Abstract
C26H36N6, triclinic, P
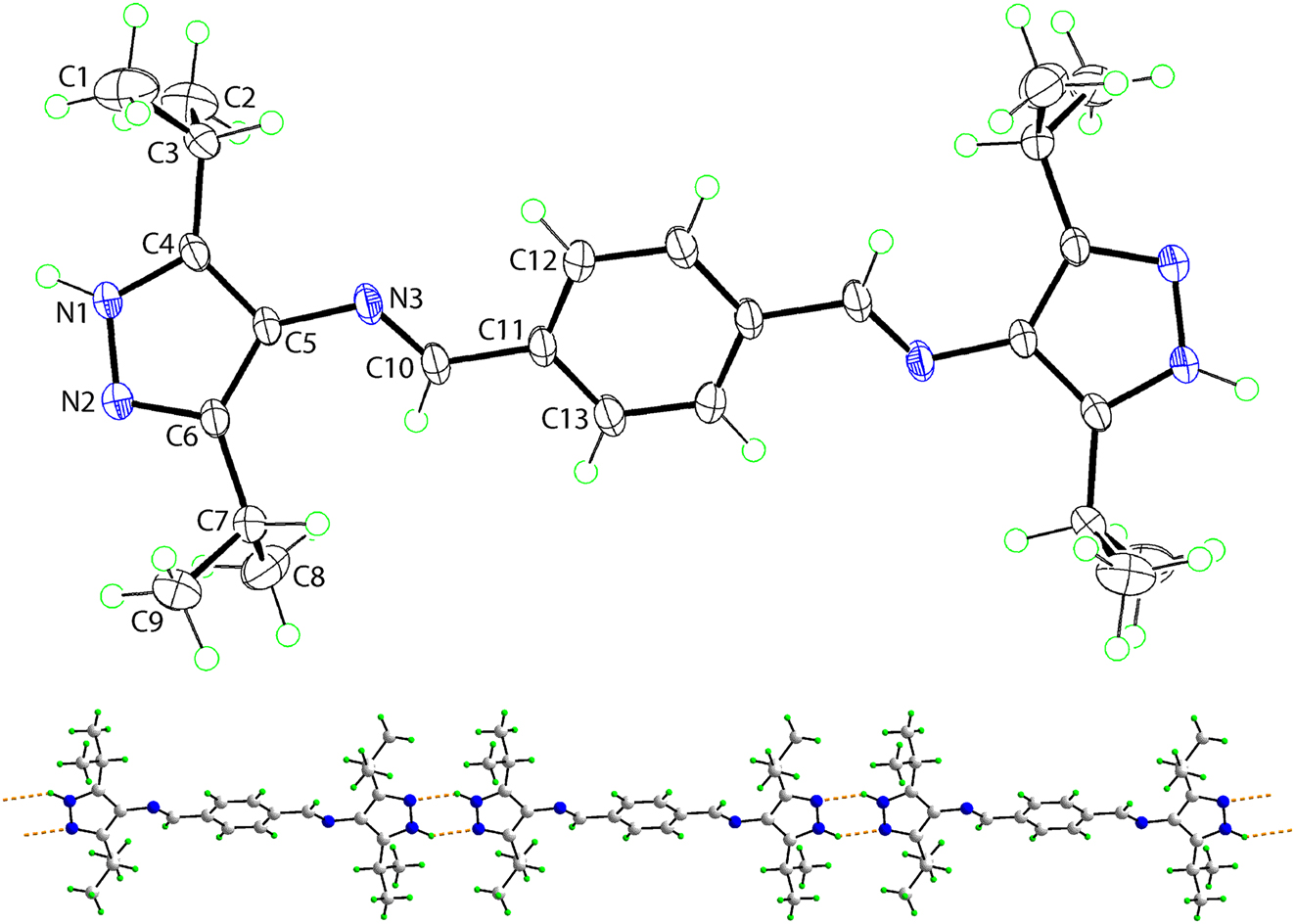
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow plate |
| Size: | 0.07 × 0.06 × 0.01 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.07 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku XtaLAB P200, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 29.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 21,711, 3240, 0.053 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2113 |
| N(param)refined: | 152 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], IL MILIONE [2], SHELX [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | X | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 0.1000 (2) | 0.12351 (11) | 0.46106 (11) | 0.0293 (3) |
| H1N | 0.133 (3) | 0.1034 (15) | 0.5329 (10) | 0.035* |
| N2 | −0.0513 (2) | 0.03672 (11) | 0.37231 (11) | 0.0292 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0993 (2) | 0.30851 (11) | 0.23643 (10) | 0.0260 (3) |
| C1 | 0.5676 (3) | 0.28535 (19) | 0.54768 (19) | 0.0532 (5) |
| H1A | 0.527942 | 0.225032 | 0.599105 | 0.080* |
| H1B | 0.678888 | 0.359121 | 0.596878 | 0.080* |
| H1C | 0.639602 | 0.236620 | 0.474085 | 0.080* |
| C2 | 0.2369 (3) | 0.42227 (16) | 0.61729 (16) | 0.0453 (4) |
| H2A | 0.098711 | 0.460681 | 0.588170 | 0.068* |
| H2B | 0.352990 | 0.494022 | 0.665484 | 0.068* |
| H2C | 0.188932 | 0.365351 | 0.670439 | 0.068* |
| C3 | 0.3449 (3) | 0.34005 (14) | 0.50578 (14) | 0.0303 (4) |
| H3 | 0.391519 | 0.400907 | 0.453679 | 0.036* |
| C4 | 0.1730 (2) | 0.23160 (13) | 0.42531 (13) | 0.0243 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0581 (2) | 0.21652 (13) | 0.30708 (12) | 0.0232 (3) |
| C6 | −0.0787 (2) | 0.09167 (13) | 0.27724 (12) | 0.0237 (3) |
| C7 | −0.2304 (3) | 0.01690 (13) | 0.16101 (13) | 0.0279 (3) |
| H7 | −0.185876 | 0.054919 | 0.091160 | 0.033* |
| C8 | −0.4896 (3) | 0.03591 (18) | 0.17697 (15) | 0.0435 (4) |
| H8A | −0.536192 | 0.002564 | 0.247220 | 0.065* |
| H8B | −0.585968 | −0.013431 | 0.100224 | 0.065* |
| H8C | −0.513273 | 0.130798 | 0.193737 | 0.065* |
| C9 | −0.1904 (3) | −0.13078 (15) | 0.12481 (16) | 0.0457 (4) |
| H9A | −0.021933 | −0.140534 | 0.118713 | 0.069* |
| H9B | −0.278414 | −0.174477 | 0.043833 | 0.069* |
| H9C | −0.244996 | −0.172129 | 0.188661 | 0.069* |
| C10 | −0.0620 (3) | 0.32335 (13) | 0.15701 (13) | 0.0263 (3) |
| H10 | −0.210474 | 0.273495 | 0.148718 | 0.032* |
| C11 | −0.0273 (2) | 0.41457 (13) | 0.07777 (12) | 0.0247 (3) |
| C12 | 0.1824 (3) | 0.49322 (14) | 0.08688 (14) | 0.0307 (3) |
| H12 | 0.308503 | 0.489268 | 0.146214 | 0.037* |
| C13 | −0.2088 (3) | 0.42275 (14) | −0.01003 (14) | 0.0312 (3) |
| H13 | −0.353387 | 0.369568 | −0.017252 | 0.037* |
1 Source of material
Under an argon atmosphere, the reaction of 4-amino-3,5-diisopropyl-1-pyrazole (0.1004 g, 0.600 mmol) with terephthalaldehyde (0.0439 g, 0.327 mmol) in anhydrous methanol (10 mL) was conducted at room temperature for four days. The solvent was then removed in vacuo. Yellow crystals of (I), were obtained by the slow evaporation at room temperature from an anhydrous methanol and n-heptane solution (4:1 v/v) of (I). Yield: 0.0454 g, 0.105 mmol, 35 % yield. The yield was improved (up to 61 %) by dehydration with molecular sieves 3 Å in methanol/n-heptane solution. Anal. Calcd. for C26H36N6: C 72.19, H 8.39, N 19.42 %. Found: C 71.91, H 8.56, N 19.30 %. 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz): δ 1.35 (d, 24H, 7 Hz, CH(CH3)2), 3.23 (sept, 4H, 7 Hz, CH(CH3)2), 7.93 (s, 4H, (C6H4)), 8.48 (s, 2H, CH=N); NH not obs. 13C{1H} NMR (CD3OD, 125 MHz): δ 22.8 (CH(CH3)2), 26.3 (CH(CH3)2), 27.9 (CH(CH3)2), 128.6 (4C-pyz), 129.7 (2,3,4,5C–benzene), 140.7 (1,6C–benzene), 152.4 (3,5C–pyz), 159.6 (CH=N). IR (KBr, cm−1): 3207s ν(N–H), 3118 s, 3050 s, 2962 s ν(C–H), 2926 s ν(C–H), 2869 s ν(C–H), 1609 m ν(C=N), 1488 s, 1012 s. Far–IR (CsI, cm−1): 633 s, 539 s, 243 m. Raman (neat solid, cm−1): 1599 s, 1559 s, 1224 m, 1161 m. Solution UV–vis (CH3OH, λmax, nm) (ε, M−1 cm−1): 231 (18,450), 291 (16,820), 370 (23,190). Solid UV–vis (Nujol, λmax, nm): 236, 305, 394. Diffuse Reflectance (solid, nm): 238, 300, 396.
2 Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C–H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). The N-bound H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined with N–H = 0.88 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). Owing to poor agreement, three reflections, i.e. (0 1 0), (0 0 1) and (0 −1 1), were omitted from the final cycles of refinement.
3 Comment
Recently, the crystal structure of amine group-introduced pyrazole, i.e. 4-amino-3,5-diisopropyl-1-pyrazole (L1HpzNH2) was described [5]. The compound was obtained by the reduction 4-nitro-3,5-diisopropyl-1-pyrazole with iron powder [5]. The synthetic method and structure of this molecule can be compared to the analogous molecule with methyl groups replacing the isopropyl substituents, i.e. 4-amino-3,5-methyl-1-pyrazole [6]. Originally, 4-amino-3,5-methyl-1-pyrazole was obtained by the direct nitration of acetylacetone with sodium nitrite (NaNO2). This amino group can readily react with aldehydes to generate covalent organic frameworks [7], [8], [9]. Thus, L1HpzNH2 can react readily with terephthalaldehyde (benzene-1,4-dicarboxaldehyde) to yield the title compound I; systematic name: (NE)–N-[(4-{N-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]carboximidoyl}phenyl)-methylidene]-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine.
New characteristic absorption bands were observed in the IR spectrum of (I). Thus, the sharp N–H2 stretching band in the spectrum of the L1HpzNH2 precursor at 3374 cm−1 disappeared and the band at 3211 cm−1 was shifted to 3207 cm−1 in the spectrum of (I). The C=N stretching bands of L1HpzNH2 at 1599 cm−1 was clearly separated into two bands at 1609 and 1575 cm−1, and the C=O band at 1693 cm−1, due to terephthalaldehyde, disappeared. In addition, new absorption bands at 231 nm (ε, 18,450 M−1 cm−1), 291 nm (ε, 16,820 M−1 cm−1) and 370 (ε, 23,190 M−1 cm−1) in the UV–vis spectrum of (I), which were clearly different from the spectrum of L1HpzNH2, i.e. an absorption appeared at 238 nm (ε, 4130 M−1 cm−1). The new bands in the spectrum of (I) were also observed in both the solid-state UV–vis and diffuse reflectance spectra, indicating the solid-state structure is retained in solution. The 1H and 13C{1H} NMR exhibited the anticipated signals and in the case of 1H NMR, integration; no resonances were observed for imine N–H.
The molecular structure of (I) was established by X-ray crystallography and is represented in the upper image of the figure (50 % displacement ellipsoids). The molecule is disposed about a centre of inversion and unlabelled atoms are related by the symmetry operation (i): −x, 1 − y, −z. As anticipated, the 1H-pyrazole ring is strictly planar (r.m.s. = 0.010 Å) with the maximum deviation of 0.009(1) Å noted for the C4 atom. Within the ring, the formal C6=N2 [1.3307(17) Å] and C4=C5 [1.3903(19) Å] double bonds are longer than their standard values, and at the same time the formal N1–N2 [1.3585(16) Å], C4–N1 [1.3406(17) Å] and C5–C6 [1.4210(18) Å] single bonds are shorter than their standard values. These results confirm the extensive delocalisation of π-electron density over the five-membered ring. The imine C10=N3 bond length is 1.2736(17) Å, and the C5–N3 link between these residues is 1.4074(16) Å. The overall molecule of (I) is non-planar, there being a twist about the C5–N3 bond [the C4–C5–N3–C10 torsion angle = −152.37(14)°] as seen in the dihedral angle of 29.76(7)° between the five- and six-membered rings. With respect to the pyrazole-bound isopropyl groups, the methine–H atoms are orientated to be directed towards the centre of the molecule.
There are no structural precedents in the literature for molecules related to (I) where a pyrazole ring is directly connected to an imine functionality. However, in an accompanying publication [10], this connectively is described in the di-methanol solvate of the all-methyl analogue of (I). The pyrazole exhibits the same attributes/electronic structure as described for (I). There are examples of molecules whereby the pyrazole ring is connected to a nitrogen atom as in (I) but that nitrogen atom is connected to two carbon atoms, for example when the nitrogen atoms are incorporated at opposite ends of a naphthalene diimide molecule [11]. In the context of the motivation of the synthesis of (I) and related derivatives, it should be mentioned that coordination polymers are formed [12] by molecules of the aforementioned type in their neutral form [11].
Employing Platon [13], an analysis of the molecular packing suggests the presence of both N–H⋯N and C–H⋯π directional interactions between molecules. Thus, pyrazole–N–H⋯N(pyrazole) hydrogen bonds [N1–H1n⋯N2ii: H1n⋯N2ii = 2.060(15) Å, N1⋯N2ii = 2.8141(17) Å with angle at H1n = 142.2(14)° for (ii): −x, −y, 1 − z] link molecules into supramolecular chains. The chain, illustrated in the lower view of the figure (the N–H⋯N hydrogen bonds are shown as orange dashed lines), is orientated along [0 1 −1] and features centrosymmetric, six-membered {⋯HNN}2 synthons. The chains are connected laterally by methyl–C–H⋯π(pyrazole) [C1–H1c⋯Cg(pyrazole)iii: H1c⋯Cg(pyrazole)iii = 2.78 Å with angle at H1c = 149° for (iii) 1 + x, y, z] resulting in supramolecular layers parallel to (0 1 1). Layers stack in an off-set fashion so the alkyl residues occupy regions defined by the phenyl rings of adjacent layers, but without directional interactions between them.
The above geometric analysis of the molecular packing was complemented by the calculation of the Hirshfeld surfaces and of the full and delineated two-dimensional fingerprint plots, using Crystal Explorer 21 [14] and literature protocols [15]. All surface contacts in the crystal of (I) involve H, with the majority being of the type H⋯H, i.e. 69.7 %. The remaining contacts comprise C⋯H/H⋯C [16.7 %] and N⋯H/H⋯N [13.6 %] contacts.
Acknowledgment
KF is grateful for support from the joint usage/research programme “Artificial Photosynthesis” based at Osaka City University.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This study was supported financially by the Joint Usage/Research Center for Catalysis (Proposals 22DS0143 and 23DS0198).
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Corporation: Oxford, UK, 2019.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., De Caro, L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G., Siliqi, D., Spagna, R. IL MILIONE: a suite of computer programs for crystal structure solution of proteins. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 609–613. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889807010941.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Fujisawa, K., Ageishi, K., Okano, M., Tiekink, E. R. T. The crystal structure of 3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C9H17N3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 1055–1057. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022–0362.10.1515/ncrs-2022-0362Suche in Google Scholar
6. Infantes, L., Foces-Foces, C., Claramunt, R. M., López, C., Elguero, J. Aminopyrazoles and their conjugated acids. An X-ray study of 3,5-dimethyl-4-aminopyrazole and the picrate of 3(5)-aminopyrazole. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1999, 36, 595–600; https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.5570360303.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Côté, A. P., Benin, A. I., Ockwig, N. W., O’Keeffe, M., Matzger, A. J., Yaghi, O. M. Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120411.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Diercks, C. S., Yaghi, O. M. The atom, the molecule, and the covalent organic framework. Science 2017, 355, eaa1585. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal1585.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Geng, K., He, T., Liu, R., Dalapati, S., Tan, K. T., Li, Z., Tao, S., Gong, Y., Jiang, Q., Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks: design, synthesis, and functions. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8614–8933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00550.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Fujisawa, K., Ageishi, K., Harakuni, S., Tiekink, E. R. T. Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH). Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1005–1008. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0322.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Ke, H., Weng, L.-J., Chen, S.-Y., Chen, J.-Z., Li, M.-J. Naphthalene diimide cocrystals: a facile approach to tune the optical properties. Dyes Pigm. 2015, 113, 318–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2014.08.020.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Li, Z., Guo, J., Xiang, F., Lin, Q., Ye, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, S., Zhang, Z., Xiang, S. Photochromic naphthalene diimide Cd–MOFs based on different second dicarboxylic acid ligands. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 7567–7573. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CE01667D.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Spek, A. L. checkCIF validation ALERTS: what they mean and how to respond. Acta Crystallogr. 2020, E76, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2056989019016244.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D., Spackman, M. A. CrystalExplorer: a program for Hirshfeld surface analysis, visualization and quantitative analysis of molecular crystals. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54, 1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576721002910.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Tan, S. L., Jotani, M. M., Tiekink, E. R. T. Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. 2019, E75, 308–318. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2056989019001129.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2

