denner, L., Evans, D. G. Crystallographic study of restricted rotation ino-formanilides. J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 1988, 18, 175–187; https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01181909.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Thakur, V., Kumar, A., Sharma, N., Shil, A. K., Das, P. Supported palladium nanoparticles catalyzed reductive carbonylation of nitroarenes to N-arylformamides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 432–437; https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201700944.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2


