Abstract
C17H16N2O8, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 7.0825(4) Å, b = 15.6168(9) Å, c = 15.1086(9) Å, β = 93.3830(10)°, V = 1668.19(17) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0543, wR ref (F2) = 0.1443, T = 170.15 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.48 × 0.28 × 0.26 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.12 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 18,714, 3807, 0.048 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3160 |
| N(param)refined: | 245 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], Shelx [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.1664 (2) | 0.60831 (10) | 0.66641 (10) | 0.0301 (4) |
| O2 | 0.2041 (2) | 0.62660 (9) | 0.94128 (10) | 0.0299 (4) |
| N1 | 0.2103 (3) | 0.53700 (12) | 0.82582 (12) | 0.0299 (4) |
| H1A | 0.245643 | 0.494218 | 0.860962 | 0.036* |
| H1B | 0.193463 | 0.528598 | 0.768312 | 0.036* |
| C1 | 0.1301 (3) | 0.68500 (13) | 0.70530 (14) | 0.0245 (4) |
| C2 | 0.1352 (3) | 0.68771 (13) | 0.79897 (14) | 0.0243 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0930 (3) | 0.76490 (14) | 0.83985 (15) | 0.0276 (4) |
| H3 | 0.092788 | 0.767164 | 0.902679 | 0.033* |
| C4 | 0.0515 (3) | 0.83813 (14) | 0.79123 (16) | 0.0322 (5) |
| H4 | 0.023675 | 0.890193 | 0.820270 | 0.039* |
| C5 | 0.0510 (3) | 0.83469 (14) | 0.69956 (16) | 0.0321 (5) |
| H5 | 0.024462 | 0.885053 | 0.665819 | 0.039* |
| C6 | 0.0886 (3) | 0.75906 (14) | 0.65654 (15) | 0.0290 (5) |
| H6 | 0.086150 | 0.757555 | 0.593623 | 0.035* |
| C7 | 0.1765 (3) | 0.60590 (14) | 0.57092 (14) | 0.0304 (5) |
| H7A | 0.268124 | 0.648925 | 0.551637 | 0.036* |
| H7B | 0.051023 | 0.618634 | 0.541472 | 0.036* |
| C8 | 0.2390 (4) | 0.51727 (16) | 0.54715 (16) | 0.0383 (6) |
| H8A | 0.148729 | 0.475257 | 0.567804 | 0.057* |
| H8B | 0.364604 | 0.506027 | 0.575499 | 0.057* |
| H8C | 0.244518 | 0.512758 | 0.482661 | 0.057* |
| C17 | 0.1850 (3) | 0.61423 (13) | 0.85870 (13) | 0.0239 (4) |
| O3 | 0.5794 (3) | 0.60686 (12) | 0.25502 (13) | 0.0505 (5) |
| O4 | 0.4651 (2) | 0.63373 (10) | 0.38157 (11) | 0.0367 (4) |
| O5 | 0.7498 (2) | 0.71289 (11) | 0.50604 (10) | 0.0359 (4) |
| O6 | 0.4659 (2) | 0.76899 (10) | 0.51791 (9) | 0.0288 (3) |
| H6A | 0.378764 | 0.786120 | 0.482051 | 0.043* |
| O7 | 0.7129 (3) | 0.91351 (11) | 0.52629 (10) | 0.0437 (5) |
| O8 | 0.7643 (3) | 1.01652 (11) | 0.42930 (11) | 0.0489 (5) |
| H8 | 0.743629 | 1.049295 | 0.471773 | 0.073* |
| N2 | 0.5450 (3) | 0.65582 (12) | 0.31529 (13) | 0.0309 (4) |
| C9 | 0.6002 (3) | 0.74615 (14) | 0.30746 (14) | 0.0254 (4) |
| C10 | 0.6291 (3) | 0.79590 (13) | 0.38380 (13) | 0.0228 (4) |
| C11 | 0.6775 (3) | 0.88201 (13) | 0.37162 (13) | 0.0233 (4) |
| C12 | 0.6908 (3) | 0.91495 (15) | 0.28633 (14) | 0.0282 (5) |
| H12 | 0.720828 | 0.973686 | 0.278758 | 0.034* |
| C13 | 0.6607 (3) | 0.86286 (16) | 0.21256 (14) | 0.0318 (5) |
| H13 | 0.670191 | 0.885978 | 0.154833 | 0.038* |
| C14 | 0.6172 (3) | 0.77783 (16) | 0.22282 (14) | 0.0308 (5) |
| H14 | 0.599108 | 0.741435 | 0.172653 | 0.037* |
| C15 | 0.6218 (3) | 0.75584 (13) | 0.47516 (13) | 0.0254 (4) |
| C16 | 0.7187 (3) | 0.93834 (14) | 0.45070 (14) | 0.0267 (4) |
1 Source of materials
A mixture of 2-ethoxybenzamide (100.0 mg, 0.6 mmol) and 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid (126.7 mg, 0.6 mmol) was dissolved in a mixed solution of 3 mL of toluene and 3 mL of ethyl acetate, and the resulting mixture was stirred and dissolved at 60 °C to obtain a clear solution, which was filtered and placed in a 10 mL glass vial. The filtrate was slowly evaporated at room temperature. A large number of colourless crystals were obtained after 2 days.
2 Experimental details
Absorption corrections were applied by using multi-scan program [1]. Using Olex2 [2], the structure was solved with the ShelXT [3] structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL [4] refinement package.
3 Comment
Increased interest in the synthesis and design of new forms of drugs, such as cocrystals, is caused by their ability to change physical and chemical properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients. The 2-ethoxybenzamide is a poorly-water soluble drug used for treatment of moderate and mild pain. Combinations of 2-ethoxybenzamide with aspirin, caffeine or paracetamol are widely used e.g. in Japan and Poland. Many structures of 2-ethoxybenzamide cocrystal have been published and deposited in CSD (Cambridge Structural Database). For example, with Furosemide (CCDC:2114160, SARQOV) [5], Sinapic Acid (CCDC:1581650, DEYQUW) [6], 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (CCDC:1522933, FENQEX), 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (CCDC:1522937, FENRIC) [7], phenol (CCDC:1879336, VUKSEC) [8], 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (CCDC:752467, WUZHOP) [9], 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (CCDC:1825011, JIFHAK) [10], 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (CCDC:1468148, ORIKIL), 2-nitrobenzoic acid (CCDC:1468153, ORIKOR), 3-nitrobenzoic acid (CCDC:1468154, ORIKUX), 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid (CCDC:1468159, ORILAE), 3-methylbenzoic acid (CCDC:1468161, ORILEI) [11], 2–hydroxybenzoic acid (CCDC:752480, REHSAA) [12] and so on. In this paper, we report a new cocrystal of 2-ethoxybenzamide.
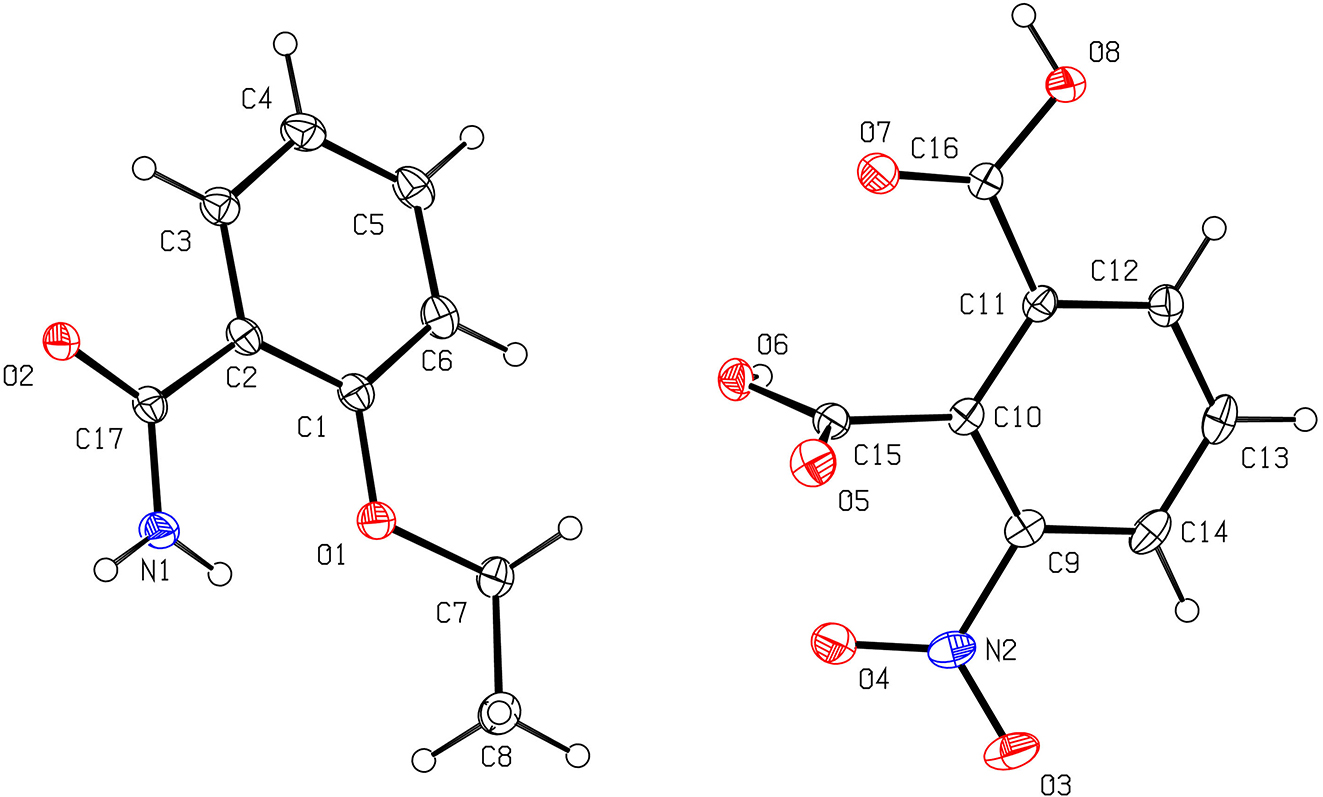
In the unit cell of the title crystal, the main forces are the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the amide groups on 2-ethoxybenzamide and the carboxyl groups and nitro group on 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid (see figure). The O2 atom on the amide group of the 2-ethoxybenzamide molecule is a hydrogen bond acceptor, and the H6A atom on the carboxyl group (O6–H6) of the 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid molecule is a hydrogen bond donor, forming an intermolecular hydrogen bond O6–H6A⃛O21 (1 = +X, 3/2 − Y, −1/2 + Z; d(O6⋯O2) = 2.680(2) Å; O6–H6A⃛O2 = 150.3°). The O2 atom on the amide group of the 2-ethoxybenzamide molecule is a hydrogen bond acceptor, and the H8 atom on the carboxyl group (O8–H8) of the 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid molecule is a hydrogen bond donor, forming an intermolecular hydrogen bond O8–H8⋯O2. The O7 atom on the carboxyl group of the 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid molecule is a hydrogen bond acceptor, and the H1 atom on the amide group (N1–H1) of the 2-ethoxybenzamide molecule is a hydrogen bond donor, forming an intermolecular hydrogen bond N1–H1⋯O7. The O3 atom on the nitro group of the 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid molecule is a hydrogen bond acceptor, and the H1 atom on the amide group (N1–H1) of the 2-ethoxybenzamide molecule is a hydrogen bond donor, forming an intermolecular hydrogen bond N1–H1⋯O3.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support by the Zhejiang Province Basic Public Welfare Research Project (LGJ20B060001).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Zhejiang Province Basic Public Welfare Research Project (LGJ20B060001).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Apex3 v. 2016.9–0 and Saint v. 8.37A; Bruker Axs Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. Olex2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Acebedo–Martínez, F. J., Alarcón–Payer, C., Rodríguez–Domingo, L., Domínguez–Martín, A., Gómez–Morales, J., Choquesillo–Lazarte, D. Furosemide/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-drug pharmaceutical solids: novel opportunities in drug formulation. Crystals 2021, 11, 1339; https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111339.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Nechipadappu, S. K., Trivedi, D. R. Cocrystal of nutraceutical sinapic acid with active pharmaceutical ingredients ethenzamide and 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid: equilibrium solubility and stability study. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1171, 898–905; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.06.074.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Khatioda, R., Saikia, B., Das, P. J., Sarma, B. Solubility and in vitro drug permeation behavior of ethenzamide cocrystals regulated in physiological pH environments. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6992–7000; https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ce01626c.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Potticary, J., Hall, C., Hamilton, V., McCabe, J. F., Hall, S. R. Crystallization from volatile deep eutectic solvents. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 2877–2884; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.0c00399.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Aitipamula, S., Chow, P. S., Tan, R. B. Polymorphs and solvates of a cocrystal involving an analgesic drug, ethenzamide, and 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 2229–2238; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg9015178.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Khatioda, R., Bora, P., Sarma, B. Trimorphic ethenzamide cocrystal: in vitro solubility and membrane efflux studies. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 4637–4645; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00603.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Hariprasad, V. M., Nechipadappu, S. K., Trivedi, D. R. Cocrystals of ethenzamide: study of structural and physicochemical properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 4473–4481; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.6b00606.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Aitipamula, S., Wong, A. B., Chow, P. S., Tan, R. B. Pharmaceutical cocrystals of ethenzamide: structural, solubility and dissolution studies. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 8515–8524; https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce26325d.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (N-([1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4′-diethyl)-2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)acetamide-κ4N,N,N″, O)tri(nitrato-kO, O′) samarium(III) - methanol - acetonitrile (1/1/1), C40H39SmN8O14
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(2-chloro-4-methyl phenolate-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV), C27H27Cl2N3O6Ti
- N′-[(1E)-(4–Fluorophenyl)methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H21FN2O
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid monohydrate, C4H2N3BrO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of dipyridine-k1N-tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-5-oxohept-3-en-3-olato-k2O,O′)dysprosium(III), DyC43H67O6N2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetraiodido-bis{μ2-1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-isopropyl-imidazol)-k2N:N}dicadmiun(II)], C26H30N10Cd2I4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (E)-3-(2-(benzylideneamino)phenyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate, C26H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4- dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-ium 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate methanol solvate, C27H32FN3O9
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1-(4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis[diaqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)–cobalt(II)], C24H20Co2I2N4O12
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(10,20-diphenylporphyrin-5,15-diyl)dibenzoate dichloromethane solvate, C49H36N4O4Cl2
- (E)-2-((E)-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)but-3-en-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide C14H23N3S1
- The crystal structure of [1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one], C16H12F3NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-amino-N′-((3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-4-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – dimethylformamide – water (1/1/2), C15H16N4O3·C3H7NO·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole, C10H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthrolinium bromide dihydrate, C12H9N2Br
- Crystal structure of N-(4′-chloro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)formamide, C13H10ClNO
- The crystal structure of nitroterephthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of (2-((4-bromo-2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl) (morpholino)methanone, C17H15BrCl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(ethanol-κO)-tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetate-κ2O:O′)-bis(trifluoroacetate-κ2O)digadolinium(III) Gd2C16H20O18F18
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-[10,20-bis(2,6-difluorophenyl)porphyrin-5,15-diyl]dibenzoate chloroform solvate, C50H32Cl6F4N4O4
- The crystal structure of N,N′-((nitroazanediyl)bis(methylene))diacetamide, C6H12O4N4
- The crystal structure of [bis(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3N,N,O)magnesium(II)]dihydrate, C22H18N4O6Mg
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(μ2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′] cobalt(II)-tetraqua-bis(1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ1N)-cobalt(II) di(2,5-thiophenedicarboxylate) dihydrate, C68H76Co2N16O16S2
- Crystal structure of poly[chlorido-μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1-[(2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κN:N’)cadmium(II)], C13H15CdN5Cl2
- The crystal structure of (4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate)-k1O-6,6′-((1E,1′E)- (ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-methoxyphenol)-κ2N,N,μ2O,O,κ2O, O)-(methanol)-cobalt(II) sodium(I), C25H27CoN2NaO9S
- Crystal structure of (1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)(4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methanone, C17H18F6N6O
- Crystal structure of bis{[(cyclohexylimino)(phenylimino)-l5-(methyl)diethylazane-κ2N:N′]-(ethyl)-zinc(II)]}, C38H62N6Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-bromobenzyl)thio]-5-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C13H8Br2N2OS2
- Crystal structure of 10-methoxy-7,11b,12,13-tetrahydro-6H-pyrazino [2′,3′:5,6]pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinoline, C15H16N4O
- The crystal structure of 1-propyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C6H9N3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid–2-ethoxybenzamide (1/1), C17H16N2O8
- The structure of RUB-1, (C8H16N)6[B6Si48O108], a boron containing levyne-type zeolite, occluding N-methyl-quinuclidinium in the cage-like pores
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(naphthalene-4,5-dicarboxylate-1,8-dicarboxylic anhydride-κ1O)-(4′-(4-(1H-benzimidazolyl-1-yl)phenyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N″)–manganese(II) dihydrate, C42H27MnN5O9·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis (3-(3-bromopropoxy)phenol), C20H22Br2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-6-(p-tolyl)-2H-pyran-2-one, C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-(1,5-dimethyl–3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H32Co2N8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-3-one O-(4-fluorobenzoyl) oxime, C28H36FNO2
- The crystal structure of 4-aminiumbiphenyl benzenesulfonate, C18H17NO3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)-N,N-dimethylmethanaminiumnitrate, C18H17N3O9
- Crystal structure of N-(Ar)-N′-(Ar′)-formamidine, C14H12Br2N2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-imidazole, C16H11Cl2FN2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4–chlorophenyl)-4-benzoyl-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C17H13ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazole, C4H6O2N4
- Crystal structure of 1,3-diisopropyl-4,5-dimethylimidazol-2-ylidene-N,N′-bis(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3,2-diazaborol-2-yl)-l2-germenediamine, C63H94B2GeN8
- The crystal structure of (bromido, chlorido)-tricarbonyl-(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine)-rhenium(I), C15H12Br0.2Cl0.8N2O3Re1
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C26H36N6
- The crystal structure of poly[2-(4-carboxypyridin-3-yl)terephthalpoly[diaqua-(μ4-2-(6-carboxylatopyridin-3-yl)terephthalato-κ5O,N:O′:O″,O‴)]) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C28H20Cd3N2O16
- Crystal structure of [tetraaqua-bis((3-carboxy-5-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoate-κ1N)cobalt(II)] tetrahydrate, C26H32CoN2O16
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-tetrakis(azido-κ1N)-tetrakis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)dibismuth(III), C48H32N26Bi2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-(4-(4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenoxy)butoxy)phenyl)acetamide, C30H31NO8
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-5-carboxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-O,O′:O″)-aqua-di-zinc dihydrate solvate], C27H28N4O16Zn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)malononitrile, C12H14N2
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(5-nitro-2-phenylpyridine-κ2N,C)-[(methylsulfinyl)methane-κ1S]platinum(II), C13H13ClN2O3PtS
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal 1,4-dioxane–4,6-bis(nitroimino)-1,3,5-triazinan-2-one(2/1), C11H19N7O9
- Crystal structure of [N(E),N′(E)]-N,N′-(1,4-phenylenedimethylidyne)bis-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-amine di-methanol solvate, C18H20N6·2(CH3OH)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-azido-k2N:N′)-(nitrato-K2N:N′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-K2N:N′)samarium(III)], C24H16N11O3Sm
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-((5-bromopentyl)oxy)benzylidene)-4,5,6-trimethoxybenzofuran-3(2H)-one, C23H25BrO6
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine-sebacic acid (2/1), C13H17N6O2

